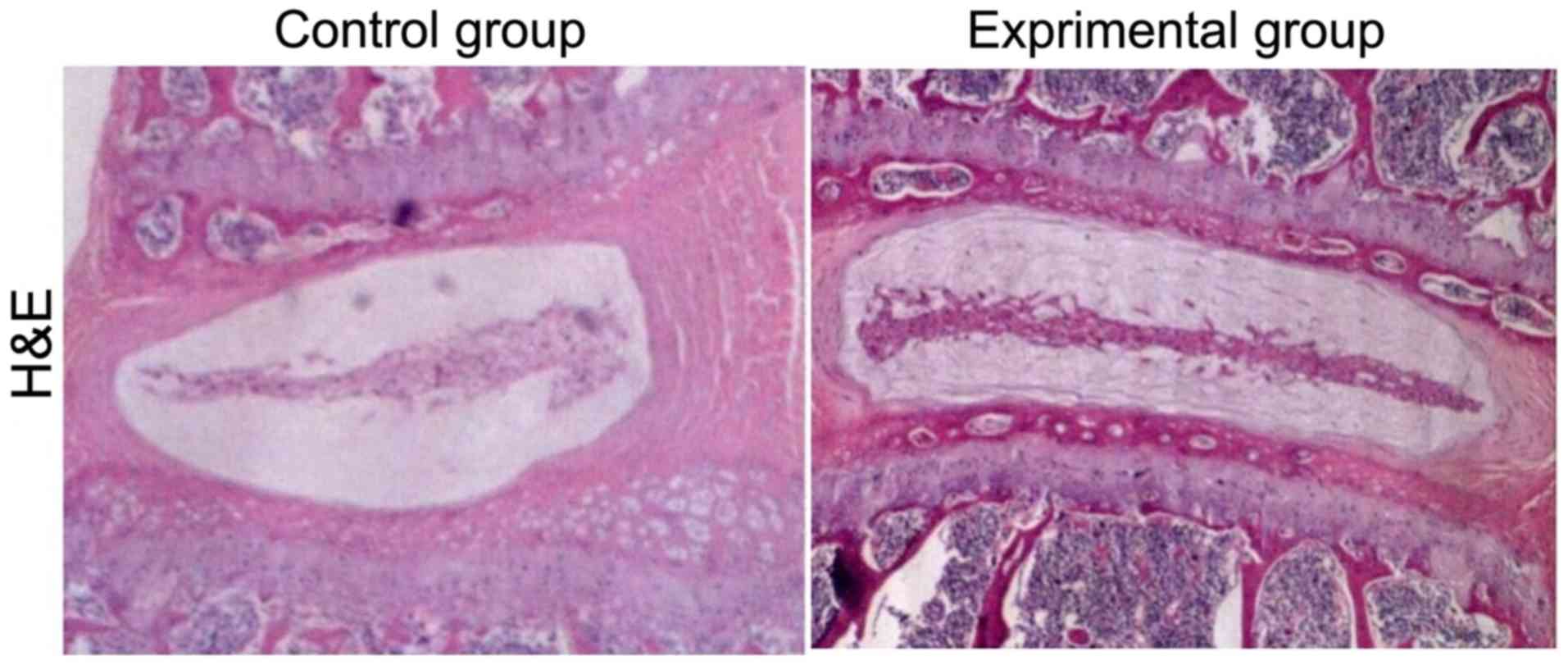
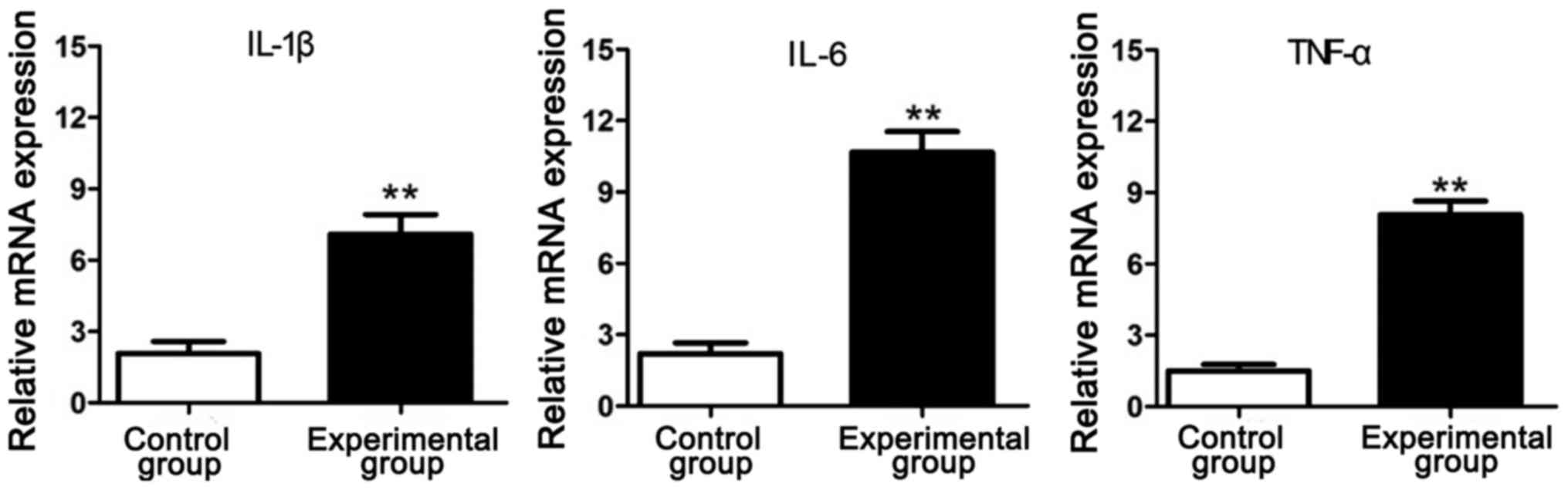
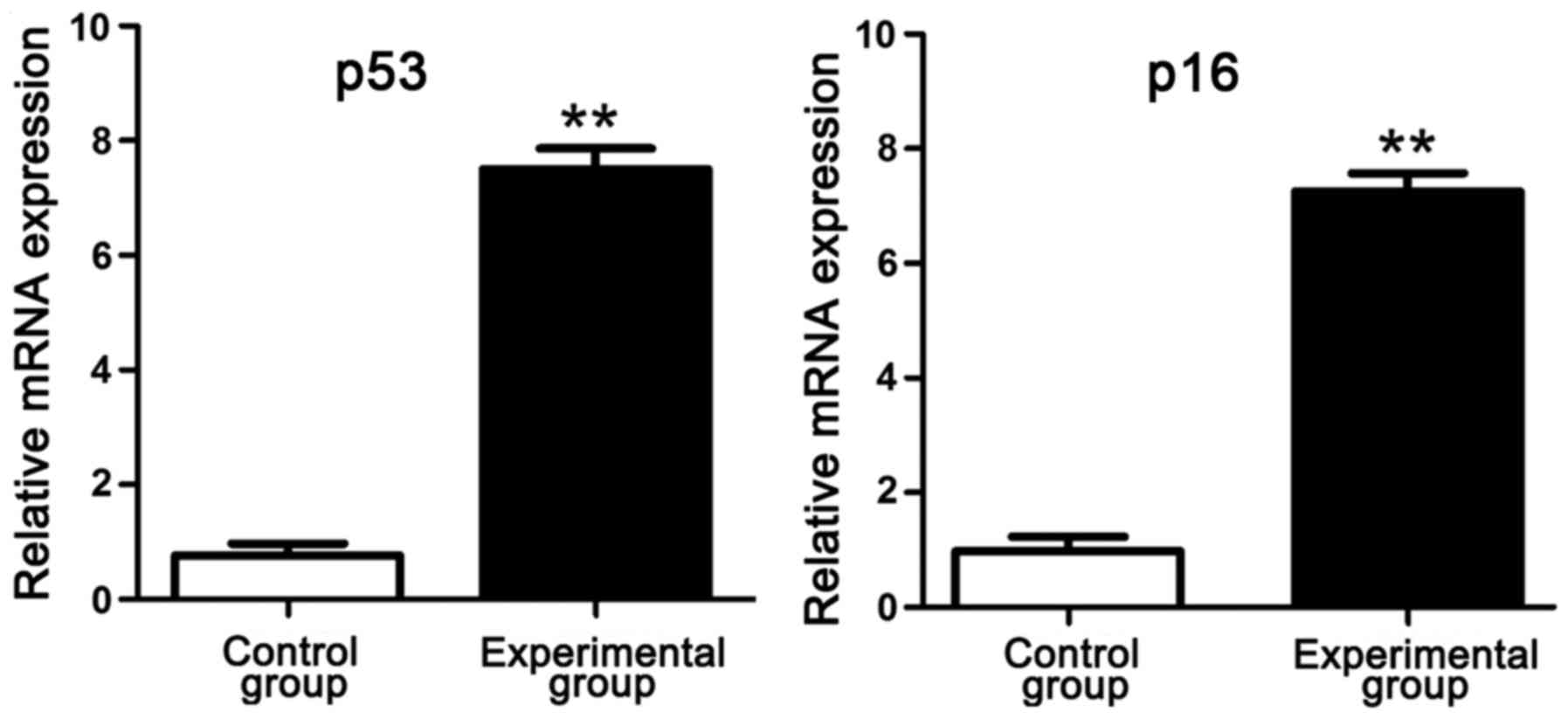
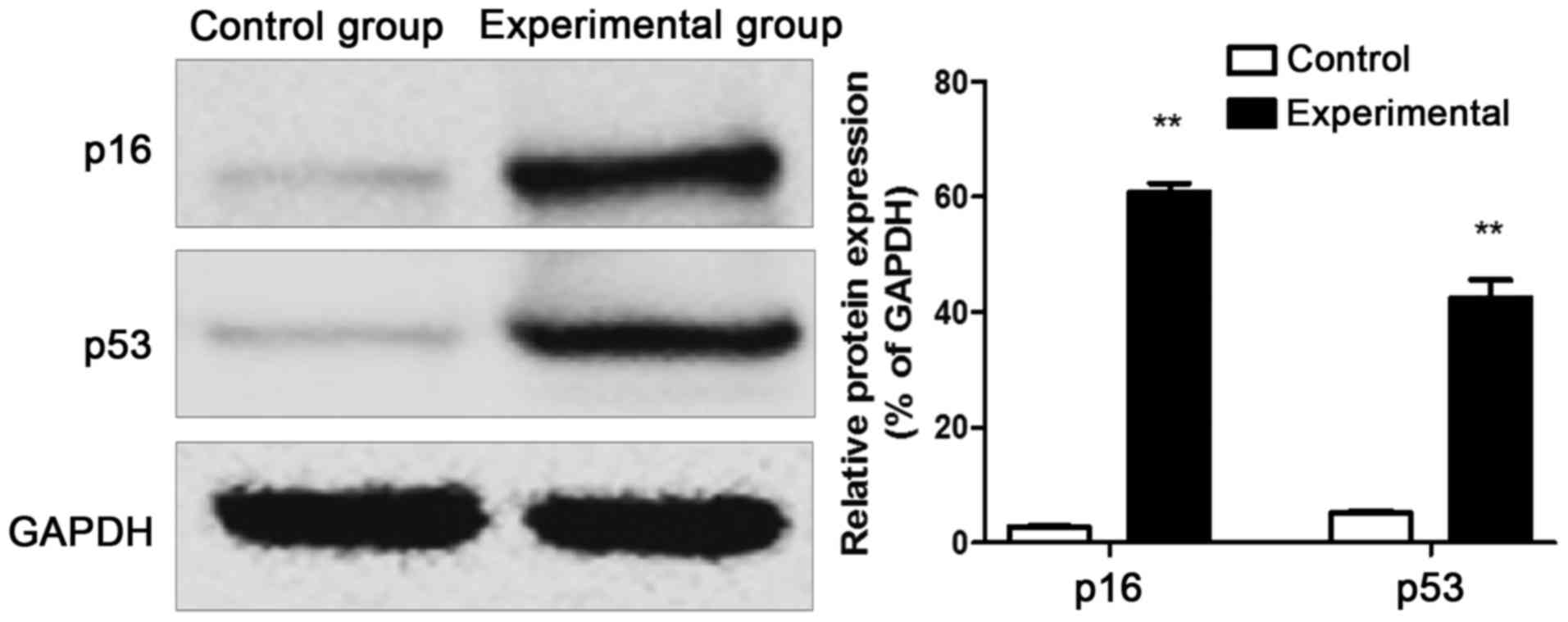
|
1
|
Morey ER and Baylink DJ: Inhibition of
bone formation during space flight. Science. 201:1138–1141. 1978.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Vico L, Collet P, Guignandon A,
Lafage-Proust MH, Thomas T, Rehaillia M and Alexandre C: Effects of
long-term microgravity exposure on cancellous and cortical
weight-bearing bones of cosmonauts. Lancet. 355:1607–1611. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hargens AR and Watenpaugh DE:
Cardiovascular adaptation to spaceflight. Med Sci Sports Exerc.
