|
1
|
Lampertico P, Agarwal K, Berg T, Buti M,
Janssen H, Papatheodoridis G, Zoulim F and Tacke F: EASL 2017
clinical practice guidelines on the management of hepatitis B virus
infection. J Hepatol. 67:370–398. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
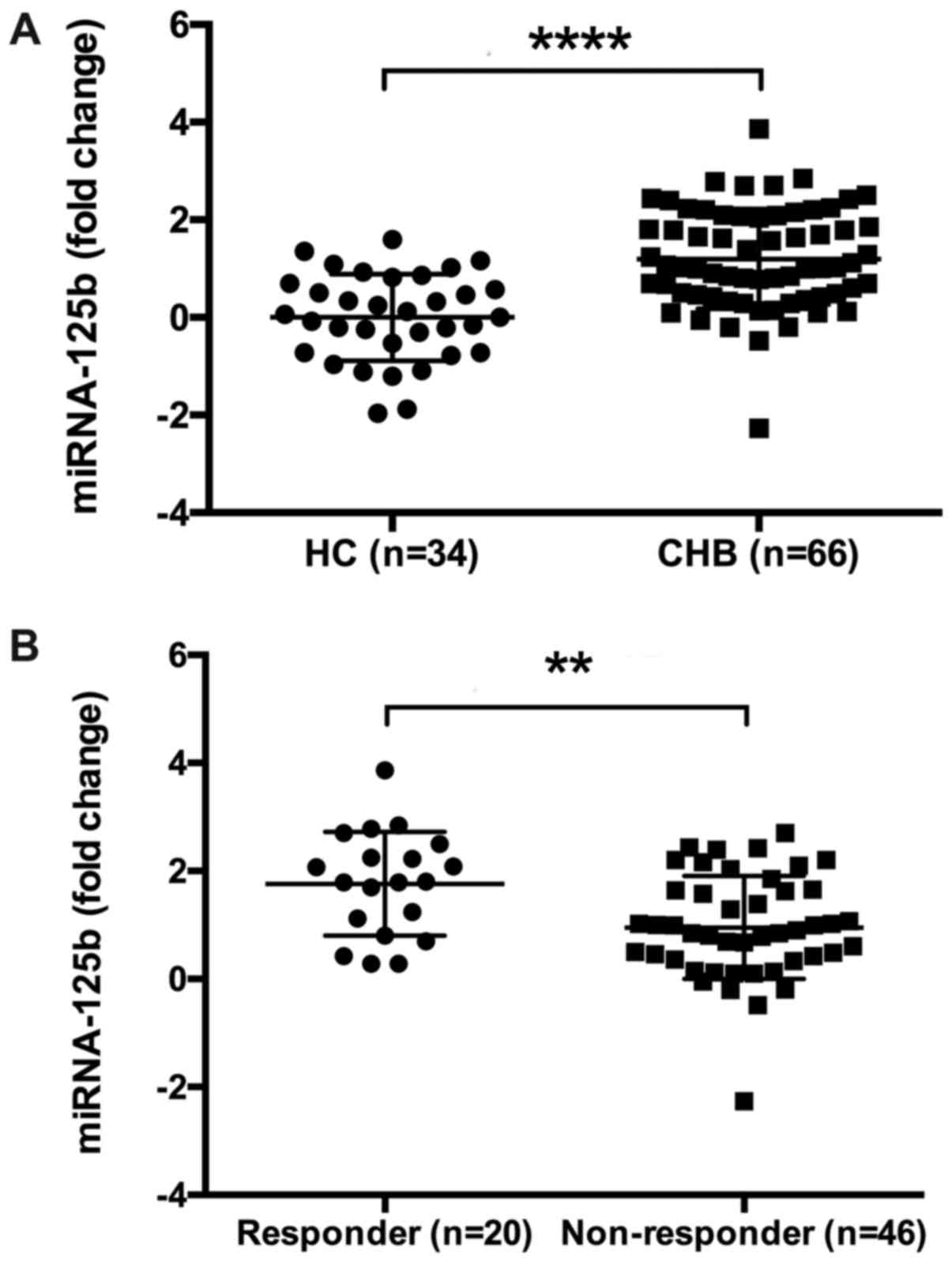
|
2
|
Terrault NA, Bzowej NH, Chang KM, Hwang
JP, Jonas MM and Murad MH: American Association for the Study of
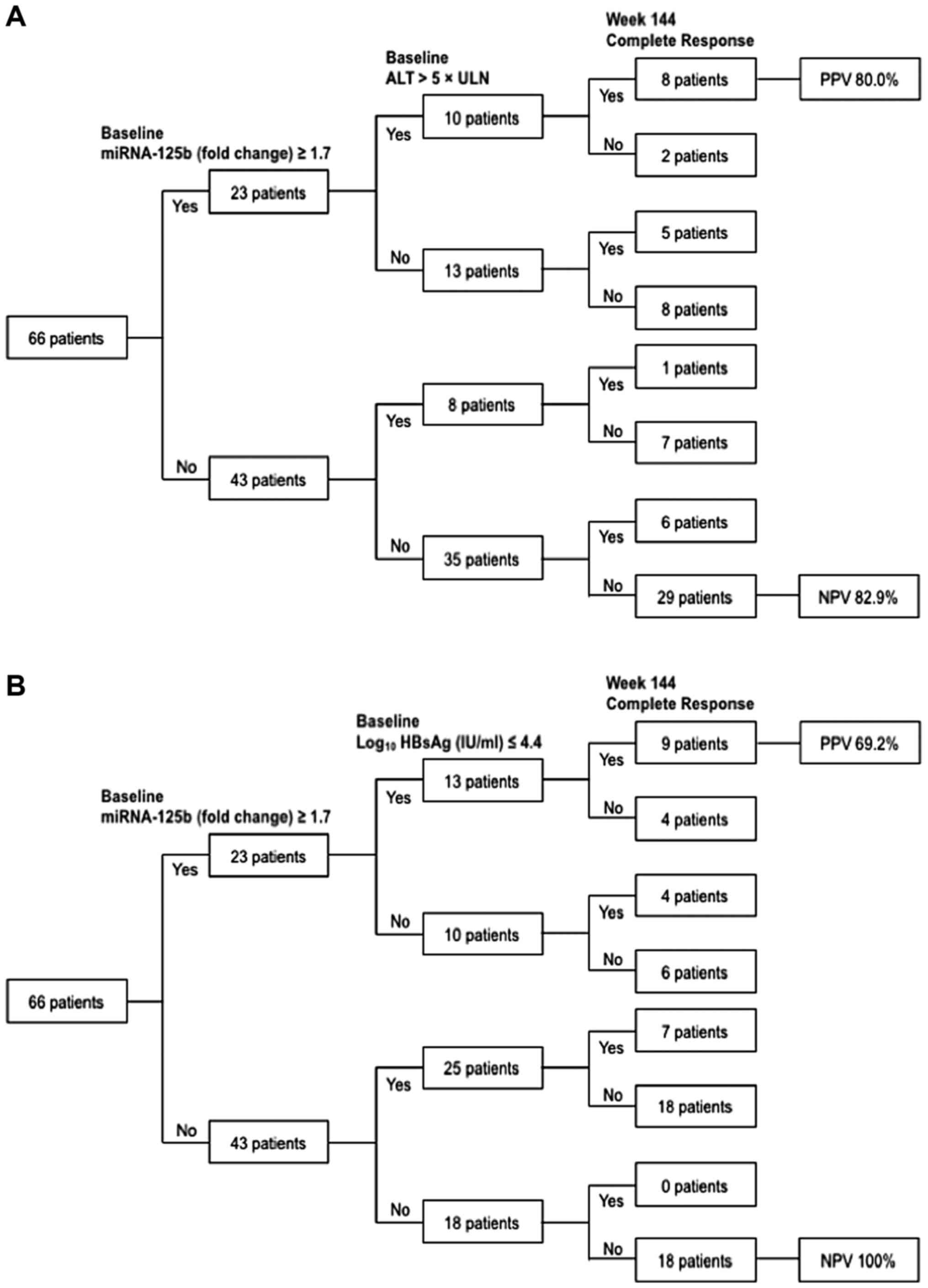
