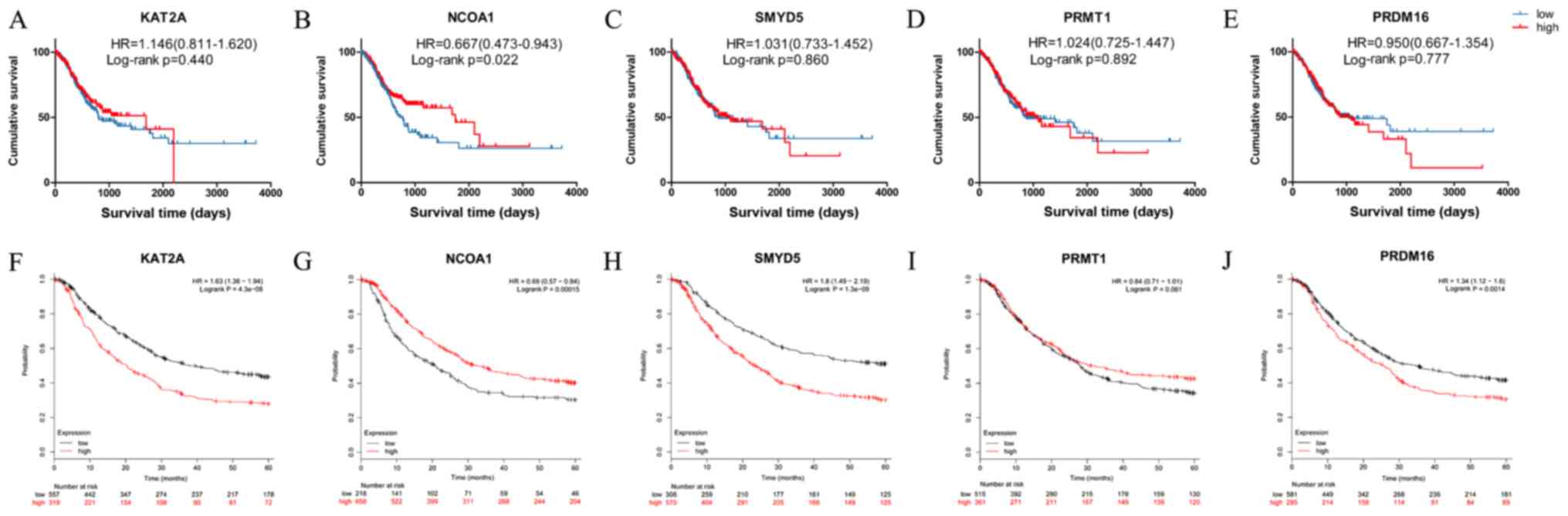
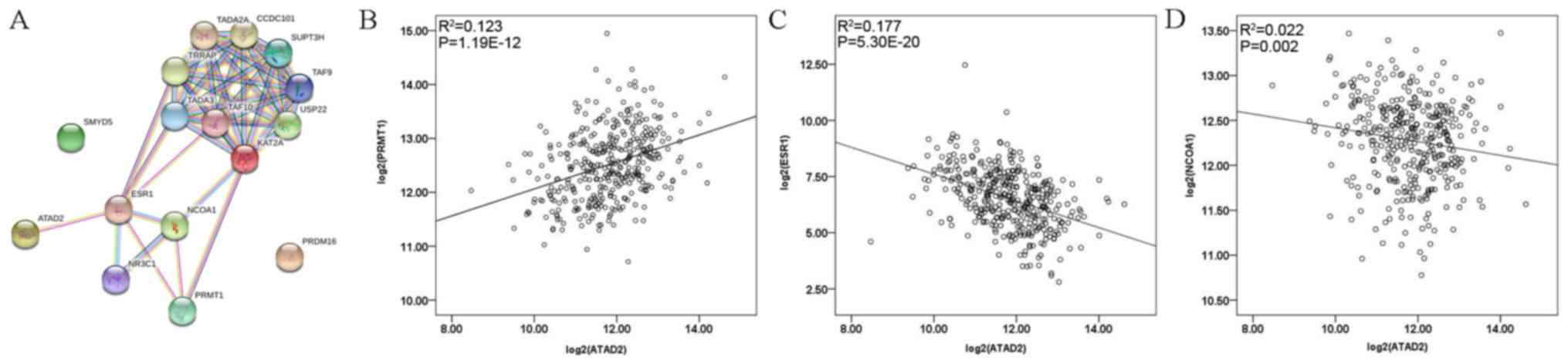
|
1
|
Nagini S: Carcinoma of the stomach: A
review of epidemiology, pathogenesis, molecular genetics and
chemoprevention. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 4:156–169. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yang WY, Gu JL and Zhen TM: Recent
advances of histone modification in gastric cancer. J Cancer Res
Ther. 10 (Suppl):S240–S245. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Rice JC and Allis CD: Histone methylation
versus histone acetylation: New insights into epigenetic
regulation. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 13:263–273. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Schiza V, Molina-Serrano D, Kyriakou D,
Hadjiantoniou A and Kirmizis A: N-alpha-terminal acetylation of
histone H4 regulates arginine methylation and ribosomal DNA
silencing. PLoS Genet. 9:e10038052013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sakuraba K, Yokomizo K, Shirahata A, Goto
T, Saito M, Ishibashi K, Kigawa G, Nemoto H and Hibi K: TIP60 as a
potential marker for the malignancy of gastric cancer. Anticancer
Res. 31:77–79. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
He LJ, Cai MY, Xu GL, Li JJ, Weng ZJ, Xu
DZ, Luo GY, Zhu SL and Xie D: Prognostic significance of
overexpression of EZH2 and H3k27me3 proteins in gastric cancer.
Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 13:3173–3178. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Goulet I, Gauvin G, Boisvenue S and Cote
J: Alternative splicing yields protein arginine methyltransferase 1
isoforms with distinct activity, substrate specificity, and
subcellular localization. J Biol Chem. 282:33009–33021. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kahl P, Gullotti L, Heukamp LC, Wolf S,
Friedrichs N, Vorreuther R, Solleder G, Bastian PJ, Ellinger J,
Metzger E, et al: Androgen receptor coactivators lysine-specific
