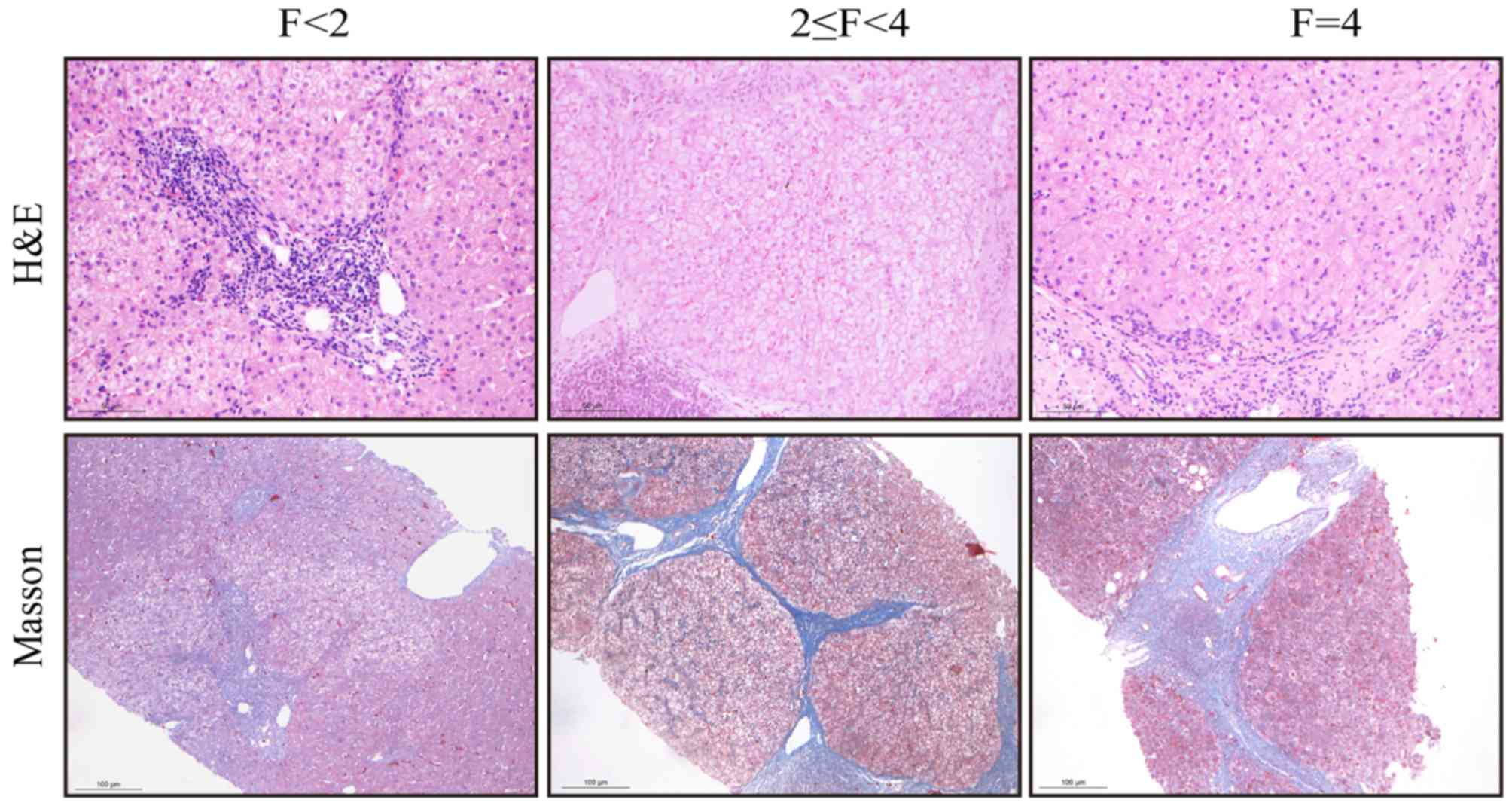
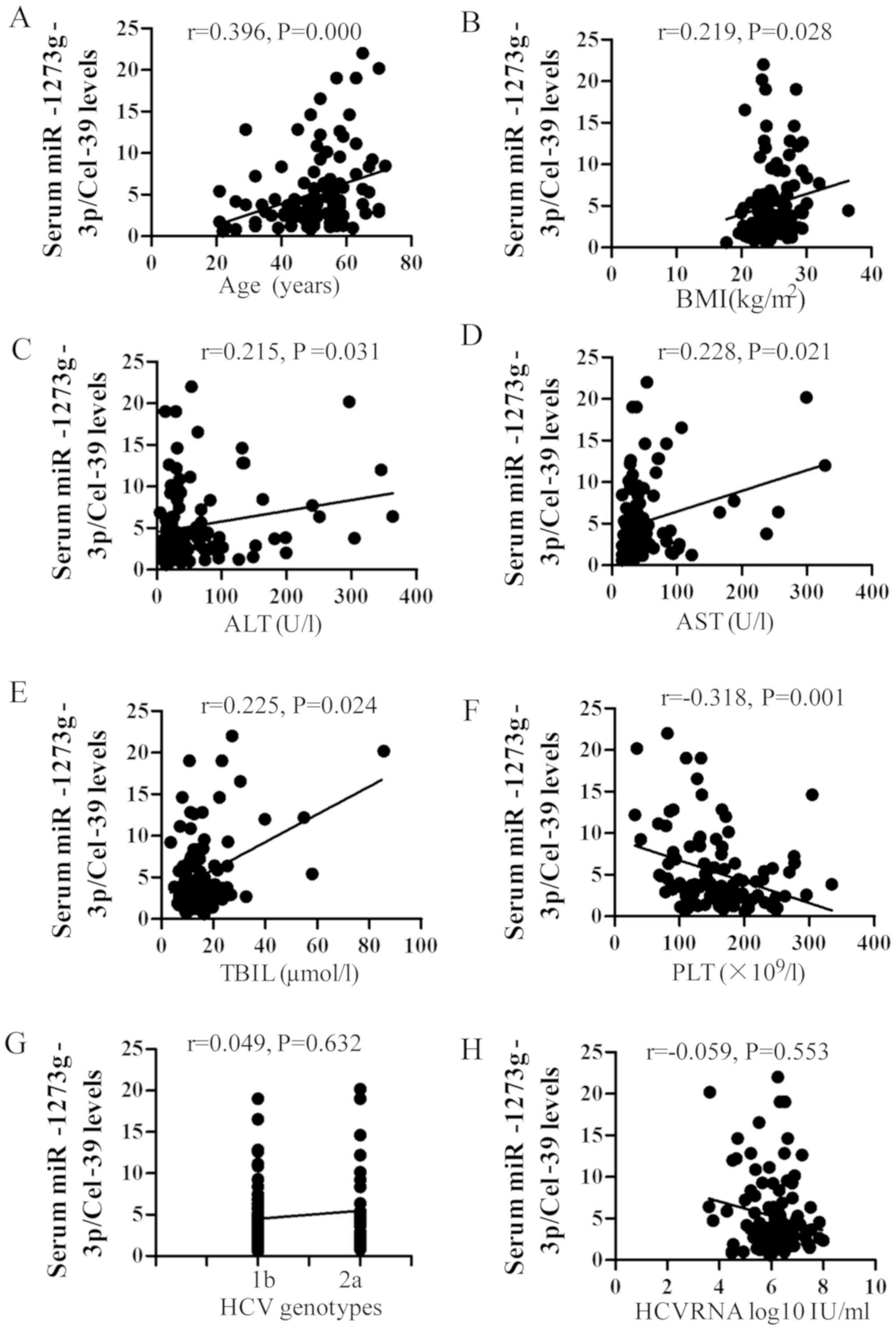
|
1
|
Wilkins T, Akhtar M, Gititu E, Jalluri C
and Ramirez J: Diagnosis and management of hepatitis C. Am Fam
Phys. 91:835–842. 2015.
