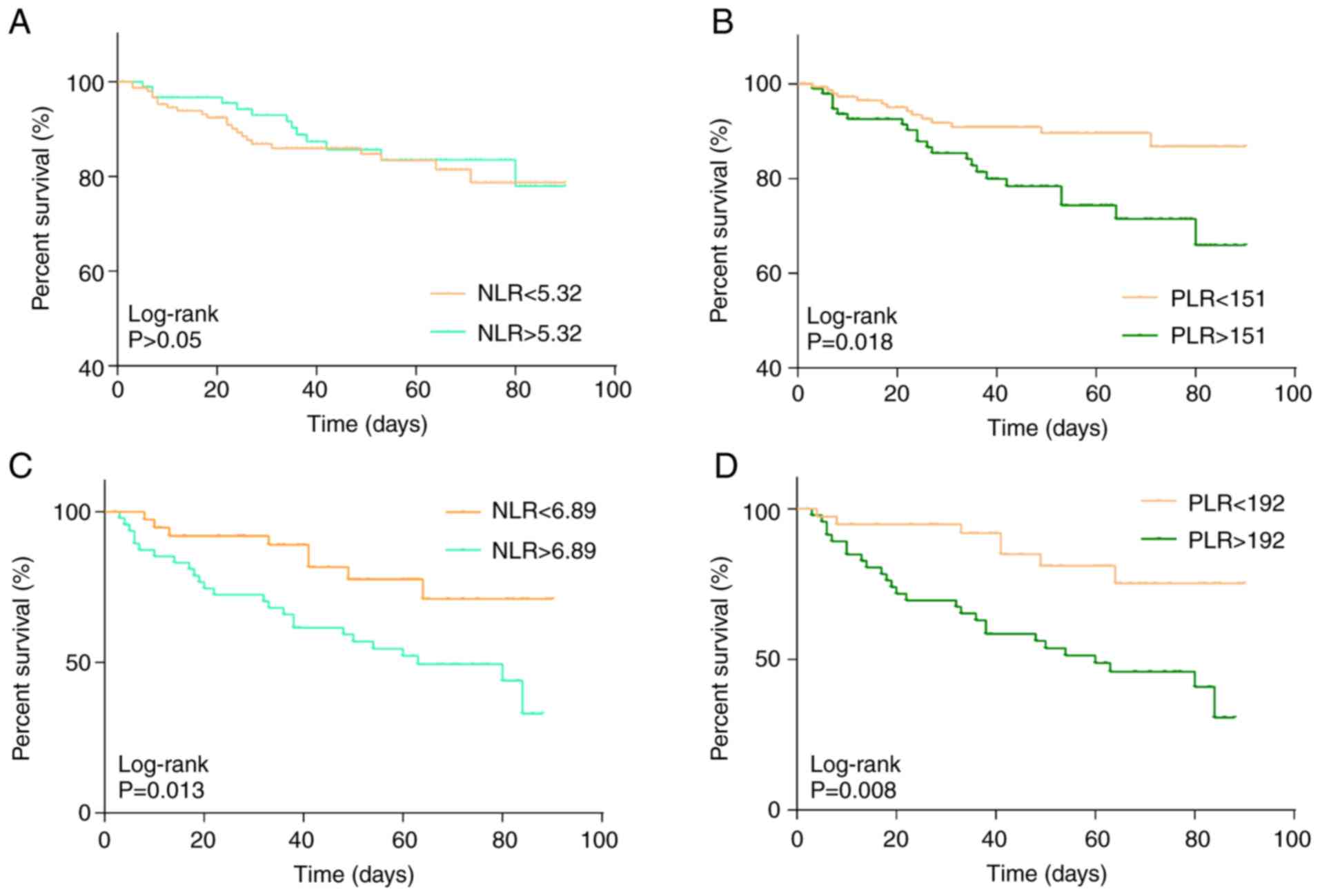
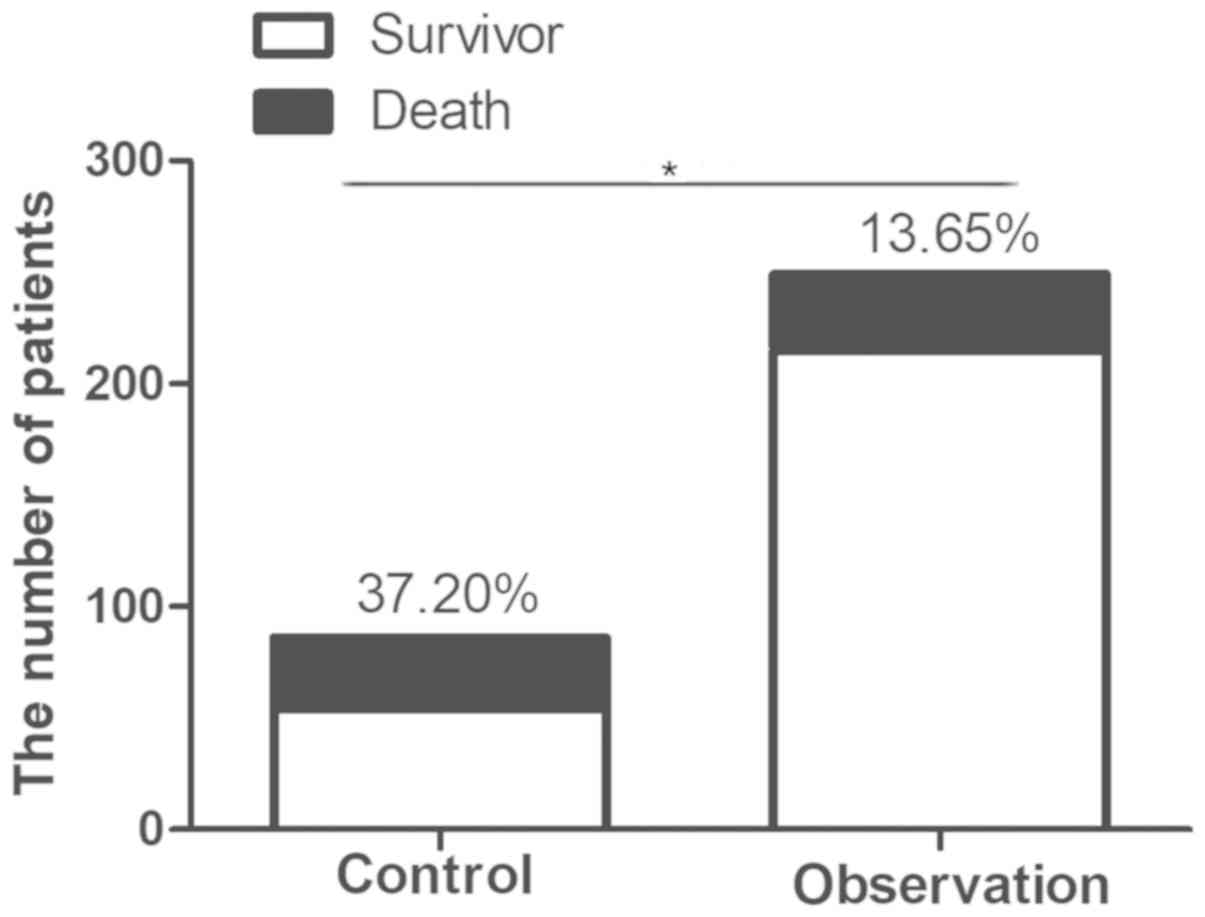
|
1
|
Santoni M, Andrikou K, Sotte V, Bittoni A,
Lanese A, Pellei C, Piva F, Conti A, Nabissi M, Santoni G and
Cascinu S: Toll like receptors and pancreatic diseases: From a
pathogenetic mechanism to a therapeutic target. Cancer Treat Rev.
41:569–576. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
O'Neill LA: The interleukin-1
receptor/Toll-like receptor superfamily: 10 years of progress.