histone demethylase 1 and four and a half LIM domain protein 2
predict risk of prostate cancer recurrence. Cancer Res.
66:11341–11347. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hirst M and Marra MA: Epigenetics and
human disease. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 41:136–146. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kang ZH, Wang CY, Zhang WL, Zhang JT, Yuan
CH, Zhao PW, Lin YY, Hong S, Li CY and Wang L: Histone deacetylase
HDAC4 promotes gastric cancer SGC-7901 cells progression via p21
repression. PLoS One. 9:e988942014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Das C, Lucia MS, Hansen KC and Tyler JK:
CBP/p300-mediated acetylation of histone H3 on lysine 56. Nature.
459:113–117. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Vire E, Brenner C, Deplus R, Blanchon L,
Fraga M, Didelot C, Morey L, Van Eynde A, Bernard D, Vanderwinden
JM, et al: The polycomb group protein EZH2 directly controls DNA
methylation. Nature. 439:871–874. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Na J, Lee K, Na W, Shin JY, Lee MJ, Yune
TY, Lee HK, Jung HS, Kim WS and Ju BG: Histone H3K27 Demethylase
JMJD3 in cooperation with NF-κB regulates keratinocyte wound
healing. J Invest Dermatol. 136:847–858. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li X, Corsa CA, Pan PW, Wu L, Ferguson D,
Yu X, Min J and Dou Y: MOF and H4 K16 acetylation play important
roles in DNA damage repair by modulating recruitment of DNA damage
repair protein Mdc1. Mol Cell Biol. 30:5335–5347. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ceol CJ, Houvras Y, Jane-Valbuena J,
Bilodeau S, Orlando DA, Battisti V, Fritsch L, Lin WM, Hollmann TJ,
Ferré F, et al: The histone methyltransferase SETDB1 is recurrently
amplified in melanoma and accelerates its onset. Nature.
471:513–517. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Xiang Y, Zhu Z, Han G, Lin H, Xu L and
Chen CD: JMJD3 is a histone H3K27 demethylase. Cell Res.