Liver Diseases: AASLD guidelines for treatment of chronic hepatitis
B. Hepatology. 63:261–83. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
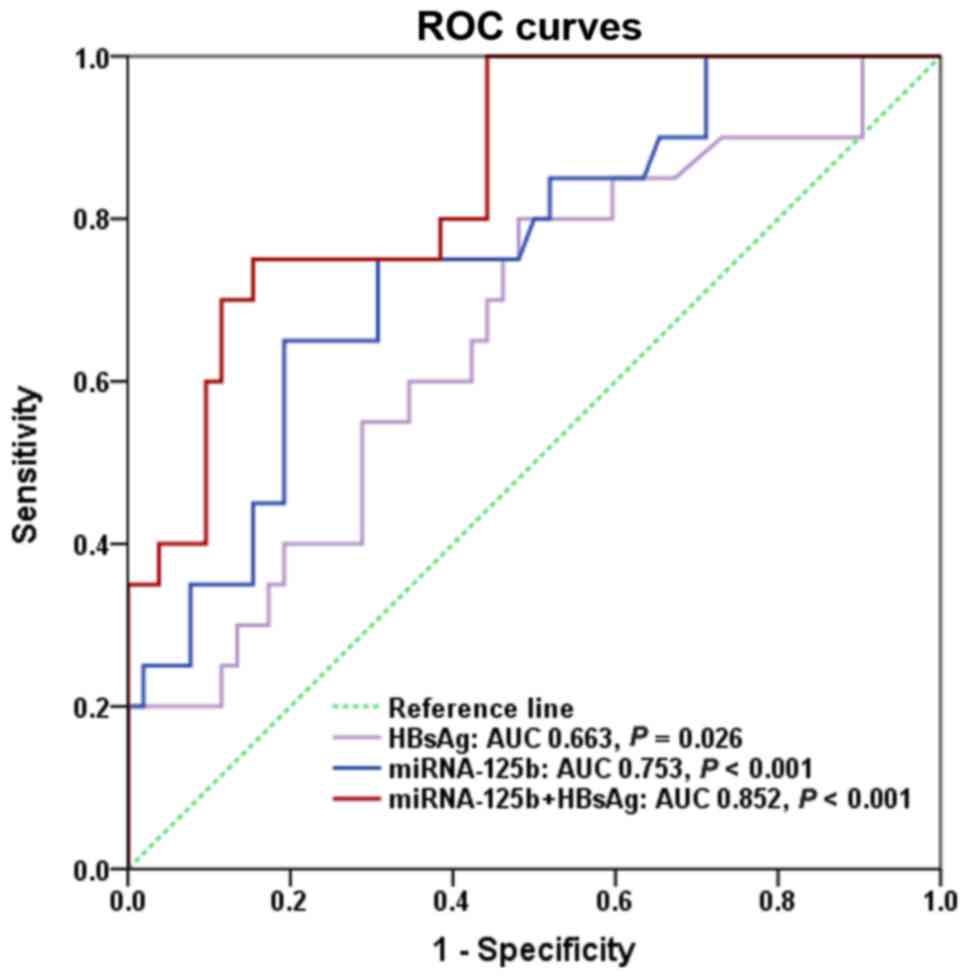
3
|
Bushati N and Cohen SM: microRNA
functions. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 23:175–205. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chen Y, Shen A, Rider PJ, Yu Y, Wu K, Mu
Y, Hao Q, Liu Y, Gong H, Zhu Y, et al: A liver-specific microRNA
binds to a highly conserved RNA sequence of hepatitis B virus and
negatively regulates viral gene expression and replication. Faseb
J. 25:4511–4521. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang S, Qiu L, Yan X, Jin W, Wang Y, Chen
L, Wu E, Ye X, Gao GF, Wang F, et al: Loss of microRNA 122
expression in patients with hepatitis B enhances hepatitis B virus
replication through cyclin G(1)-modulated P53 activity. Hepatology.