28:977–982. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Vico L, Novikov VE, Very JM, Chappard D
and Alexandre C: Effects of a 40 day tail-suspension on rat
weight-bearing bones. Physiologist. 33 Suppl 1:S96–S97.
1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Globus RK, Bikle DD, Halloran B and
Morey-Holton E: Skeletal response to dietary calcium in a rat model
simulating weightlessness. J Bone Miner Res. 1:191–197. 1986.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sayson JV and Hargens AR: Pathophysiology
of low back pain during exposure to microgravity. Aviat Space
Environ Med. 79:365–373. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Johnston SL, Campbell MR, Scheuring R and
Feiveson AH: Risk of herniated nucleus pulposus among U.S.
astronauts. Aviat Space Environ Med. 81:566–574. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Földes I, Kern M, Szilágyi T and Oganov
VS: Histology and histochemistry of intervertebral discs of rats
participated in spaceflight. Acta Biol Hung. 47:145–156.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Vergroesen PP, Kingma I, Emanuel KS,
Hoogendoorn RJ, Welting TJ, van Royen BJ, van Dieën JH and Smit TH:
Mechanics and biology in intervertebral disc degeneration: A
vicious circle. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 23:1057–1070. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Webley K, Bond JA, Jones CJ, Blaydes JP,
Craig A, Hupp T and Wynford-Thomas D: Posttranslational
modifications of p53 in replicative senescence overlapping but
distinct from those induced by DNA damage. Mol Cell Biol.
20:2803–2808. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Schmitt CA, Fridman JS, Yang M, Lee S,
Baranov E, Hoffman RM and Lowe SW: A senescence program controlled
by p53 and p16INK4a contributes to the outcome of cancer therapy.
Cell. 109:335–346. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Toussaint O, Medrano EE and von Zglinicki
T: Cellular and molecular mechanisms of stress-induced premature
senescence (SIPS) of human diploid fibroblasts and melanocytes. Exp
Gerontol. 35:927–945. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ben-Porath I and Weinberg RA: The signals
and pathways activating cellular senescence. Int J Biochem Cell
Biol. 37:961–976. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gruber HE, Watts JA, Hoelscher GL, Bethea
SF, Ingram JA, Zinchenko NS and Hanley EN Jr: Mitochondrial gene
expression in the human annulus: In vivo data from annulus cells
and selectively harvested senescent annulus cells. Spine J.
11:782–791. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Le Maitre CL, Freemont AJ and Hoyland JA:
Accelerated cellular senescence in degenerate intervertebral discs:
A possible role in the pathogenesis of intervertebral disc
degeneration. Arthritis Res Ther. 9:R452007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gruber HE, Ingram JA, Norton HJ and Hanley
EN Jr: Senescence in cells of the aging and degenerating
intervertebral disc: Immunolocalization of senescence-associated
beta-galactosidase in human and sand rat discs. Spine. 32:321–327.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Risbud MV and Shapiro IM: Role of
cytokines in intervertebral disc degeneration: Pain and disc
content. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 10:44–56. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Acosta JC, O'loghlen A, Banito A, Guijarro
MV, Augert A, Raguz S, Fumagalli M, Da Costa M, Brown C, Popov N,
et al: Chemokine signaling via the CXCR2 receptor reinforces
senescence. Cell. 133:1006–1018. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Acosta JC, Banito A, Wuestefeld T,
Georgilis A, Janich P, Morton JP, Athineos D, Kang TW, Lasitschka
F, Andrulis M, et al: A complex secretory program orchestrated by
the inflammasome controls paracrine senescence. Nat Cell Biol.