Immunol Rev. 226:10–18. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kawai T and Akira S: The role of
pattern-recognition receptors in innate immunity: Update on
toll-like receptors. Nat Immunol. 11:373–384. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kong Y and Le Y: Toll-like receptors in
inflammation of the central nervous system. Int Immunopharmacol.
11:1407–1414. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Abdi J, Engels F, Garssen J and Redegeld
F: The role of toll-like receptor mediated signalling in the
pathogenesis of multiple myeloma. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol.
80:225–240. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hammond MD, Taylor RA, Mullen MT, Ai Y,
Aguila HL, Mack M, Kasner SE, McCullough LD and Sansing LH:
CCR2+ Ly6C(hi) inflammatory monocyte recruitment
exacerbates acute disability following intracerebral hemorrhage. J
Neurosci. 34:3901–3909. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang J and Dore S: Inflammation after
intracerebral hemorrhage. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 27:894–908.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Atkinson JJ and Senior RM: Matrix
metalloproteinase-9 in lung remodeling. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol.
28:12–24. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tian XC, Liu XL, Zeng FR, Chen Z and Wu
DH: Platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio acts as an independent risk factor
for patients with hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular
carcinoma who received transarterial chemoembolization. Eur Rev Med
Pharmacol Sci. 20:2302–2309. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Suppiah A, Malde D, Arab T, Hamed M,
Allgar V, Smith AM and Morris-Stiff G: The prognostic value of the
neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) in acute pancreatitis:
Identification of an optimal NLR. J Gastrointest Surg. 17:675–681.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Morotti A, Phuah CL, Anderson CD, Jessel
MJ, Schwab K, Ayres AM, Pezzini A, Padovani A, Gurol ME,
Viswanathan A, et al: Leukocyte count and intracerebral hemorrhage
expansion. Stroke. 47:1473–1478. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gong C, Hoff JT and Keep RF: Acute
inflammatory reaction following experimental intracerebral
hemorrhage in rat. Brain Res. 871:57–65. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wijdicks EF: Cushing's ulcer: The eponym
and his own. Neurosurgery. 68:1695–1698. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Crooks CJ, Card TR and West J: Excess
long-term mortality following non-variceal upper gastrointestinal
bleeding: A population-based cohort study. PLoS Med.
10:e10014372013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wijdicks EF, Fulgham JR and Batts KP:
Gastrointestinal bleeding in stroke. Stroke. 25:2146–2148. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen CM, Hsu HC, Chuang YW, Chang CH, Lin
CH and Hong CZ: Study on factors affecting the occurrence of upper
gastrointestinal bleeding in elderly acute stroke patients
undergoing rehabilitation. J Nutr Health Aging. 15:632–636. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Agnihotri S, Czap A, Staff I, Fortunato G
and McCullough LD: Peripheral leukocyte counts and outcomes after
intracerebral hemorrhage. J Neuroinflammation. 8:1602011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Imtiaz F, Shafique K, Mirza SS, Ayoob Z,
Vart P and Rao S: Neutrophil lymphocyte ratio as a measure of
systemic inflammation in prevalent chronic diseases in asian
population. Int Arch Med. 5:22012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gokhan S, Ozhasenekler A, Mansur DH, Akil
E, Ustundag M and Orak M: Neutrophil lymphocyte ratios in stroke
subtypes and transient ischemic attack. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
17:653–657. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lattanzi S, Cagnetti C, Provinciali L and
Silvestrini M: Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio predicts the outcome
of acute intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke. 47:1654–1657. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Altintas O, Altintas MO, Tasal A,
Kucukdagli OT and Asil T: The relationship of
platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio with clinical outcome and final
infarct core in acute ischemic stroke patients who have undergone
endovascular therapy. Neurol Res. 38:759–765. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tao C, Wang J, Hu X, Ma J, Li H and You C:
Clinical value of neutrophil to lymphocyte and platelet to
lymphocyte ratio after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Neurocrit Care. 26:393–401. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|