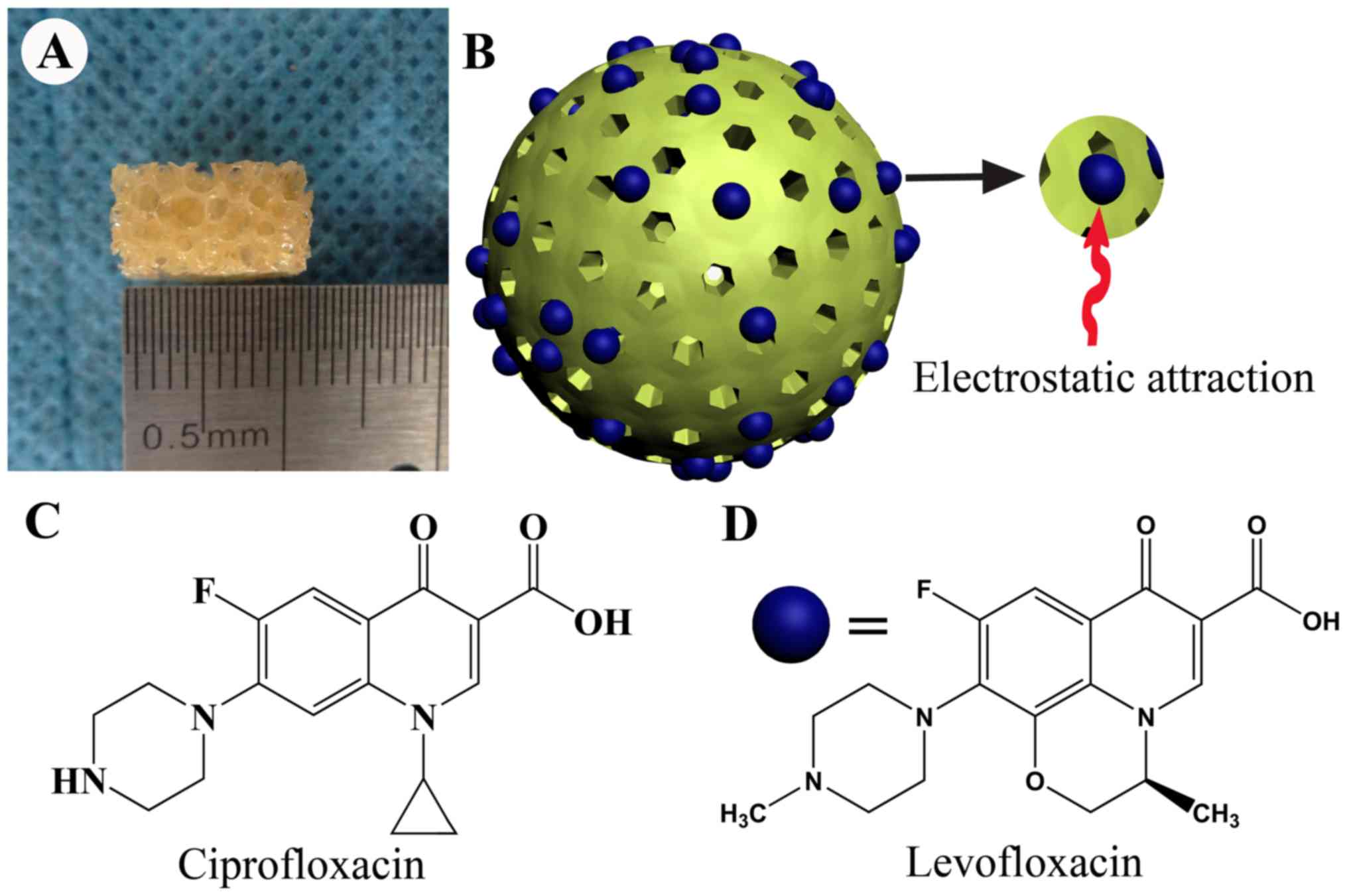
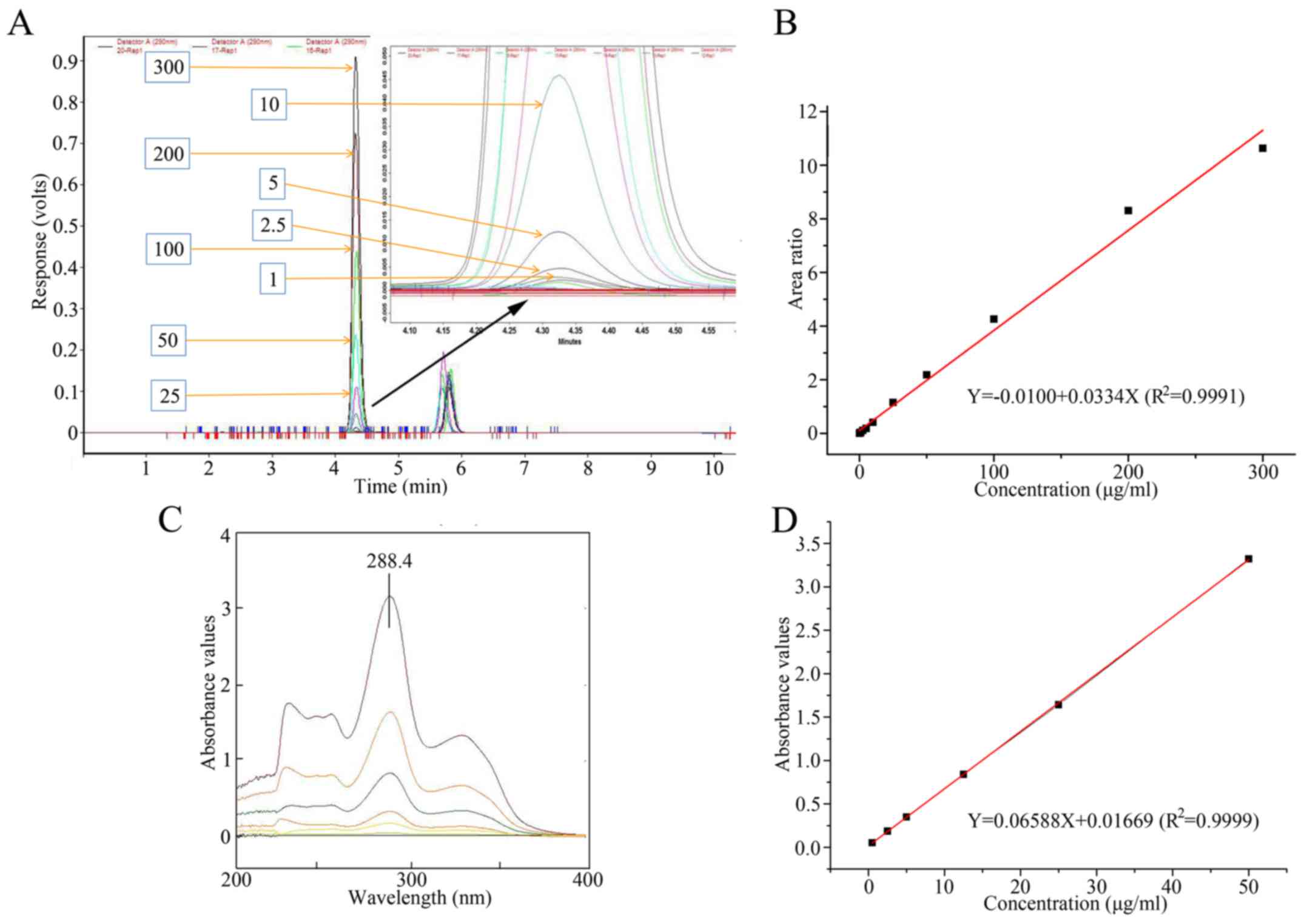
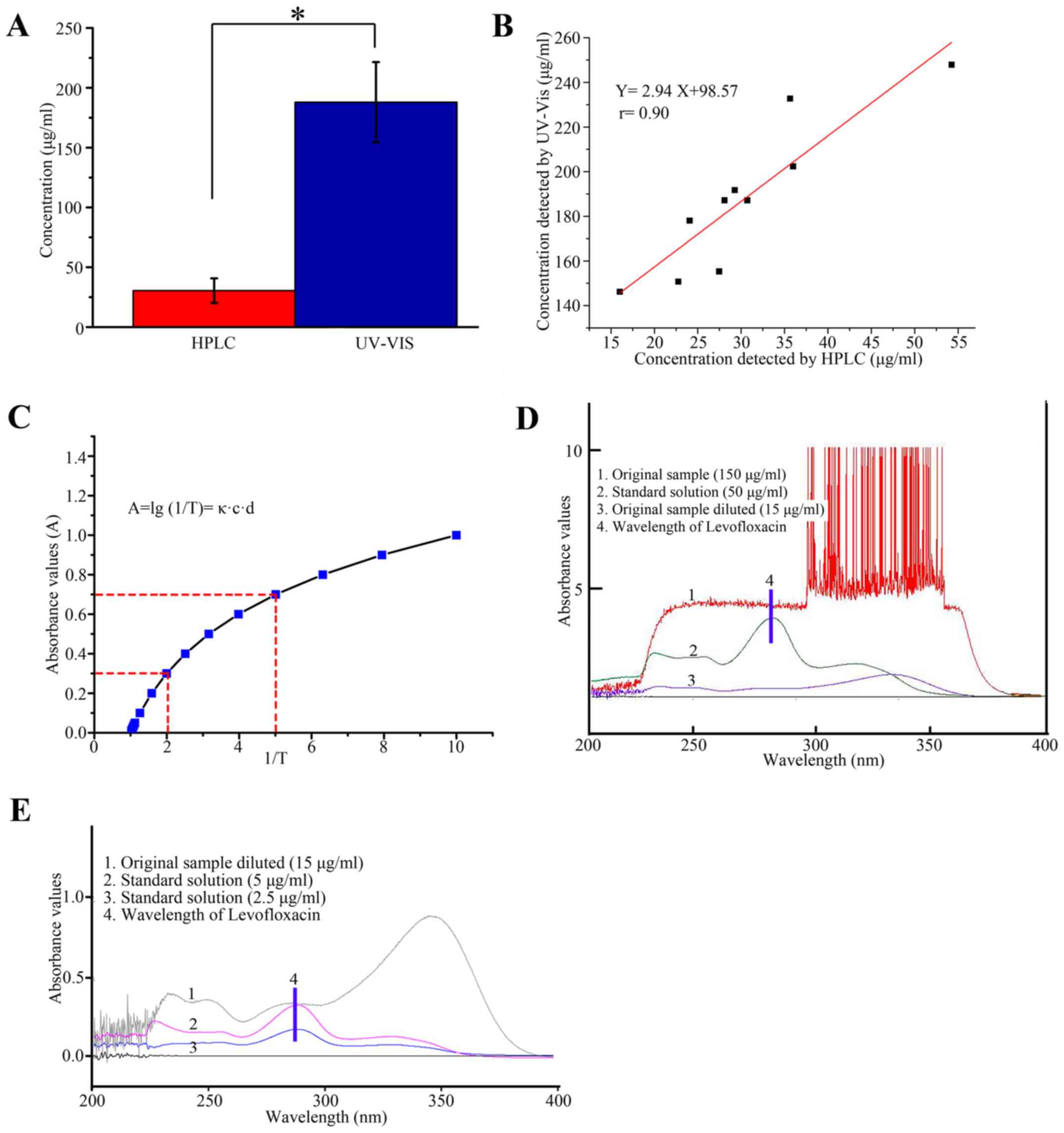
|
1
|
Das A, Mukherjee J, Dey G, Sarkar AK,
Sahoo BK, Chakrabarty US, Nandi U and Pal TK: Bioequivalence study
of levofloxacin tablets in healthy Indian volunteers using HPLC.
Arzneimittelforschung. 61:61–65. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wimer SM, Schoonover L and Garrison MW:
Levofloxacin: A therapeutic review. Clin Ther. 20:1049–1070. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Carral N, Lukas JC, Oteo I and Suarez E:
Impact of poor compliance with levofloxacin and moxifloxacin on
respiratory tract infection antimicrobial efficacy: A
pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic simulation study. Int J Antimicrob
Agents. 45:79–83. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sun H, Wang H and Ge X: Simultaneous
determination of the combined drugs of ceftriaxone sodium,
metronidazole, and levofloxacin in human urine by high-performance
liquid chromatography. J Clin Lab Anal. 26:486–492. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang SS, Ratliff PD and Judd WR:
Retrospective review of ceftriaxone versus levofloxacin for
treatment of E.coli urinary tract infections. Int J Clin Pharm.
40:143–149. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cicuéndsez M, Izquierdo-Barba I, Portolés
MT and Vallet-Regí M: Biocompatibility and levofloxacin delivery of
mesoporous materials. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 84:115–124. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Croissant JG, Fatieiev Y, Almalik A and
Khashab NM: Mesoporous silica and organosilica nanoparticles:
Physical chemistry, biosafety, delivery strategies, and biomedical
applications. Adv Healthc Mater. 7:2018.doi:
10.1002/adhm.201700831. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Shi S, Chen F and Cai W: Biomedical
applications of functionalized hollow mesoporous silica
nanoparticles: Focusing on molecular imaging. Nanomedicine (Lond).
