Introduction
Stroke is one of the leading causes of neurological
dysfunction and mortality worldwide (1). Intravenous thrombolytic therapy has
been demonstrated to effectively restore cerebral blood flow;
however, the narrow therapeutic window (within 3–4.5 h following
stroke onset) and serious hemorrhagic complications limit this
treatment to only a small proportion of stroke sufferers (2). Endovascular intracranial thrombectomy
allows an extension of this therapeutic window and potentially
diminishes the risk of intracranial bleeding; however, mechanical
recanalization devices also exhibit limitations due to vessel
tortuosity, arterial stenosis and inaccessibility of the thrombus
(3). Therefore, there is an urgent
need to investigate safer and more effective treatment to restore
brain function. In recent years, multipotent mesenchymal stromal
cells (MSCs) have emerged as promising candidates among the
innovative treatment options, which may significantly promote the
recovery of neural function following a stroke (4,5).
However, rather than directly replacing parenchymal brain cells,
the secretion of extracellular vesicles (EVs) is suggested to be
the primary therapeutic mechanism of MSC therapy (6,7).
EV-based therapy circumvents the disadvantages and limitations of
MSC transplantation, including embolization and possible tumor
differentiation, therefore it may be an alternative to MSCs in
restoring neurological function (8).
In the present review, recent advances regarding the components,
functions and therapeutic potential of EVs have been summarized and
the future of MSC-derived EVs as a promising cell-free therapeutic
approach for stroke has been discussed.
Therapeutic potential of MSCs in the
treatment of stroke
MSC are multipotent adult progenitor cells, which
can be isolated from various sources, such as bone marrow,
placenta, umbilical cord, umbilical cord blood and adipose tissues
(9,10). MSCs have the unique abilities of
self-renewal, proliferation and multipotent differentiation, and
can differentiate into the different cell types of the three germ
layers; neurons, adipocytes, osteoblasts, hepatocytes, endothelial
cells and islet b cells (11–13). In
recent years, MSCs have received attention from researchers
worldwide and several features have identified them as promising
candidates for the treatment of diseases of the central nervous
system. For instance, MSCs may be derived, cultured and expanded
with no serious ethical issues, and they can migrate into the brain
parenchyma via the circulatory system (14). It has also been determined that MSCs
exhibit immunosuppressive properties and immune privilege and
therefore may be applied in allogeneic cellular transplantation
(15,16). In addition, they release a number of
anti-inflammatory factors, including indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase,
prostaglandin E2 and interleukin-10 following transplantation and
reduce the inflammatory immune response following cerebral ischemia
injury (17).
A number of previous studies have confirmed the
remarkable neuroregenerative ability of MSCs. MSC infusion in
animal models of stroke have led to reduced infarct volume,
enhanced synaptogenesis, increased vessel density and improved
neurological function (9). In
clinical trials, transplantation of MSCs was demonstrated to be a
safe and feasible therapeutic strategy for stroke patients
(Table I) (18–24).
 | Table I.Clinical trials of MSC therapy in
patients with stroke. |
Table I.
Clinical trials of MSC therapy in
patients with stroke.
| Lead author,
year | Study design | Brain infarct | Cells used | Route of
application | Cell dose | Adverse
effects | Outcome | (Refs.) |
|---|
| Bang, 2005 | Control, n=25;
treatment, n=5; 1-year follow up | Acute MCA
infarct | Autologous
BM-MSCs | IV | 5×107
cells in two doses | None | Improved BI;
decreased mRS | (18) |
| Lee, 2010 | Control, n=36;
treatment, n=16; 5-year follow up | Acute MCA
infarct | Autologous
BM-MSCs | IV | 5×107
cells in two doses | None | Decreased mRS | (19) |
| Honmou, 2011 | No control group;
treatment, n=12; 1-year follow up | Chronic
ischemic | Autologous
BM-MSCs | IV | Single dose of
0.6–1.6×108 cells | None | Decreased NIHSS,
reduced lesion volume | (20) |
| Bhasin, 2011 | Control, n=6;
treatment, n=6; 6-month follow up | Chronic MCA
infarct | Autologous
BM-MSCs | IV | 5–6×107
cells | None | Increased F-M score
and mBI | (21) |
| Jiang, 2013 | No control group;
treatment, n=3; 6-month follow up | Acute MCA
infarct | Allogeneic
UC-MSCs | IA | Single dose of
2×107 cells | None | Improved muscle
strength and mRS | (22) |
| Bhasin, 2013 | Control, n=20;
treatment, n=6; 6-month follow up | Chronic
ischemic | Autologous
BM-MSCs | IV | 5–6×107
cells | None | Increased mBI | (23) |
| Steinberg,
2016 | No control group;
treatment, n=16; 1-year follow up | Chronic Ischemic
BM-MSCs | Modified
allogeneic | IC | Single doses of
2.5×106, 5.0×106, or 10×106
cells | None | Increased ESS, F-M
score; decreased NIHSS | (24) |
Following cell transplantation in a previous study,
MSCs were hypothesized to integrate and differentiate into neural
cells and replace damaged brain tissue, however, the majority of
grafted cells became mechanically entrapped at the precapillary
level and, ultimately, long-term survival was only observed in a
limited number of delivered MSCs in the brain (25). Previous data have suggested that the
therapeutic effects are attributed to the secretion of paracrine
factors by MSCs rather than the differentiation of the administered
cells (26–28). A previous study has identified a
class of MSC-released EVs, which may be associated with the brain
restoration and repair effects of MSC therapy (29). EVs serve an important role in
intercellular communication by transferring protein and RNA cargo
between parent and target cells. The EVs released by MSCs function
in the brain and vessels and induce neurovascular remodeling,
anti-apoptosis and anti-inflammatory effects, which are considered
to be novel molecular mechanisms of MSC therapy (6,30–32).
Constitution and characteristics of
extracellular vesicles
Aside from the biologically active cytokines or
factors being important components of cell secretions, it seems
that the majority of cells are able to release EVs constitutively
or following stimulation (33). EVs
are cell-derived membrane-bound entities that contain cytoplasmic
components. Structural analyses have revealed that EVs are
surrounded by phospholipid bilayers, which are predominantly
composed of phosphatidylcholine, sphingomyelin,
phosphatidylethanolamine and phosphatidylserine (PS) (34). In particular, the structure of the
bi-lipid membrane provides an efficient platform for the
interaction of EVs and target cells through vesicle-cell channels
(35). With an endosomal origin, EVs
contain various types of cellular components, such as cytoskeleton
proteins, signaling proteins, lipids, RNA and DNA. The cargos of
EVs are dependent on the original cell types and may be affected by
the conditions of cell culture (36). Furthermore, EV proteins and RNAs
typically participate in cell-cell communication to determine the
biological effects of EVs on recipient cells (37,38).
Present in all biological fluids in the body, such as serum, urine
and cerebrospinal fluid, EVs may contain certain specific
biomarkers of diseases, thus they are promising candidates in the
diagnosis of different disorders (39,40). The
abilities of transporting biomolecules and targeting specific cell
populations further raise the possibility of EVs as therapeutics
(41).
To date, the biochemical structure, composition,
biological characteristics and physiological effects of EVs have
only been partially elucidated. Nevertheless, the important role of
EVs in intercellular communication has received much attention in
the last 10 years, as these particles are capable of transferring
biological molecules such as proteins, lipids, mRNAs and microRNAs
to target cells (42). The timeline
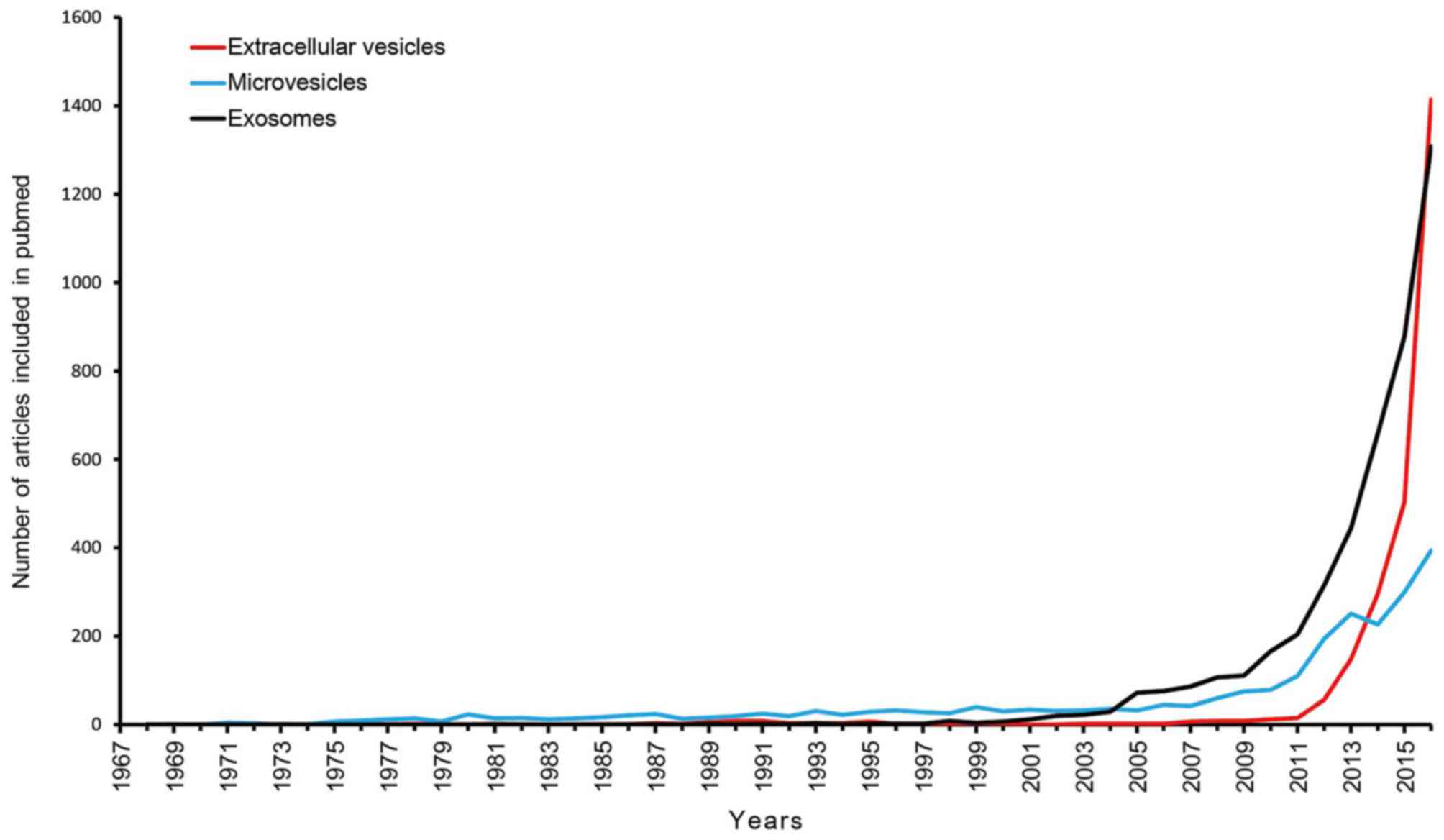
(1969–2016) of articles referring to extracellular vesicles,
microvesicles and exosomes are presented in Fig. 1. The present study conducted a search
for literature in the PubMed database (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/) and the
following search terms were utilized: ‘extracellular vesicles’,
‘microvesicles’ and ‘exosomes’. The original studies published in
various languages were retrieved, while the reviews, editorials and
articles investigating irrelevant objects were excluded.
