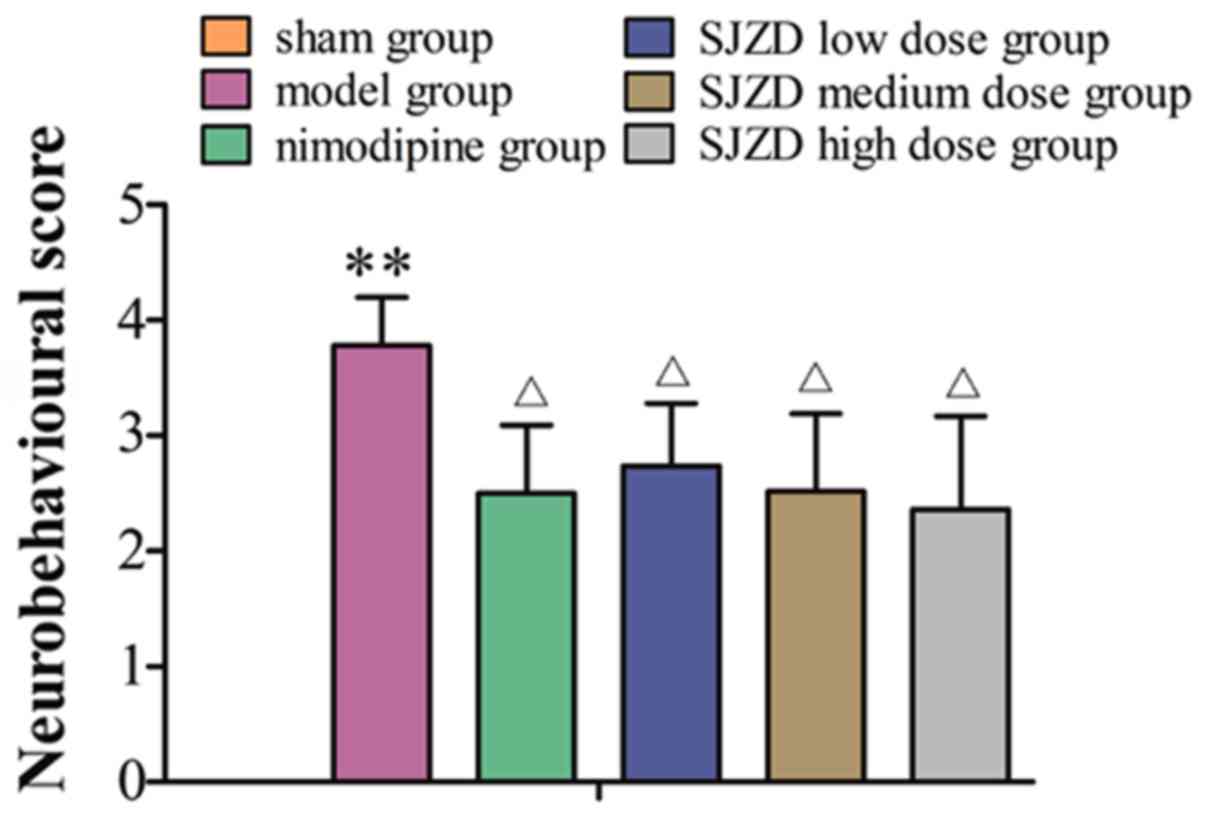
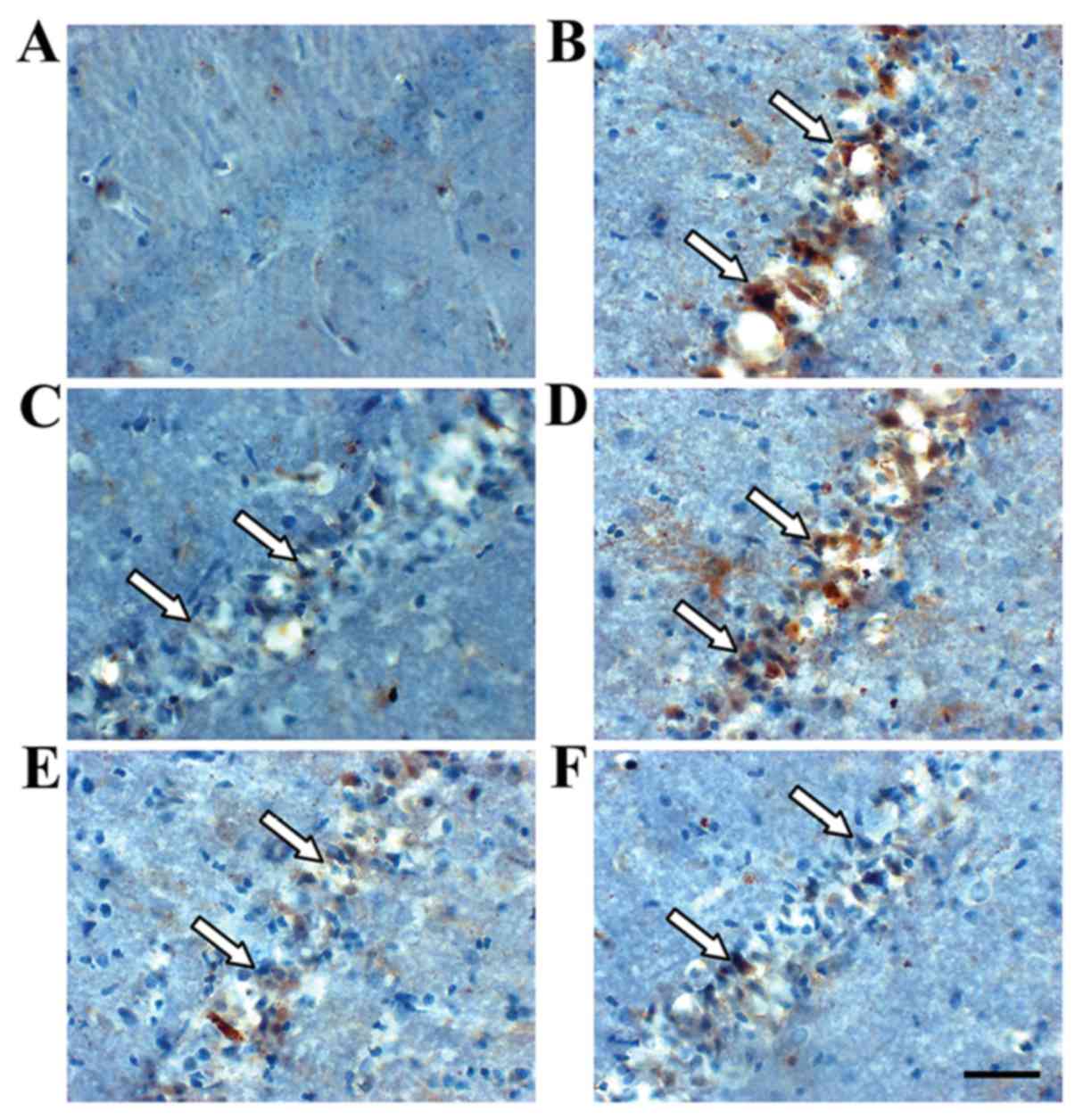
|
1
|
Arnberg F, Grafström J, Lundberg J,
Nikkhou-Aski S, Little P, Damberg P, Mitsios N, Mulder J, Lu L,
Söderman M, et al: Imaging of a clinically relevant stroke model:
Glucose hypermetabolism revisited. Stroke. 46:835–842. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jickling GC, Liu D, Ander BP, Stamova B,
Zhan X and Sharp FR: Targeting neutrophils in ischemic stroke:
Translational insights from experimental studies. J Cereb Blood
Flow Metab. 35:888–901. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Meschia JF, Bushnell C, Boden-Albala B,
Braun LT, Bravata DM, Chaturvedi S, Creager MA, Eckel RH, Elkind
MS, Fornage M, et al: Guidelines for the primary prevention of
stroke: A statement for healthcare professionals from the American
Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke.
45:3754–3832. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lv Z, Liu C, Zhai M, Zhang Q, Li J, Zheng
F and Peng M: LPS Pretreatment attenuates cerebral
ischaemia/reperfusion injury by inhibiting inflammation and
apoptosis. Cell Physiol Biochem. 45:2246–2256. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Carneiro BR, Pernambuco Filho PC, Mesquita
AP, da Silva DS, Pinhal MA, Nader HB and Lopes CC: Acquisition of
anoikis resistance up-regulates syndecan-4 expression in
endothelial cells. PLoS One. 9:e1160012014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hill JW, Poddar R, Thompson JF, Rosenberg
GA and Yang Y: Intranuclear matrix metalloproteinases promote DNA
damage and apoptosis induced by oxygen-glucose deprivation in
neurons. Neuroscience. 220:277–290. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sater AP, Rael LT, Tanner AH, Lieser MJ,
Acuna DL, Mains CW and Bar-Or D: Cell death after traumatic brain
injury: Detrimental role of anoikis in healing. Clin Chim Acta.
