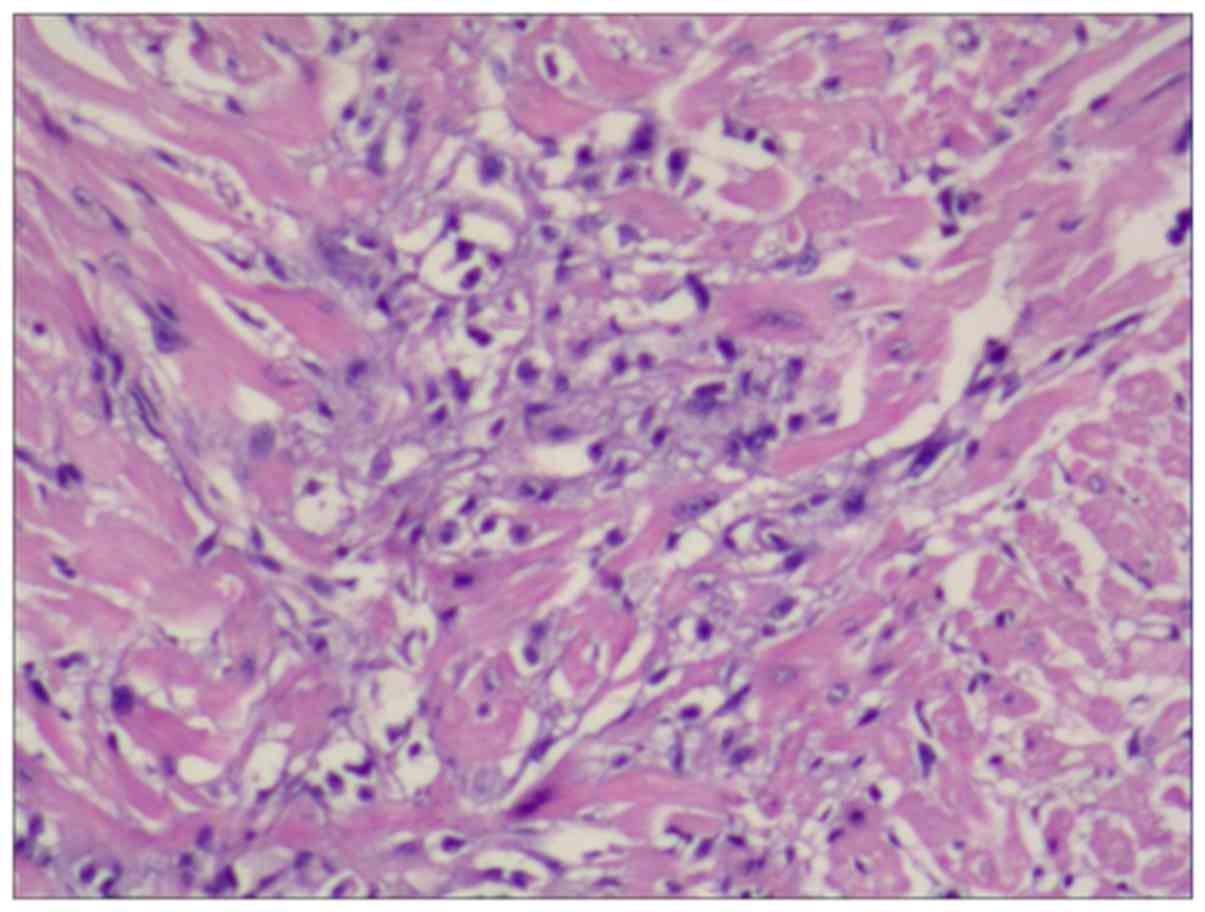
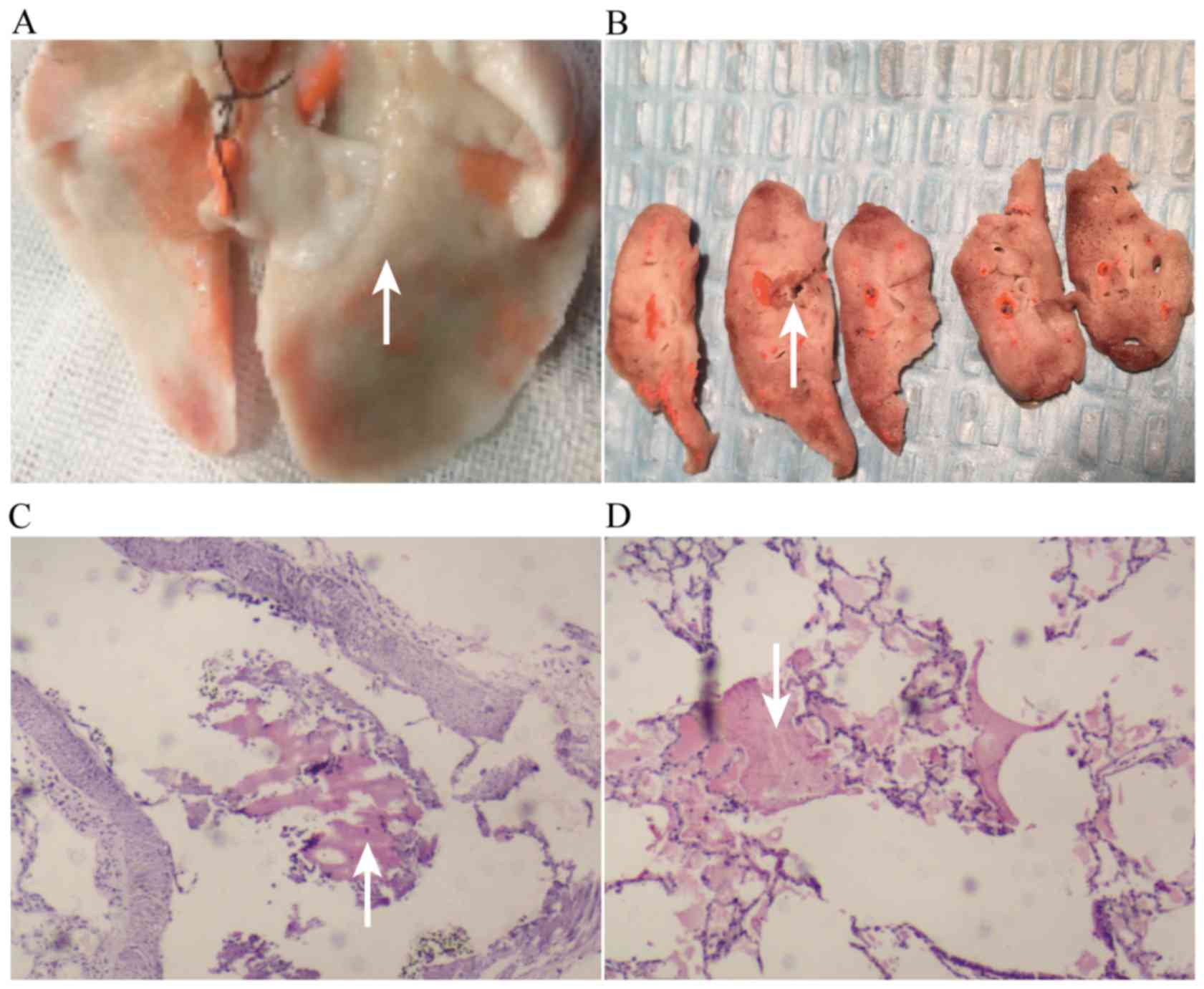
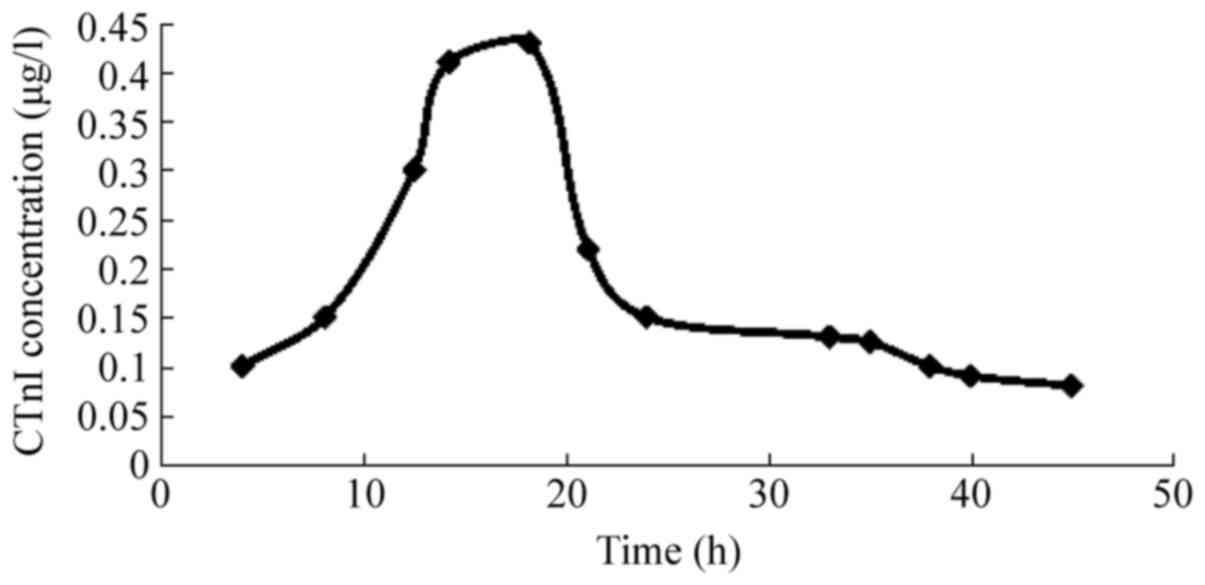
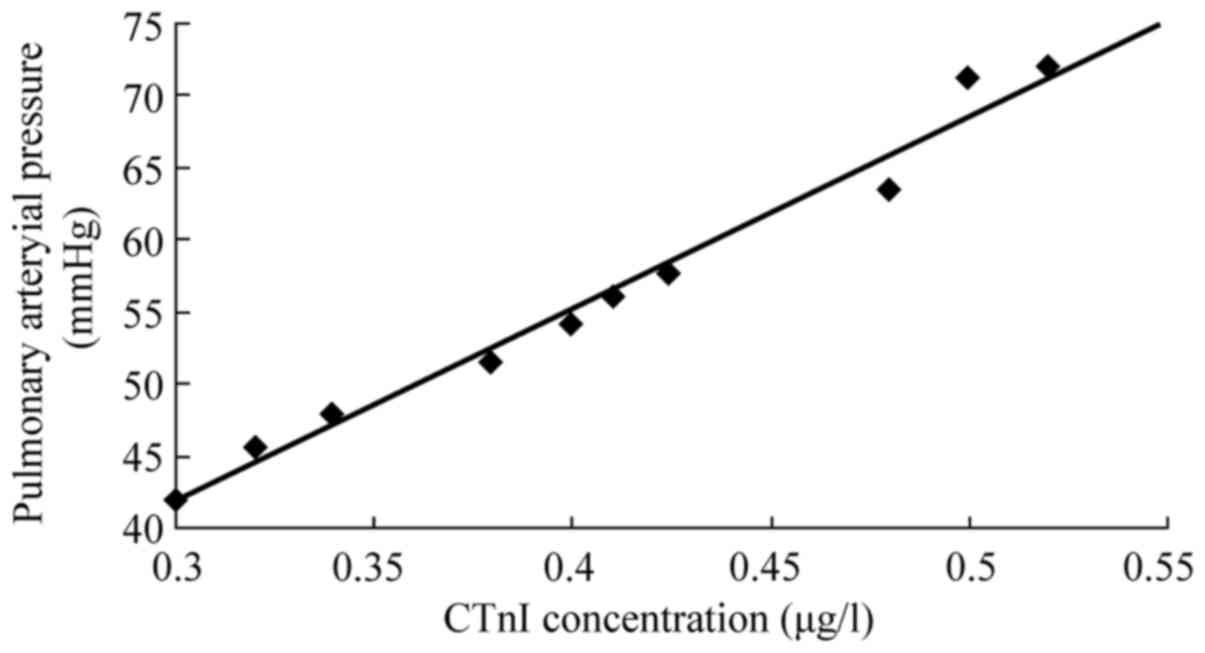
|
1
|
Darze ES, Casqueiro JB, Ciuffo LA, Santos
JM, Magalhães IR and Latado AL: Pulmonary embolism mortality in
Brazil from 1989 to 2010: Gender and regional disparities. Arq Bras
Cardiol. 106:4–12. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yavuz S, Toktas F, Goncu T, Eris C, Gucu
A, Ay D, Erdolu B, Tenekecioglu E, Karaagac K, Vural H and
Ozyazicioglu A: Surgical embolectomy for acute massive pulmonary
embolism. Int J Clin Exp Med. 7:5362–5375. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Dalen JE and Alpert JS: Natural history of
pulmonary embolism. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 17:259–270. 1975.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Soloff A and Rodman T: Acute pulmonary
embolism. II. Clinical. Am Heart J. 74:829–847. 1967. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Jones AE, Watts JA, Debelak JP, Thornton
LR, Younger JG and Kline JA: Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis
during polystyrene microsphere-induced pulmonary embolism in the
rat. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 284:L1072–L1081. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cho JH, Sridharan Kutti G, Kim SH, Kaw R,
Abburi T, Irfan A and Kocheril AG: Right ventricular dysfunction as
an echocardiographic prognostic factor in hemodynamically stable
patients with acute pulmonary embolism: A meta-analysis. BMC
Cardiovasc Disord. 14:642014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Meyer T, Binder L, Hruska N, Luthe H and
Buchwald AB: Cardiac troponin I elevation in acute pulmonary
embolism is associated with right ventricular dysfunction. J Am
Coll Cardiol. 36:1632–1636. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
French Intensive Care Society, .