Types of EVs
EVs can be categorized into three major types based
on size and intracellular origin; exosomes, microvesicles (MVs) and
apoptotic bodies. Exosomes originate from multivesicular bodies
(MVBs) and are discharged via p53-regulated exocytosis, which is
dependent on cytoskeleton reorganization but independent of
intracellular calcium concentration (43). When MVBs fuse with cell membranes,
the intraluminal particles are released from the cell and these
particles are referred to as exosomes. Typically, exosomes are
reported to be homogenous in size (30–120 nm) and have a density in
sucrose of 1.13–1.19 g/ml (44). The
most common markers of exosomes are tetraspanins [cluster of
differentiation (CD)63, CD81 and CD9], heat-shock protein (Hsp)60,
Hsp70, Hsp90, ALG-2-interacting protein X (Alix) and the
origin-cell-specific markers (45).
In addition, exosomes are rich in annexins, clathrin, lipid raft
markers (flotillin-1 and flotillin-2), tumor susceptibility gene
101 (Tsg101), major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules and
Rab family proteins, whereas PS is expressed at a low level in
exosomes (45).
MVs, also known as microparticles, nanoparticles,
ectosomes and shedding vesicles, are formed in response to specific
stimuli (46). MVs have a diameter
of 100–1,000 nm and a density in sucrose of 1.04–1.07 g/ml. They
are released via direct budding and shedding from cytomembranes and
this process is dependent on activation of calpain, calcium influx
and the cytoskeleton (8,47). Large amounts of PS and lipid
raft-associated molecules are characteristic markers of MVs and the
membranes of MVs are rich in cholesterol, sphingomyelin and
ceramide (43).
Apoptotic bodies, which are derived from cells
undergoing apoptosis, represent the last kind of EVs. They are
typically >1,000 nm and contain membrane contents, tightly
packed organelles and fragmented DNA (48). Apoptotic bodies are exocytosed under
the regulation of adenosine triphosphate-dependent enzymes from the
cytomembrane, they express PS on the surface and have permeable
membranes (45). Apoptotic bodies
have been suggested to induce anti-inflammatory or tolerogenic
responses when taken in by nearby cells; however, their specific
role remains undefined (49).
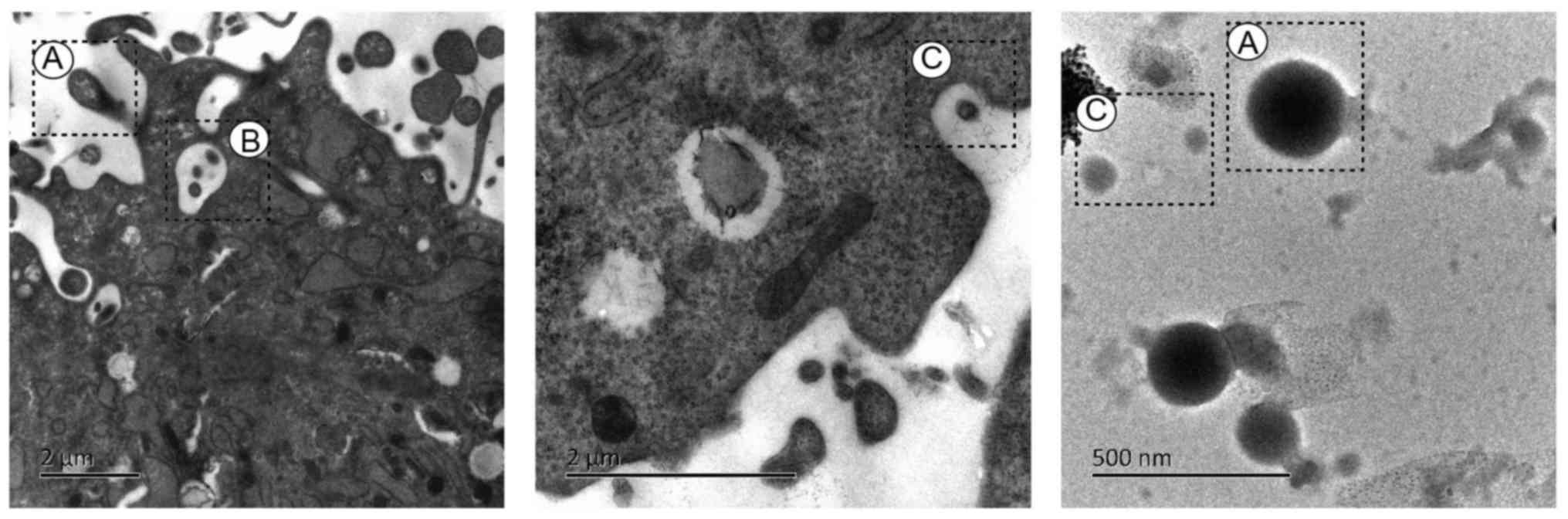
The electron micrographs of exosomes and MVs
released by human umbilical cord-MSCs are presented in Fig. 2. The ultrastructure of human
umbilical cord-MSCs was visualized using transmission electron
microscopy. The umbilical cord tissue was obtained in April 2017
from a patient at the Obstetrical department of the First
Affiliated Hospital of Hunan University of Traditional Chinese
Medicine (Changsa, China). Briefly, MSCs were washed with PBS three
times and digested with 0.25% trypsin-EDTA (cat. no. 25200-056;
Invitrogen; Thermo Fisher scientific, Inc., Waltham, MA, USA) at
37°C for 2 min. Following trypsinization with 10% fetal bovine
serum (Invitrogen; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.), cells were
pelleted via centrifugation at 200 × g for 5 min at 4°C. The
supernatant was removed and the cells were fixed with 1%
glutaraldehyde solution at 4°C overnight. Subsequently, the
glutaraldehyde was discarded and 1% osmium tetroxide solution was
added to the pellets and incubated for 24 h at 4°C. The sample was
dehydrated via graded ethanol washes and embedded in Durcupan resin
for 6 h at room temperature. Sections (thickness, 60 nm) were cut
using an ultramicrotome and placed on copper grids. A solution of
3% Uuranyl acetate and 2% lead citrate was used to counterstain the
sections for 1 h at 37°C. The sample was observed with a
transmission electron microscope (Hitachi, Ltd., Tokyo, Japan,
HT7800) at 80 kV. The key characteristics of the three types of EVs
are summarized in Table II.
 | Table II.Key characteristics of extracellular
vesicles. |
Table II.
Key characteristics of extracellular
vesicles.
| Characteristic | Exosomes | Microvesicles | Apoptotic
bodies |
|---|
| Size | 30–120 nm | 100–1,000 nm | ≥1,000 nm |
| Density in
sucrose | 1.13–1.19 g/ml | 1.04–1.07 g/ml | 1.16–1.28 g/ml |
| Origin | By exocytosis of
MVB; process dependent on cytoskeleton reorganization but
independent on Ca2+ | Outward budding of
plasma membrane; process dependent on Ca2+, calpain and
cytoskeleton activation | Outward budding of
apoptotic cell membrane |
| Markers | Tetraspanins,
Tsg101, Alix, Hsp, annexins, Low exposure of PS, the
origin-cell-specific markers | Lipid
raft-associated molecules, high expression of PS | Expression of
PS |
| Content | Proteins, lipids,
mRNA and miRNA, rare DNA | Proteins, lipids,
mRNA, miRNA, plasmid DNA | Intracellular
fragments and cellular organelles |
| Isolation
technique |
Ultracentrifugation, electron
microscopy |
Ultracentrifugation, electron
microscopy | Flow cytometry,
electron microscopy |
| Storage | −80°C | −80°C | Not available |
The strict separation of these vesicles by size or
biogenesis has not yet been established. As all of these vesicle
types are present in vitro and in vivo, the mixed
vesicles cannot be dissected from each other once they have left
the cell and in the present review, the term EVs is used to
collectively describe the extracellular membrane vesicles.