482:149–154. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Guo Z, Sun X, He Z, Jiang Y and Zhang X:
Role of matrix metalloproteinase-9 in apoptosis of hippocampal
neurons in rats during early brain injury after subarachnoid
hemorrhage. Neurol Sci. 31:143–149. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Frisch SM, Schaller M and Cieply B:
Mechanisms that link the oncogenic epithelial-mesenchymal
transition to suppression of anoikis. J Cell Sci. 126:21–29. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mazumder MK, Bhattacharya P and Borah A:
Inhibition of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and 9 by Piroxicam confer
neuroprotection in cerebral ischemia: An in silico evaluation of
the hypothesis. Med Hypotheses. 83:697–701. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Cheema ZF, Santillano DR, Wade SB, Newman
JM and Miranda RC: The extracellular matrix, p53 and estrogen
compete to regulate cell-surface Fas/Apo-1 suicide receptor
expression in proliferating embryonic cerebral cortical precursors,
and reciprocally, Fas-ligand modifies estrogen control of
cell-cycle proteins. BMC Neurosci. 5:112004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tian G, Wu C, Li J, Liang B, Zhang F, Fan
X, Li Z, Wang Y, Li Z, Liu D, et al: Network pharmacology based
investigation into the effect and mechanism of modified sijunzi
decoction against the subtypes of chronic atrophic gastritis.
Pharmacol Res. 144:158–166. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li J, Qian J, Jia JG, Jin X, Yu DJ, Xie B,
Qian LY, Zhang LG and Guo CX: Effect of Sijunzi decoction on the
proliferation of side population cells of human gastric cancer cell
line. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 34:704–709. 2014.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hu KL, Li H, Liu WH, He Q, Zhong YL and
Peng ZY: Effect of modified Si Junzitang on expression of ERK1/2,
Akt, Bax in rats with cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. Chin J
Exp Traditional Med Formulae. 24:152–158. 2008.(In Chinese).
|
|
15
|
Liu S, Zhang YB, Cao WG, Zhang D and Liu
L: Comparision of the effects of three Chinese medicinal recipes to
cerebral ischemia. Pharmacol Clin Chin Materia Medica. 25:6–7.
2009.(In Chinese).
|
|
16
|
Liu F and McCullough LD: Middle cerebral
artery occlusion model in rodents: Methods and potential pitfalls.
J Biomed Biotechnol. 2011:4647012011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ng YS, Stein J, Ning M and Black-Schaffer
RM: Comparison of clinical characteristics and functional outcomes
of ischemic stroke in different vascular territories. Stroke.
38:2309–2314. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission, .
Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China. 1. 2015th. Chinese
Medical Science and Technology Press; Beijing: pp. 8–240. 2015
|
|
19
|
Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S and
Cummins R: Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without
craniectomy in rats. Stroke. 20:84–91. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang Q, Zhou M, Wu X, Li Z, Liu B, Gao W,
Yue J and Liu T: Promoting therapeutic angiogenesis of focal
cerebral ischemia using thrombospondin-4 (TSP4) gene-modified bone
marrow stromal cells (BMSCs) in a rat model. J Transl Med.
17:1112019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hao FL, Han XF, Wang XL, Zhao ZR, Guo AH,
Lu XJ and Zhao XF: The neurovascular protective effect of
alogliptin in murine MCAO model and brain endothelial cells. Biomed
Pharmacother. 109:181–187. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Xu JH, Huang YM, Ling W, Li Y, Wang M,
Chen XY, Sui Y and Zhao HL: Wen Dan Decoction for hemorrhagic
stroke and ischemic stroke. Complement Ther Med. 23:298–308. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hu HX, Lin RH, Zhu XQ, Li ZF and Chen LD:
Anti-inflammatory effects of Gualou Guizhi decoction in transient
focal cerebral ischemic brains [Corrected]. Mol Med Rep.
12:1321–1327. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Guo Q, Zhong M, Xu H, Mao X, Zhang Y and
Lin N: A systems biology perspective on the molecular mechanisms
underlying the therapeutic effects of buyang huanwu decoction on
ischemic stroke. Rejuvenation Res. 18:313–325. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang DS, Liu YL, Zhu DQ, Huang XJ and Luo
CH: Point application with angong niuhuang sticker protects
hippocampal and cortical neurons in rats with cerebral ischemia.
Neural Regen Res. 10:286–291. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang C, Wen Y, Fan XN, Tian G, Zhou XY,
Deng SZ and Meng ZH: Therapeutic effects of different durations of
acupuncture on rats with middle cerebral artery occlusion. Neural
Regen Res. 10:159–164. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhong YL, Li H, Liu WH and Hu D: The
effect of spleen-strengthening therapy on the mRNA and protein
expression levels of INTβ3, ILK and FAK in Rats with cerebral
ischemia/reperfusion injury. Lishizhen Med Mat Med Res. 28:513–516.
