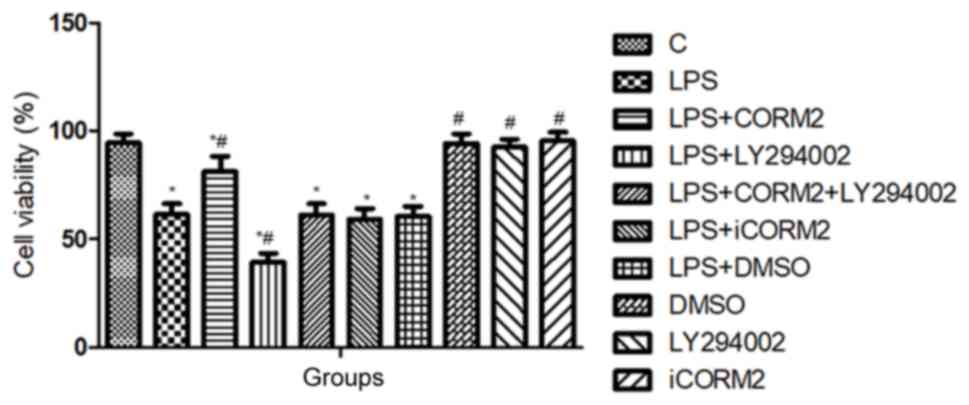
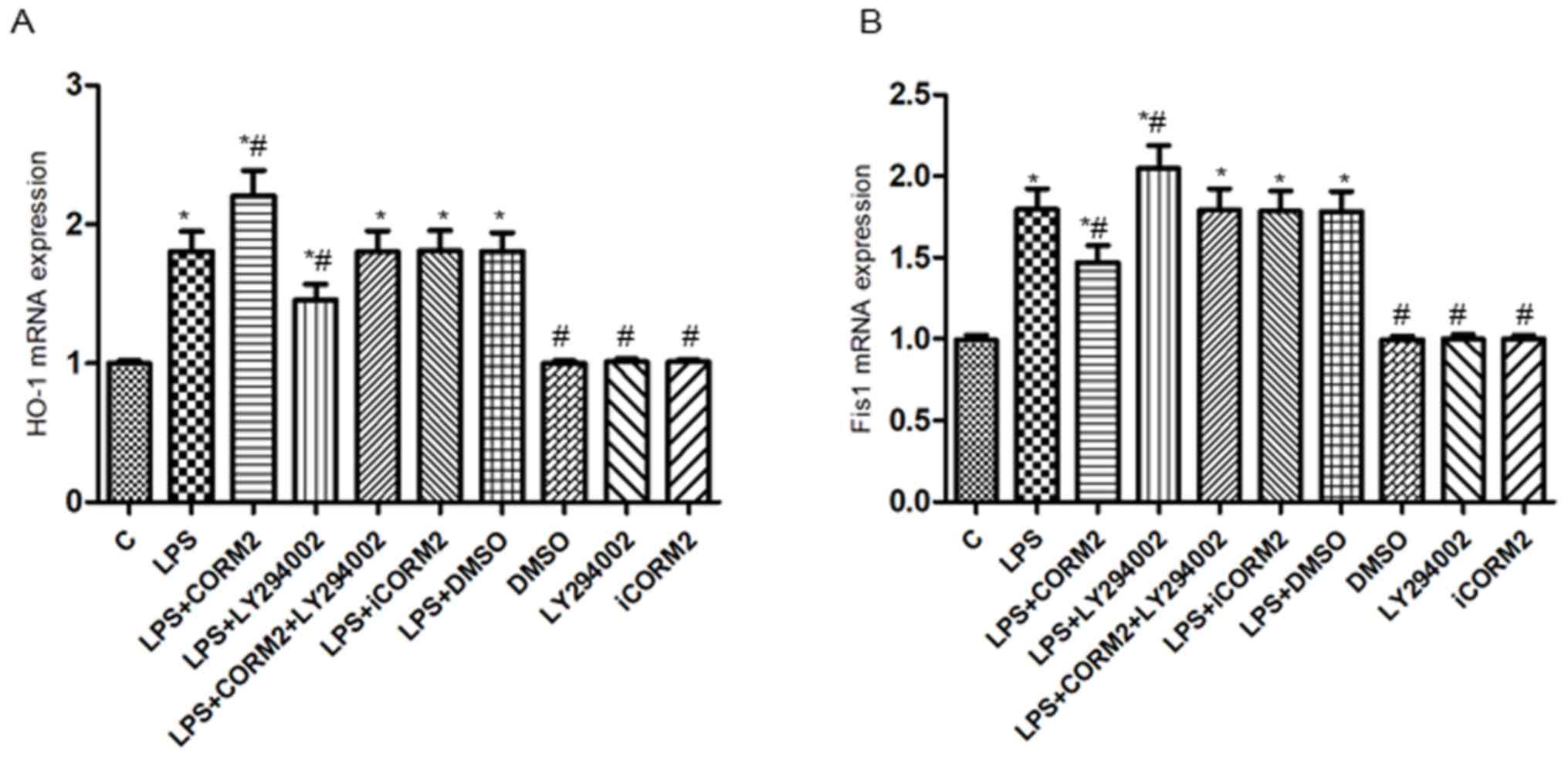
|
1
|
Pierrakos C and Vincent JL: The changing
pattern of acute respiratory distress syndrome over time: A
comparison of two periods. Eur Respir J. 40:589–595. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Moussa MD, Santonocito C, Fagnoul D,
Donadello K, Pradier O, Gaussem P, De Backer D and Vincent JL:
Evaluation of endothelial damage in sepsis-related ARDS using
circulating endothelial cells. Intensive Care Med. 41:231–238.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yu JB, Shi J, Wang D, Dong SA, Zhang Y,
Wang M, Gong LR, Fu Q and Liu DQ: Heme oxygenase-1/carbon
monoxide-regulated mitochondrial dynamic equilibrium contributes to
the attenuation of endotoxin-induced acute lung injury in rats and
in lipopolysaccharide-activated macrophages. Anesthesiology.