15:978–990. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang R, Ran HH, Cai LL, Zhu L, Sun JF,
Peng L, Liu XJ, Zhang LN, Fang Z, Fan YY, et al: Simulated
microgravity-induced mitochondrial dysfunction in rat cerebral
arteries. FASEB J. 28:2715–2724. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jin L, Feng G, Reames DL, Shimer AL, Shen
FH and Li X: The effects of simulated microgravity on
intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine J. 13:235–242. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Pfirrmann CW, Metzdorf A, Zanetti M,
Hodler J and Boos N: Magnetic resonance classification of lumbar
intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).
26:1873–1878. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wing PC, Tsang IK, Susak L, Gagnon F,
Gagnon R and Potts JE: Back pain and spinal changes in
microgravity. Orthop Clin North Am. 22:255–262. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hutton WC, Elmer WA, Boden SD, Hyon S,
Toribatake Y, Tomita K and Hair GA: The effect of hydrostatic
pressure on intervertebral disc metabolism. Spine. 24:1507–1515.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Muller M: Cellular senescence: Molecular
mechanisms, in vivo significance, and redox considerations.
Antioxid Redox Signal. 11:59–98. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gire V, Roux P, Wynford-Thomas D,
Brondello JM and Dulic V: DNA damage checkpoint kinase Chk2
triggers replicative senescence. EMBO J. 23:2554–2563. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Herbig U, Jobling WA, Chen BP, Chen DJ and
Sedivy JM: Telomere shortening triggers senescence of human cells
through a pathway involving ATM, p53, and p21(CIP1), but not
p16(INK4a). Mol Cell. 14:501–513. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kim KW, Chung HN, Ha KY, Lee JS and Kim
YY: Senescence mechanisms of nucleus pulposus chondrocytes in human
intervertebral discs. Spine J. 9:658–666. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Jeong SW, Lee JS and Kim KW: In vitro
lifespan and senescence mechanisms of human nucleus pulposus
chondrocytes. Spine J. 14:499–504. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Itahana K, Zou Y, Itahana Y, Martinez JL,
Beausejour C, Jacobs JJ, Van Lohuizen M, Band V, Campisi J and
Dimri GP: Control of the replicative life span of human fibroblasts
by p16 and the polycomb protein Bmi-1. Mol Cell Biol. 23:389–401.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ressler S, Bartkova J, Niederegger H,
Bartek J, Scharffetter-Kochanek K, Jansen-Dürr P and Wlaschek M:
p16INK4A is a robust in vivo biomarker of cellular aging in human
skin. Aging Cell. 5:379–389. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Heathfield SK, Le Maitre CL and Hoyland
JA: Caveolin-1 expression and stress-induced premature senescence
in human intervertebral disc degeneration. Arthritis Res Ther.
10:R872008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Park JS, Park JB, Park IJ and Park EY:
Accelerated premature stress-induced senescence of young annulus
fibrosus cells of rats by high glucose-induced oxidative stress.
Int Orthop. 38:1311–1320. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kong JG, Park JB, Lee D and Park EY:
Effect of high glucose on stress-induced senescence of nucleus
pulposus cells of adult rats. Asian Spine J. 9:155–161. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Park JB, Byun CH and Park EY: Rat
notochordal cells undergo premature stress-induced senescence by
high glucose. Asian Spine J. 9:495–502. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
van Deursen JM: The role of senescent
cells in ageing. Nature. 509:439–446. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Muñoz-Espín D and Serrano M: Cellular
senescence: From physiology to pathology. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
15:482–496. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Han C, Jiang C, Yu C and Shen H:
Differentiation of transforming growth factor β1-induced
mesenchymal stem cells into nucleus pulposus-like cells under
simulated microgravity conditions. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand).
61:50–55. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Luo W, Xiong W, Qiu M, Lv Y, Li Y and Li
F: Differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells towards a nucleus
pulposus-like phenotype utilizing simulated microgravity In vitro.
J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 31:1992011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|