2017.(In Chinese).
|
|
28
|
Li H, Liu WH, Zhou XQ and He Q: Effects of
spleen-strengthening therapy on MMP2 expression in brain tissue and
blood brain barrier permeability in rats with cerebral
ischemia/reperfusion injury. Hunan J TCM. 29:115–117. 2013.
|
|
29
|
Li H, Liu WH, Liao LY, Liu BY and Cai GX:
Effect of tonifying spleen therapy on the degradation of laminin in
rats with cerebral ischemia-reperfusion. Chin J Geriatr Heart Brain
Vessel Dis. 12:645–647. 2010.(In Chinese).
|
|
30
|
Adamczak JM, Schneider G, Nelles M, Que I,
Suidgeest E, van der Weerd L, Löwik C and Hoehn M: In vivo
bioluminescence imaging of vascular remodeling after stroke. Front
Cell Neurosci. 8:2742014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Reinhard J, Renner M, Wiemann S, Shakoor
DA, Stute G, Dick HB, Faissner A and Joachim SC: Ischemic injury
leads to extracellular matrix alterations in retina and optic
nerve. Sci Rep. 7:434702017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ravi S, Caves JM, Martinez AW, Xiao J, Wen
J, Haller CA, Davis ME and Chaikof EL: Effect of bone
marrow-derived extracellular matrix on cardiac function after
ischemic injury. Biomaterials. 33:7736–7745. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ma NK, Lim JK, Leong MF, Sandanaraj E, Ang
BT, Tang C and Wan AC: Collaboration of 3D context and
extracellular matrix in the development of glioma stemness in a 3D
model. Biomaterials. 78:62–73. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Klingberg F, Chow ML, Koehler A, Boo S,
Buscemi L, Quinn TM, Costell M, Alman BA, Genot E and Hinz B:
Prestress in the extracellular matrix sensitizes latent TGF-β1 for
activation. J Cell Biol. 207:283–297. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Faissner A and Reinhard J: The
extracellular matrix compartment of neural stem and glial
progenitor cells. Glia. 63:1330–1349. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Dzyubenko E, Gottschling C and Faissner A:
Neuron-glia interactions in neural plasticity: Contributions of
neural extracellular matrix and perineuronal nets. Neural Plast.
2016:52149612016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Pandey AK, Bhattacharya P, Shukla SC, Paul
S and Patnaik R: Resveratrol inhibits matrix metalloproteinases to
attenuate neuronal damage in cerebral ischemia: A molecular docking
study exploring possible neuroprotection. Neural Regen Res.
10:568–575. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Neuwelt EA, Bauer B, Fahlke C, Fricker G,
Iadecola C, Janigro D, Leybaert L, Molnár Z, O'Donnell ME,
Povlishock JT, et al: Engaging neuroscience to advance
translational research in brain barrier biology. Nat Rev Neurosci.
12:169–182. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Limmer S, Weiler A, Volkenhoff A, Babatz F
and Klämbt C: The Drosophila blood-brain barrier: Development and
function of a glial endothelium. Front Neurosci. 8:3652014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ronaldson PT and Davis TP: Blood-brain
barrier integrity and glial support: Mechanisms that can be
targeted for novel therapeutic approaches in stroke. Curr Pharm
Des. 18:3624–3644. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wong AD, Ye M, Levy AF, Rothstein JD,
Bergles DE and Searson PC: The blood-brain barrier: An engineering
perspective. Front Neuroeng. 6:72013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Hladky SB and Barrand MA: Fluid and ion
transfer across the blood-brain and blood-cerebrospinal fluid
barriers; a comparative account of mechanisms and roles. Fluids
Barriers CNS. 13:192016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Sazonova OV, Isenberg BC, Herrmann J, Lee
KL, Purwada A, Valentine AD, Buczek-Thomas JA, Wong JY and Nugent
MA: Extracellular matrix presentation modulates vascular smooth
muscle cell mechanotransduction. Matrix Biol. 41:36–43. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Li S, Jin Z, Koirala S, Bu L, Xu L, Hynes
RO, Walsh CA, Corfas G and Piao X: GPR56 regulates pial basement
membrane integrity and cortical lamination. J Neurosci.