Isolation of EVs
At present, there are a number of approaches used to
isolate EVs, including ultracentrifugation (UC), polymeric
precipitation, the use of size exclusions and aqueous two phase
system (ATPS) (50).
UC is the most accepted method, which involves a
series of centrifugation steps (8).
Cell fragments and large vesicles are separated from EV-containing
fluid by gradually raising the centrifugal force (from 2,500–10,000
× g) and EVs are precipitated with two rounds of centrifugation at
100,000 × g for 2–3 h each time. This method is reliable,
inexpensive and highly reproducible, but is lengthy and requires
specialized laboratory apparatus (30).
Another isolation method is polymeric precipitation
(e.g., ExoQuick-TC™; System Biosciences, LLC, Palo Alto, CA, USA),
which can decrease the solubility of MVs and form precipitation
(51,52). This approach has the advantages of a
high yield and efficiency, but the poor purity obtained reduces the
reliability of the results (53).
Size exclusions (e.g., filters) are applied by
passing the sample through 0.8-µm pore filters to remove large
particles and followed by centrifugation to concentrate the eluted
EVs (30,54). It's a simple and low-cost technique,
which can be used alone or in conjunction with UC, but this method
has a low throughput as lots of EVs may adhere to the filters
(55). Furthermore, the products may
be contaminated by other vesicles of the same size (53).
Recently, Shin et al (55) demonstrated a simple and efficient
method to isolate EVs from saliva using an ATPS. ATPS rapidly
separated EVs from a mixture of vesicles and proteins by
partitioning different types of vesicles into different phases;
this method achieved a high yield and purity within a short time.
However, the application of ATPS has not yet been tested
extensively and a standard isolation method is still utilized in EV
research. A schematic diagram for separation of EVs is represented
in Fig. 3.
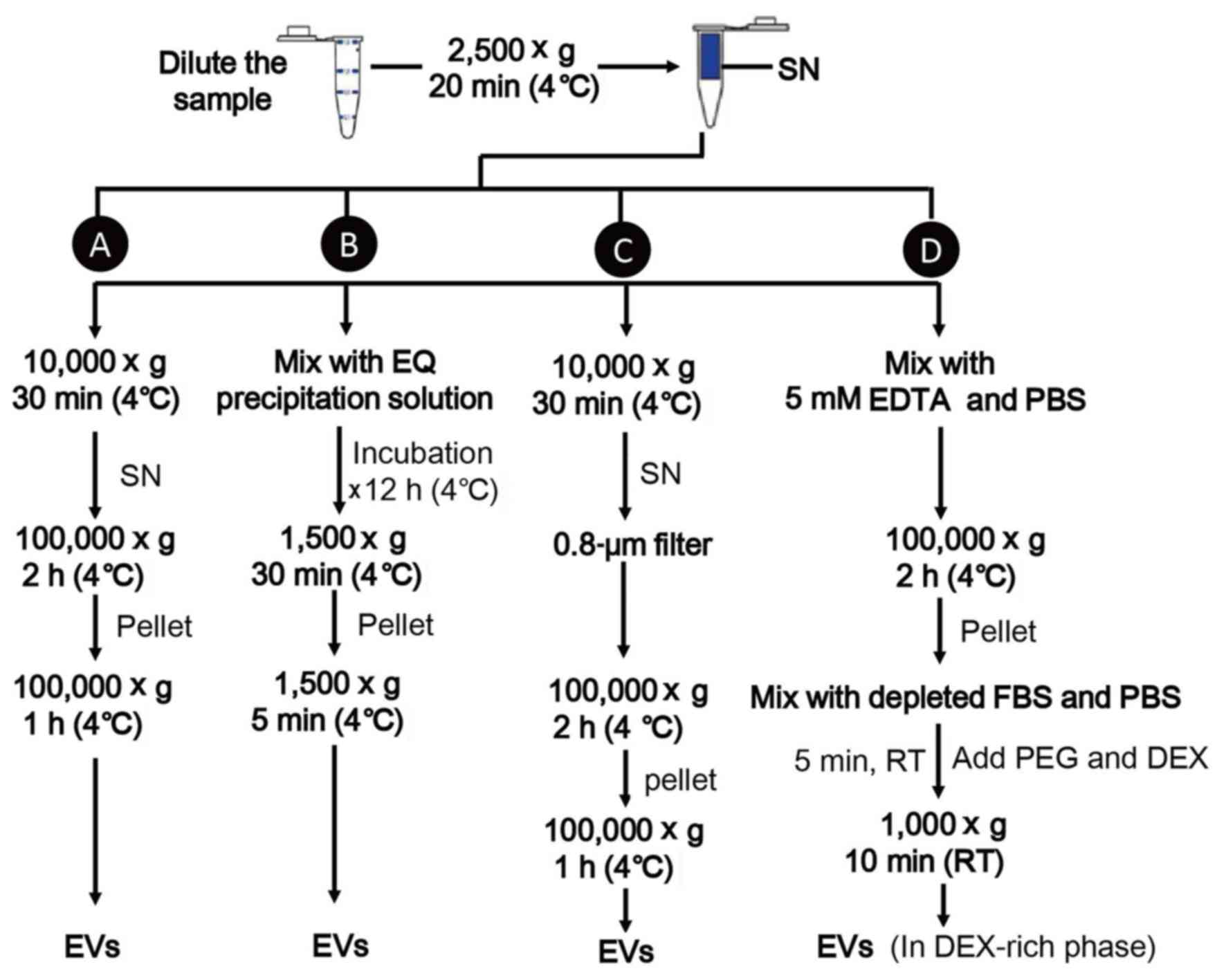 | Figure 3.Isolation of extracellular vesicles.
(A) Ultracentrifugation. (B) Polymeric precipitation. (C) Size
exclusions, (D) ATPS. ATPS, aqueous two phase system; DEX, dextran;
EDTA, ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid; EQ, ExoQuick; FBS, fetal
bovine serum; EVs, extracellular vesicles; PEG, polyethylene
glycol; RT, room temperature; SN, supernatant. |
Characterization of EVs
Due to the ability of fluorescence activated cell
sorting (FACS) to identify the same individual vesicles by
different parameters, is the most commonly used method for the
study of EV. The operational process of FACS is simple and the
results can be quantified to a high level of quality (56). The main disadvantage is that a flow
cytometer has poor discrimination under 500 nm and is only fit for
detection of big vesicles. Previously, high-definition cytometers
have appeared on the market and they are capable of detecting
nanoparticles as small as 0.1–0.2 µm in diameter (57). Electron microscopy is typically
combined with FACS to provide morphological information about the
EVs (54). However, this technique
has limitations in quantitative examination and the process is
complicated and costly (58).
Nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA) is typically applied to
analyze the mean size, modal value and size distribution of EVs
(50). The vesicles with a diameter
from 30–10,000 nm can be precisely and easily detected in only 5
min. The main limitation of this technique is that the quality of
NTA is influenced by particle concentration and the samples need to
be diluted properly to obtain reliable results (59). Additionally, enzyme linked ELISA and
western blotting (WB) are used to analyze the proteins associated
with EVs (60,61). Commonly used markers include
tetraspanins, Tsg101, Alix, annexins, lipid raft-associated
molecules and the origin-cell-specific surface proteins (62). However, both ELISAs and WB are
unsuitable to quantify the protein expression level in EVs and can
only be employed to demonstrate the presence of proteins (50). Commonly used methods for
characterization of EVs are summarized in Table III.
 | Table III.Common methods for extracellular
vesicle characterization. |
Table III.
Common methods for extracellular
vesicle characterization.
| Technique | Information
acquired | Limitations |
|---|
| Electron
microscopy | Morphology,
size | Unquantifiable,
complicated and costly |
| Fluorescence
activated cell sorting | Phenotype,
number | Limited working
range |
| Nanoparticle
tracking analysis | Size,
concentration, size distribution | Dilution
needed |
| ELISA and western
blotting | Phenotype | Unquantifiable |
Storage of isolated EVs
Reservoir vessels, buffers, storage temperature and
programs have specific marked impacts on the results of EV
experiments. It is advisable to store EVs in silicified vessels to
prevent the adhesion of EVs to the vessel surfaces (50). PBS is considered to be the optimal
choice for EV resuspension and the standard temperature for MV
storage is suggested to be −80°C (63). As for any bioactive substances, it is
recommended to have the samples frozen and thawed quickly and to
minimize the cycles of freezing and thawing, although it has
previously been suggested that freeze/thaw cycles have no negative
effect on EVs (58,64). In general, further study is required
to determine the optimal storage conditions.
