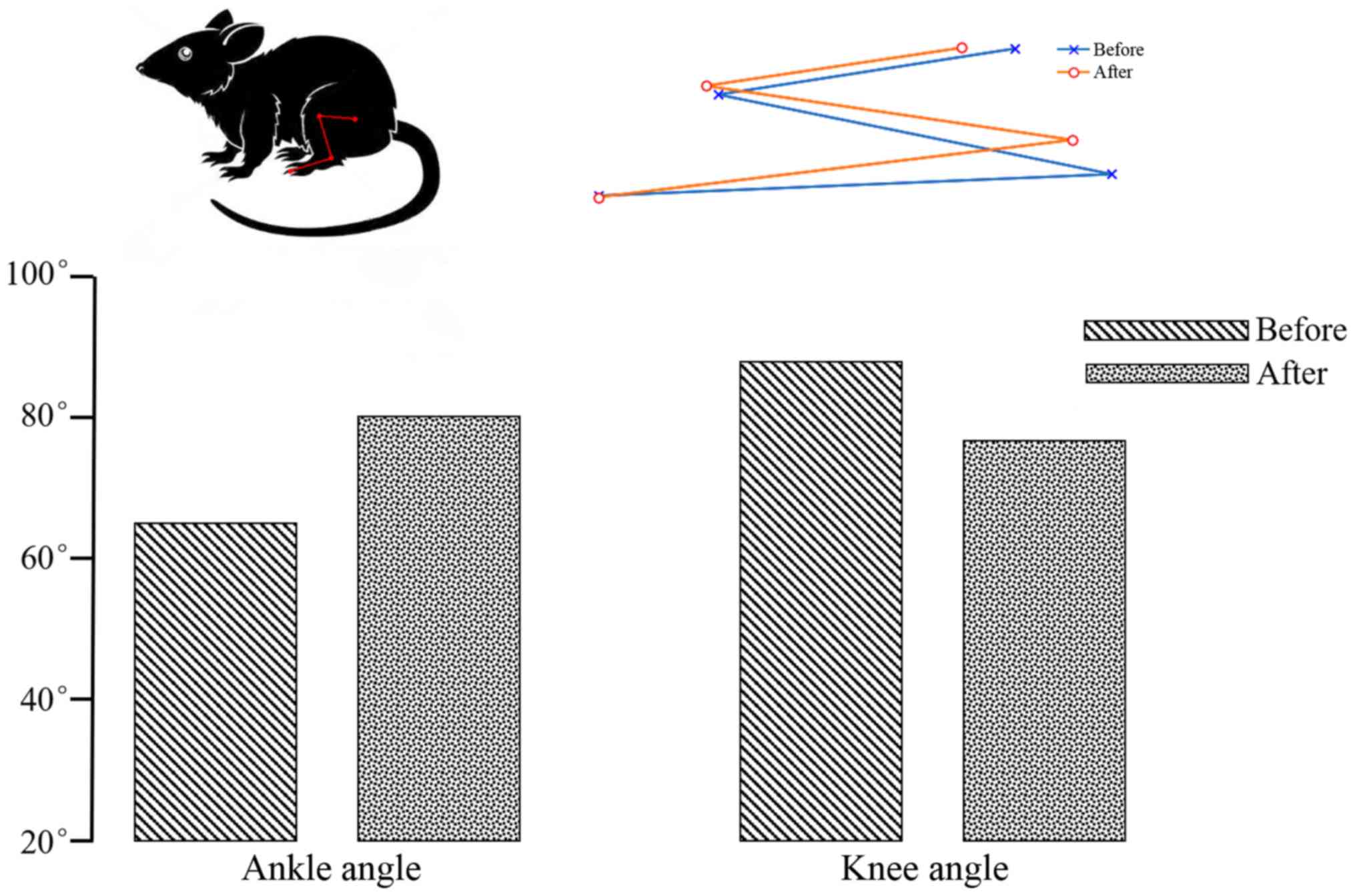
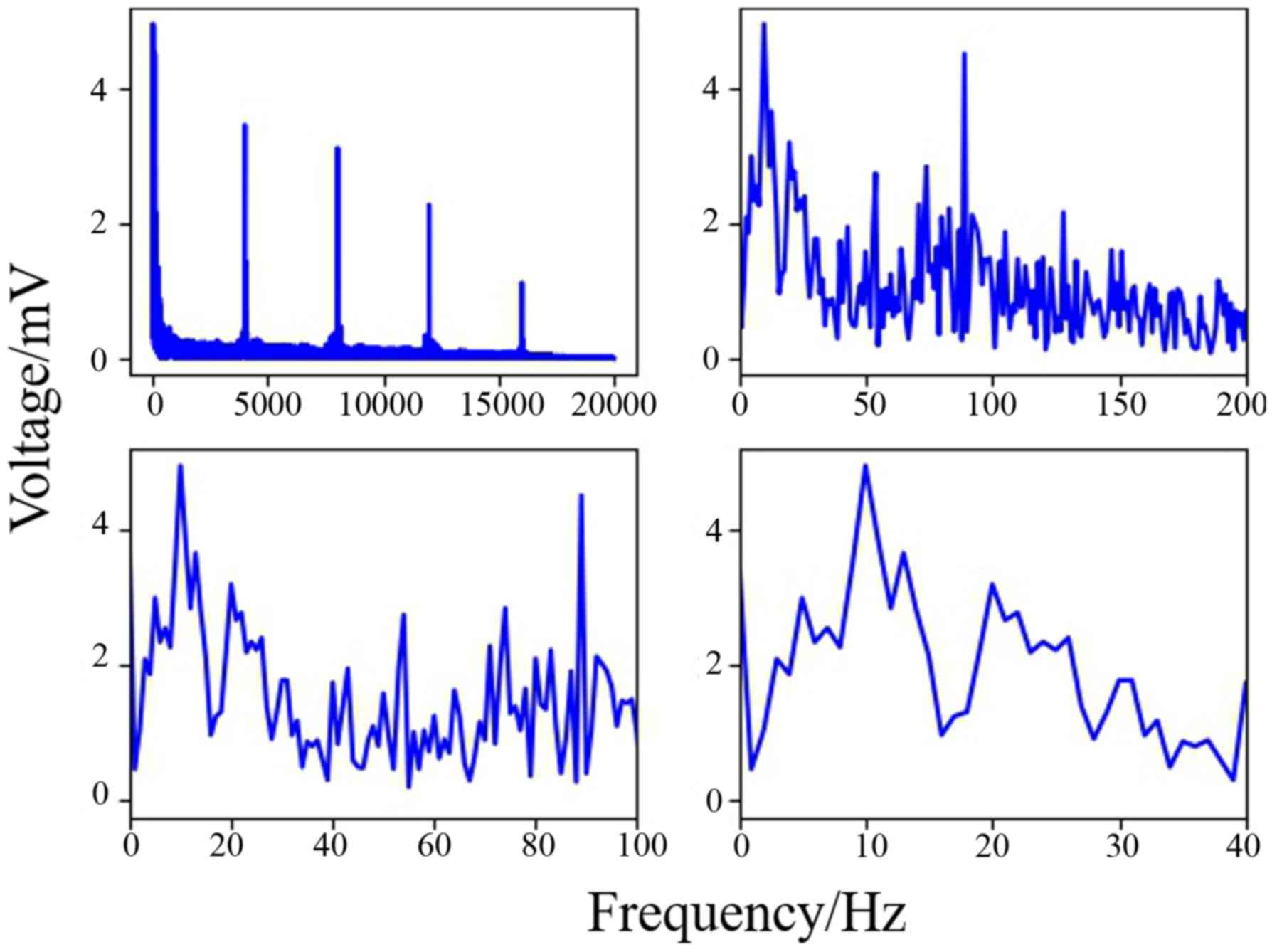
|
1
|
Gao X and Chen J: Mild traumatic brain
injury results in extensive neuronal degeneration in the cerebral
cortex. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 70:183–191. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Iizuka H, Sakatani K and Young W: Neural
damage in the rat thalamus after cortical infarcts. Stroke.
