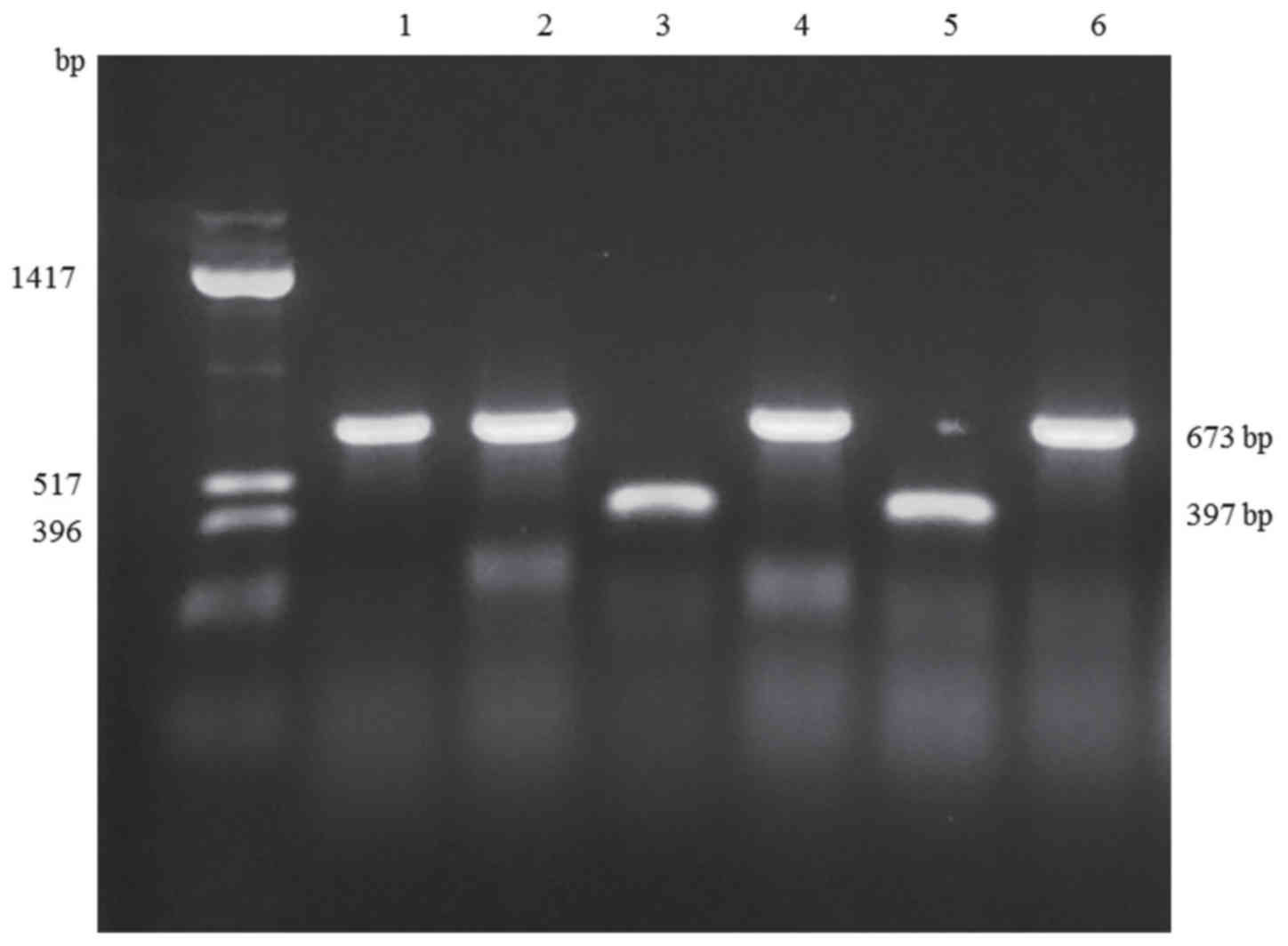
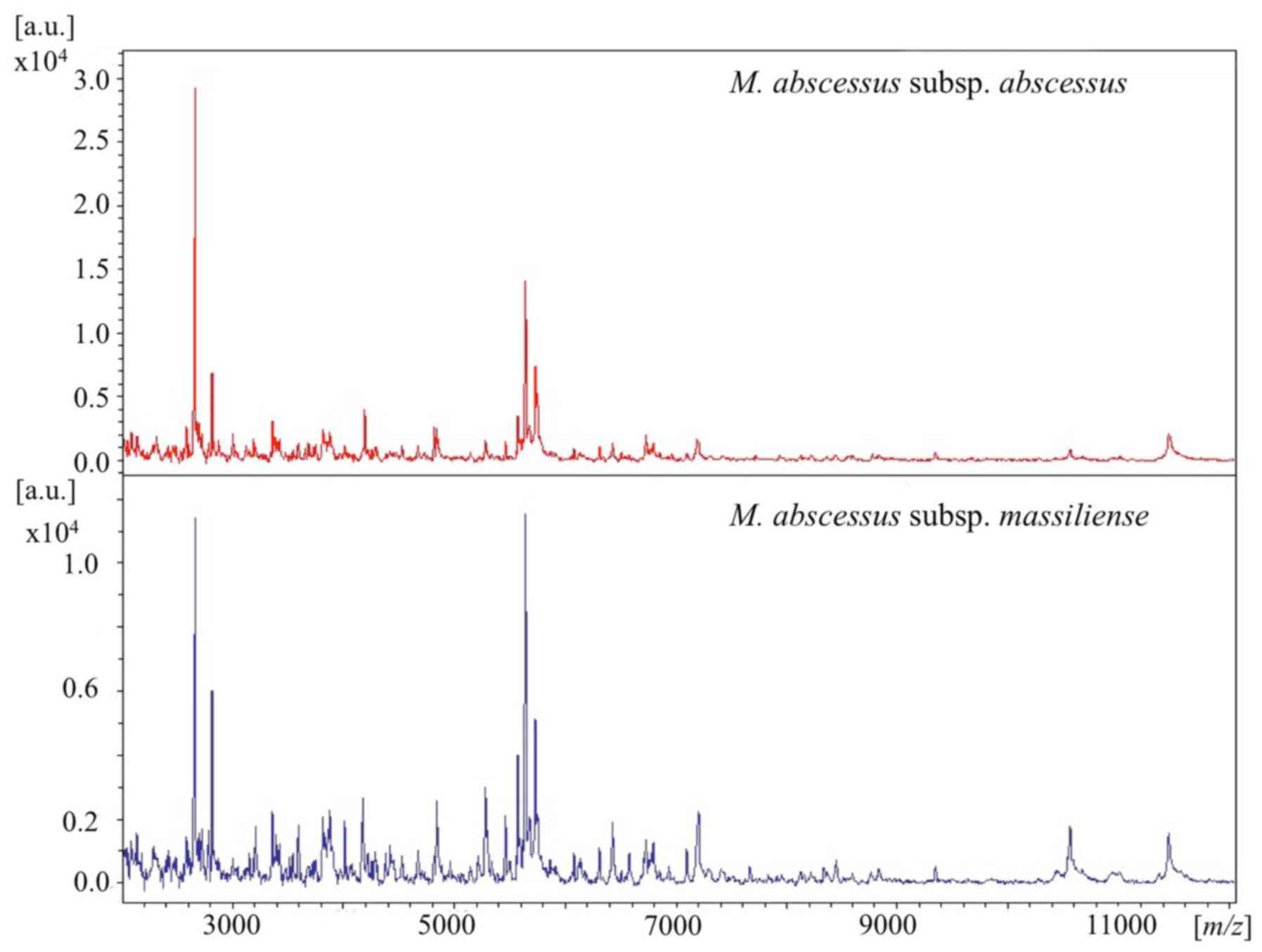
|
1
|
Namkoong H, Kurashima A, Morimoto K,
Hoshino Y, Hasegawa N, Ato M and Mitarai S: Epidemiology of
pulmonary nontuberculous Mycobacterial disease, Japan. Emerg Infect
Dis. 22:1116–1117. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lee MR, Sheng WH, Hung CC, Yu CJ, Lee LN
and Hsueh PR: Mycobacterium abscessus complex infections in humans.
