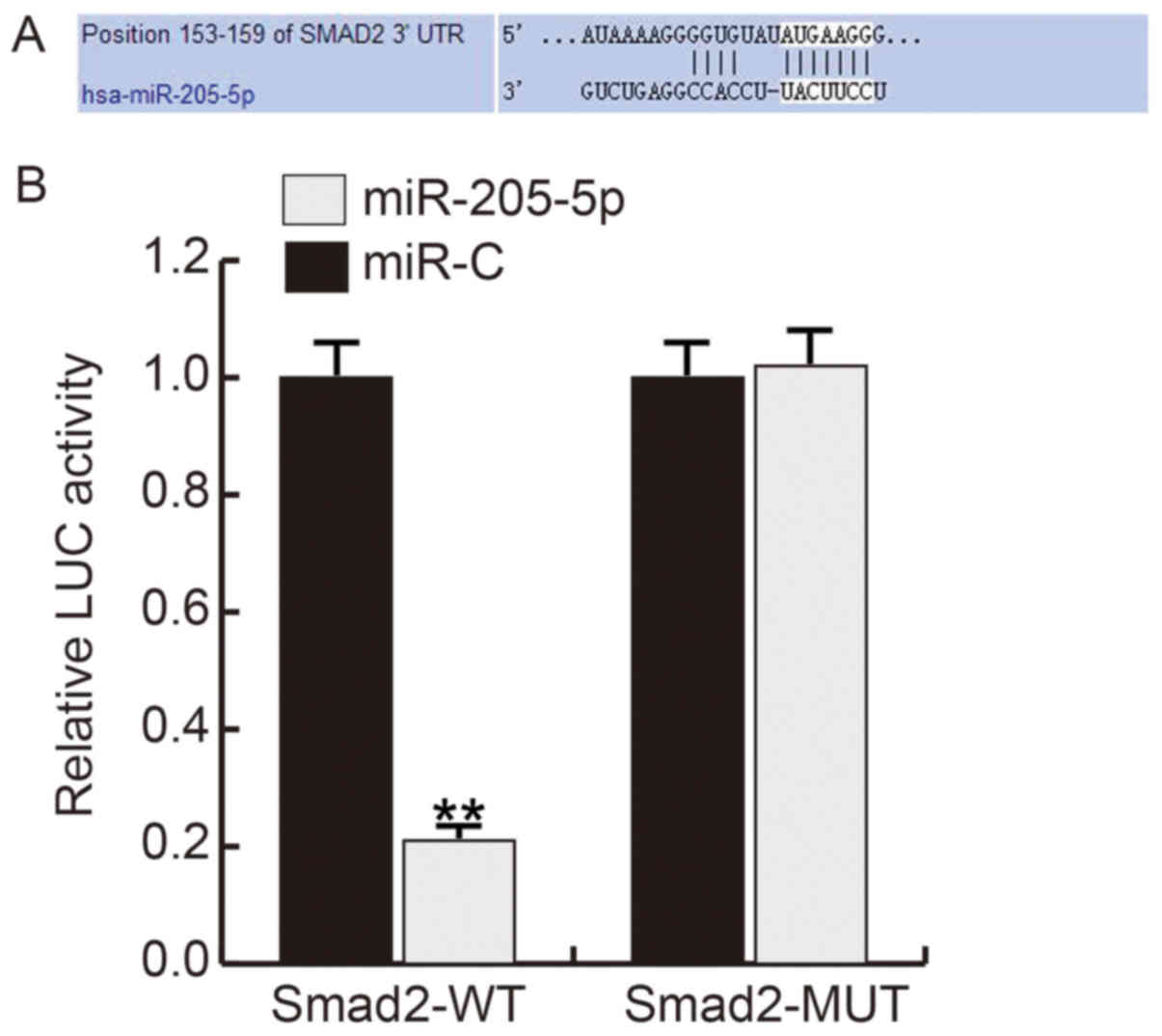
|
1
|
Aarabi S, Bhatt KA, Shi Y, Paterno J,
Chang EI, Loh SA, Holmes JW, Longaker MT, Yee H and Gurtner GC:
Mechanical load initiates hypertrophic scar formation through
decreased cellular apoptosis. FASEB J. 21:3250–3261. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
van der Veer WM, Bloemen MC, Ulrich MM,
Molema G, van Zuijlen PP, Middelkoop E and Niessen FB: Potential
cellular and molecular causes of hypertrophic scar formation.
Burns. 35:15–29. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Younai S, Nichter LS, Wellisz T, Reinisch
J, Nimni ME and Tuan TL: Modulation of collagen synthesis by
transforming growth factor-beta in keloid and hypertrophic scar
fibroblasts. Ann Plast Surg. 33:148–154. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Shi-Wen X, Leask A and Abraham D:
Regulation and function of connective tissue growth factor/CCN2 in
tissue repair, scarring and fibrosis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev.
19:133–144. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kashiyama K, Mitsutake N, Matsuse M, Ogi
T, Saenko VA, Ujifuku K, Utani A, Hirano A and Yamashita S:
miR-196a downregulation increases the expression of type I and III
collagens in keloid fibroblasts. J Invest Dermatol. 132:1597–1604.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Li P, He QY and Luo CQ: Overexpression of
miR-200b inhibits the cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis of
human hypertrophic scar fibroblasts in vitro. J Dermatol.