55:730–741. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Guo H, Liu H, Mitchelson K, Rao H, Luo M,
Xie L, Sun Y, Zhang L, Lu Y, Liu R, et al: MicroRNAs-372/373
promote the expression of hepatitis B virus through the targeting
of nuclear factor I/B. Hepatology. 54:808–819. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wei X, Xiang T, Ren G, Tan C, Liu R, Xu X
and Wu Z: miR-101 is down-regulated by the hepatitis B virus ×
protein and induces aberrant DNA methylation by targeting DNA
methyltransferase 3A. Cell Signal. 25:439–446. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li F, Zhou P, Deng W, Wang J, Mao R, Zhang
Y, Li J, Yu J, Yang F, Huang Y, et al: Serum microRNA-125b
correlates with hepatitis B viral replication and liver
necroinflammation. Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 22:384.e1–384.e10.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Giray BG, Emekdas G, Tezcan S, Ulger M,
Serin MS, Sezgin O, Altintas E and Tiftik EN: Profiles of serum
microRNAs; miR-125b-5p and miR223-3p serve as novel biomarkers for
HBV-positive hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Biol Rep. 41:4513–4519.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhang Z, Chen J, He Y, Zhan X, Zhao R,
Huang Y, Xu H, Zhu Z and Liu Q: miR-125b inhibits hepatitis B virus
expression in vitro through targeting of the SCNN1A gene. Arch
virol. 159:3335–3343. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ninomiya M, Kondo Y, Kimura O, Funayama R,
Nagashima T, Kogure T, Morosawa T, Tanaka Y, Nakayama K and
Shimosegawa T: The expression of miR-125b-5p is increased in the
serum of patients with chronic hepatitis B infection and inhibits
the detection of hepatitis B virus surface antigen. J Viral Hepat.
23:330–339. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liaw YF: Hepatitis flares and hepatitis B
e antigen seroconversion: Implication in anti-hepatitis B virus
therapy. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 18:246–252. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kwon JH, Jang JW, Lee S, Lee J, Chung KW,
Lee YS and Choi J: Pretreatment HBeAg level and an early decrease
in HBeAg level predict virologic response to entecavir treatment
for HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B. J Viral Hepat. 19:e41–e47.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kao JH, Asselah T, Dou XG and Hamed K:
Telbivudine therapy for chronic hepatitis B: A journey to identify
super-responders and to optimize treatment using the roadmap model.
J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 32:73–81. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang X, Lin SM, Ye F, Chen TY, Liu M,
Chen YR, Zheng SQ, Zhao YR and Zhang SL: An early decrease in serum
HBeAg titre is a strong predictor of virological response to
entecavir in HBeAg-positive patients. J Viral Hepat. 18:e184–e190.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Fan R, Sun J, Yuan Q, Xie Q, Bai X, Ning
Q, Cheng J, Yu Y, Niu J, Shi G, et al: Baseline quantitative
hepatitis B core antibody titre alone strongly predicts HBeAg
seroconversion across chronic hepatitis B patients treated with
peginterferon or nucleos(t)ide analogues. Gut. 65:313–320. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Martinot-Peignoux M, Asselah T and
Marcellin P: HBsAg quantification to optimize treatment monitoring
in chronic hepatitis B patients. Liver Int. 35 Suppl:S82–S90. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Zoulim F, Carosi G, Greenbloom S, Mazur W,
Nguyen T, Jeffers L, Brunetto M, Yu S and Llamoso C: Quantification
of HBsAg in nucleos(t)ide-naive patients treated for chronic
hepatitis B with entecavir with or without tenofovir in the BE-LOW
study. J Hepatol. 62:56–63. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fu XY, Tan DM, Liu CM, Gu B, Hu LH, Peng
ZT, Chen B, Xie YL, Gong HY, Hu XX, et al: Early hepatitis B viral
DNA clearance predicts treatment response at week 96. World J
Gastroenterol. 23:2978–2986. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Schmittgen TD and Livak KJ: Analyzing
real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc.
