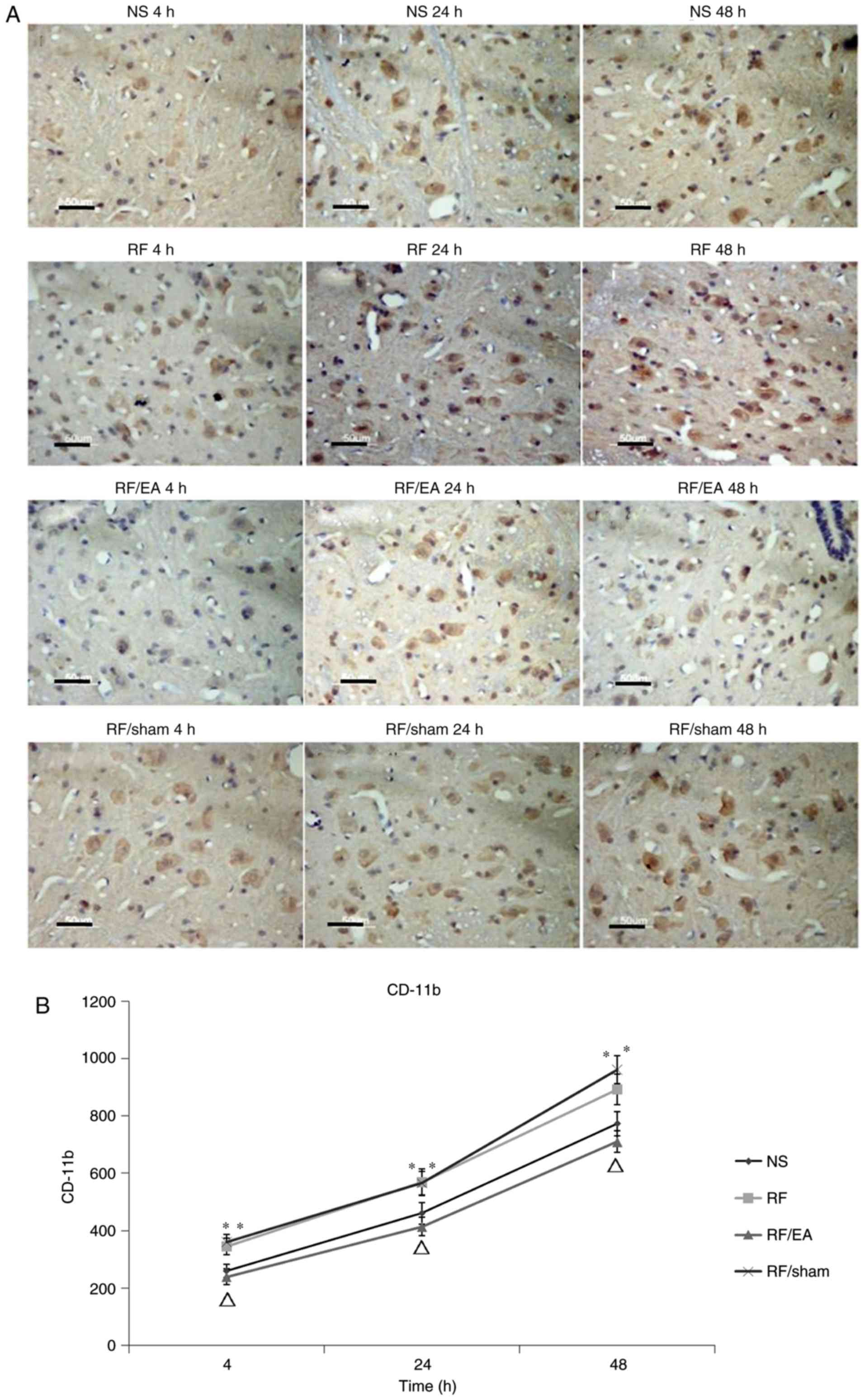
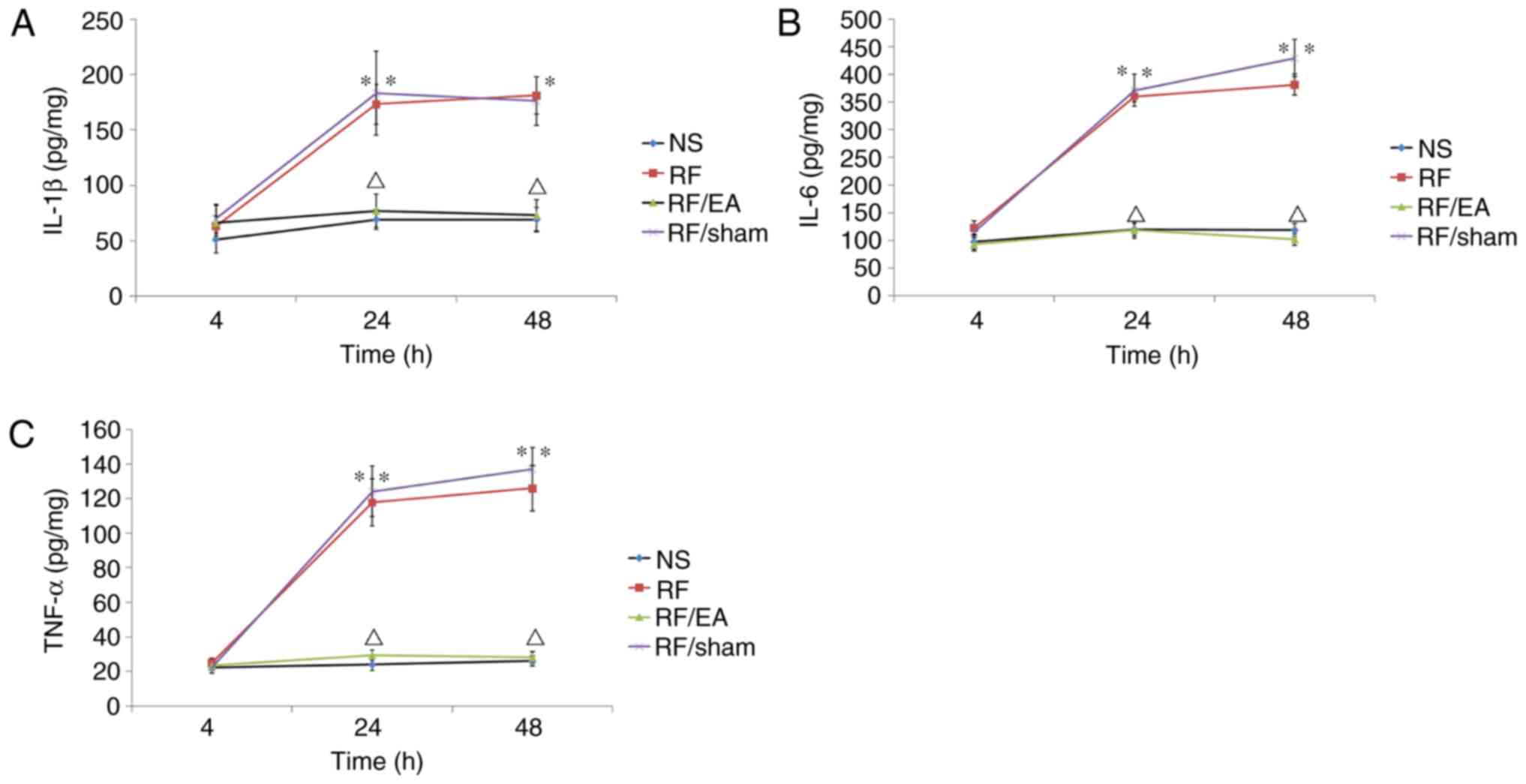
|
1
|
Khanykin B, Siddiqi R, Jensen PF, Bigler
DR and Atroshchenko GV: Comparison of remifentanil and low-dose
fentanyl for fast-track cardiac anesthesia: A prospective
randomized study. Heart Surg Forum. 16:E324–328. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Douma MR, Verwey RA, Kam-Endtz CE, van der
Linden PD and Stienstra R: Obstetric analgesia: A comparison of
patient-controlled meperidine, remifentanil, and fentanyl in
labour. Br J Anaesth. 104:209–215. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Fletcher D and Martinez V: Opioid-induced
hyperalgesia in patients after surgery: A systematic review and a
meta-analysis. Br J Anaesth. 112:991–1004. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Rivosecchi RM, Rice MJ, Smithburger PL,
Buckley MS, Coons JC and Kane-Gill SL: An evidence based systematic
review of remifentanil associated opioid-induced hyperalgesia.
Expert Opin Drug Saf. 13:587–603. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Petrenko AB, Ishii H, Kohno T and Baba H:
When similar is not alike: Decreased sensory thresholds after
intravenous infusion of remifentanil may not be
remifentanil-induced hyperalgesia. Anesth Analg. 115:9772012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Berta T, Park CK, Xu ZZ, Xie RG, Liu T, Lü
N, Liu YC and Ji RR: Extracellular caspase-6 drives murine
inflammatory pain via microglial TNF-α secretion. J Clin Invest.