|
|
2
|
WHO guidelines approved by the guidelines
review committee: In: Guidelines for the screening, care and
treatment of persons with hepatitis C infection. Geneva: 2014
|
|
3
|
Kayadibi H, Yasar B, Ozkara S, Serdar MA,
Kurdas OO and Gonen C: The diagnostic accuracy of the Forns index,
platelet count and AST to platelet ratio index derived fibrosis
index for the prediction of Hepatitis C virus-related significant
liver fibrosis and cirrhosis. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 74:240–247.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ghany MG, Strader DB, Thomas DL and Seeff
LB: American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases:
Diagnosis, management, and treatment of hepatitis C: An update.
Hepatology. 49:1335–1374. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bravo AA, Sheth SG and Chopra S: Liver
biopsy. N Engl J Med. 344:495–500. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Noetel A, Kwiecinski M, Elfimova N, Huang
J and Odenthal M: microRNA are central players in anti- and
profibrotic gene regulation during liver fibrosis. Front Physiol.
3:492012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kosaka N, Iguchi H and Ochiya T:
Circulating microRNA in body fluid: A new potential biomarker for
cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Cancer Sci. 101:2087–2092. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lee HM, Nguyen DT and Lu LF: Progress and
challenge of microRNA research in immunity. Front Genet. 5:1782014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Othman N and Nagoor NH: The role of
microRNAs in the regulation of apoptosis in lung cancer and its
application in cancer treatment. Biomed Res Int. 2014:3180302014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Shenoy A and Blelloch RH: Regulation of
microRNA function in somatic stem cell proliferation and
differentiation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 15:565–576. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Du J, Niu X, Wang Y, Kong L, Wang R, Zhang
Y, Zhao S and Nan Y: MiR-146a-5p suppresses activation and
proliferation of hepatic stellate cells in nonalcoholic fibrosing
steatohepatitis through directly targeting Wnt1 and Wnt5a. Sci Rep.
5:161632015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Abdollahi M, Pouri A, Ghojazadeh M,
Estakhri R and Somi M: Non-invasive serum fibrosis markers: A study
in chronic hepatitis. Bioimpacts. 5:17–23. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bala S, Petrasek J, Mundkur S, Catalano D,
Levin I, Ward J, Alao H, Kodys K and Szabo G: Circulating microRNAs
in exosomes indicate hepatocyte injury and inflammation in
alcoholic, drug-induced, and inflammatory liver diseases.
Hepatology. 56:1946–1957. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Halász T, Horváth G, Pár G, Werling K,
Kiss A, Schaff Z and Lendvai G: miR-122 negatively correlates with
liver fibrosis as detected by histology and FibroScan. World J
Gastroenterol. 21:7814–7823. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Mahgoub A and Steer CJ: MicroRNAs in the
evaluation and potential treatment of liver diseases. J Clin Med.
5:E522016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Cortez MA and Calin GA: MicroRNA
identification in plasma and serum: A new tool to diagnose and
monitor diseases. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 9:703–711. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cortez MA, Bueso-Ramos C, Ferdin J,
Lopez-Berestein G, Sood AK and Calin GA: MicroRNAs in body
fluids-the mix of hormones and biomarkers. Nat Rev Clin Oncol.