Biological functions of extracellular
vesicles
EVs are released from cell membranes when the cells
are stimulated by biological agonists (e.g. interleukin, endotoxin
and apoptosis factors) or chemical stress (oxidative or hypoxic
stress) (8,40). EVs were previously treated as only
cell fragments or debris and their biological activities were
ignored (35); however, an
increasing number of studies have demonstrated that these tiny
vesicles are important messengers in cell-to-cell communication as
they can preserve and deliver cellular signals (65–67). EVs
contain various types of proteins (cytoskeleton, surface molecules,
receptors and enzymes), lipids similar to the cytomembrane and
nucleic acids [mRNA, microRNA (miRNA), long non-coding RNA and DNA]
(68–70). As multicomponent lipid vesicles, EVs
have the ability to transfer cellular cargos to target cells and
induce alterations of phenotype and behavior. Furthermore, they can
protect the cytoplasmic components from damage or degradation by
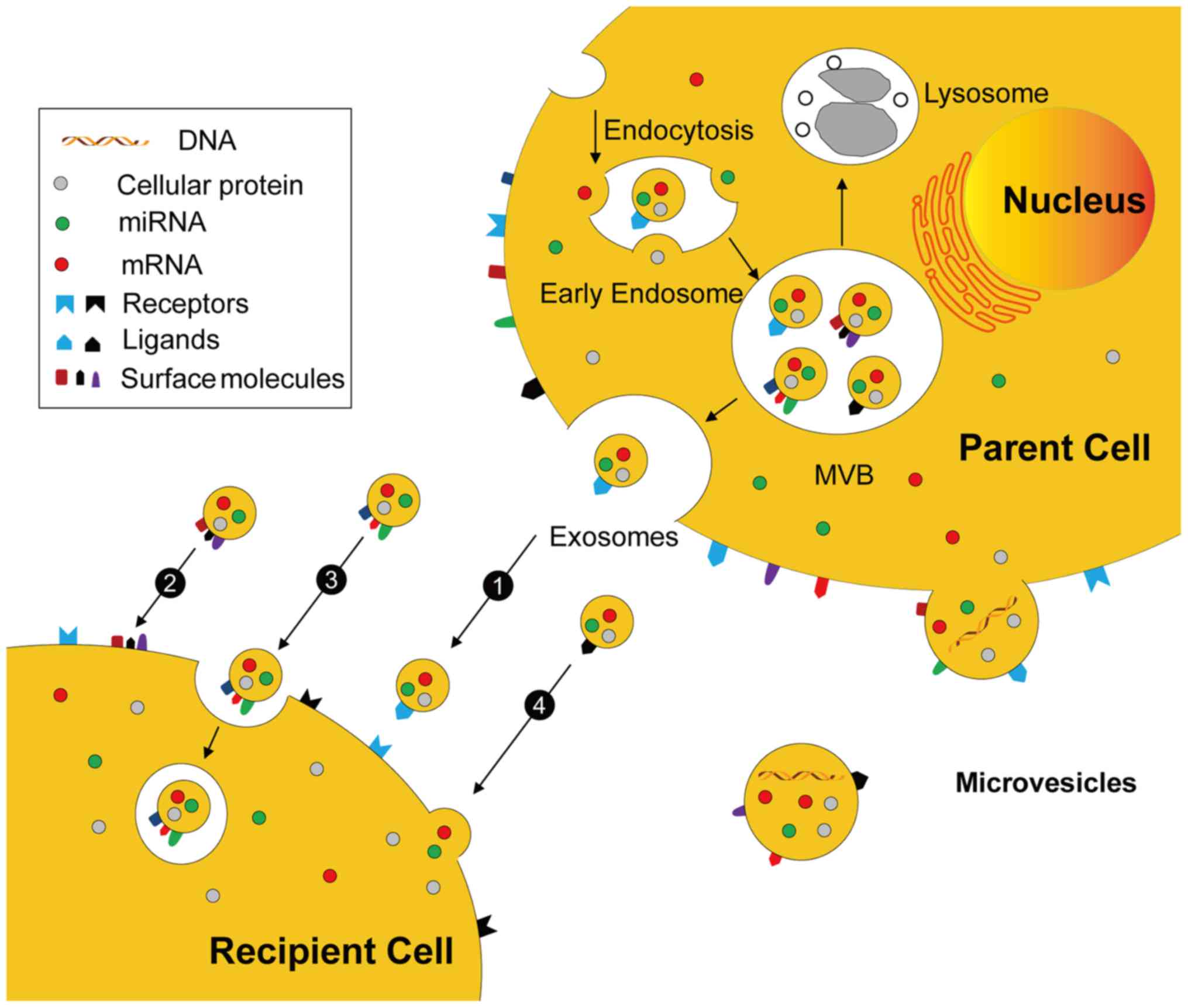
chemicals and enzymes (71,72). In general, EVs are able to mediate
cellular interaction and exchange of information primarily through
the pathways illustrated in Fig.
4.
Exosomes originate from MVBs and are discharged by
membrane fusion, whereas MVs are released by direct budding from
the cytomembrane. EVs may mediate cell-cell communication
mechanisms including: i) Stimulation of recipient cells by
functioning as signal complexes; ii) transfer of surface receptors
or lipids into recipient cells; iii) delivery of cytoplasmic
proteins and nucleic acids by the endocytic pathway; and iv)
delivery of cytoplasmic proteins and nucleic acids by the membrane
fusion.
EVs may directly stimulate the recipient cells by
functioning as signal complexes. Previous studies have demonstrated
that EVs contain several types of surface molecules and receptor
proteins including Fas-L protein, co-stimulator factors, adhesion
molecules, MHC I and MHC II molecules (43,73,74).
Therefore, cells with various receptors may be activated by EV
ligands, e.g., exosomes expressing delta-like ligand 4, a
membrane-spanning Notch ligand, which interacts with Notch
receptors presented on endotheliocytes or neurocytes and causes
angiogenesis and neurogenesis, respectively (75).
EVs may transfer surface receptors or lipids into
recipient cells. For example, microparticles from platelets can
deliver CD41 to endotheliocytes via membrane fusion, resulting in
the proadhesive abilities of these cells (76). In addition, EVs are also able to act
as vehicles for spreading infective agents between cells. The
chemokine receptor 5 or C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 from T
lymphocytes can be diverted to non-lymphoid cells and this
microparticle-mediated transfer may render these cells susceptible
to human immunodeficiency virus infection (77,78).
Furthermore as part of the ligand and receptor
interaction, EVs may also affect the function of target cells via
the delivery of cytoplasmic proteins (79). EVs released by endotheliocytes can
promote angiogenesis through the secretion of angiogenic
stimulators, e.g., growth factors, proteases and their activators
(80–82). In addition, Mitra et al
(83) recently demonstrated that
endotoxin-activated mononuclear cells induced cell apoptosis by
transporting caspase-1 in microparticles. As a consequence,
EV-mediated transfer of cellular factors and bioactive molecules
may support the interaction effects between cell populations.
Finally, growing evidence indicates that EVs
contribute to the transfer of nucleic acids and genetic information
may be delivered to target cells, causing alterations of cellular
activities and functions. Katsman et al (84) previously demonstrated that MVs
released from embryonic stem cells (ESCs) contained a large amount
of miRNAs, which may be transferred to human Müller cells in
vitro. In addition, it was demonstrated that ESC-released MVs
increased the pluripotency and proliferation of hematopoietic
progenitor cells (HPC) via delivery of ESC-derived mRNAs (85). The pretreatment of MVs with RNase may
eliminate the biological effects on HPCs and this observation
further confirmed the important role of mRNA transfer via MVs
(85).
Extracellular vesicles as an alternative to
MSCs
MSCs were demonstrated to release the highest amount
of EVs out of a group of different cell lines, e.g., the human
acute monocytic leukemia cell line, the primary human small airway
epithelial cells and the mouse embryonic stem cell-derived
insulin-producing cell line (86).
There is no difference in morphological characteristics between the
EVs released by MSCs and other cell types. In addition, aside from
the common biomarkers, MSC-released EVs express certain specific
surface antigens (including CD44, CD73, CD90 and CD105), which can
be detected for their identification (30). As to the contents of the vesicles,
the protein components of MSC-released EVs do not remain unchanged.
In three independent batches of exosomes obtained from conditioned
medium (CM) of MSCs, 379, 432 and 420 proteins were identified
respectively, and only 154 unique proteins (~20%) were demonstrated
to be in present in all (87).
Functional clustering of those proteins was also performed in this
study, which revealed that exosomes exhibit potential to initiate
many biological processes, which is in accordance with the multiple
therapeutic efficacies of MSCs (87).
Conversely, it has recently been demonstrated that
MSCs produce many EVs that contain selected classes of mRNAs and
miRNAs with specific functions (67,88,89).
Based on gene ontology analysis, Eirin et al (66) demonstrated that EVs from
adipose-derived MSC (AD-MSCs) were rich in different types of RNAs
and their microRNA cargos (miRNA148a, miRNA 532–5p, miRNA 378)
could target transcription factors or genes to induce angiogenesis,
adipogenesis, apoptosis and proteolysis in recipient cells. In
addition, it was reported that human bone marrow (BM)-MSCs are able
to release exosomes containing mRNA for insulin-like growth factor
1 receptor (IGF-1R) and the transfer of IGF-1R mRNA may ameliorate
cisplatin-induced renal dysfunction by increasing the proliferation
of proximal tubular cells (90).
Together, this suggested the possibility that MSCs may alter the
expression of gene products and regulate the features and action of
neighboring cells by EV-mediated delivery of nucleic acids, e.g.,
mRNA, small interfering RNA and miRNA.
