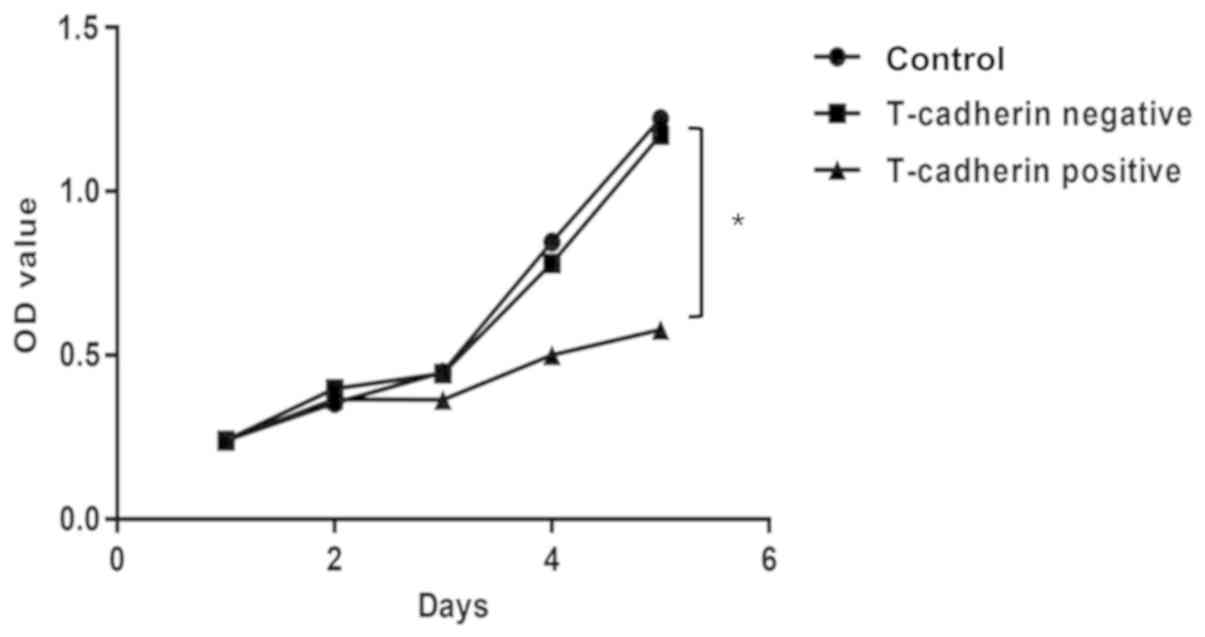
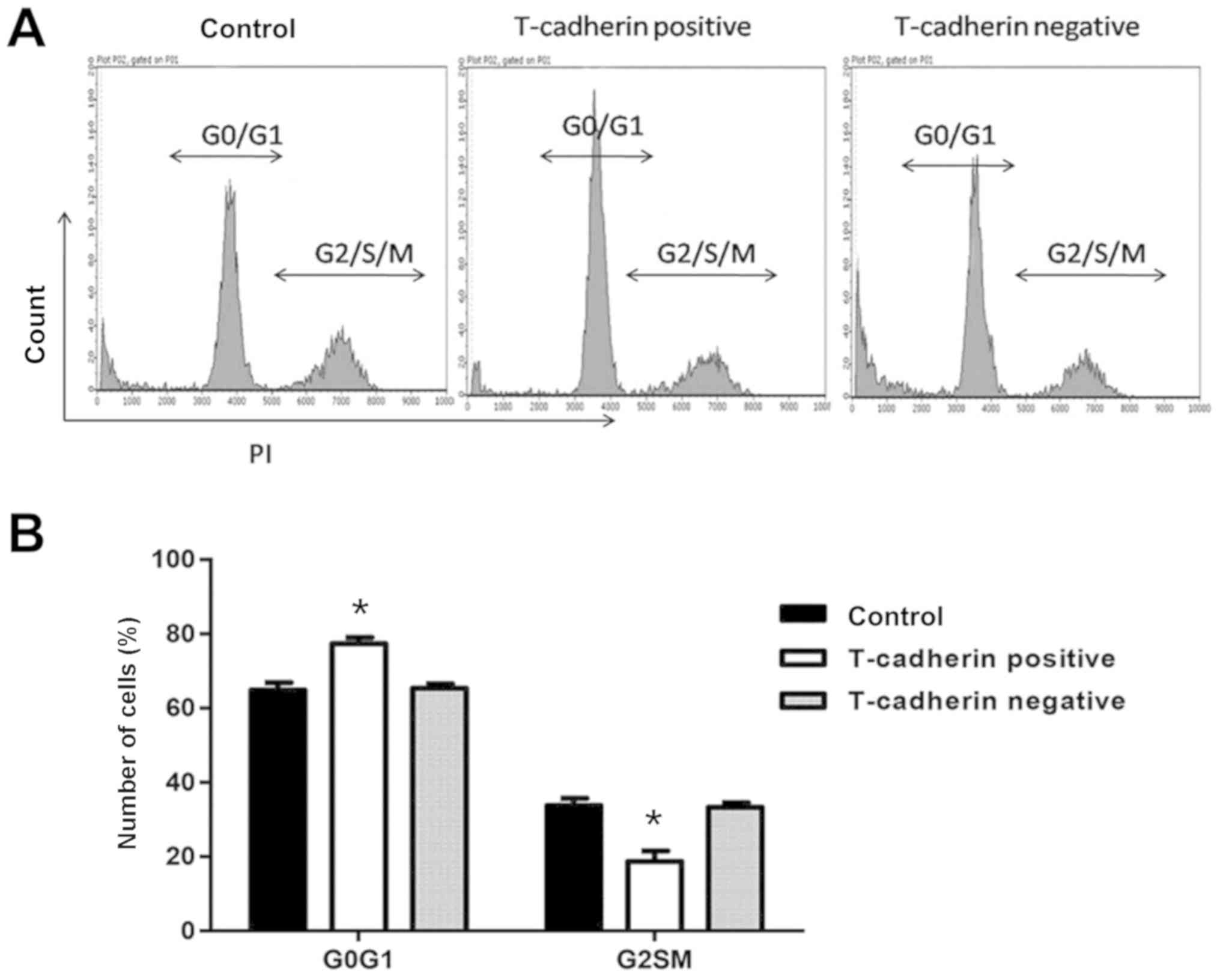
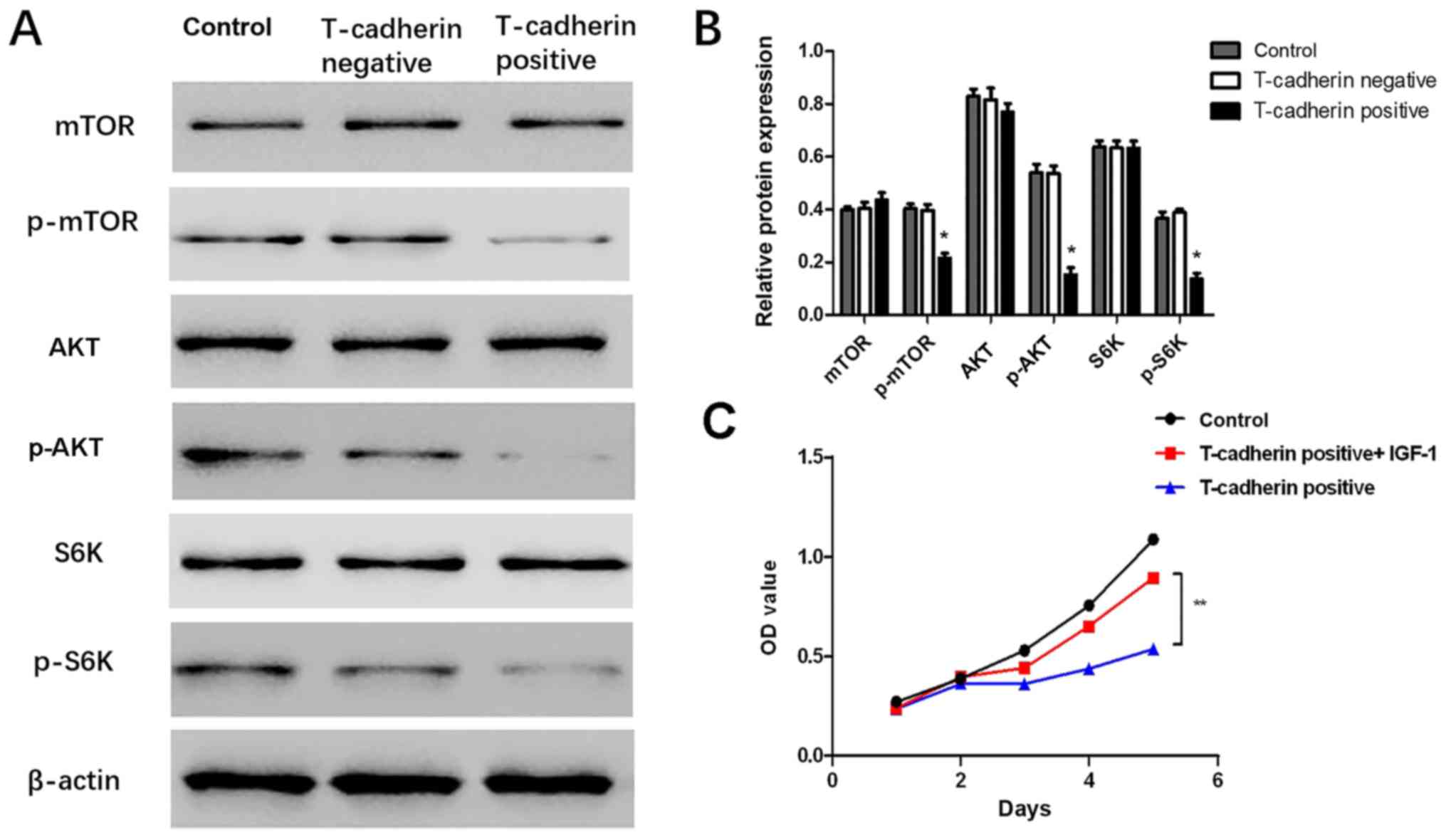
|
1
|
Lin Y, Ueda J, Kikuchi S, Totsuka Y, Wei
WQ, Qiao YL and Inoue M: Comparative epidemiology of gastric cancer
between Japan and China. World J Gastroenterol. 17:4421–4428. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Uemura N, Okamoto S, Yamamoto S, Matsumura
N, Yamaguchi S, Yamakido M, Taniyama K, Sasaki N and Schlemper RJ:
Helicobacter pylori infection and the development of gastric
cancer. N Engl J Med. 345:784–789. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhang Y, Yang J, Wang J, Guo H and Jing N:
LMO1 is a novel oncogene in lung cancer, and its overexpression is
a new predictive marker for anti-EGFR therapy. Med Oncol.
31:992014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Angst BD, Marcozzi C and Magee AI: The
cadherin superfamily: Diversity in form and function. J Cell Sci.