17:850–857. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zheng YC, Duan YC, Ma JL, Xu RM, Zi X, Lv
WL, Wang MM, Ye XW, Zhu S, Mobley D, et al:
Triazole-dithiocarbamate based selective lysine specific
demethylase 1 (LSD1) inactivators inhibit gastric cancer cell
growth, invasion, and migration. J Med Chem. 56:8543–8560. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Rhodes DR, Kalyana-Sundaram S, Mahavisno
V, Varambally R, Yu J, Briggs BB, Barrette TR, Anstet MJ,
Kincead-Beal C, Kulkarni P, et al: Oncomine 3.0: Genes, pathways,
and networks in a collection of 18,000 cancer gene expression
profiles. Neoplasia. 9:166–180. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chandrashekar DS, Bashel B, Balasubramanya
SAH, Creighton CJ, Ponce-Rodriguez I, Chakravarthi BVSK and
Varambally S: UALCAN: A portal for facilitating tumor subgroup gene
expression and survival analyses. Neoplasia. 19:649–658. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gyorffy B, Surowiak P, Budczies J and
Lanczky A: Online survival analysis software to assess the
prognostic value of biomarkers using transcriptomic data in
non-small-cell lung cancer. PLoS One. 8:e822412013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wu G, Liu H, He H, Wang Y, Lu X, Yu Y, Xia
S, Meng X and Liu Y: miR-372 down-regulates the oncogene ATAD2 to
influence hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation and metastasis.
BMC Cancer. 14:1072014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Venkatesh S and Workman JL: Histone
exchange, chromatin structure and the regulation of transcription.
Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 16:178–189. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Audia JE and Campbell RM: Histone
modifications and cancer. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol.
8:a0195212016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chan EM, Chan RJ, Comer EM, Goulet RJ III,
Crean CD, Brown ZD, Fruehwald AM, Yang Z, Boswell HS, Nakshatri H
and Gabig TG: MOZ and MOZ-CBP cooperate with NF-kappaB to activate
transcription from NF-kappaB-dependent promoters. Exp Hematol.
35:1782–1792. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yang XJ: The diverse superfamily of lysine
acetyltransferases and their roles in leukemia and other diseases.
Nucleic Acids Res. 32:959–976. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Rasti M, Grand RJ, Mymryk JS, Gallimore PH
and Turnell AS: Recruitment of CBP/p300, TATA-binding protein, and
S8 to distinct regions at the N terminus of adenovirus E1A. J
Virol. 79:5594–5605. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Xu J, Wu RC and O'Malley BW: Normal and
cancer-related functions of the p160 steroid receptor co-activator
(SRC) family. Nat Rev Cancer. 9:615–630. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Fleming FJ, Hill AD, McDermott EW,
O'Higgins NJ and Young LS: Differential recruitment of coregulator
proteins steroid receptor coactivator-1 and silencing mediator for
retinoid and thyroid receptors to the estrogen receptor-estrogen
response element by beta-estradiol and 4-hydroxytamoxifen in human
breast cancer. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 89:375–383. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Qin L, Chen X, Wu Y, Feng Z, He T, Wang L,
Liao L and Xu J: Steroid receptor coactivator-1 upregulates
integrin α5 expression to promote breast cancer cell
adhesion and migration. Cancer Res. 71:1742–1751. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Qin L, Liu Z, Chen H and Xu J: The steroid
receptor coactivator-1 regulates twist expression and promotes
breast cancer metastasis. Cancer Res. 69:3819–3827. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Gouon-Evans V, Rothenberg ME and Pollard
JW: Postnatal mammary gland development requires macrophages and
eosinophils. Development. 127:2269–2282. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Frycz BA, Murawa D, Borejsza-Wysocki M,
Wichtowski M, Spychala A, Marciniak R, Murawa P, Drews M and
Jagodziński PP: mRNA expression of steroidogenic enzymes, steroid
hormone receptors and their coregulators in gastric cancer. Oncol
Lett. 13:3369–3378. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Tai H, Kubota N and Kato S: Involvement of
nuclear receptor coactivator SRC-1 in estrogen-dependent cell
growth of MCF-7 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 267:311–316.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Boorjian SA, Heemers HV, Frank I, Farmer
SA, Schmidt LJ, Sebo TJ and Tindall DJ: Expression and significance
of androgen receptor coactivators in urothelial carcinoma of the
bladder. Endocr Relat Cancer. 16:123–137. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Sheppard HM, Harries JC, Hussain S, Bevan
C and Heery DM: Analysis of the steroid receptor coactivator 1
(SRC1)-CREB binding protein interaction interface and its
importance for the function of SRC1. Mol Cell Biol. 21:39–50. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yan H, Dobbie Z, Gruber SB, Markowitz S,
Romans K, Giardiello FM, Kinzler KW and Vogelstein B: Small changes
in expression affect predisposition to tumorigenesis. Nat Genet.