125:1190–1201. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sebastián D, Palacín M and Zorzano A:
Mitochondrial dynamics: Coupling mitochondrial fitness with healthy
aging. Trends Mol Med. 23:201–215. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Westermann B: Mitochondrial fusion and
fission in cell life and death. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 11:872–884.
2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chang CR and Blackstone C: Dynamic
regulation of mitochondrial fission through modification of the
dynamin-related protein Drp1. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1201:34–39. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lee S, Park YY, Kim SH, Nguyen OT, Yoo YS,
Chan GK, Sun X and Cho H: Human mitochondrial Fis1 links to cell
cycle regulators at G2/M transition. Cell Mol Life Sci. 71:711–725.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mai S, Klinkenberg M, Auburger G,
Bereiter-Hahn J and Jendrach M: Decreased expression of Drp1 and
Fis1 mediates mitochondrial elongation in senescent cells and
enhances resistance to oxidative stress through PINK1. J Cell Sci.
123:917–926. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ryter SW and Choi AM: Targeting heme
oxygenase-1 and carbon monoxide for therapeutic modulation of
inflammation. Transl Res. 167:7–34. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Constantin M, Choi AJ, Cloonan SM and
Ryter SW: Therapeutic potential of heme oxygenase-1/carbon monoxide
in lung disease. Int J Hypertens. 2012:8592352012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Qin W, Zhang J, Lv W, Wang X and Sun B:
Effect of carbon monoxide-releasing molecules II-liberated CO on
suppressing inflammatory response in sepsis by interfering with
nuclear factor kappa B activation. PLoS One. 8:e758402013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ryter SW and Choi AM: Cytoprotective and
anti-inflammatory actions of carbon monoxide in organ injury and
sepsis models. Novartis Found Symp. 280:165–175. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Shi J, Yu JB, Liu W, Wang D, Zhang Y, Gong
LR, Dong SA and Liu DQ: Carbon monoxide alleviates
lipopolysaccharide-induced oxidative stress injury through
suppressing the expression of Fis1 in NR8383 cells. Exp Cell Res.
349:162–167. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Cantley LC: The phosphoinositide 3-kinase
pathway. Science. 296:1655–1657. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lin Y, Kuang W, Wu B, Xie C, Liu C and Tu
Z: IL-12 induces autophagy in human breast cancer cells through
AMPK and the PI3K/Akt pathway. Mol Med Rep. 16:4113–4118. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jiang YQ, Chang GL, Wang Y, Zhang DY, Cao
L and Liu J: Geniposide prevents hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced
apoptosis in H9c2 Cells: Improvement of mitochondrial dysfunction
and activation of GLP-1R and the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 39:407–421. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zheng T, Yang X, Wu D, Xing S, Bian F, Li
W, Chi J, Bai X, Wu G, Chen X, et al: Salidroside ameliorates
insulin resistance through activation of a mitochondria-associated
AMPK/PI3K/Akt/GSK3β pathway. Br J Pharmacol. 172:3284–3301. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang J, Chen H, Liu Y, Zhou W, Sun R and
Xia M: Retinol binding protein 4 induces mitochondrial dysfunction
and vascular oxidative damage. Atherosclerosis. 240:335–344. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wu D, Pan P, Su X, Zhang L, Qin Q, Tan H,
Huang L and Li Y: Interferon regulatory factor-1 mediates alveolar
macrophages pyroptosis during LPS-induced acute lung injury in
mice. Shock. 46:329–338. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Williams JG, Bernstein S and Prager M:
Effect of melatonin on activated macrophage TNF, IL-6, and reactive
oxygen intermediates. Shock. 9:406–411. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ying Z, Xie X, Chen M, Yi K and
Rajagopalan S: Alpha-lipoic acid activates eNOS through activation
of PI3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway. Vascul Pharmacol. 64:28–35.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sawle P, Foresti R, Mann BE, Johnson TR,
Green CJ and Motterlini R: Carbon monoxide-releasing molecules
(CO-RMs) attenuate the inflammatory response elicitedby
lipopolysaccharide in RAW264.7 murine macrophages. Br J Pharmacol.