114:629–641. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Dasen B, Vlajnic T, Mengus C, Ruiz C,
Bubendorf L, Spagnoli G, Wyler S, Erne P, Resink TJ and Philippova
M: T-cadherin in prostate cancer: Relationship with cancer
progression, differentiation and drug resistance. J Pathol Clin
Res. 3:44–57. 2016. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Philippova M, Joshi M, Kyriakakis E, Pfaff
D, Erne P and Resink T: A guide and guard: The many faces of
T-cadherin. Cell Signal. 21:1035–1044. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Schmalhofer O, Brabletz S and Brabletz T:
E-cadherin, beta-catenin, and ZEB1 in malignant progression of
cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 28:151–166. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Fedor-Chaiken M, Hein PW, Stewart JC,
Brackenbury R and Kinch MS: E-cadherin binding modulates EGF
receptor activation. Cell Commun Adhes. 10:105–118. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Suyama K, Shapiro I, Guttman M and Hazan
RB: A signaling pathway leading to metastasis is controlled by
N-cadherin and the FGF receptor. Cancer Cell. 2:301–314. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Derycke LD and Bracke ME: N-cadherin in
the spotlight of cell-cell adhesion, differentiation,
embryogenesis, invasion and signalling. Int J Dev Biol. 48:463–476.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tryndyak VP, Beland FA and Pogribny IP:
E-cadherin transcriptional down-regulation by epigenetic and
microRNA-200 family alterations is related to mesenchymal and
drug-resistant phenotypes in human breast cancer cells. Int J
Cancer. 126:2575–2583. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ivanov D, Philippova M, Allenspach R, Erne
P and Resink T: T-cadherin upregulation correlates with cell-cycle
progression and promotes proliferation of vascular cells.
Cardiovasc Res. 64:132–143. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tang Y, Dai Y and Huo J: Decreased
expression of T-cadherin is associated with gastric cancer
prognosis. Hepatogastroenterology. 59:1294–1298. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kong DD, Yang J, Li L, Wang W, Chen YN,
Wang SB and Zhou YZ: T-cadherin association with
clinicopathological features and prognosis in axillary lymph
node-positive breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 150:119–126.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang Z, Wang B, Guo H, Shi G and Hong X:
Clinicopathological significance and potential drug target of
T-cadherin in NSCLC. Drug Des Devel Ther. 9:207–216.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ren JZ and Huo JR: Correlation between
T-cadherin gene expression and aberrant methylation of T-cadherin
promoter in human colon carcinoma cells. J Med Oncol. 29:915–918.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Philippova M, Pfaff D, Kyriakakis E,
Buechner SA, Iezzi G, Spagnoli GC, Schoenenberger AW, Erne P and
Resink TJ: T-cadherin loss promotes experimental metastasis of
squamous cell carcinoma. Eur J Cancer. 49:2048–2058. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bosserhoff AK, Ellmann L, Quast AS, Eberle
J, Boyle GM and Kuphal S: Loss of T-cadherin (CDH-13) regulates AKT
signaling and desensitizes cells to apoptosis in melanoma. Mol
Carcinog. 53:635–647. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Toyooka KO, Toyooka S, Virmani AK,
Sathyanarayana UG, Euhus DM, Gilcrease M, Minna JD and Gazdar AF:
Loss of expression and aberrant methylation of the CDH13
(H-cadherin) gene in breast and lung carcinomas. Cancer Res.
61:4556–4560. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang XD, Wang BE, Soriano R, Zha J, Zhang
Z, Modrusan Z, Cunha GR and Gao WQ: Expression profiling of the
mouse prostate after castration and hormone replacement:
Implication of H-cadherin in prostate tumorigenesis.
Differentiation. 75:219–234. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Takeuchi T, Misaki A, Liang SB, Tachibana
A, Hayashi N, Sonobe H and Ohtsuki Y: Expression of T-cadherin
(CDH13, H-Cadherin) in human brain and its characteristics as a
negative growth regulator of epidermal growth factor in
neuroblastoma cells. J Neurochem. 74:1489–1497. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lee SW: H-cadherin, a novel cadherin with
growth inhibitory functions and diminished expression in human
breast cancer. Nat Med. 2:776–782. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Takeuchi T, Misaki A, Chen BK and Ohtsuki
Y: H-cadherin expression in breast cancer. Histopathology.
