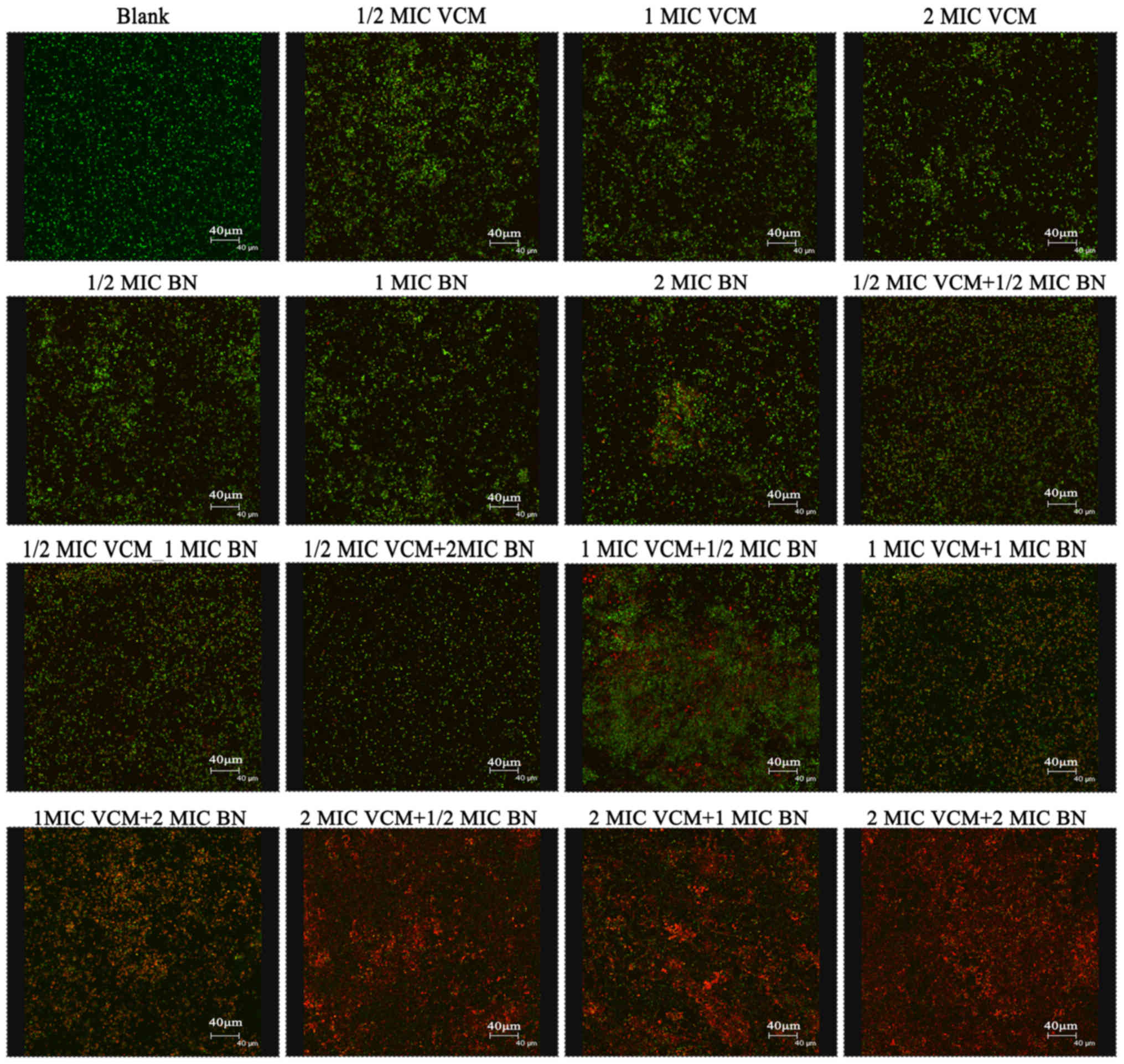
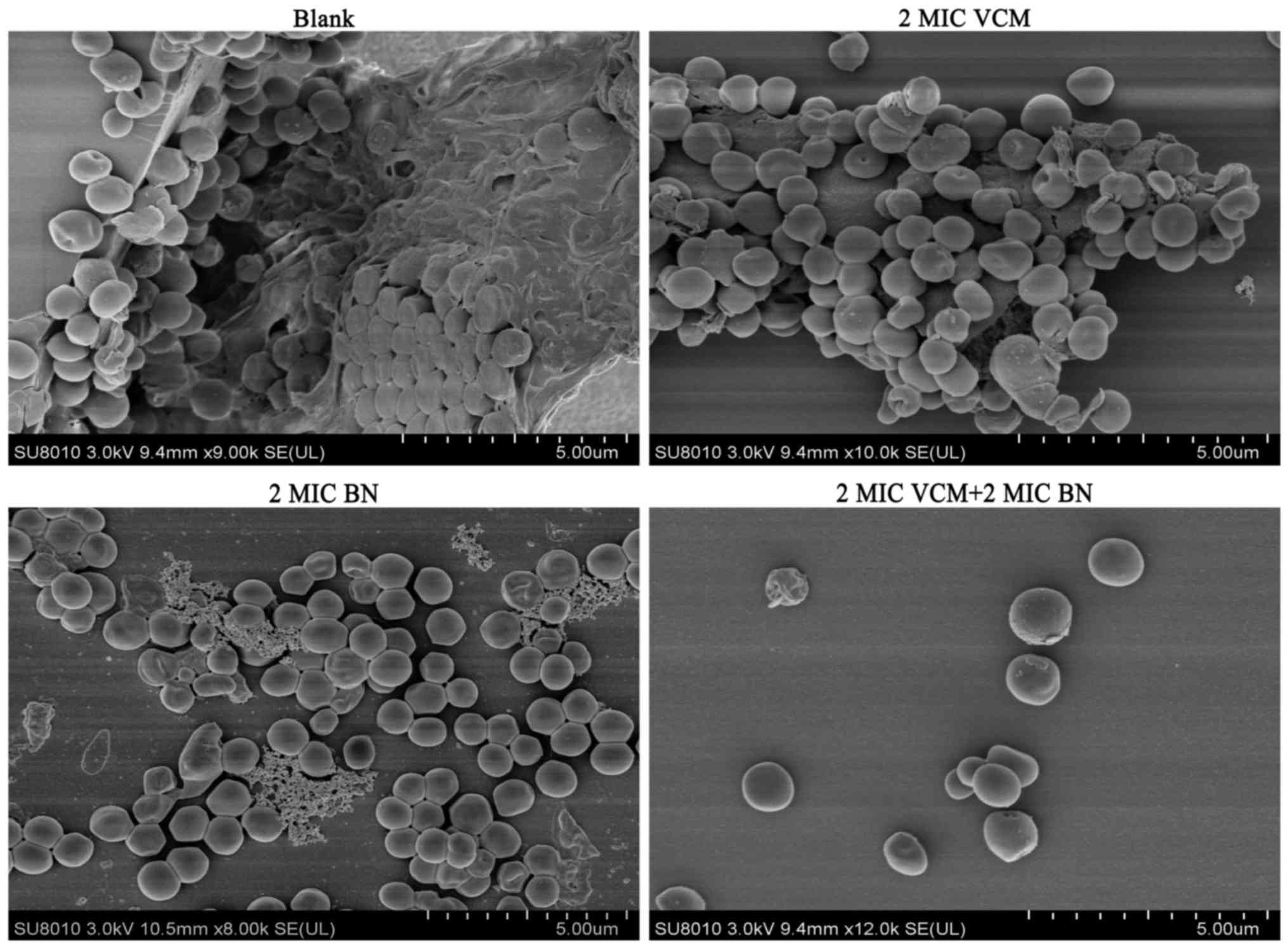
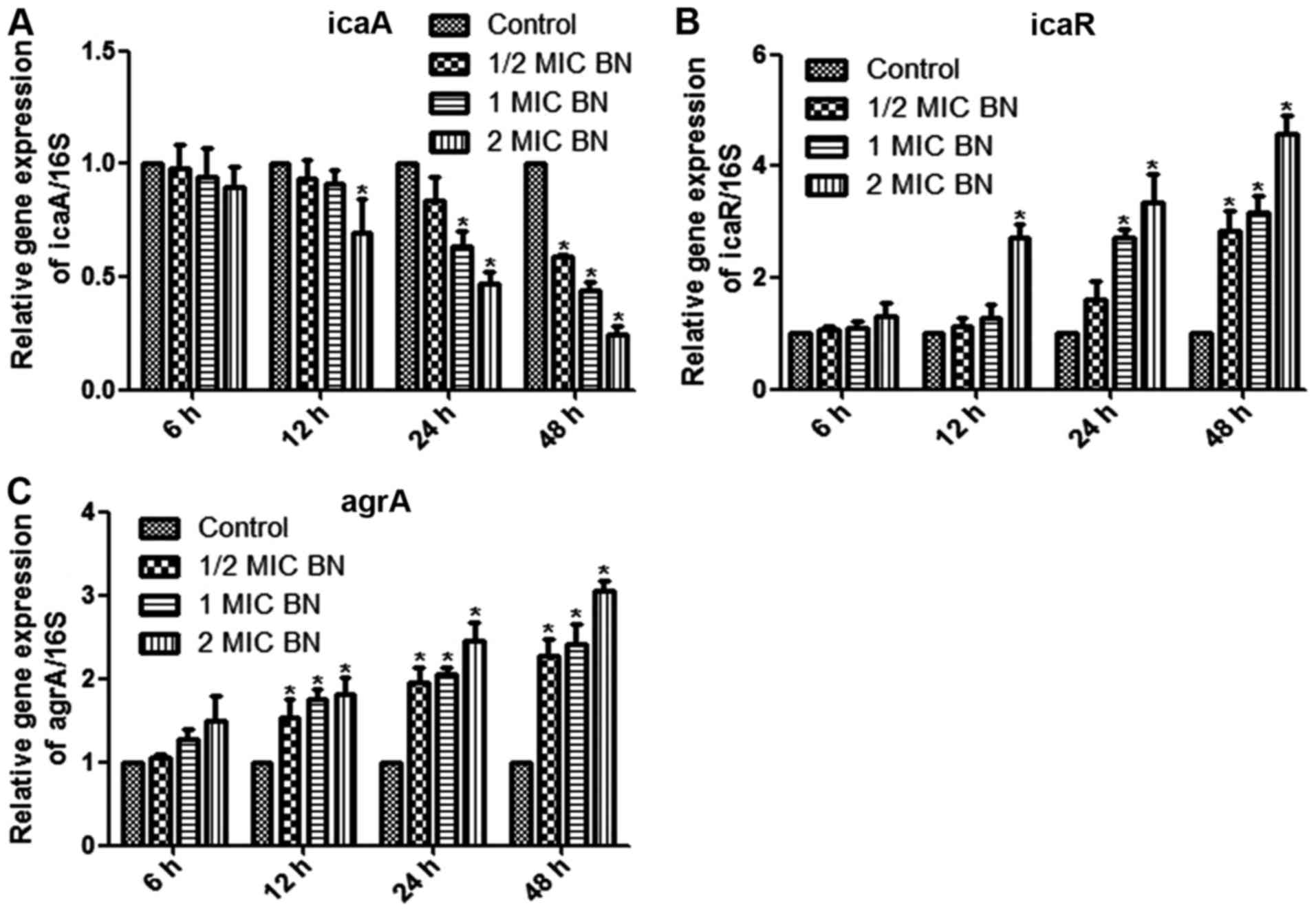
|
1
|
Yu L, Hisatsune J, Hayashi I, Tatsukawa N,
Sato'o Y, Mizumachi E, Kato F, Hirakawa H, Pier GB and Sugaia M: A
Novel Repressor of the ica locus discovered in clinically isolated
super-biofilm-elaborating Staphylococcus aureus. MBio.
8:pii:e02282. –16. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Yoshii Y, Okuda KI, Yamada S, Nagakura M,
Sugimoto S, Nagano T, Okabe T, Kojima H, Iwamoto T, Kuwano K and
Mizunoe Y: Norgestimate inhibits staphylococcal biofilm formation
and resensitizes methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
to β-lactam antibiotics. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes. 3:182017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sollid JU, Furberg AS, Hanssen AM and
Johannessen M: Staphylococcus aureus: Determinants of human
carriage. Infect Genet Evol. 21:531–541. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kong C, Chee CF, Richter K, Thomas N,
Rahman Abd N and Nathan S: Suppression of Staphylococcus
aureus biofilm formation and virulence by a benzimidazole
derivative, UM-C162. Sci Rep. 8:27582018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Waryah CB, Wells K, Ulluwishewa D,
Chen-Tan N, Gogoi-Tiwari J, Ravensdale J, Costantino P, Gökçen A,
Vilcinskas A, Wiesner J and Mukkur T: In vitro antimicrobial
efficacy of tobramycin against Staphylococcus aureus
biofilms in combination with or without DNase I and/or Dispersin B:
A preliminary investigation. Microb Drug Resist. 23:384–390. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lázaro-Díez M, Remuzgo-Martínez S,