As a consequence, EVs, by transferring specific
types of biological molecules and genetic information, are
suggested to be notable paracrine factors associated with signaling
between MSCs and target cells and they may be an alternative to
MSCs to restore organism function. A previous study demonstrated
that the injured lung cells may deliver EVs containing
lung-specific genes to BM cells, causing the expression of
lung-specific proteins on MSCs (91). As a result, BM-MSCs were able to
convert into cells with a pulmonary epithelial cell phenotype
following transplantation into lethally X-ray-irradiated mice
(91). Therefore, MSCs and injured
cells may have bi-directional cell-cell communication during the
process of tissue reparation. EVs secreted by injured cells may
trigger the physiological activities of MSCs and MSC-derived EVs
may induce the reparative and proliferative alterations of tissue
cells (92,93).
Therapeutic effects of MSC-released
extracellular vesicles on stroke
Although the application of MSC transplantation has
attracted attention in neural regeneration research, the use of
MSC-released EVs has also received intense scholarly interest. EVs
may regulate neural survival, apoptosis, proliferation and
regeneration following brain damage (Table IV) (32). MSC-secreted EVs have been
demonstrated to promote neural repair and functional recovery in
animal models of ischemic stroke. It was indicated that intravenous
delivery of exosome-enriched EVs generated from BM-MSCs
significantly improved axonal plasticity and neurite remodeling in
the ischemic cortex of middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) rats
(94). In addition, a similar
neurorestorative effect of MSC-derived EVs was exhibited by
cortical neuron models of glutamate excitotoxicity (95). Following exposure to glutamate for 15
min, neurons were co-cultured with CM containing EVs of AD-MSC for
18 h. Compared with the control groups, MSC-CM reduced LDH release,
inhibited neuron apoptosis and promoted neuronal regeneration and
bioenergy restoration (95).
 | Table IV.Therapeutic Effects of MSC-released
extracellular vesicles on stroke. |
Table IV.
Therapeutic Effects of MSC-released
extracellular vesicles on stroke.
| Model | Name/size (nm) | Isolation | Identify | Origin | Administration | Biological
function | (Refs.) |
|---|
| Mice/MCAO | Extracellular
vesicles/not shown | PEG plus UC | Micro BCA, WB | BM-MSCs | IV | Improved
neurological impairment and angioneuro-genesis, suppressed immune
responses | (31) |
| Cortical neurons;
glutamate excite-toxicity | MSC conditioned
medium/- | − - | − - | Human AD-MSCs | In vitro
co-culture | Inhibited neuronal
cell apoptosis, promoted nerve regeneration and repair, restored
bioenergy | (95) |
| PC12 cells;
glutamate excitotoxicity | Microvesicles/not
shown | UC | Flow cytometry,
Bradford method, TEM | BM-MSCs | In vitro
co-culture | Activated the
phosphoinositide 3-kinase/protein kinase B signaling pathway | (96) |
| Cortical neurons;
not shown | Exosomes/40–100
nm | UC | TEM | BM-MSCs | In vitro
co-culture | Increased neurite
branch number, total neurite length and microRNA-133b levels | (97) |
| Rats/MCAO | Exosomes/not
shown | UC | Micro BCA
assay | BM-MSCs | IV | Improved functional
recovery, neurogenesis, neurite remodeling and angiogenesis | (98) |
| Rats; subcortical
infarct model | Extracellular
vesicles/50–100 nm | Exosome extraction
kit | Electron
microscopy, Nano Sight, | AD-MSCs | IV | Improved functional
recovery, fiber tract integrity, axonal sprouting WB and
immunofluorescence and white matter repair markers and restored
white matter integrity | (109) |
| Rats; MCAO | Exosomes/not
shown | UC | WB, TEM, micro BCA
assay, qNano particle analysis | BM-MSCs | Intra-arterial
injection | Increased
functional improvement, neurite remodeling and brain
plasticity | (110) |
Furthermore, EVs from MSCs were reported to modulate
signaling pathways to treat ischemic stroke. Lin et al noted
that MVs released by BM-MSCs were able to protect PC12 cells from
glutamate-induced damage (96). In
that study, MVs enhanced protein kinase B (Akt) phosphorylation and
B-cell lymphoma-2 (Bcl-2) expression and reduced Bcl-2-associated X
protein and caspase-3 expression, and these effects were removed by
inhibition of phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K). This suggested that
MSC-MVs acted as neural protective agents via activation of the
PI3K/Akt pathway. In addition, Xin et al (97) previously observed that the expression
of miRNA-133b in MSC-released exosomes increased when MSCs were
cultured with ischemic brain extracts from rats subjected to MCAO.
Further research demonstrated that EVs from BM-MSCs were able to
transfer miRNA-133b to astrocytes and neurons in the ischemic
boundary zone of rats, resulting in promotion of neural plasticity
and functional recovery (94). These
studies indicated that EV-mediated secretion of miRNAs contributed
to the neuroprotective effects of MSCs on stroke.
With the exception of the beneficial effects on
neurogenesis, EVs can improve angiogenesis following cerebral
ischemia. It was demonstrated that intravenous administration of
MSC-generated exosomes significantly increased the percentage of
newly formed von Willebrand factor-positive cells in the ischemic
zone (98). Compared with
PBS-treated controls, rats receiving exosome treatment also
demonstrated an improvement in neurovascular plasticity in the
stroke affected hemisphere and promotion of neurological function
recovery. Finally, it is important to emphasize that EVs may have
immunosuppressive effects on cerebral inflammatory-related
diseases. Doeppner et al (31) proposed that EVs from BM-derived MSC
lineages were able to modify immune reactions and restore the
reshaping ability of the injured brain following focal cerebral
ischemia. Alongside the normalization of B lymphocytes, natural
killer cells and T lymphocytes, a deactivation of dendritic cells
was observed in the peripheral blood of MSC-EV-treated mice and the
suppression of immune responses provided an appropriate
extracellular environment for neurovascular remodeling and
contributed to the functional recovery following a stroke.
Advantages and challenges of MSC-EV
therapy
In spite of the indicated promised of MSC-based
therapy in regenerative medicine, EVs demonstrate a number of
advantages over MSCs in clinical applications. First, exogenous
administration of MSCs may cause some serious side effects, e.g.,
malignant transformation, tumor generation or microvascular
obstruction (99–101). In contrast, EVs, given their
nanometer dimensions, have no vascular obstructive effects or
apparent adverse effects following the in vivo allogeneic
administration. Compared to the direct delivery of cells, EVs have
a unique capability to easily cross the blood brain barrier, which
is very important in the treatment of neurological disorders
(102,103). Additionally, EVs can be stored at
−80°C for 6 months without degradation of their contents and this
is important for the protection of soluble molecules including
biological factors and nucleic acids (63). Notably, MSC-derived EVs can be
modified to express a high level of biological factors, surface
proteins, mRNAs and miRNAs that promote tissue repair and
functional recovery and these engineered EVs may be utilized as a
novel class of cell-based therapeutics (40,104).
Nevertheless, specific problems must be resolved if
EVs are to be suitable for clinical applications. First, it must be
determined to what extent EVs contribute to the therapeutic
benefits of MSC-administration. Second, novel techniques are
required to obtain large-scale production of EVs. Chen et al
(105) previously suggested that
transformation of the Myc gene may be a useful strategy to
ensure an infinite supply of MSCs for the production of EVs and the
high proliferative rate of MSCs may reduce the time and economic
costs, and increase the output of EV-production. Third, further
studies should look into the detailed mechanisms of the interaction
between EVs and target cells and the contents of EVs, i.e.,
proteins, lipids and nucleic acids, must be intensively researched.
Finally, it's imperative to investigate the potential side effects
of EVs in therapy. Salido-Guadarrama et al (106) reported that tumor cells could
achieve cell-cell communication by the release and transfer of
miRNAs packed into tumor-secreted exosomes and, tumor-secreted
exosomes served an important role in the establishment, maintenance
and enhancement of tumor microenvironment, and they may act as
mediators in cancer metastasis. Although EVs have no potential to
directly form tumors, this does not mean that MSC-EV application
has no risk of tumor promotion. Therefore, further studies are
required to evaluate the long-term biological safety of EV
administration. Table V exhibits the
advantages and challenges of MSC based therapy and MSC-EV based
therapy.
 | Table V.Advantages and challenges of MSC
based therapy and MSC-EV based therapy. |
Table V.
Advantages and challenges of MSC
based therapy and MSC-EV based therapy.
| Type of
therapy | Advantages | Challenges |
|---|
| MSC based
therapy | Potential of
proliferation and differentiation, release of MVs and other
biological factors | Malignant
transformation, tumor generation, microvascular obstruction |
| MSC-EV based
therapy | No apparent adverse
effects, capability to cross the blood brain barrier, no vascular
obstructive effects, easy to be stored and engineered | Determine the
specific benefits and mechanisms of MV administration, in-depth
study of MV contents, potential side effects: tumor promotion |
Conclusion
In recent years, the therapeutic potential of
MSC-derived EVs has attracted a lot of attention. EVs should not be
regarded as mere cell fragments or cellular waste and evidence has
demonstrated that they are associated with the regulation of
cell-cell communication and have significant biological effects on
recipient cells. Remarkably, the idea of using EVs as a cell-free
vaccine to eradicate tumors was conceived ~20 years ago (107) and clinical trials of EV-based
therapy in cancer patients were initially conducted in the early
2000s (108). Currently, no
clinical trials have been applied for an MSC-EV administration to
treat strokes (http://clinicaltrials.gov) and it is too early to
claim that MSC-derived EVs could be clinically used for functional
recovery following cerebral ischemia. The specific mechanisms and
the potential side effects of EV administration need to be fully
investigated and novel techniques are required to obtain
large-scale production of EVs. In addition, there is currently no
internationally recognized standard for clinical level production
and quality control of EV-based therapeutics. These unresolved
problems are the remaining impediments to this therapy and,
therefore, more animal experiments and clinical tests are required
prior to MSC-EV application as a conventional treatment.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
The present review was supported by the National
Natural Science Foundation of China (grant nos. 81273751, 81372140,
81360627, 81572689 and 81573941) and the China Postdoctoral Science
Foundation (grant no. 2017M610509).