124:1173–1186. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Huang CT, Chiang RP, Chen CL and Tsai YJ:
Sleep deprivation aggravates median nerve injury-induced
neuropathic pain and enhances microglial activation by suppressing
melatonin secretion. Sleep. 37:1513–1523. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mika J, Popiolek-Barczyk K, Rojewska E,
Makuch W, Starowicz K and Przewlocka B: Delta-opioid receptor
analgesia is independent of microglial activation in a rat model of
neuropathic pain. PloS One. 9:e1044202014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Vickers AJ, Rusch VW, Malhotra VT, Downey
RJ and Cassileth BR: Acupuncture is a feasible treatment for
post-thoracotomy pain: Results of a prospective pilot trial. BMC
Anesthesiol. 6:52006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Milligan ED, Twining C, Chacur M,
Biedenkapp J, O'Connor K, Poole S, Tracey K, Martin D, Maier SF and
Watkins LR: Spinal glia and proinflammatory cytokines mediate
mirror-image neuropathic pain in rats. J Neurosci. 23:1026–1040.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang L, Berta T, Xu ZZ, Liu T, Park JY
and Ji RR: TNF-α contributes to spinal cord synaptic plasticity and
inflammatory pain: Distinct role of TNF receptor subtypes 1 and 2.
Pain. 152:419–427. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Maresz K, Pryce G, Ponomarev ED, Marsicano
G, Croxford JL, Shriver LP, Ledent C, Cheng X, Carrier EJ, Mann MK,
et al: Direct suppression of CNS autoimmune inflammation via the
cannabinoid receptor CB1 on neurons and CB2 on autoreactive T
cells. Nat Med. 13:492–497. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sun Y, Zhang W, Liu Y, Liu X, Ma Z and Gu
X: Intrathecal injection of JWH015 attenuates remifentanil-induced
postoperative hyperalgesia by inhibiting activation of spinal glia
in a rat model. Anesth Analg. 118:841–853. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Song JW, Lee YW, Yoon KB, Park SJ and Shim
YH: Magnesium sulfate prevents remifentanil-induced postoperative
hyperalgesia in patients undergoing thyroidectomy. Anesth Analg.
113:390–397. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Echevarria G, Elgueta F, Fierro C, Bugedo
D, Faba G, Iñiguez-Cuadra R, Muñoz HR and Cortínez LI: Nitrous
oxide (N(2)O) reduces postoperative opioid-induced hyperalgesia
after remifentanil-propofol anaesthesia in humans. Br J Anaesth.
107:959–965. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Elterman KG, Mallampati SR, Kaye AD and
Urman RD: Postoperative alterations in taste and smell. Anesth Pain
Med. 4:e185272014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chen T, Wang K, Xu J, Ma W and Zhou J:
Electroacupuncture reduces postoperative pain and analgesic
consumption in patients undergoing thoracic surgery: A randomized
study. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2016:21264162016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Linde K, Vickers A, Hondras M, ter Riet G,
Thormählen J, Berman B and Melchart D: Systematic reviews of
complementary therapies - an annotated bibliography. Part 1:
Acupuncture. BMC Complement Altern Med. 1:32001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Park JH, Han JB, Kim SK, Park JH, Go DH,
Sun B and Min BI: Spinal GABA receptors mediate the suppressive
effect of electroacupuncture on cold allodynia in rats. Brain Res.
1322:24–29. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ma W, Zhu YM, Zhou H, Fu GQ, Pan H and
Shen WD: Protecting action of acupuncture-drug compound anesthesia
with different frequency electroacupuncture on stress reaction in
pneumonectomy. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 31:1020–1024. 2011.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Robinson CR, Zhang H and Dougherty PM:
Astrocytes, but not microglia, are activated in oxaliplatin and
bortezomib-induced peripheral neuropathy in the rat. Neuroscience.
274:308–317. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Xie YH, Chai XQ, Wang YL, Gao YC and Ma J:
Effect of electro-acupuncture stimulation of Ximen (PC4) and
Neiguan (PC6) on remifentanil-induced breakthrough pain following
thoracal esophagectomy. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci.
34:569–574. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Su TF, Zhang LH, Peng M, Wu CH, Pan W,
Tian B, Shi J, Pan HL and Li M: Cannabinoid CB2 receptors
contribute to upregulation of β-endorphin in inflamed skin tissues
by electroacupuncture. Mol Pain. 7:982011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Fais RS, Reis GM, Silveira JW, Dias QM,
Rossaneis AC and Prado WA: Amitriptyline prolongs the
antihyperalgesic effect of 2- or 100-Hz electro-acupuncture in a
rat model of post-incision pain. Eur J Pain. 16:666–675. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Onda A, Jiao Q, Nagano Y, Akimoto T,
Miyamoto T, Minamisawa S and Fukubayashi T: Acupuncture ameliorated
skeletal muscle atrophy induced by hindlimb suspension in mice.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 410:434–439. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Cooper ZD, Truong YN, Shi YG and Woods JH:
Morphine deprivation increases self-administration of the fast- and
short-acting mu-opioid receptor agonist remifentanil in the rat. J
Pharmacol Exp Ther. 326:920–929. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hanisch UK and Kettenmann H: Microglia:
Active sensor and versatile effector cells in the normal and
pathologic brain. Nat Neurosci. 10:1387–1394. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hua X, LI C, Zhou H, Song D and Hu Y: The
trituration of the atlas of the rat acupoints. Shiyan Dongwu Yu
Dongwu Shiyan. 3:1–5. 1991.