Rodríguez-Mirones C, Acosta F, Icardo JM, Martínez-Martínez L and
Ramos-Vivas J: Effects of subinhibitory concentrations of
ceftaroline on methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
(MRSA) biofilms. PLoS One. 11:e01475692016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Feuillie C, Formosa-Dague C, Hays LM,
Vervaecka O, Derclayea S, Brennanc MP, Fosterb TJ, Geogheganb JA
and Dufrêne YF: Molecular interactions and inhibition of the
staphylococcal biofilm-forming protein SdrC. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 114:3738–3743. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Howlin RP, Brayford MJ, Webb JS, Cooper
JJ, Aiken SS and Stoodley P: Antibiotic-loaded synthetic Calcium
sulfate beads for prevention of bacterial colonization and biofilm
formation in periprosthetic infections. Antimicrob Agents
Chemother. 59:111–120. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Koch G, Yepes A, Förstner KU, Wermser C,
Stengel ST, Modamio J, Ohlsen K, Foster KR and Lopez D: Evolution
of resistance to a last-resort antibiotic in Staphylococcus
aureus via bacterial competition. Cell. 158:1060–1071. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Howden BP, Davies JK, Johnson PD, Stinear
TP and Grayson ML: Reduced vancomycin susceptibility in
Staphylococcus aureus, including vancomycin-intermediate and
heterogeneous vancomycin-intermediate strains: Resistance
mechanisms, laboratory detection, and clinical implications. Clin
Microbiol Rev. 23:99–139. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Kiedrowski MR and Horswill AR: New
approaches for treating staphylococcal biofilm infections. Ann N Y