145:800–810. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ballweg K, Mutze K, Königshoff M,
Eickelberg O and Meiners S: Cigarette smoke extract affects
mitochondrial function in alveolar epithelial cells. Am J Physiol
Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 307:L895–L907. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C (T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Guo C, Yang L, Luo J, Zhang C, Xia Y, Ma T
and Kong L: Sophoraflavanone G from Sophora alopecuroides inhibits
lipopolysaccharide-inducedinflammation in RAW264.7 cells by
targeting PI3K/Akt, JAK/STAT and Nrf2/HO-1 pathways. Int
Immunopharmacol. 38:349–356. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Reidy MF and Wright JR: Surfactant protein
A enhances apoptotic cell uptake and TGF-beta1 release by
inflammatory alveolar macrophages. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol
Physiol. 285:L854–L861. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wu Y, Wang H, Zhang J, Ma X, Meng J, Li Y,
Hou Z and Luo X: Adenosine deaminase that acts on RNA 1p150 in
alveolar macrophage is involved in LPS-induced lung injury. Shock.
31:410–415. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gonzalez AS, Elguero ME, Finocchietto P,
Holod S, Romorini L, Miriuka SG, Peralta JG, Poderoso JJ and
Carreras MC: Abnormal mitochondrial fusion-fission balance
contributes to the progression of experimental sepsis. Free Radic
Res. 48:769–783. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Preau S, Delguste F, Yu Y, Remy-Jouet I,
Richard V, Saulnier F, Boulanger E and Neviere R: Endotoxemia
engages the RhoA kinase pathway to impair cardiac function by
altering cytoskeleton, mitochondrial fission, and autophagy.
Antioxid Redox Signal. 24:529–542. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gomes LC and Scorrano L: High levels of
Fis1, a pro-fission mitochondrial protein, trigger autophagy.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1777:860–866. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ikeda Y, Sciarretta S, Nagarajan N,
Rubattu S, Volpe M, Frati G and Sadoshima J: New insights into the
role of mitochondrial dynamics and autophagy during oxidative
stress and aging in the heart. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2014:2109342014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lee YJ, Jeong SY, Karbowski M, Smith CL
and Youle RJ: Roles of the mammalian mitochon-drial fission and
fusion mediators Fis1, Drp1, and Opa1 in apoptosis. Mol Biol Cell.
15:5001–5011. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yu JB, Wang Y, Li Z, Dong SA, Wang D, Gong
LR, Shi J, Zhang Y, Liu DQ and Mu R: Effect of heme oxygenase-1 on
mitofusion-1 protein in LPS-induced ALI/ARDS in rats. Sci Rep.
6:365302016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lu CY, Yang YC, Li CC, Liu KL, Lii CK and
Chen HW: Andrographolide inhibits TNFα-induced ICAM-1 expression
via suppression of NADPH oxidase activation and induction of HO-1
and GCLM expression through the PI3K/Akt/Nrf2 and PI3K/Akt/AP-1
pathways in human endothelial cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 91:40–50.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kim KC, Kang KA, Zhang R, Piao MJ, Kim GY,
Kang MY, Lee SJ, Lee NH, Surh YJ and Hyun JW: Up-regulation of
Nrf2-mediated heme oxygenase-1 expression by eckol, a phlorotannin
compound, through activation of Erk and PI3K/Akt. Int J Biochem
Cell Biol. 42:297–305. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Monick MM, Mallampalli RK, Carter AB,
Flaherty DM, McCoy D, Robeff PK, Peterson MW and Hunninghake GW:
Ceramide regulates lipopolysaccharide-induced phosphatidylinositol
3-kinase and Akt activity in human alveolar macrophages. J Immunol.
167:5977–5985. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chen H, Xie K, Han H, Li Y, Liu L, Yang T
and Yu Y: Molecular hydrogen protects mice against polymicrobial
sepsis by ameliorating endothelial dysfunction via an Nrf2/HO-1
signaling pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 28:643–654. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yu JB, Shi J, Gong LR, Dong SA, Xu Y,
Zhang Y, Cao XS and Wu LL: Role of Nrf2/ARE pathway in protective
effect of electroacupuncture against endotoxic shock-induced acute
lung injury in rabbits. PLoS One. 9:e1049242014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Chen HH, Chen YT, Huang YW, Tsai HJ and
Kuo CC: 4-Ketopinoresinol, a novel naturally occurring ARE
activator, induces the Nrf2/HO-1 axis and protects against
oxidative stress-induced cell injury via activation of PI3K/AKT
signaling. Free Radic Biol Med. 52:1054–1066. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|