21:790–794. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Xie H, Kane JT, Dennis MJ, Mooney RD,
Bauer WR, Wang X and Wall JT: Case series evidence for changed
interhemispheric relationships in cortical structure in some
amputees. J Clin Neurosci. 20:523–526. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Salat DH, Kaye JA and Janowsky JS:
Selective regional degeneration and preservation within the
prefrontal cortex in healthy aging and Alzheimer's disease. Arch
Neurol. 58:1403–1408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kline AE, Chen MJ, Tso-Olivas DY and
Feeney DM: Methylphenidate treatment following ablation-induced
hemiplegia in rat: Experience during drug action alters effects on
recovery of function. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 48:773–779. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Khan MA, Tariq M, Naime M and Akhtar J:
Falij-E-Nisfi (Hemiplegia) cause and treatment in Unani medicine: A
review. J Pharm Pharm Sci. 7:293–300. 2018.
|
|
7
|
Perry JC and Rosen J: Upper-limb powered
exoskeleton design. IEEE/ASME Trans Mechatronics. 12:408–417. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Twitchell TE: The restoration of motor
function following hemiplegia in man. Brain. 74:443–480. 1951.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gallas S, Marie JP, Leroi AM and Verin E:
Sensory transcutaneous electrical stimulation improves post-stroke
dysphagic patients. Dysphagia. 25:291–297. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kwong PWH, Ng GYF, Chung RCK and Ng SSM:
Bilateral transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation improves
lower-limb motor function in subjects with chronic stroke: A
randomized controlled trial. J Am Heart Assoc. 7(pii):
e0073412018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Laddha D, Ganesh GS, Pattnaik M, Mohanty P
and Mishra C: Effect of transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation
on plantar flexor muscle spasticity and walking speed in stroke
patients. Physiother Res Int. 21:247–256. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ghoname ESA, White PF, Ahmed HE, Hamza MA,
Craig WF and Noe CE: Percutaneous electrical nerve stimulation: An
alternative to TENS in the management of sciatica. Pain.
83:193–199. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Goldner JL, Nashold BS Jr and Hendrix PC:
Peripheral nerve electrical stimulation. Clin Orthop Relat Res.
33–41. 1982.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Davies PM: The comprehensive treatment of
patients with hemiplegia. 2000.
|
|
15
|
Cramer SC: Repairing the human brain after
stroke: I. Mechanisms of spontaneous recovery. Ann Neurol.
63:272–287. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Monte-Silva K, Piscitelli D,
Norouzi-Gheidari N, Batalla MAP, Archambault P and Levin MF:
Electromyogram-related neuromuscular electrical stimulation for
restoring wrist and hand movement in Poststroke hemiplegia: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurorehabil Neural Repair.
33:96–111. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wilson RD, Bennett ME, Nguyen VQC, Bock
WC, O'Dell MW, Watanabe TK, Amundson RH, Hoyen HA and Chae J: Fully
implantable peripheral nerve stimulation for hemiplegic shoulder
pain: A multi-site case series with two-year follow-up.
Neuromodulation. 21:290–295. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lee JH, Baker LL, Johnson RE and Tilson
JK: Effectiveness of neuromuscular electrical stimulation for
management of shoulder subluxation post-stroke: A systematic review
with meta-analysis. Clin Rehabil. 31:1431–1444. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Paik YR, Park HS, Oh DH, Lee JH and Lee
DH: Effect of mirror therapy and electrical stimulation on upper
extremity function in stroke with hemiplegic patient: A pilot
study. J Phys Ther Sci. 29:2085–2086. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Russo C, Souza Carneiro MI, Bolognini N
and Fregni F: Safety review of transcranial direct current
stimulation in stroke. Neuromodulation. 20:215–222. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Guiraud D, Azevedo Coste C, Benoussaad M
and Fattal C: Implanted functional electrical stimulation: Case
report of a paraplegic patient with complete SCI after 9 years. J
Neuroeng Rehabil. 11:152014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Herman R, He J, D'Luzansky S, Willis W and
Dilli S: Spinal cord stimulation facilitates functional walking in
a chronic, incomplete spinal cord injured. Spinal Cord. 40:65–68.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Harkema S, Gerasimenko Y, Hodes J, Burdick
J, Angeli C, Chen Y, Ferreira C, Willhite A, Rejc E, Grossman RG
and Edgerton VR: Effect of Epidural stimulation of the lumbosacral
spinal cord on voluntary movement, standing and assisted stepping
after motor complete paraplegia: A case study susan. Lancet.