Acad Sci. 1241:104–121. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bhattacharya M, Wozniak DJ, Stoodley P and
Hall-Stoodley L: Prevention and treatment of Staphylococcus
aureus biofilms. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 13:1499–1516.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Salem AH, Elkhatib WF and Noreddin AM:
Pharmacodynamic assessment of vancomycin-rifampicin combination
against methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus biofilm:
A parametric response surface analysis. J Pharma Pharmacol.
63:73–79. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Olson ME, Slater SR, Rupp ME and Fey PD:
Rifampicin enhances activity of daptomycin and vancomycin against
both a polysaccharide intercellular adhesin (PIA)-dependent and
-independent Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilm. J
Antimicrob Chemother. 65:2164–2171. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Fontaine BM, Nelson K, Lyles JT, Jariwala
PB, García-Rodriguez JM, Quave CL and Weinert EE: Identification of
ellagic acid rhamnoside as a bioactive component of a complex
botanical extract with anti-biofilm activity. Front Microbiol.
8:4962017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Fu B, Wu Q, Dang M, Bai D, Guo Q, Shen L
and Duan K: Inhibition of pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm formation
by traditional chinese medicinal herb herba patriniae. Biomed Res
Int. 2017:95847032017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Luo J, Dong B, Wang K, Cai S, Liu T, Cheng
X, Lei D and Chen Y, Li Y, Kong J and Chen Y: Baicalin inhibits
biofilm formation, attenuates the quorum sensing-controlled