8:467–477. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Etheridge A, Lee I, Hood L, Galas D and
Wang K: Extracellular microRNA: A new source of biomarkers. Mutat
Res. 717:85–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Castera L, Winnock M, Pambrun E, Paradis
V, Perez P, Loko MA, Asselineau J, Dabis F, Degos F and Salmon D:
Comparison of transient elastography (FibroScan), FibroTest, APRI
and two algorithms combining these non-invasive tests for liver
fibrosis staging in HIV/HCV coinfected patients: ANRS CO13 HEPAVIH
and FIBROSTIC collaboration. HIV Med. 15:30–39. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang R, Ren W, Zhao S, Niu X, Tan P, Du H
and Nan Y: Clinical study on FibroTouch and multi-parameter model
for diagnosis of hepatic fibrosis in patients with chronic liver
disease. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 23:265–269. 2015.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Crespo G, Fernández-Varo G, Mariño Z,
Casals G, Miquel R, Martínez SM, Gilabert R, Forns X, Jiménez W and
Navasa M: ARFI, FibroScan, ELF, and their combinations in the
assessment of liver fibrosis: A prospective study. J Hepatol.
57:281–287. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Friedrich-Rust M, Ong MF, Martens S,
Sarrazin C, Bojunga J, Zeuzem S and Herrmann E: Performance of
transient elastography for the staging of liver fibrosis: A
meta-analysis. Gastroenterology. 134:960–974. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Fraquelli M, Rigamonti C, Casazza G,
Donato MF, Ronchi G, Conte D, Rumi M, Lampertico P and Colombo M:
Etiology-related determinants of liver stiffness values in chronic
viral hepatitis B or C. J Hepatol. 54:621–628. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Baranova A, Lal P, Birerdinc A and
Younossi ZM: Non-invasive markers for hepatic fibrosis. BMC
Gastroenterol. 11:912011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
European Association for the Study of the
Liver: EASL clinical practice guidelines: Management of hepatitis C
virus infection. J Hepatol. 55:245–264. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese
Society of Infectious Diseases, Parasitology of Chinese Medical
Association. The guideline for prevention and treatment of
hepatitis C. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 12:194–198. 2004.(In
Chinese).
|
|
27
|
Sun ZH, Yang HL, Wei M, Wang SY, Wang CR,
Shi YL and Ma WL: Preparation and application of oligo microarrays
for hepatitis virus detection and genotyping. Zhonghua Gan Zang
Bing Za Zhi. 15:816–820. 2007.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Intraobserver and interobserver variations
in liver biopsy interpretation in patients with chronic hepatitis
C. The French METAVIR Cooperative Study Group = Hepatology.
20:15–20. 1994.
|
|
29
|
Amorim TG, Staub GJ, Lazzarotto C, Silva
AP, Manes J, Ferronato Mda G, Shiozawa MB, Narciso-Schiavon JL,
Dantas-Correa EB and Schiavon Lde L: Validation and comparison of
simple noninvasive models for the prediction of liver fibrosis in
chronic hepatitis C. Ann Hepatol. 11:855–861. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Schumann G, Bonora R, Ceriotti F, Férard
G, Ferrero CA, Franck PF, Gella FJ, Hoelzel W, Jørgensen PJ, Kanno
T, et al: IFCC primary reference procedures for the measurement of
catalytic activity concentrations of enzymes at 37 degrees C.
International federation of clinical chemistry and laboratory
medicine. Part 4. Reference procedure for the measurement of
catalytic concentration of alanine aminotransferase. Clin Chem Lab
Med. 40:718–724. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ye YW, Wang YS and Shen ZY: National guide
to clinical laboratory procedures. (3rd). Southeast University
Press. (Nanjing). 2006.(In Chinese).