30:25–26. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Pavón MA, Parreño M, Téllez-Gabriel M,
León X, Arroyo-Solera I, López M, Céspedes MV, Casanova I, Gallardo
A, López-Pousa A, et al: CKMT1 and NCOA1 expression as a predictor
of clinical outcome in patients with advanced-stage head and neck
squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck. 38 (Suppl 1):E1392–E1403. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Qin L, Wu YL, Toneff MJ, Li D, Liao L, Gao
X, Bane FT, Tien JC, Xu Y, Feng Z, et al: NCOA1 directly targets
M-CSF1 expression to promote breast cancer metastasis. Cancer Res.
74:3477–3488. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Gao H, Chakraborty G, Lee-Lim AP, Mavrakis
KJ, Wendel HG and Giancotti FG: Forward genetic screens in mice
uncover mediators and suppressors of metastatic reactivation. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 111:16532–16537. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Krebs AR, Karmodiya K, Lindahl-Allen M,
Struhl K and Tora L: SAGA and ATAC histone acetyl transferase
complexes regulate distinct sets of genes and ATAC defines a class
of p300-independent enhancers. Mol Cell. 44:410–423. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Xu W, Edmondson DG, Evrard YA, Wakamiya M,
Behringer RR and Roth SY: Loss of Gcn5l2 leads to increased
apoptosis and mesodermal defects during mouse development. Nat
Genet. 26:229–232. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Sonnet M, Claus R, Becker N, Zucknick M,
Petersen J, Lipka DB, Oakes CC, Andrulis M, Lier A, Milsom MD, et
al: Early aberrant DNA methylation events in a mouse model of acute
myeloid leukemia. Genome Med. 6:342014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Li Y, Zhu R, Wang W, Fu D, Hou J, Ji S,
Chen B, Hu Z, Shao X, Yu X, et al: Arginine Methyltransferase 1 in
the nucleus accumbens regulates behavioral effects of cocaine. J
Neurosci. 35:12890–12902. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Boisvert FM, Rhie A, Richard S and Doherty
AJ: The GAR motif of 53BP1 is arginine methylated by PRMT1 and is
necessary for 53BP1 DNA binding activity. Cell Cycle. 4:1834–1841.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Qian C and Zhou MM: SET domain protein
lysine methyltransferases: Structure, specificity and catalysis.
Cell Mol Life Sci. 63:2755–2763. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Abu-Farha M, Lanouette S, Elisma F,
Tremblay V, Butson J, Figeys D and Couture JF: Proteomic analyses
of the SMYD family interactomes identify HSP90 as a novel target
for SMYD2. J Mol Cell Biol. 3:301–308. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Wang Y, Qu Y, Zhang XL, Xing J, Niu XL,
Chen X and Li ZM: Autocrine production of interleukin-6 confers
ovarian cancer cells resistance to tamoxifen via ER isoforms and
SRC-1. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 382:791–803. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Liao HW, Hsu JM, Xia W, Wang HL, Wang YN,
Chang WC, Arold ST, Chou CK, Tsou PH, Yamaguchi H, et al:
PRMT1-mediated methylation of the EGF receptor regulates signaling
and cetuximab response. J Clin Invest. 125:4529–4543. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Tan SX, Hu RC, Xia Q, Tan YL, Liu JJ, Gan
GX and Wang LL: The methylation profiles of PRDM promoters in
non-small cell lung cancer. Onco Targets Ther. 11:2991–3002. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Peng X, Xue H, Lü L, Shi P and Wang J and
Wang J: Accumulated promoter methylation as a potential biomarker
for esophageal cancer. Oncotarget. 8:679–691. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Bibi F, Ali I, Naseer MI, Ali Mohamoud HS,
Yasir M, Alvi SA, Jiman-Fatani AA, Sawan A and Azhar EI: Detection
of genetic alterations in gastric cancer patients from Saudi Arabia
using comparative genomic hybridization (CGH). PLoS One.