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current
study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable
request.
Authors' contributions
Dr YL, Professor QC and Professor GH wrote the
draft; Dr TD and Dr QW assisted with the literature search; and
Professor JZ, and Professor XS revised and proofed the manuscript,
and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring
that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of
the work are appropriately investigated and resolved. All authors
read and approved the final manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
The protocol for analysis of human umbilical cord
was approved by the ethics committee of the First Affiliated
Hospital of Hunan University of Traditional Chinese Medicine
(Changsa, China). Donors of human umbilical cord provided informed
written consent prior to their inclusion in the present study.
Consent for publication
The patients have provided written informed consent
for the publication of any associated data and accompanying
images.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests and they have no financial relationships to disclose.
Glossary
Abbreviations
Abbreviations:
|
AD-MSCs
|
adipose-derived mesenchymal stromal
cells
|
|
ATPS
|
aqueous two phase system
|
|
BI
|
barthel index
|
|
BM-MSC
|
bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell
|
|
CM
|
conditioned media
|
|
CNS
|
central nervous system
|
|
DEX
|
dextran
|
|
ESC
|
embryonic stem cells
|
|
EVs
|
extracellular vesicles
|
|
FACS
|
fluorescence activated cell
sorting
|
|
FBS
|
fetal bovine serum
|
|
F-M Score
|
Fugl-Meyer score
|
|
HPCs
|
hematopoietic progenitor cells
|
|
Hsp
|
heat-shock protein
|
|
IGF-1R
|
insulin-like growth factor 1
receptor
|
|
LDH
|
lactate dehydrogenase
|
|
MCA
|
middle cerebral artery
|
|
MSCs
|
mesenchymal stromal cells
|
|
MVs
|
microvesicles
|
|
MVBs
|
multivesicular bodies
|
|
NIHSS
|
National Institutes of Health Stroke
Scale
|
|
PBS
|
phosphate buffer solution
|
|
PC12 cells
|
rat adrenal pheochromocytoma cells
|
|
PEG
|
polyethylene glycol
|
|
PS
|
phosphatidylserine
|
|
RT
|
room temperature
|
|
SN
|
supernatant
|
|
Tsg101
|
tumor susceptibility gene 101
|
|
UC
|
ultracentrifugation
|
|
WB
|
western-blotting
|
References
|
1
|
Moskowitz MA, Lo EH and Iadecola C: The
science of stroke: Mechanisms in search of treatments. Neuron.
67:181–198. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Demaerschalk BM, Kleindorfer DO, Adeoye
OM, Demchuk AM, Fugate JE, Grotta JC, Khalessi AA, Levy EI, Palesch
YY, Prabhakaran S, et al: Scientific rationale for the inclusion
and exclusion criteria for intravenous alteplase in acute ischemic
stroke: A statement for healthcare professionals from the american
heart association/american stroke association. Stroke. 47:581–641.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Grunwald IQ, Wakhloo AK, Walter S,
Molyneux AJ, Byrne JV, Nagel S, Kühn AL, Papadakis M, Fassbender K,
Balami JS, et al: Endovascular stroke treatment today. AJNR Am J
Neuroradiol. 32:238–243. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tu J, Yang F, Wan J, Liu Y, Zhang J, Wu B,
Liu Y, Zeng S and Wang L: Light-controlled astrocytes promote human
mesenchymal stem cells toward neuronal differentiation and improve
the neurological deficit in stroke rats. Glia. 62:106–121. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wei ZZ, Gu X, Ferdinand A, Lee JH, Ji X,
Ji XM, Yu SP and Wei L: Intranasal delivery of bone marrow
mesenchymal stem cells improved neurovascular regeneration and
rescued neuropsychiatric deficits after neonatal stroke in rats.
Cell Transplant. 24:391–402. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhang ZG and Chopp M: Exosomes in stroke
pathogenesis and therapy. J Clin Invest. 126:1190–1197. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lopatina T, Bruno S, Tetta C, Kalinina N,
Porta M and Camussi G: Platelet-derived growth factor regulates the
secretion of extracellular vesicles by adipose mesenchymal stem
cells and enhances their angiogenic potential. Cell Commun Signal.
12:262014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tan X, Gong YZ, Wu P, Liao DF and Zheng
XL: Mesenchymal stem cell-derived microparticles: A promising
therapeutic strategy. Int J Mol Sci. 15:14348–14363. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li Y, Hu G and Cheng Q: Implantation of
human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells for ischemic stroke:
Perspectives and challenges. Front Med. 9:20–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Marquez-Curtis LA, Janowska-Wieczorek A,
McGann LE and Elliott JA: Mesenchymal stromal cells derived from
various tissues: Biological, clinical and cryopreservation aspects.
Cryobiology. 71:181–197. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Olson AL and McNiece IK: Novel clinical
uses for cord blood derived mesenchymal stromal cells. Cytotherapy.
17:796–802. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC, Jaiswal
RK, Douglas R, Mosca JD, Moorman MA, Simonetti DW, Craig S and
Marshak DR: Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem
cells. Science. 284:143–147. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jiang Y, Jahagirdar BN, Reinhardt RL,
Schwartz RE, Keene CD, Ortiz-Gonzalez XR, Reyes M, Lenvik T, Lund
T, Blackstad M, et al: Pluripotency of mesenchymal stem cells
derived from adult marrow. Nature. 418:41–49. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hao L, Zou Z, Tian H, Zhang Y, Zhou H and
Liu L: Stem cell-based therapies for ischemic stroke. Biomed Res
Int. 2014:4687482014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bernardo ME and Fibbe WE: Mesenchymal
stromal cells: Sensors and switchers of inflammation. Cell Stem
Cell. 13:392–402. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gornostaeva A, Andreeva E and Buravkova L:
Factors governing the immunosuppressive effects of multipotent
mesenchymal stromal cells in vitro. Cytotechnology. 68:565–577.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Khubutiya MS, Vagabov AV, Temnov AA and
Sklifas AN: Paracrine mechanisms of proliferative, anti-apoptotic
and anti-inflammatory effects of mesenchymal stromal cells in
models of acute organ injury. Cytotherapy. 16:579–585. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bang OY, Lee JS, Lee PH and Lee G:
Autologous mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in stroke
patients. Ann Neurol. 57:874–882. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lee JS, Hong JM, Moon GJ, Lee PH, Ahn YH
and Bang OY: STARTING collaborators: A long-term follow-up study of
intravenous autologous mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in
patients with ischemic stroke. Stem Cells. 28:1099–1106. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Honmou O, Houkin K, Matsunaga T, Niitsu Y,
Ishiai S, Onodera R, Waxman SG and Kocsis JD: Intravenous
administration of auto serum-expanded autologous mesenchymal stem
cells in stroke. Brain. 134:1790–1807. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bhasin A, Srivastava MV, Kumaran SS,
Mohanty S, Bhatia R, Bose S, Gaikwad S, Garg A and Airan B:
Autologous mesenchymal stem cells in chronic stroke. Cerebrovasc
Dis Extra. 1:93–104. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jiang Y, Zhu W, Zhu J, Wu L, Xu G and Liu
X: Feasibility of delivering mesenchymal stem cells via catheter to
the proximal end of the lesion artery in patients with stroke in
the territory of the middle cerebral artery. Cell Transplant.
22:2291–2298. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bhasin A, Srivastava MV, Mohanty S, Bhatia
R, Kumaran SS and Bose S: Stem cell therapy: A clinical trial of
stroke. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 115:1003–1008. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Steinberg GK, Kondziolka D, Wechsler LR,
Lunsford LD, Coburn ML, Billigen JB, Kim AS, Johnson JN, Bates D,
King B, et al: Clinical outcomes of transplanted modified bone
marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in stroke: A phase 1/2a
study. Stroke. 47:1817–1824. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Toma C, Wagner WR, Bowry S, Schwartz A and
Villanueva F: Fate of culture-expanded mesenchymal stem cells in
the microvasculature: In vivo observations of cell kinetics. Circ
Res. 104:398–402. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lin YC, Ko TL, Shih YH, Lin MY, Fu TW,
Hsiao HS, Hsu JY and Fu YS: Human umbilical mesenchymal stem cells
promote recovery after ischemic stroke. Stroke. 42:2045–2053. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Vu Q, Xie K, Eckert M, Zhao W and Cramer
SC: Meta-analysis of preclinical studies of mesenchymal stromal
cells for ischemic stroke. Neurology. 82:1277–1286. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Caplan AI and Correa D: The MSC: An injury
drugstore. Cell Stem Cell. 9:11–15. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Basso M and Bonetto V: Extracellular
vesicles and a novel form of communication in the brain. Front
Neurosci. 10:1272016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yu B, Zhang X and Li X: Exosomes derived
from mesenchymal stem cells. Int J Mol Sci. 15:4142–4157. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Doeppner TR, Herz J, Görgens A, Schlechter
J, Ludwig AK, Radtke S, de Miroschedji K, Horn PA, Giebel B and
Hermann DM: Extracellular vesicles improve post-stroke
neuroregeneration and prevent postischemic immunosuppression. Stem
Cells Transl Med. 4:1131–1143. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Xin H, Li Y and Chopp M: Exosomes/miRNAs
as mediating cell-based therapy of stroke. Front Cell Neurosci.