|
|
32
|
Hill VL, Simpson VZ, Higgins JM, Hu Z,
Stevens RA, Metcalf JA and Baseler M: Evaluation of the performance
of the Sysmex XT-2000i hematology analyzer with whole bloods stored
at room temperature. Lab Med. 40:709–718. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Teshale E, Lu M, Rupp LB, Holmberg SD,
Moorman AC, Spradling P, Vijayadeva V, Boscarino JA, Schmidt MA and
Gordon SC: CHeCS Investigators: APRI and FIB-4 are good predictors
of the stage of liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B: The Chronic
Hepatitis Cohort Study (CHeCS). J Viral Hepat. 21:917–920. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Castéra L, Vergniol J, Foucher J, Le Bail
B, Chanteloup E, Haaser M, Darriet M, Couzigou P and De Lédinghen
V: Prospective comparison of transient elastography, Fibrotest,
APRI, and liver biopsy for the assessment of fibrosis in chronic
hepatitis C. Gastroenterology. 128:343–350. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Mummadi RR, Petersen JR, Xiao SY and
Snyder N: Role of simple biomarkers in predicting fibrosis
progression in HCV infection. World J Gastroenterol. 16:5710–5715.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kroh EM, Parkin RK, Mitchell PS and Tewari
M: Analysis of circulating microRNA biomarkers in plasma and serum
using quantitative reverse transcription-PCR (qRT-PCR). Methods.
50:298–301. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Arroyo JD, Chevillet JR, Kroh EM, Ruf IK,
Pritchard CC, Gibson DF, Mitchell PS, Bennett CF,
Pogosova-Agadjanyan EL, Stirewalt DL, et al: Argonaute2 complexes
carry a population of circulating microRNAs independent of vesicles
in human plasma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:5003–5008. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Bedossa P, Dargère D and Paradis V:
Sampling variability of liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C.
Hepatology. 38:1449–1457. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Yokoi T and Nakajima M: Toxicological
implications of modulation of gene expression by microRNAs. Toxicol
Sci. 123:1–14. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Niu X, Fu N, Du J, Wang R, Wang Y, Zhao S,
Du H, Wang B, Zhang Y, Sun D and Nan Y: miR-1273g-3p modulates
activation and apoptosis of hepatic stellate cells by directly
targeting PTEN in HCV-related liver fibrosis. FEBS Lett.
590:2709–2724. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Trebicka J, Anadol E, Elfimova N, Strack
I, Roggendorf M, Viazov S, Wedemeyer I, Drebber U, Rockstroh J,
Sauerbruch T, et al: Hepatic and serum levels of miR-122 after
chronic HCV-induced fibrosis. J Hepatol. 58:234–239. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wang J, Chu ES, Chen HY, Man K, Go MY,
Huang XR, Lan HY, Sung JJ and Yu J: microRNA-29b prevents liver
fibrosis by attenuating hepatic stellate cell activation and
inducing apoptosis through targeting PI3K/AKT pathway. Oncotarget.
6:7325–7338. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Murakami Y, Toyoda H, Tanaka M, Kuroda M,
Harada Y, Matsuda F, Tajima A, Kosaka N, Ochiya T and Shimotohno K:
The progression of liver fibrosis is related with overexpression of
the miR-199 and 200 families. PloS One. 6:e160812011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Roderburg C, Urban GW, Bettermann K, Vucur
M, Zimmermann H, Schmidt S, Janssen J, Koppe C, Knolle P, Castoldi
M, et al: Micro-RNA profiling reveals a role for miR-29 in human
and murine liver fibrosis. Hepatology. 53:209–218. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zekri AN, Youssef AS, El-Desouky ED, Ahmed
OS, Lotfy MM, Nassar AA and Bahnassey AA: Serum microRNA panels as
potential biomarkers for early detection of hepatocellular
carcinoma on top of HCV infection. Tumour Biol. 37:12273–12286.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Liu J, Liu Y, Dong C, Yao S, Li S, Yuan J,
Chen C, Zhao M, Lin Y and Peng Z: ARFI, Forns index, FIB-4 and APRI
diagnosis liver fibrosis in patients with chronic liver diseases.
Zhongguo Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 6:18–21. 2014.(In Chinese).
|
|
48
|
Vergniol J, Boursier J, Coutzac C,
Bertrais S, Foucher J, Angel C, Chermak F, Hubert IF, Merrouche W,
Oberti F, et al: Evolution of noninvasive tests of liver fibrosis
is associated with prognosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C.
Hepatology. 60:65–76. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|