13:e02025762018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Burghel GJ, Lin WY, Whitehouse H, Brock I,
Hammond D, Bury J, Stephenson Y, George R and Cox A: Identification
of candidate driver genes in common focal chromosomal aberrations
of microsatellite stable colorectal cancer. PLoS One. 8:e838592013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Ma YS, Wu TM, Lv ZW, Lu GX, Cong XL, Xie
RT, Yang HQ, Chang ZY, Sun R, Chai L, et al: High expression of
miR-105-1 positively correlates with clinical prognosis of
hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting oncogene NCOA1. Oncotarget.
8:11896–11905. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Guo J, Cao R, Yu X, Xiao Z and Chen Z:
MicroRNA-223-3p inhibits human bladder cancer cell migration and
invasion. Tumour Biol. 39:10104283176916782017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Minchenko OH, Garmash IA, Minchenko DO,
Kuznetsova AY and Ratushna OO: Inhibition of IRE1 modifies hypoxic
regulation of G6PD, GPI, TKT, TALDO1, PGLS and RPIA genes
expression in U87 glioma cells. Ukr Biochem J. 89:38–49. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Ding SZ, Goldberg JB and Hatakeyama M:
Helicobacter pylori infection, oncogenic pathways and
epigenetic mechanisms in gastric carcinogenesis. Future Oncol.
6:851–862. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Tzelepis K, Koike-Yusa H, De Braekeleer E,
Li Y, Metzakopian E, Dovey OM, Mupo A, Grinkevich V, Li M, Mazan M,
et al: A CRISPR dropout screen identifies genetic vulnerabilities
and therapeutic targets in acute myeloid leukemia. Cell Rep.
17:1193–1205. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Zhu S, Xu Y, Song M, Chen G, Wang H, Zhao
Y, Wang Z and Li F: PRDM16 is associated with evasion of apoptosis
by prostatic cancer cells according to RNA interference screening.
Mol Med Rep. 14:3357–3361. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Blanc RS, Vogel G, Li X, Yu Z, Li S and
Richard S: Arginine methylation by PRMT1 regulates muscle stem cell
fate. Mol Cell Biol. 37(pii): e00457–16. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Kidder BL, He R, Wangsa D, Padilla-Nash
HM, Bernardo MM, Sheng S, Ried T and Zhao K: SMYD5 controls
heterochromatin and chromosome integrity during embryonic stem cell
differentiation. Cancer Res. 77:6729–6745. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Katsuno Y, Qin J, Oses-Prieto J, Wang H,
Jackson-Weaver O, Zhang T, Lamouille S, Wu J, Burlingame A, Xu J
and Derynck R: Arginine methylation of SMAD7 by PRMT1 in
TGF-β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and epithelial
stem-cell generation. J Biol Chem. 293:13059–13072. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Gao B, Kong Q, Zhang Y, Yun C, Dent SYR,
Song J, Zhang DD, Wang Y, Li X and Fang D: The histone
acetyltransferase Gcn5 positively regulates T Cell activation. J
Immunol. 198:3927–3938. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Wu GS and Bassing CH: Flip the switch:
BTG2-PRMT1 protein complexes antagonize pre-B-cell proliferation to
promote B-cell development. Cell Mol Immunol. 15:808–811. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Lei Q, Liu X, Fu H, Sun Y, Wang L, Xu G,
Wang W, Yu Z, Liu C, Li P, et al: miR-101 reverses hypomethylation
of the PRDM16 promoter to disrupt mitochondrial function in
astrocytoma cells. Oncotarget. 7:5007–5022. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Altan B, Yokobori T, Ide M, Mochiki E,
Toyomasu Y, Kogure N, Kimura A, Hara K, Bai T, Bao P, et al:
Nuclear PRMT1 expression is associated with poor prognosis and
chemosensitivity in gastric cancer patients. Gastric Cancer.
19:789–797. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Wu G, Lu X, Wang Y, He H, Meng X, Xia S,
Zhen K and Liu Y: Epigenetic high regulation of ATAD2 regulates the
Hh pathway in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Oncol.
45:351–361. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Zou JX, Revenko AS, Li LB, Gemo AT and
Chen HW: ANCCA, an estrogen-regulated AAA+ ATPase coactivator for
ERalpha, is required for coregulator occupancy and chromatin
modification. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:18067–18072. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Jin Q, Wang C, Kuang X, Feng X, Sartorelli
V, Ying H, Ge K and Dent SY: Gcn5 and PCAF regulate PPARγ and
Prdm16 expression to facilitate brown adipogenesis. Mol Cell Biol.
34:3746–3753. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|