virulence and enhances Pseudomonas aeruginosa clearance in a mouse
peritoneal implant infection model. PLoS One. 12:e01768832017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
García-Heredia A, García S,
Merino-Mascorro JÁ, Feng P and Heredia N: Natural plant products
inhibits growth and alters the swarming motility, biofilm
formation, and expression of virulence genes in enteroaggregative
and enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli. Food Microbiol. 59:124–132.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kim J, Lee HK, Chang TS, Kang KS and Hwang
GS: Inhibitory effect of brazilin on osteoclast differentiation and
its mechanism of action. Int Immunopharmacol. 29:628–634. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gao XJ, Wang TC, Zhang ZC, Cao YG, Zhang
NS and Guo MY: Brazilin plays an anti-inflammatory role with
regulating Toll-like receptor 2 and TLR 2 downstream pathways in
Staphylococcus aureus-induced mastitis in mice. Int
Immunopharmacol. 27:130–137. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Dan P, Zhou X and Chen Z: Research
progress on mechanism and treatment of Staphylococcus aureus
biofilms. Molecular Biomedicine. 23:3745–3749. 2017.
|
|
22
|
Nirmal NP and Panichayupakaranant P:
Antioxidant, antibacterial, and anti-inflammatory activities of
standardized brazilin-rich Caesalpinia sappan extract. Pharm Biol.
53:1339–1343. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yan Y, Chen YC, Lin YH, Guo J, Niu ZR, Li
L, Wang SB, Fang LH and Du GH: Brazilin isolated from the heartwood
of Caesalpinia sappan L induces endothelium-dependent
and-independent relaxation of rat aortic rings. Acta Pharmacol Sin.