28:5817–5826. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Johnson KM, Milner R and Crocker SJ:
Extracellular matrix composition determines astrocyte responses to
mechanical and inflammatory stimuli. Neurosci Lett. 600:104–109.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Moore MC, Pandolfi V and McFetridge PS:
Novel human-derived extracellular matrix induces in vitro and in
vivo vascularization and inhibits fibrosis. Biomaterials. 49:37–46.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zhang Z, Wang F, Wang BJ, Chu G, Cao Q,
Sun BG and Dai QY: Inhibition of leptin-induced vascular
extracellular matrix remodelling by adiponectin. J Mol Endocrinol.
53:145–154. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Xie Y, Mustafa A, Yerzhan A, Merzhakupova
D, Yerlan P, N Orakov A, Wang X, Huang Y and Miao L: Nuclear matrix
metalloproteinases: Functions resemble the evolution from the
intracellular to the extracellular compartment. Cell Death Discov.
3:170362017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Chopra K, Baveja A and Kuhad A: MMPs: A
novel drug target for schizophrenia. Expert Opin Ther Targets.
19:77–85. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Fu S, Gu Y, Jiang JQ, Chen X, Xu M, Chen X
and Shen J: Calycosin-7-O-β-D-glucoside regulates nitric
oxide/caveolin-1/matrix metalloproteinases pathway and protects
blood-brain barrier integrity in experimental cerebral
ischemia-reperfusion injury. J Ethnopharmacol. 155:692–701. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Wang JJ, Huan SK, Hsieh KH, Chou HC, Hsiao
G, Jayakumar T and Sheu JR: Inhibitory effect of midazolam on
MMP-9, MMP-1 and MMP-13 expression in PMA-stimulated human
chondrocytes via recovery of NF-kB signaling. Arch Med Sci.
9:332–339. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
He ZJ, Huang ZT, Chen XT and Zou ZJ:
Effects of matrix metalloproteinase 9 inhibition on the blood brain
barrier and inflammation in rats following cardiopulmonary
resuscitation. Chin Med J (Engl). 122:2346–2351. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Kwon M, Seo S, Chun H, Chung JM, Chung IK
and Hur KC: Dual effect of nerve growth factor on cell death of
PC12 cells Induced by serum deprivation. Mol Cells. 13:167–174.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Kim YS and Joh TH: Matrix
metalloproteinases, new insights into the understanding of
neurodegenerative disorders. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 20:133–143. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Visse R and Nagase H: Matrix
metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases:
Structure, function, and biochemistry. Circ Res. 92:827–839. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Li JS, Liu K, Liu JX, Wang MH, Zhao YW and
Liu ZG: Relationship between the changes in ischemia/reperfusion
cerebro-microvessel basement membrane injury and gelatinase system
in senile rat. Zhongguo Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 20:656–659.
2008.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Michalski D, Hobohm C, Weise C, Pelz J,
Heindl M, Kamprad M, Kacza J and Härtig W: Interrelations between
blood-brain barrier permeability and matrix metalloproteinases are
differently affected by tissue plasminogen activator and hyperoxia
in a rat model of embolic stroke. Med Gas Res. 2:22012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Liu XR, Luo M, Yan F, Zhang CC, Li SJ,
Zhao HP, Ji XM and Luo YM: Ischemic postconditioning diminishes
matrix metalloproteinase 9 expression and attenuates loss of the
extracellular matrix proteins in rats following middle cerebral
artery occlusion and reperfusion. CNS Neurosci Ther. 18:855–863.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Gu Y, Dee CM and Shen J: Interaction of
free radicals, matrix metalloproteinases and caveolin-1 impacts
blood-brain barrier permeability. Front Biosci (Schol Ed).
3:1216–1231. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Zhu M, Xing D, Lu Z, Fan Y, Hou W and Dong
H, Xiong L and Dong H: DDR1 may play a key role in destruction of
the blood-brain barrier after cerebral ischemia-reperfusion.
Neurosci Res. 96:14–19. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Tan F, Fu W, Cheng N, Meng DI and Gu Y:
Ligustrazine reduces blood-brain barrier permeability in a rat
model of focal cerebral ischemia and reperfusion. Exp Ther Med.
9:1757–1762. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Li DD, Song JN, Huang H, Guo XY, An JY,
Zhang M, Li Y, Sun P, Pang HG, Zhao YL and Wang JF: The roles of
MMP-9/TIMP-1 in cerebral edema following experimental acute
cerebral infarction in rats. Neurosci Lett. 550:168–172. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Lenglet S, Montecucco F, Mach F, Schaller
K, Gasche Y and Copin JC: Analysis of the expression of nine
secreted matrix metalloproteinases and their endogenous inhibitors
in the brain of mice subjected to ischaemic stroke. Thromb Haemost.
112:363–378. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|