|
|
29
|
Romita VV, Suk A and Henry JL: Parametric
studies on electroacupuncture-like stimulation in a rat model:
Effects of intensity, frequency, and duration of stimulation on
evoked antinociception. Brain Res Bull. 42:289–296. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lao L, Zhang RX, Zhang G, Wang X, Berman
BM and Ren K: A parametric study of electroacupuncture on
persistent hyperalgesia and Fos protein expression in rats. Brain
Res. 1020:18–29. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Fang JL, Krings T, Weidemann J, Meister IG
and Thron A: Functional MRI in healthy subjects during acupuncture:
Different effects of needle rotation in real and false acupoints.
Neuroradiology. 46:359–362. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Brennan TJ, Vandermeulen EP and Gebhart
GF: Characterization of a rat model of incisional pain. Pain.
64:493–501. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yuan Y, Wang JY, Yuan F, Xie KL, Yu YH and
Wang GL: Glycogen synthase kinase-3β contributes to
remifentanil-induced postoperative hyperalgesia via regulating
N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor trafficking. Anesth Analg.
116:473–481. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Gu X, Wu X, Liu Y, Cui S and Ma Z:
Tyrosine phosphorylation of the N-Methyl-D-Aspartate receptor 2B
subunit in spinal cord contributes to remifentanil-induced
postoperative hyperalgesia: The preventive effect of ketamine. Mol
Pain. 5:762009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Celerier E, Gonzalez JR, Maldonado R,
Cabanero D and Puig MM: Opioid-induced hyperalgesia in a murine
model of postoperative pain: Role of nitric oxide generated from
the inducible nitric oxide synthase. Anesthesiology. 104:546–555.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ji M, Wang X, Chen M, Shen Y, Zhang X and
Yang J: The efficacy of acupuncture for the treatment of sciatica:
A systematic review and meta-analysis. Evid Based Complement
Alternat Med. 2015:1928082015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Iacobone M, Citton M, Zanella S, Scarpa M,
Pagura G, Tropea S, Galligioni H, Ceccherelli F, Feltracco P, Viel
G and Nitti D: The effects of acupuncture after thyroid surgery: A
randomized, controlled trial. Surgery. 156:1605–1612. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wang H, Xie Y, Zhang Q, Xu N, Zhong H,
Dong H, Liu L, Jiang T, Wang Q and Xiong L: Transcutaneous electric
acupoint stimulation reduces intra-operative remifentanil
consumption and alleviates postoperative side-effects in patients
undergoing sinusotomy: A prospective, randomized,
placebo-controlled trial. Br JAnaesth. 112:1075–1082. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Sator-Katzenschlager SM, Wolfler MM,
Kozek-Langenecker SA, Sator K, Sator PG, Li B, Heinze G and Sator
MO: Auricular electro-acupuncture as an additional perioperative
analgesic method during oocyte aspiration in IVF treatment. Hum
Reprod. 21:2114–2120. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhang Q, Li YN, Guo YY, Yin CP, Gao F, Xin
X, Huo SP, Wang XL and Wang QJ: Effects of preconditioning of
electro-acupuncture on postoperative cognitive dysfunction in
elderly: A prospective, randomized, controlled trial. Medicine
(Baltimore). 96:e73752017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zhao M and Joo DT: Enhancement of spinal
N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor function by remifentanil action at
delta-opioid receptors as a mechanism for acute opioid-induced
hyperalgesia or tolerance. Anesthesiology. 109:308–317. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhang Y, Zhang RX, Zhang M, Shen XY, Li A,
Xin J, Ren K, Berman BM, Tan M and Lao L: Electroacupuncture
inhibition of hyperalgesia in an inflammatory pain rat model:
Involvement of distinct spinal serotonin and norepinephrine
receptor subtypes. Br J Anaesth. 109:245–252. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Liu W, Wu J, Huang J, Zhuo P, Lin Y, Wang
L, Lin R, Chen L and Tao J: Electroacupuncture regulates
hippocampal synaptic plasticity via miR-134-Mediated LIMK1 function
in rats with ischemic stroke. Neural Plast. 2017:95456462017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhu Y, Deng L, Tang H, Gao X, Wang Y, Guo
K, Kong J and Yang C: Electroacupuncture improves neurobehavioral
function and brain injury in rat model of intracerebral hemorrhage.
Brain Res Bull. 131:123–132. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|