36:1318–1326. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Clinical and Laboratory Standards
Institute: Methods for dilution antimicrobial susceptibility tests
for bacteria that grow aerobically; approved standard, 9th ed CLSI
document M7-A9. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute; Wayne,
PA: 2012
|
|
25
|
Shi SF, Jia JF, Guo XK, Zhao YP, Chen DS,
Guo YY and Zhang XL: Reduced Staphylococcus aureus biofilm
formation in the presence of chitosan-coated iron oxide
nanoparticles. Int J Nanomedicine. 11:6499–6506. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Balasubramanian S, Othman EM, Kampik D,
Stopper H, Hentschel U, Ziebuhr1 W, Oelschlaeger1 TA and
Abdelmohsen UR: Marine sponge-derived Streptomyces sp. SBT343
extract inhibits Staphylococcal biofilm formation. Front Microbiol.
8:2362017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sugimoto S, Sato F, Miyakawa R, Chiba A,
Onodera S, Hori S and Mizunoe Y: Broad impact of extracellular DNA
on biofilm formation by clinically isolated Methicillin-resistant
and-sensitive strains of Staphylococcus aureus. Sci Rep.
8:22542018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Singh AK, Prakash P, Achra A, Singh GP,
Das A and Singh RK: Standardization and classification of in
vitro biofilm formation by clinical isolates of
Staphylococcus aureus. J Glob Infect Dis. 9:93–101. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Brooks JL and Jefferson KK: Staphylococcal
biofilms: Quest for the magic bullet. Adv Appl Microbiol. 81:63–87.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
van Hal SJ, Lodise TP and Paterson DL: The
clinical significance of vancomycin minimum inhibitory
concentration in Staphylococcus aureus infections: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Infect Dis. 54:755–771.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chen Y, Liu T, Wang K, Hou C, Cai S, Huang
Y, Du Z, Huang H, Kong J and Chen Y: Baicalein inhibits
Staphylococcus aureus biofilm formation and the quorum
sensing system in vitro. PLoS One. 11:e01534682016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
O'gara JP: Ica and beyond: Biofilm
mechanisms and regulation in Staphylococcus epidermidis and
Staphylococcus aureus. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 270:179–188.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Figueiredo AMS, Ferreira FA, Beltrame CO
and Côrtes MF: The role of biofilms in persistent infections and
factors involved in ica-independent biofilm development and gene
regulation in Staphylococcus aureus. Crit Rev Microbiol.
43:602–620. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ma R, Qiu S, Jiang Q, Sun H, Xue T, Cai G
and Sun B: AI-2 quorum sensing negatively regulates rbf expression
and biofilm formation in Staphylococcus aureus. Int J Med
Microbiol. 307:257–267. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Gupta A and Mishra S, Singh S and Mishra
S: Prevention of IcaA regulated poly N-acetyl glucosamine formation
in Staphylococcus aureus biofilm through new-drug like
inhibitors: In silico approach and MD simulation study. Microb
Pathog. 110:659–669. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Skurnik D, Cywes-Bentley C and Pier GB:
The exceptionally broad-based potential of active and passive
vaccination targeting the conserved microbial surface
polysaccharide PNAG. Expert Rev Vaccines. 15:1041–1053. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Formosa-Dague C, Feuillie C, Beaussart A,
Derclaye S, Kucharíková S, Lasa I, Van Dijck P and Dufrêne YF:
Sticky matrix: Adhesion mechanism of the staphylococcal
polysaccharide intercellular adhesin. ACS Nano. 10:3443–3452. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Doulgeraki AI, Di Ciccio P, Ianieri A and
Nychas GE: Methicillin-resistant food-related Staphylococcus
aureus: A review of current knowledge and biofilm formation for
future studies and applications. Res Microbiol. 168:1–15. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Pamp SJ, Frees D, Engelmann S, Hecker M
and Ingmer H: Spx is a global effector impacting stress tolerance
and biofilm formation in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol.
188:4861–4870. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kinkel TL, Roux CM, Dunman PM and Fang FC:
The Staphylococcus aureus SrrAB two-component system
promotes resistance to nitrosative stress and hypoxia. MBio.
4:e00696–e13. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Coelho LR, Souza RR, Ferreira FA,
Guimarães MA, Ferreira-Carvalho BT and Figueiredo AM: Agr RNAIII
divergently regulates glucose-induced biofilm formation in clinical
isolates of Staphylococcus aureus. Microbiology.
154:3480–3490. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Atwood DN, Beenken KE, Loughran AJ, Meeker
DG, Lantz TL, Graham JW, Spencer HJ and Smeltzer MS: XerC
contributes to diverse forms of Staphylococcus aureus
infection via agr-dependent and agr-independent pathway. Infect
Immun. 84:1214–1225. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Le KY and Otto M: Quorum-sensing
regulation in staphylococci-an overview. Front Microbiol.
6:11742015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Boles BR and Horswill AR: Agr-mediated
dispersal of Staphylococcus aureus biofilms. PLoS Pathog.
4:e10000522008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|