8:2027–2039. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Guisasola E, Asín L, Beola L, de la Fuente
JM, Baeza A and Vallet-Regí M: Beyond traditional hyperthermia: In
vivo cancer treatment with magnetic-responsive mesoporous silica
nanocarriers. ACS App Mater Interfaces. 10:12518–12525. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Wang Q, Chen C, Liu W, He X, Zhou N, Zhang
D, Gu H, Li J, Jiang J and Huang W: Levofloxacin loaded mesoporous
silica microspheres/nano-hydroxyapatite/polyurethane composite
scaffold for the treatment of chronic osteomyelitis with bone
defects. Sci Rep. 7:418082017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Szerkus O, Jacyna J, Gibas A, Sieczkowski
M, Siluk D, Matuszewski M, Kaliszan R and Markuszewski MJ: Robust
HPLC-MS/MS method for levofloxacin and ciprofloxacin determination
in human prostate tissue. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 132:173–183. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gao XX, Yao GC, Guo N, An F and Guo XJ: A
simple and rapid high performance liquid chromatography method to
determine levofloxacin in human plasma and its use in a
bioequivalence study. Drug Discov Ther. 1:136–140. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Netz DJ, Sepulveda P, Pandolfelli VC,
Spadaro AC, Alencastre JB, Bentley MV and Marchetti JM: Potential
use of gelcasting hydroxyapatite porous ceramic as an implantable
drug delivery system. Int J Pharm. 213:117–125. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Siewert S: Validation of a levofloxacin
HPLC assay in plasma and dialysate for pharmacokinetic studies. J
Pharm Biomed Anal. 41:1360–1362. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Arayne MS, Sultana N and Siddiqui FA:
Optimization of levofloxacin analysis by RP-HPLC using multivariate
calibration technique. Pak J Pharm Sci. 20:100–106. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lalitha Devi M and Chandrasekhar KB: A
validated stability-indicating RP-HPLC method for levofloxacin in
the presence of degradation products, its process related
impurities and identification of oxidative degradant. J Pharm
Biomed Anal. 50:710–717. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Argyo C, Weiss V, Bräuchle C and Bein T:
Multifunctional mesoporous silica nanoparticles as a universal
platform for drug delivery. Chemistry Materials. 26:435–451. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Sepulveda P, Binner JG, Rogero SO, Higa OZ
and Bressiani JC: Production of porous hydroxyapatite by the
gel-casting of foams and cytotoxic evaluation. J Biomed Mater Res.
50:27–34. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ghaffar KA, Hussein WM, Khalil ZG, Capon
RJ, Skwarczynski M and Toth I: Levofloxacin and indolicidin for
combination antimicrobial therapy. Curr Drug Deliv. 12:108–114.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Guenter SG, Iven H, Boos C, Bruch HP and
Muhl E: Pharmacokinetics of levofloxacin during continuous
venovenous hemodiafiltration and continuous venovenous
hemofiltration in critically ill patients. Pharmacotherapy.
22:175–183. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Langergraber G, Fleischmann N and
Hofstädter F: A multivariate calibration procedure for UV/VIS
spectrometric quantification of organic matter and nitrate in
wastewater. Water Sci Technol. 47:63–71. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Nagaraja P, Al-Tayar NG, Shivakumar A,
Shrestha AK and Gowda AK: A simple and sensitive spectrophotometric
method for the determination of trace amounts of nitrite in
environmental and biological samples using
4-amino-5-hydroxynaphthalene-2,7-disulphonic acid monosodium salt.
Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 75:1411–1416. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chamseddin C and Jira TH: Comparison of
the chromatographic behavior of levofloxacin, ciprofloxacin and
moxifloxacin on various HPLC phases. Pharmazie. 66:244–248.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Nguyen HA, Grellet J, Ba BB, Quentin C and
Saux MC: Simultaneous determination of levofloxacin, gatifloxacin
and moxifloxacin in serum by liquid chromatography with column
switching. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci.
810:77–83. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Watabe S, Yokoyama Y, Nakazawa K,
Shinozaki K, Hiraoka R, Takeshita K and Suzuki Y: Simultaneous
measurement of pazufloxacin, ciprofloxacin, and levofloxacin in
human serum by high-performance liquid chromatography with
fluorescence detection. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life
Sci. 878:1555–1561. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ji HY, Jeong DW, Kim YH, Kim HH, Sohn DR
and Lee HS: Hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography-tandem
mass spectrometry for the determination of levofloxacin in human
plasma. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 41:622–627. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Borcan LC, Dudas Z, Len A, Fuzi J, Borcan
F and Tomescu MC: Synthesis and characterization of a polyurethane
carrier used for a prolonged transmembrane transfer of a chili
pepper extract. Int J Nanomedicine. 6:7155–7166. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Rahimi S, Khoee S and Ghandi M:
Development of photo and pH dual crosslinked coumarin-containing
chitosan nanoparticles for controlled drug release. Carbohydr
Polym. 201:236–245. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|