377:1938–1947. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zheng ZT, Dong XL, Li YD, Gao WW, Zhou Y,
Jiang RC, Yue SY, Zhou ZW and Zhang JN: Electrical stimulation
improved cognitive deficits associated with traumatic brain injury
in rats. Brain Behav. 7:e006672017. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Koyama S, Xia J, Leblanc BW, Gu JW and
Saab CY: Sub-paresthesia spinal cord stimulation reverses thermal
hyperalgesia and modulates low frequency EEG in a rat model of
neuropathic pain. Sci Rep. 8:71812018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yip M, Jin R, Nakajima HH, Stankovic KM
and Chandrakasan AP: A fully-implantable cochlear implant SoC with
piezoelectric middle-ear sensor and arbitrary waveform neural
stimulation. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits. 50:214–229. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kim D, Yeon C, Chung E and Kim K: A
non-invasive flexible multi-channel electrode for in vivo mouse EEG
recordingProceedings of IEEE Sensors Conference. Valencia, Spain:
2-5. Novemb; pp. 1111–1114. 2014
|
|
28
|
Zhang P, Ma X, Chen L, Zhou J, Wang C, Li
W and He J: Decoder calibration with ultra small current sample set
for intracortical brain-machine interface. J Neural Eng.
15:0260192018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhang P, Huang J, Li W, Ma X, Yang P, Dai
J and He J: Using high frequency local field potentials from
multi-cortex to decode reaching and grasping movements in monkey.
IEEE Trans Cogn Dev Syst. Sep;2018.DOI: 10.1109/TCDS.2018.2869587.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
National Institute of Health (NIH), .
Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory AnimalsThe National
Academies Press; Washington, D.C.: 1996
|
|
31
|
Wongsarnpigoon A and Grill WM:
Energy-efficient waveform shapes for neural stimulation revealed
with a genetic algorithm. J Neural Eng. 7:0460092010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Delorme A and Makeig S: EEGLAB: An open
source toolbox for analysis of single-trial EEG dynamics including
independent component analysis. J Neurosci Methods. 134:9–21. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Klimesch W: EEG alpha and theta
oscillations reflect cognitive and memory performance: A review and
analysis. Brain Res Rev. 29:169–195. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chatrian GE, Petersen MC and Lazarte JA:
The blocking of the rolandic wicket rhythm and some central changes
related to movement. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol.
11:497–510. 1959. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Babiloni C, Carducci F, Cincotti F,
Rossini PM, Neuper C, Pfurtscheller G and Babiloni F: Human
movement-related potentials vs desynchronization of EEG alpha
rhythm: A high-resolution EEG study related to movement.
Neuroimage. 10:658–665. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wall PD and Sweet WH: Temporary abolition
of pain in man. Science. 155:108–109. 1967. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Slavin KV: Peripheral nerve stimulation
for neuropathic pain. US Neurol. 7:1442015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Levine AB, Steven DA, Parrent AG and
MacDougall KW: Successful long-term nerve root stimulation for
chronic neuropathic pain: A real world, single center Canadian
experience. Pain Physician. 20:95–106. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Malis LI, Pribram KH and Kruger L: Action
potentials in ‘Motor’ cortex evoked by peripheral nerve
stimulation. Methods. 16:161–167. 1953.
|
|
40
|
Merrill DR, Bikson M and Jefferys JG:
Electrical stimulation of excitable tissue: Design of efficacious
and safe protocols. J Neurosci Methods. 141:171–198. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Dong W, Zhu C, Hu W, Xiao L and Huang Y:
Stretchable human-machine interface based on skin-conformal sEMG
electrodes with self-similar geometry. J Semicond. 39:0140012018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
O'Suilleabhain PE, Frawley W, Giller C and
Dewey RB Jr: Tremor response to polarity, voltage, pulsewidth and
frequency of thalamic stimulation. Neurology. 60:786–790. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Mooziraji FB and Shoaei O: A high power
efficient multi-waveform current stimulator used in implantable
neural stimulation. Analog Integr Circuits Signal Process.
86:459–469. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Shealy CN, Mortimer JT and Reswick JB:
Electrical inhibition of pain by stimulation of the dorsal columns:
Preliminary clinical report. Anesth Analg. 46:489–491. 1967.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Cogan SF, Ludwig KA, Welle CG and Takmakov
P: Tissue damage thresholds during therapeutic electrical
stimulation. J Neural Eng. 13:210012016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Levy RM: Device complication and failure
management in neuromodulation. Neuromodulation. 16:495–502. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|