8:3772014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Couzin J: Cell biology: The ins and outs
of exosomes. Science. 308:1862–1863. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
van der Pol E, Boing AN, Harrison P, Sturk
A and Nieuwland R: Classification, functions, and clinical
relevance of extracellular vesicles. Pharmacol Rev. 64:676–705.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yáñez-Mó M, Siljander PR, Andreu Z, Zavec
AB, Borràs FE, Buzas EI, Buzas K, Casal E, Cappello F, Carvalho J,
et al: Biological properties of extracellular vesicles and their
physiological functions. J Extracell Vesicles. 4:270662015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Raposo G and Stoorvogel W: Extracellular
vesicles: Exosomes, microvesicles, and friends. J Cell Biol.
200:373–383. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Katakowski M, Buller B, Zheng X, Lu Y,
Rogers T, Osobamiro O, Shu W, Jiang F and Chopp M: Exosomes from
marrow stromal cells expressing miR-146b inhibit glioma growth.
Cancer Lett. 335:201–204. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhang HG and Grizzle WE: Exosomes: A novel
pathway of local and distant intercellular communication that
facilitates the growth and metastasis of neoplastic lesions. Am J
Pathol. 184:28–41. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Fais S, O'Driscoll L, Borras FE, Buzas E,
Camussi G, Cappello F, Carvalho J, da Silva Cordeiro A, Del
Portillo H, El Andaloussi S, et al: Evidence-based clinical use of
nanoscale extracellular vesicles in nanomedicine. ACS Nano.
10:3886–3899. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ratajczak MZ: The emerging role of
microvesicles in cellular therapies for organ/tissue regeneration.
Nephrol Dial Transplant. 26:1453–1456. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Reiner AT, Witwer KW, van Balkom BWM, de
Beer J, Brodie C, Corteling RL, Gabrielsson S, Gimona M, Ibrahim
AG, de Kleijn D, et al: Concise review: Developing best-practice
models for the therapeutic use of extracellular vesicles. Stem
Cells Transl Med. 6:1730–1739. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Antonyak MA and Cerione RA: Emerging
picture of the distinct traits and functions of microvesicles and
exosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 112:3589–3590. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Biancone L, Bruno S, Deregibus MC, Tetta C
and Camussi G: Therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem
cell-derived microvesicles. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 27:3037–3042.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Lai CP and Breakefield XO: Role of
exosomes/microvesicles in the nervous system and use in emerging
therapies. Front Physiol. 3:2282012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Konala VB, Mamidi MK, Bhonde R, Das AK,
Pochampally R and Pal R: The current landscape of the mesenchymal
stromal cell secretome: A new paradigm for cell-free regeneration.
Cytotherapy. 18:13–24. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Gyorgy B, Hung ME, Breakefield XO and
Leonard JN: Therapeutic applications of extracellular vesicles:
Clinical promise and open questions. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol.
55:439–464. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Kanninen KM, Bister N, Koistinaho J and
Malm T: Exosomes as new diagnostic tools in CNS diseases. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1862:403–410. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Ban LA, Shackel NA and McLennan SV:
Extracellular vesicles: A new frontier in biomarker discovery for
non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Int J Mol Sci. 17:3762016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Lai FW, Lichty BD and Bowdish DM:
Microvesicles: Ubiquitous contributors to infection and immunity. J
Leukoc Biol. 97:237–245. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Witwer KW, Buzàs EI, Bemis LT, Bora A,
Lässer C, Lötvall J, Hoen Nolte-'t EN, Piper MG, Sivaraman S, Skog
J, et al: Standardization of sample collection, isolation and
analysis methods in extracellular vesicle research. J Extracell
Vesicles. 2:203602013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Zlotogorski-Hurvitz A, Dayan D, Chaushu G,
Korvala J, Salo T, Sormunen R and Vered M: Human saliva-derived
exosomes: Comparing methods of isolation. J Histochem Cytochem.
63:181–189. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Van Deun J, Mestdagh P, Sormunen R,
Cocquyt V, Vermaelen K, Vandesompele J, Bracke M, De Wever O and
Hendrix A: The impact of disparate isolation methods for
extracellular vesicles on downstream RNA profiling. J Extracell
Vesicles. 3:248582014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Sàenz-Cuesta M, Osorio-Querejeta I and
Otaegui D: Extracellular vesicles in multiple sclerosis: What are
they telling us? Front Cell Neurosci. 8:1002014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
György B, Módos K, Pàllinger E, Pálóczi K,
Pásztói M, Misják P, Deli MA, Sipos A, Szalai A, Voszka I, et al:
Detection and isolation of cell-derived microparticles are
compromised by protein complexes resulting from shared biophysical
parameters. Blood. 117:e39–e48. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Shin H, Han C, Labuz JM, Kim J, Kim J, Cho
S, Gho YS, Takayama S and Park J: High-yield isolation of
extracellular vesicles using aqueous two-phase system. Sci Rep.
5:131032015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Lacroix R, Robert S, Poncelet P and
Dignat-George F: Overcoming limitations of microparticle
measurement by flow cytometry. Semin Thromb Hemost. 36:807–818.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
van der Vlist EJ, Hoen Nolte-'t EN,
Stoorvogel W, Arkesteijn GJ and Wauben MH: Fluorescent labeling of
nano-sized vesicles released by cells and subsequent quantitative
and qualitative analysis by high-resolution flow cytometry. Nat
Protoc. 7:1311–1326. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Sokolova V, Ludwig AK, Hornung S, Rotan O,
Horn PA, Epple M and Giebel B: Characterisation of exosomes derived
from human cells by nanoparticle tracking analysis and scanning
electron microscopy. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 87:146–150.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Szatanek R, Baj-Krzyworzeka M, Zimoch J,
Lekka M, Siedlar M and Baran J: The methods of choice for
extracellular vesicles (EVs) characterization. Int J Mol Sci.
18:pii: E1153. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Mokarizadeh A, Delirezh N, Morshedi A,
Mosayebi G, Farshid AA and Mardani K: Microvesicles derived from
mesenchymal stem cells: Potent organelles for induction of
tolerogenic signaling. Immunol Lett. 147:47–54. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Chen TS, Lai RC, Lee MM, Choo AB, Lee CN
and Lim SK: Mesenchymal stem cell secretes microparticles enriched
in pre-microRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 38:215–224. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Wang J, Zhong Y, Ma X, Xiao X, Cheng C,
Chen Y, Iwuchukwu I, Gaines KJ, Zhao B, Liu S, et al: Analyses of
endothelial cells and endothelial progenitor cells released
Microvesicles by using microbead and Q-dot based nanoparticle
tracking analysis. Sci Rep. 6:246792016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Théry C, Amigorena S, Raposo G and Clayton
A: Isolation and characterization of exosomes from cell culture
supernatants and biological fluids. Curr Protoc Cell Biol. Chapter
3: Unit 3.22. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Jayachandran M, Miller VM, Heit JA and
Owen WG: Methodology for isolation, identification and
characterization of microvesicles in peripheral blood. J Immunol
Methods. 375:207–214. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Li Y, Liu Z, Xin H and Chopp M: The role
of astrocytes in mediating exogenous cell-based restorative therapy
for stroke. Glia. 62:1–16. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Eirin A, Riester SM, Zhu XY, Tang H, Evans
JM, O'Brien D, van Wijnen AJ and Lerman LO: MicroRNA and mRNA cargo
of extracellular vesicles from porcine adipose tissue-derived
mesenchymal stem cells. Gene. 551:55–64. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Phinney DG, Di Giuseppe M, Njah J, Sala E,
Shiva S, St Croix CM, Stolz DB, Watkins SC, Di YP, Leikauf GD, et
al: Mesenchymal stem cells use extracellular vesicles to outsource
mitophagy and shuttle microRNAs. Nat Commun. 6:84722015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Fleury A, Martinez MC and Le Lay S:
Extracellular vesicles as therapeutic tools in cardiovascular
diseases. Front Immunol. 5:3702014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Taylor DD and Gercel-Taylor C:
Exosomes/microvesicles: Mediators of cancer-associated
immunosuppressive microenvironments. Semin Immunopathol.