41:903–911. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hammond SM: An overview of microRNAs. Adv
Drug Deliv Rev. 87:3–14. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wilson RC and Doudna JA: Molecular
mechanisms of RNA interference. Annu Rev Biophys. 42:217–239. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sun W, Julie Li YS, Huang HD, Shyy JY and
Chien S: microRNA: A master regulator of cellular processes for
bioengineering systems. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 12:1–27. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Guo H, Ingolia NT, Weissman JS and Bartel
DP: Mammalian microRNAs predominantly act to decrease target mRNA
levels. Nature. 466:835–840. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Flynt AS and Lai EC: Biological principles
of microRNA-mediated regulation: Shared themes amid diversity. Nat
Rev Genet. 9:831–842. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Miska EA: How microRNAs control cell
division, differentiation and death. Curr Opin Genet Dev.
15:563–568. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bushati N and Cohen SM: microRNA
functions. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 23:175–205. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liang P, Lv C, Jiang B, Long X, Zhang P,
Zhang M, Xie T and Huang X: MicroRNA profiling in denatured dermis
of deep burn patients. Burns. 38:534–540. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bi S, Chai L, Yuan X, Cao C and Li S:
MicroRNA-98 inhibits the cell proliferation of human hypertrophic
scar fibroblasts via targeting Col1A1. Biol Res. 50:222017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Xiao K, Luo X, Wang X and Gao Z:
MicroRNA-185 regulates transforming growth factor-β1 and collagen-1
in hypertrophic scar fibroblasts. Mol Med Rep. 15:1489–1496. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li G, Zhou R, Zhang Q, Jiang B, Wu Q and
Wang C: Fibroproliferative effect of microRNA-21 in hypertrophic
scar derived fibroblasts. Exp Cell Res. 345:93–99. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zeng Y, Zhu J, Shen D, Qin H, Lei Z, Li W,
Liu Z and Huang JA: MicroRNA-205 targets SMAD4 in non-small cell
lung cancer and promotes lung cancer cell growth in vitro and in
vivo. Oncotarget. 8:30817–30829. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nguyen-Vu T, Wang J, Mesmar F,
Mukhopadhyay S, Saxena A, McCollum CW, Gustafsson JÅ, Bondesson M
and Williams C: Estrogen receptor beta reduces colon cancer
metastasis through a novel miR-205-PROX1 mechanism. Oncotarget.
7:42159–42171. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tucci P, Agostini M, Grespi F, Markert EK,
Terrinoni A, Vousden KH, Muller PA, Dötsch V, Kehrloesser S, Sayan
BS, et al: Loss of p63 and its microRNA-205 target results in
enhanced cell migration and metastasis in prostate cancer. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:15312–15317. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Pan F, Mao H, Bu F, Tong X, Li J, Zhang S,
Liu X, Wang L, Wu L, Chen R, et al: Sp1-mediated transcriptional
activation of miR-205 promotes radioresistance in esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget. 8:5735–5752. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jiang M, Zhong T, Zhang W, Xiao Z, Hu G,
Zhou H and Kuang H: Reduced expression of miR-205-5p promotes
apoptosis and inhibits proliferation and invasion in lung cancer
A549 cells by upregulation of ZEB2 and downregulation of erbB3. Mol
Med Rep. 15:3231–3238. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jang SJ, Choi IS, Park G, Park G, Moon DS,
Choi JS, Nam MH, Yoon SY, Choi CH and Kang SH: MicroRNA-205-5p is
upregulated in myelodysplastic syndromes and induces cell
proliferation via PTEN suppression. Leuk Res. 47:172–177. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tredget EE, Nedelec B, Scott PG and
Ghahary A: Hypertrophic scars, keloids, and contractures. The
cellular and molecular basis for therapy. Surg Clin North Am.
77:701–730. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Armour A, Scott PG and Tredget EE:
Cellular and molecular pathology of HTS: Basis for treatment. Wound
Repair Regen. 15 Suppl 1:S6–S17. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Schäfer M and Werner S: Transcriptional
control of wound repair. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 23:69–92. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kwan P, Hori K, Ding J and Tredget EE:
Scar and contracture: Biological principles. Hand Clin. 25:511–528.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Babalola O, Mamalis A, Lev-Tov H and
Jagdeo J: The role of microRNAs in skin fibrosis. Arch Dermatol
Res. 305:763–776. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Syed V: TGF-β signaling in cancer. J Cell
Biochem. 117:1279–1287. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Volk SW, Wang Y, Mauldin EA, Liechty KW
and Adams SL: Diminished type III collagen promotes myofibroblast
differentiation and increases scar deposition in cutaneous wound
healing. Cells Tissues Organs. 194:25–37. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhou R, Zhang Q, Zhang Y, Fu S and Wang C:
Aberrant miR-21 and miR-200b expression and its pro-fibrotic
potential in hypertrophic scars. Exp Cell Res. 339:360–366. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Satish L, Gallo PH, Baratz ME, Johnson S
and Kathju S: Reversal of TGF-β1 stimulation of α-smooth muscle
actin and extracellular matrix components by cyclic AMP in
Dupuytren's-derived fibroblasts. BMC Musculoskelet Disord.
12:1132011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lu Q, Zuo WZ, Ji XJ, Zhou YX, Liu YQ, Yao
XQ, Zhou XY, Liu YW, Zhang F and Yin XX: Ethanolic Ginkgo biloba
leaf extract prevents renal fibrosis through Akt/mTOR signaling in
diabetic nephropathy. Phytomedicine. 22:1071–1078. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|