3:1101–1108. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hsu CW, Chao YC, Lee CM, Chang TT and Chen
YC: Efficacy of telbivudine in Taiwanese chronic hepatitis B
patients compared with GLOBE extension study and predicting
treatment outcome by HBV DNA kinetics at week 24. BMC
gastroenterology. 12:1782012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ma SW, Huang X, Li YY, Tang LB, Sun XF,
Jiang XT, Zhang YX, Sun J, Liu ZH, Abbott WG, et al: High serum
IL-21 levels after 12 weeks of antiviral therapy predict HBeAg
seroconversion in chronic hepatitis B. J Hepatol. 56:775–781. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Guo R, Mao H, Hu X, Zheng N, Yan D, He J
and Yang J: Slow reduction of IP-10 Levels predicts HBeAg
seroconversion in chronic hepatitis B patients with 5 years of
entecavir treatment. Sci Rep. 6:370152016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Akamatsu S, Hayes CN, Tsuge M, Miki D,
Akiyama R, Abe H, Ochi H, Hiraga N, Imamura M, Takahashi S, et al:
Differences in serum microRNA profiles in hepatitis B and C virus
infection. J Infect. 70:273–287. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Alpini G, Glaser SS, Zhang JP, Francis H,
Han Y, Gong J, Stokes A, Francis T, Hughart N, Hubbleet L, et al:
Regulation of placenta growth factor by microRNA-125b in
hepatocellular cancer. J Hepatol. 55:1339–1345. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Liang L, Wong CM, Ying Q, Fan DN, Huang S,
Ding J, Yao J, Yan M, Li J, Yao M, et al: MicroRNA-125b
suppressesed human liver cancer cell proliferation and metastasis
by directly targeting oncogene LIN28B2. Hepatology. 52:1731–1740.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhou JN, Zeng Q, Wang HY, Zhang B, Li ST,
Nan X, Cao N, Fu CJ, Yan XL, Jia YL, et al: MicroRNA-125b
attenuates epithelial-mesenchymal transitions and targets stem-like
liver cancer cells through small mothers against decapentaplegic 2
and 4. Hepatology. 62:801–815. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kim JK, Noh JH, Jung KH, Eun JW, Bae HJ,
Kim MG, Chang YG, Shen Q, Park WS, Lee JY, et al: Sirtuin7
oncogenic potential in human hepatocellular carcinoma and its
regulation by the tumor suppressors MiR-125a-5p and MiR-125b.
Hepatology. 57:1055–1067. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Fan DN, Tsang FH, Tam AH, Au SL, Wong CC,
Wei L, Lee JM, He X, Ng IO and Wong CM: Histone lysine
methyltransferase, suppressor of variegation 3–9 homolog 1,
promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression and is negatively
regulated by microRNA-125b. Hepatology. 57:637–647. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Tan Z, Yin Y, Zhou J, Wu L, Xu C and Hou
H: Telbivudine treatment of hepatitis B virus-infected pregnant
women at different gestational stages for the prevention of
mother-to-child transmission: Outcomes of telbivudine treatment
during pregnancy. Medicine (Baltimore). 95:e48472016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wang W, Wang J, Dang S and Zhuang G:
Cost-effectiveness of antiviral therapy during late pregnancy to
prevent perinatal transmission of hepatitis B virus. Peer J.
4:e17092016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Gordon SC, Krastev Z, Horban A, Petersen
J, Sperl J, Dinh P, Martins EB, Yee LJ, Flaherty JF, Kitrinos KM,
et al: Efficacy of tenofovir disoproxil fumarate at 240 weeks in
patients with chronic hepatitis B with high baseline viral load.
Hepatology. 58:505–513. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hou J, Yin YK, Xu D, Tan D, Niu J, Zhou X,
Wang Y, Zhu L, He Y, Ren H, et al: Telbivudine versus lamivudine in
Chinese patients with chronic hepatitis B: Results at 1 year of a
randomized, double-blind trial. Hepatology. 47:447–454. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Banerjee S, Gunda P, Drake RF and Hamed K:
Telbivudine for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B in
HBeAg-positive patients in China: A health economic analysis.
Springerplus. 5:17192016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhang Y, Hu P, Qi X, Ren H, Mao RC and
Zhang JM: A comparison of telbivudine and entecavir in the
treatment of hepatitis B e antigen-positive patients: A prospective
cohort study in China. Clin Microbiol Infect. 22(287): e1–9.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Liaw YF, Gane E, Leung N, Zeuzem S, Wang
Y, Lai CL, Heathcote EJ, Manns M, Bzowej N, Niu J, et al: 2-Year
GLOBE trial results: Telbivudine is superior to lamivudine in
patients with chronic hepatitis B. Gastroenterology. 136:486–495.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wang Z, Huang Y, Wen S, Zhou B and Hou J:
Hepatitis B virus genotypes and subgenotypes in China. Hepatol Res.
37:S36–S41. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|