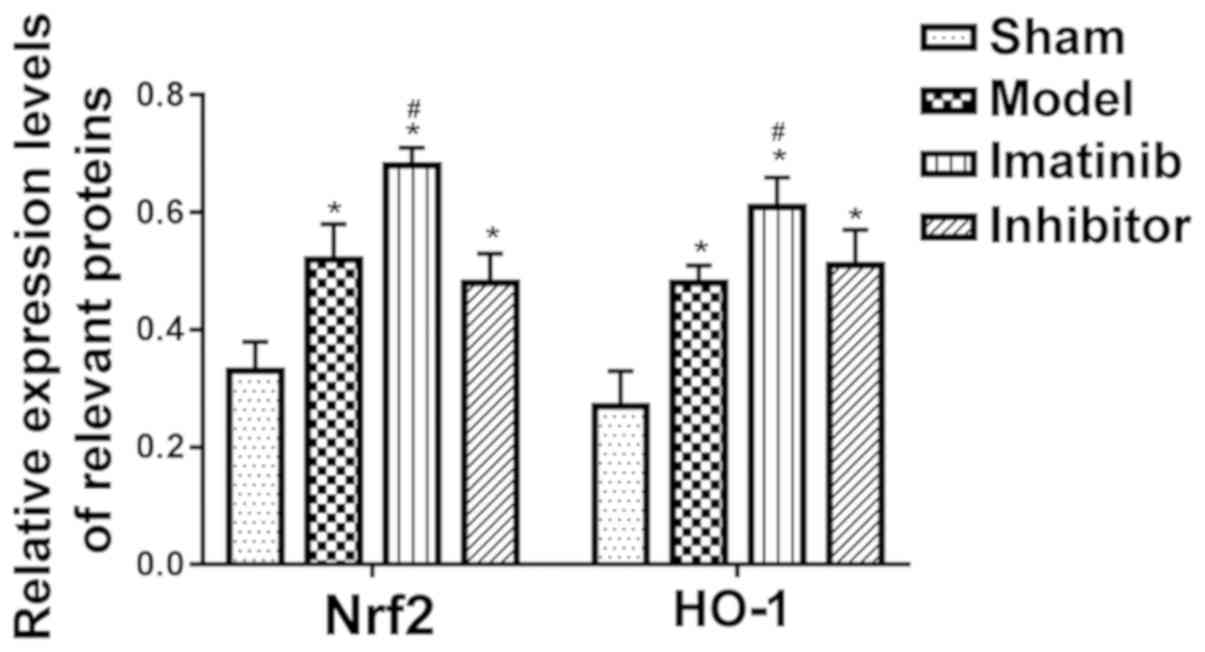
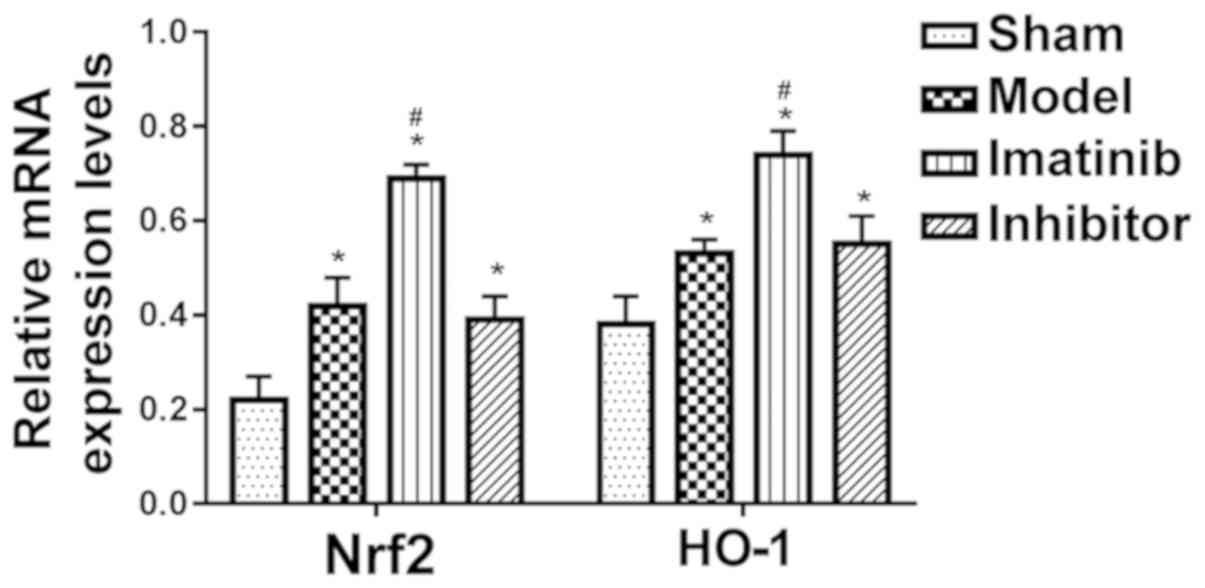
|
1
|
Dai J, Xu LJ, Han GD, Sun HL, Zhu GT,
Jiang HT, Yu GY and Tang XM: MiR-137 attenuates spinal cord injury
by modulating NEUROD4 through reducing inflammation and oxidative
stress. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 22:1884–1890. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Young W: Spinal cord regeneration. Cell
Transplant. 23:573–611. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wang W, Shen H, Xie JJ, Ling J and Lu H:
Neuroprotective effect of ginseng against spinal cord injury
induced oxidative stress and inflammatory responses. Int J Clin Exp
Med. 8:3514–3521. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Özdemir US, Nazıroğlu M, Şenol N and
Ghazizadeh V: Hypericum perforatum attenuates spinal cord
injury-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in the dorsal root
ganglion of rats: Involvement of TRPM2 and TRPV1 channels. Mol
Neurobiol. 53:3540–3551. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ali T, Kim T, Rehman SU, Khan MS, Amin FU,
Khan M, Ikram M and Kim MO: Natural dietary supplementation of
anthocyanins via PI3K/Akt/Nrf2/HO-1 pathways mitigate oxidative
stress, neurodegeneration, and memory impairment in a mouse model
of Alzheimer's disease. Mol Neurobiol. 55:6076–6093. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wei CC, Kong YY, Li GQ, Guan YF, Wang P
and Miao CY: Nicotinamide mononucleotide attenuates brain injury
after intracerebral hemorrhage by activating Nrf2/HO-1 signaling
pathway. Sci Rep. 7:7172017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hochhaus A, Saglio G, Hughes TP, Larson
RA, Kim DW, Issaragrisil S, le Coutre PD, Etienne G,
Dorlhiac-Llacer PE, Clark RE, et al: Long-term benefits and risks
of frontline nilotinib vs imatinib for chronic myeloid leukemia in
chronic phase: 5-year update of the randomized ENESTnd trial.
Leukemia. 30:1044–1054. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Topuz K, Colak A, Cemil B, Kutlay M,
Demircan MN, Simsek H, Ipcioglu O, Kucukodaci Z and Uzun G:
Combined hyperbaric oxygen and hypothermia treatment on oxidative
stress parameters after spinal cord injury: An experimental study.
Arch Med Res. 41:506–512. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tan J, Zhang F, Liang F, Wang Y, Li Z,
Yang J and Liu X: Protective effects of hyperbaric oxygen treatment
against spinal cord injury in rats via toll-like receptor 2/nuclear
factor-κB signaling. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 7:1911–1919.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Visavadiya NP, Patel SP, VanRooyen JL,
Sullivan PG and Rabchevsky AG: Cellular and subcellular oxidative