35:87–88. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lin J, Chen Z, Huang Z, Chen F, Ye Z, Lin
S and Wang W: Upregulation of T-cadherin suppresses cell
proliferation, migration and invasion of gastric cancer in vitro.
Exp Ther Med. 14:4194–4200. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wei B, Shi H, Lu X, Shi A, Cheng Y and
Dong L: Association between the expression of T-cadherin and
vascular endothelial growth factor and the prognosis of patients
with gastric cancer. Mol Med Rep. 12:2075–2081. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chan DW, Lee JMF, Chan PC and Ng IO:
Genetic and epigenetic inactivation of T-cadherin in human
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Int J Cancer. 123:1043–1052. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Adachi Y, Takeuchi T, Nagayama T and
Furihata M: T-cadherin modulates tumor-associated molecules in
gallbladder cancer cells. Cancer Invest. 28:120–126. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lin Y, Sun G, Liu X, Chen Y and Zhang C:
Clinical significance of T-cadherin tissue expression in patients
with bladder transitional cell carcinoma. Urol Int. 86:340–345.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lin YL, Xie PG and Ma JG: Aberrant
methylation of CDH13 is a potential biomarker for predicting the
recurrence and progression of non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer.
Med Sci Monit. 20:1572–1577. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lin YL, He ZK, Li ZG and Guan TY:
Downregulation of CDH13 expression promotes invasiveness of bladder
transitional cell carcinoma. Urol Int. 90:225–232. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Fujishima Y, Maeda N, Matsuda K, Masuda S,
Mori T, Fukuda S, Sekimoto R, Yamaoka M, Obata Y, Kita S, et al:
Adiponectin association with T-cadherin protects against neointima
proliferation and atherosclerosis. FASEB J. 31:1571–1583. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kong DD, Wang MH, Yang J, Li L, Wang W,
Wang SB and Zhou YZ: T-cadherin is associated with prognosis in
triple-negative breast cancer. Oncology letters. 14:2975–2981.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Riou P, Saffroy R, Chenailler C, Franc B,
Gentile C, Rubinstein E, Resink T, Debuire B, Piatier-Tonneau D and
Lemoine A: Expression of T-cadherin in tumor cells influences
invasive potential of human hepatocellular carcinoma. FASEB J.
20:2291–2301. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yan Q, Zhang ZF, Chen XP, Gutmann DH,
Xiong M, Xiao ZY and Huang ZY: Reduced T-cadherin expression and
promoter methylation are associated with the development and
progression of hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 32:1057–1063.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Huang ZY, Wu Y, Hedrick N and Gutmann DH:
T-cadherin-mediated cell growth regulation involves G2 phase arrest
and requires p21(CIP1/WAF1) expression. Mol Cell Biol. 23:566–578.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Akagi T and Kimoto T: Human cell line
(HGC-27) derived from the metastatic lymph node of gastric cancer.
Acta Medica Okayama. 30:215–219. 1976.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Brown GT and Murray GI: Current
mechanistic insights into the roles of matrix metalloproteinases in
tumour invasion and metastasis. J Pathol. 237:227–281. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Hebbard LW, Garlatti M, Young LJ, Cardiff
RD, Oshima RG and Ranscht B: T-cadherin supports angiogenesis and
adiponectin association with the vasculature in a mouse mammary
tumor model. Cancer Res. 68:1407–1416. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Claudio F: Targeting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR
pathway in prostate cancer development and progression: Insight to
therapy. Clin Cancer Drugs. 20:R83–R99. 2016.
|
|
41
|
Ewald F, Nörz D, Grottke A, Bach J,
Herzberger C, Hofmann BT, Nashan B and Jücker M: Vertical targeting
of AKT and mTOR as well as dual targeting of AKT and MEK signaling
is synergistic in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cancer. 6:1195–1205.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|