International congress-Réanimation 2016. Ann Intensive Care. 6
Suppl 1:S502016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Kreit JW: The impact of right ventricular
dysfunction on the prognosis and therapy of normotensive patients
with pulmonary embolism. Chest. 125:1539–1545. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kline JA, Hernandez J, Garrett JS and
Jones AE: Pilot study of a protocol to administer inhaled nitric
oxide to treat severe acute submassive pulmonary embolism. Emerg
Med J. 31:459–462. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Trummer G, Berchtold-Herz M, Martin J and
Beyersdorf F: Successful treatment of pulmonary hypertension with
inhaled nitric oxide after pulmonary embolectomy. Ann Thorac Surg.
73:1299–1301. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Waldow T, Witt W, Janke A, Ulmer A, Buzin
A and Matschke K: Cell-cell junctions and vascular endothelial
growth factor in rat lung as affected by ischemia/reperfusion and
preconditioning with inhaled nitric oxide. J Surg Res. 157:30–42.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Qi Y, Qian L, Sun B, Liu L, Wu P and Sun
L: Inhaled NO contributes to lung repair in piglets with acute
respiratory distress syndrome via increasing circulating
endothelial progenitor cells. PLoS One. 7:e338592012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Strijdom H, Chamane N and Lochner A:
Nitric oxide in the cardiovascular system: A simple molecule with
complex actions. Cardiovasc J Afr. 20:303–310. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Elias A, Mallett S, Daoud-Elias M, Poggi
JN and Clarke M: Prognostic models in acute pulmonary embolism: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open. 6:e0103242016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Müller-Bardorff M, Weidtmann B, Giannitsis
E, Kurowski V and Katus HA: Release kinetics of cardiac troponin T
in survivors of confirmed severe pulmonary embolism. Clin Chem.
48:673–675. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Go AS, Mozaffarian D, Roger VL, Benjamin
EJ, Berry JD, Blaha MJ, Dai S, Ford ES, Fox CS, Franco S, et al:
Heart disease and stroke statistics-2014 update: A report from the
American Heart Association. Circulation. 129:e28–e292. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zagorski J, Gellar MA, Obraztsova M, Kline
JA and Watts JA: Inhibition of CINC-1 decreases right ventricular
damage caused by experimental pulmonary embolism in rats. J
Immunol. 179:7820–7826. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lannan KL, Phipps RP and White RJ:
Thrombosis, platelets, microparticles and PAH: More than clot. Drug
Discov Today. 19:1230–1235. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
von Brühl ML, Stark K, Steinhart A,
Chandraratne S, Konrad I, Lorenz M, Khandoga A, Tirniceriu A,
Coletti R, Köllnberger M, et al: Monocytes, neutrophils, and
platelets cooperate to initiate and propagate venous thrombosis in
mice in vivo. J Exp Med. 209:819–835. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sullivan DM, Watts JA and Kline JA:
Biventricular cardiac dysfunction after acute massive pulmonary
embolism in the rat. J Appl Physiol (1985). 90:1648–1656. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Montani D, Günther S, Dorfmüller P, Perros
F, Girerd B, Garcia G, Jaïs X, Savale L, Artaud-Macari E, Price LC,
et al: Pulmonary arterial hypertension. Orphanet J Rare Dis.
8:972013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Xu Q, Huang K, Zhai Z, Yang Y, Wang J and
Wang C: Initial thrombolysis treatment compared with
anticoagulation for acute intermediate-risk pulmonary embolism: A
meta-analysis. J Thorac Dis. 7:810–821. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tanus-Santos JE and Moreno H Jr: The use
of inhaled nitric oxide during gas embolism. Chest. 115:1220–1221.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yang Y, Feng Y, Zhou XG, Pan JJ and Zhou
XY: Inhaled nitric oxide in preterm infants: An updated
meta-analysis. J Res Med Sci. 21:412016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Nong Z, Hoylaerts M, Van Pelt N, Collen D
and Janssens S: Nitric oxide inhalation inhibits platelet
aggregation and platelet-mediated pulmonary thrombosis in rats.
Circ Res. 81:865–869. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|