stress parameters following severe spinal cord injury. Redox Biol.
8:59–67. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Xiong Y, Rabchevsky AG and Hall ED: Role
of peroxynitrite in secondary oxidative damage after spinal cord
injury. J Neurochem. 100:639–649. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sohn HM, Hwang JY, Ryu JH, Kim J, Park S,
Park JW and Han SH: Simvastatin protects ischemic spinal cord
injury from cell death and cytotoxicity through decreasing
oxidative stress: In vitro primary cultured rat spinal cord model
under oxygen and glucose deprivation-reoxygenation conditions. J
Orthop Surg Res. 12:362017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang W, Cheng L, Hou Y, Si M, Zhao YP and
Nie L: Plumbagin protects against spinal cord injury-induced
oxidative stress and inflammation in Wistar rats through Nrf-2
upregulation. Drug Res (Stuttg). 65:495–499. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jia Z, Zhu H, Li J, Wang X, Misra H and Li
Y: Oxidative stress in spinal cord injury and antioxidant-based
intervention. Spinal Cord. 50:264–274. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hall ED: Antioxidant therapies for acute
spinal cord injury. Neurotherapeutics. 8:152–167. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kesherwani V, Atif F, Yousuf S and Agrawal
SK: Resveratrol protects spinal cord dorsal column from hypoxic
injury by activating Nrf-2. Neuroscience. 241:80–88. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang ZH, Xie YX, Zhang JW, Qiu XH, Cheng
AB, Tian L, Ma BY and Hou YB: Carnosol protects against spinal cord
injury through Nrf-2 upregulation. J Recept Signal Transduct Res.
36:72–78. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kilic U, Kilic E, Tuzcu Z, Tuzcu M,
Ozercan IH, Yilmaz O, Sahin F and Sahin K: Melatonin suppresses
cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity via activation of Nrf-2/HO-1
pathway. Nutr Metab (Lond). 10:72013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zeng T, Zhang CL, Song FY, Zhao XL, Yu LH,
Zhu ZP and Xie KQ: The activation of HO-1/Nrf-2 contributes to the
protective effects of diallyl disulfide (DADS) against
ethanol-induced oxidative stress. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1830:4848–4859. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Pollack IF, Jakacki RI, Blaney SM, Hancock
ML, Kieran MW, Phillips P, Kun LE, Friedman H, Packer R, Banerjee
A, et al: Phase I trial of imatinib in children with newly
diagnosed brainstem and recurrent malignant gliomas: A Pediatric
Brain Tumor Consortium report. Neuro Oncol. 9:145–160. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|