33:441–454. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Kanada M, Bachmann MH, Hardy JW,
Frimannson DO, Bronsart L, Wang A, Sylvester MD, Schmidt TL, Kaspar
RL, Butte MJ, et al: Differential fates of biomolecules delivered
to target cells via extracellular vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
112:E1433–E1442. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Turchinovich A and Cho WC: The origin,
function and diagnostic potential of extracellular microRNA in
human body fluids. Front Genet. 5:302014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Liu RT, Wang SW and Liu J: Exosomes: The
novel vehicles for intercellular communication. Prog Biochem
Biophys. 40:719–727. 2013.
|
|
73
|
György B, Szabó TG, Pàsztói M, Pál Z,
Misják P, Aradi B, László V, Pállinger E, Pap E, Kittel A, et al:
Membrane vesicles, current state-of-the-art: Emerging role of
extracellular vesicles. Cell Mol Life Sci. 68:2667–2688. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Thery C, Ostrowski M and Segura E:
Membrane vesicles as conveyors of immune responses. Nat Rev
Immunol. 9:581–593. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Sheldon H, Heikamp E, Turley H, Dragovic
R, Thomas P, Oon CE, Leek R, Edelmann M, Kessler B, Sainson RC, et
al: New mechanism for Notch signaling to endothelium at a distance
by Delta-like 4 incorporation into exosomes. Blood. 116:2385–2394.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Janowska-Wieczorek A, Majka M, Kijowski J,
Baj-Krzyworzeka M, Reca R, Turner AR, Ratajczak J, Emerson SG,
Kowalska MA and Ratajczak MZ: Platelet-derived microparticles bind
to hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells and enhance their
engraftment. Blood. 98:3143–3149. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Mause SF and Weber C: Microparticles:
Protagonists of a novel communication network for intercellular
information exchange. Circ Res. 107:1047–1057. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Rozmyslowicz T, Majka M, Kijowski J,
Murphy SL, Conover DO, Poncz M, Ratajczak J, Gaulton GN and
Ratajczak MZ: Platelet- and megakaryocyte-derived microparticles
transfer CXCR4 receptor to CXCR4-null cells and make them
susceptible to infection by X4-HIV. AIDS. 17:33–42. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Desrochers LM, Bordeleau F, Reinhart-King
CA, Cerione RA and Antonyak MA: Microvesicles provide a mechanism
for intercellular communication by embryonic stem cells during
embryo implantation. Nat Commun. 7:119582016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Yong PJ, Koh CH and Shim WS: Endothelial
microparticles: Missing link in endothelial dysfunction? Eur J Prev
Cardiol. 20:496–512. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Liu Y, Huang W, Zhang R, Wu J, Li L and
Tang Y: Proteomic analysis of TNF-α-activated endothelial cells and
endothelial microparticles. Mol Med Rep. 7:318–326. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
de Jong OG, Verhaar MC, Chen Y, Vader P,
Gremmels H, Posthuma G, Schiffelers RM, Gucek M and van Balkom BW:
Cellular stress conditions are reflected in the protein and RNA
content of endothelial cell-derived exosomes. J Extracell Vesicles.
1:183962012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Mitra S, Wewers MD and Sarkar A:
Mononuclear phagocyte-derived microparticulate caspase-1 induces
pulmonary vascular endothelial cell injury. PLoS One.
10:e01456072015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Katsman D, Stackpole EJ, Domin DR and
Farber DB: Embryonic stem cell-derived microvesicles induce gene
expression changes in Muller cells of the retina. PLoS One.
7:e504172012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Ratajczak J, Miekus K, Kucia M, Zhang J,
Reca R, Dvorak P and Ratajczak MZ: Embryonic stem cell-derived
microvesicles reprogram hematopoietic progenitors: Evidence for
horizontal transfer of mRNA and protein delivery. Leukemia.
20:847–856. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Yeo RW, Lai RC, Zhang B, Tan SS, Yin Y,
Teh BJ and Lim SK: Mesenchymal stem cell: An efficient mass
producer of exosomes for drug delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev.
65:336–341. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Lai RC, Tan SS, Teh BJ, Sze SK, Arslan F,
de Kleijn DP, Choo A and Lim SK: Proteolytic potential of the MSC
exosome proteome: Implications for an exosome-mediated delivery of
therapeutic proteasome. Int J Proteomics. 2012:9719072012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Collino F, Bruno S, Incarnato D, Dettori
D, Neri F, Provero P, Pomatto M, Oliviero S, Tetta C, Quesenberry
PJ and Camussi G: AKI recovery induced by mesenchymal stromal
cell-derived extracellular vesicles carrying MicroRNAs. J Am Soc
Nephrol. 26:2349–2360. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Koniusz S, Andrzejewska A, Muraca M,
Srivastava AK, Janowski M and Lukomska B: Extracellular vesicles in
physiology, pathology, and therapy of the immune and central
nervous system, with focus on extracellular vesicles derived from
mesenchymal stem cells as therapeutic tools. Front Cell Neurosci.
10:1092016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Tomasoni S, Longaretti L, Rota C, Morigi
M, Conti S, Gotti E, Capelli C, Introna M, Remuzzi G and Benigni A:
Transfer of growth factor receptor mRNA via exosomes unravels the
regenerative effect of mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells Dev.
22:772–780. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Dooner MS, Aliotta JM, Pimentel J, Dooner
GJ, Abedi M, Colvin G, Liu Q, Weier HU, Johnson KW and Quesenberry
PJ: Conversion potential of marrow cells into lung cells fluctuates
with cytokine-induced cell cycle. Stem Cells Dev. 17:207–219. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Pegtel DM, Peferoen L and Amor S:
Extracellular vesicles as modulators of cell-to-cell communication
in the healthy and diseased brain. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol
Sci. 369:pii: 20130516. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Lozito TP and Tuan RS: Endothelial and
cancer cells interact with mesenchymal stem cells via both
microparticles and secreted factors. J Cell Mol Med. 18:2372–2384.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Xin H, Li Y, Liu Z, Wang X, Shang X, Cui
Y, Zhang ZG and Chopp M: MiR-133b promotes neural plasticity and
functional recovery after treatment of stroke with multipotent
mesenchymal stromal cells in rats via transfer of exosome-enriched
extracellular particles. Stem Cells. 31:2737–2746. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Hao P, Liang Z, Piao H, Ji X, Wang Y, Liu
Y, Liu R and Liu J: Conditioned medium of human adipose-derived
mesenchymal stem cells mediates protection in neurons following
glutamate excitotoxicity by regulating energy metabolism and GAP-43
expression. Metab Brain Dis. 29:193–205. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Lin SS, Zhu B, Guo ZK, Huang GZ, Wang Z,
Chen J, Wei XJ and Li Q: Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived
microvesicles protect rat pheochromocytoma PC12 cells from
glutamate-induced injury via a PI3K/Akt dependent pathway.
Neurochem Res. 39:922–931. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Xin H, Li Y, Buller B, Katakowski M, Zhang
Y, Wang X, Shang X, Zhang ZG and Chopp M: Exosome-mediated transfer
of miR-133b from multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells to neural
cells contributes to neurite outgrowth. Stem Cells. 30:1556–1564.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Xin H, Li Y, Cui Y, Yang JJ, Zhang ZG and
Chopp M: Systemic administration of exosomes released from
mesenchymal stromal cells promote functional recovery and
neurovascular plasticity after stroke in rats. J Cereb Blood Flow
Metab. 33:1711–1715. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Mousavinejad M, Andrews PW and Shoraki EK:
Current biosafety considerations in stem cell therapy. Cell J.
18:281–287. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Wong RS: Mesenchymal stem cells: Angels or
demons? J Biomed Biotechnol. 2011:4595102011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Jeong JO, Han JW, Kim JM, Cho HJ, Park C,
Lee N, Kim DW and Yoon YS: Malignant tumor formation after
transplantation of short-term cultured bone marrow mesenchymal stem
cells in experimental myocardial infarction and diabetic
neuropathy. Circ Res. 108:1340–1347. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Shao H, Chung J, Balaj L, Charest A,
Bigner DD, Carter BS, Hochberg FH, Breakefield XO, Weissleder R and
Lee H: Protein typing of circulating microvesicles allows real-time
monitoring of glioblastoma therapy. Nat Med. 18:1835–1840. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Alvarez-Erviti L, Seow Y, Yin H, Betts C,
Lakhal S and Wood MJ: Delivery of siRNA to the mouse brain by
systemic injection of targeted exosomes. Nat Biotechnol.
29:341–345. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Lener T, Gimona M, Aigner L, Börger V,
Buzas E, Camussi G, Chaput N, Chatterjee D, Court FA, Del Portillo
HA, et al: Applying extracellular vesicles based therapeutics in
clinical trials-an ISEV position paper. J Extracell Vesicles.
4:300872015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Chen TS, Arslan F, Yin Y, Tan SS, Lai RC,
Choo AB, Padmanabhan J, Lee CN, de Kleijn DP and Lim SK: Enabling a
robust scalable manufacturing process for therapeutic exosomes
through oncogenic immortalization of human ESC-derived MSCs. J
Transl Med. 9:472011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Salido-Guadarrama I, Romero-Cordoba S,
Peralta-Zaragoza O, Hidalgo-Miranda A and Rodríguez-Dorantes M:
MicroRNAs transported by exosomes in body fluids as mediators of
intercellular communication in cancer. Onco Targets Ther.
7:1327–1338. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Zitvogel L, Regnault A, Lozier A, Wolfers
J, Flament C, Tenza D, Ricciardi-Castagnoli P, Raposo G and
Amigorena S: Eradication of established murine tumors using a novel
cell-free vaccine: Dendritic cell-derived exosomes. Nat Med.
4:594–600. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Escudier B, Dorval T, Chaput N, André F,
Caby MP, Novault S, Flament C, Leboulaire C, Borg C, Amigorena S,
et al: Vaccination of metastatic melanoma patients with autologous
dendritic cell (DC) derived-exosomes: Results of thefirst phase I
clinical trial. J Transl Med. 3:102005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Otero-Ortega L, Laso-García F, Gómez-de
Frutos MD, Rodríguez-Frutos B, Pascual-Guerra J, Fuentes B,
Díez-Tejedor E and Gutiérrez-Fernández M: White matter repair after
extracellular vesicles administration in an experimental animal
model of subcortical stroke. Sci Rep. 7:444332017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Xin H, Wang F, Li Y, Lu QE, Cheung WL,
Zhang Y, Zhang ZG and Chopp M: Secondary release of exosomes from
astrocytes contributes to the increase in neural plasticity and
improvement of functional recovery after stroke in rats treated
with exosomes harvested from MicroRNA 133b-overexpressing
multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. Cell Transplant. 26:243–257.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|