Emerg Infect Dis. 21:1638–1646. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wallace RJ, Meier A, Brown BA, Zhang Y,
Sander P, Onyi GO and Böttger EC: Genetic basis for clarithromycin
resistance among isolates of Mycobacterium chelonae and
Mycobacterium abscessus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother.
40:1676–1681. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Nash KA, Brown-Elliott AB and Wallace RJ
Jr: A Novel gene, erm(41), confers inducible macrolide resistance
to clinical isolates of Mycobacterium abscessus but is
absent from mycobacterium chelonae. Antimicrob Agents
Chemother. 53:1367–1376. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Teng SH, Chen CM, Lee MR, Lee TF, Chien
KY, Teng LJ and Hsueh PR: Matrix-assisted laser desorption
ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry can accurately
differentiate between Mycobacterium masilliense (M.
abscessus subspecies bolletti) and M. abscessus
(Sensu Stricto). J Clin Microbiol. 51:3113–3116. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fangous MS, Mougari F, Gouriou S, Calvez
E, Raskine L, Cambau E, Payan C and Hery-Arnaud G: Classification
algorithm for subspecies identification within the Mycobacterium
abscessus species, based on matrix-assisted laser desorption
ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry. J Clin Microbiol.
52:3362–3369. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Panagea T, Pincus DH, Grogono D, Jones M,
Bryant J, Parkhill J, Floto RA and Gilligan P: Mycobacterium
abscessus complex identification with matrix-assisted laser
desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry. J Clin
Microbiol. 53:2355–2358. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Suzuki H, Yoshida S, Yoshida A, Okuzumi K,
Fukusima A and Hishinuma A: A novel cluster of Mycobacterium
abscessus complex revealed by matrix-assisted laser desorption
ionization-time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS). Diagn
Microbiol Infect Dis. 83:365–370. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Buckwalter SP, Olson SL, Connelly BJ,
Lucas BC, Rodning AA, Walchak RC, Deml SM, Wohifiel SL and
Wengenack NL: Evaluation of matrix-assisted laser desorption
ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry for identification of
Mycobacterium species, Nocardia species, and other
aerobic actinomycetes. J Clin Microbiol. 54:376–384. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kehrmann J, Wessel S, Murali R, Hampel A,
Bange FC, Buer J and Mosel F: Principal component analysis of MALDI
TOF MS mass spectra separates M. abscessus (sensu
stricto) from M. massiliense isolates. BMC Microbiol.
16:242016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Harada T, Akiyama Y, Kurashima A, Nagai H,
Tsuyuguchi K, Fujii T, Yano S, Shigeto R, Kuraoka T, Kajiki A, et
al: Clinical and microbiological differences between
Mycobacterium abscessus and Mycobacterium massiliense
lung diseases. J Clin Microbiol. 50:3556–3561. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Fukuchi K, Hagiwara T, Nakamura K,
Ichimura S, Tatsumi K and Gomi K: Identification of the regulatory
region required for ubiquitination of the cyclin kinase inhibitor,
p21. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 293:120–125. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Woods GL, Brown-Elliott BA, Conville PS,
Desmond EP, Hall GS and Lin G: Susceptibility testing of
Mycobacteria, Nocardia and other aerobic actinomycetes; Approved
Standard-Second edition. Clin Lab Stand Inst. 26:1–61. 2011.
|
|
14
|
Macheras E, Roux AL, Bastian S, Leao SC,
Palaci M, Tardy VS, Gutierrez C, Richter E, Gerdes SR, Pfyffer G,
et al: Multilocus sequence analysis and rpoB sequencing of
Mycobacterium abscessus (sensu lato) strains. J Clin
Microbiol. 49:491–499. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Griffith DE, Aksamit T, Brown-Elliott BA,
Catanzaro A, Daley C, Gordin F, Holland SM, Horsburgh R, Huitt G,
Iademarco MF, et al: An official ATS/IDSA statement: Diagnosis,
treatment, and prevention of nontuberculous mycobacterial diseases.
Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 175:367–416. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yoshida S, Tsuyuguchi K, Suzuki K, Tomita
M, Okada M, Hayashi S, Iwamoto T and Saito H: Further isolation of
Mycobacterium abscessus subsp. abscessus and subsp.
bolletii in different regions of Japan and susceptibility of
these isolates to antimicrobial agents. Int J Antimicrob Agents.
42:226–231. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Nakanaga K, Sekizuka T, Fukano H,
Sakakibara Y, Takeuchi F, Wada S, Ishii N, Makino M, Kuroda M and
Hoshino Y: Discrimination of Mycobacterium abscessus subsp.
massiliense from Mycobacterium abscessus subsp.
abscessus in clinical isolates by multiplex PCR. J Clin
Microbiol. 52:251–259. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yoshida S, Arikawa K, Tsuyuguchi K,
Kurashima A, Harada T, Nagai H, Suzuki K, Iwamoto T and Hayashi S:
Investigation of the population structure of Mycobacterium
abscessus complex strains using 17-locus variable number tandem
repeat typing and the further distinction of mycobacterium
massiliense hsp65 genotypes. J Med Microbiol. 64:254–261. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kusuki M, Osawa K, Arikawa K, Tamura M,
Shigemura K, Shirakawa T, Nakamura T, Nakamachi Y, Fujisawa M,
Saegusa J and Tokimatsu I: Determination of the antimicrobial
susceptibility and molecular profile of clarithromycin resistance
in the Mycobacterium abscessus complex in Japan by variable
number tandem repeat analysis. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis.
91:256–259. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Koh WJ, Jeon K, Lee NY, Kim BJ, Kook YH,
Lee SH, Park YK, Kim CK, Shin SJ, Huitt GA, et al: Clinical
significance of differentiation of Mycobacterium massiliense
from Mycobacterium abscessus. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
183:405–410. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kim HY, Kim BJ, Kook Y, Yun YJ, Shin JH,
Kim BJ and Kook YH: Mycobacterium massiliense is
differentiated from Mycobacterium abscessus and
mycobacterium bolletii by erythromycin ribosome
methyltransferase gene (erm) and clarithromycin susceptibility
patterns. Microbiol Immunol. 54:347–353. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kim BJ, Yi SY, Shim TS, Do SY, Yu SK, Park
YG, Kook YH and Kim BJ: Discovery of a novel hsp65 genotype within
Mycobacterium massiliense associated with the rough colony
morphology. PLoS One. 7:e384202012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kim SY, Kang YA, Bae IK, Yim JJ, Park MS,
Kim YS, Kim SK, Chang J and Jeong SH: Standardization of multilocus
sequence typing scheme for Mycobacterium abscessus and
Mycobacterium massiliense. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis.
77:143–149. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Luo L, Li B, Chu H, Huang D, Zhang Z,
Zhang J, Gui T, Xu L, Zhao L, Sun X and Xiao H: Characterization of
Mycobacterium abscessus subtypes in Shanghai of China: Drug
sensitivity and bacterial epidemicity as well as clinical
manifestations. Medicine (Baltimore). 95:e23382016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Koh WJ, Jeong BH, Kim SY, Jeon K, Park KU,
Jhun BW, Lee H, Park HY, Kim DH, Huh HJ, et al: Mycobacterial
characteristics and treatment outcomes in Mycobacterium
abscessus lung disease. Clin Infect Dis. 64:309–316. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Davidson RM, Hasan NA, Reynolds PR, Totten
S, Garcia B, Levin A, Ramamoorthy P, Heifets L, Daley CL and Strong
M: Genome sequencing of Mycobacterium abscessus isolates
from patients in the United States and comparisons to globally
diverse clinical strains. J Clin Microbiol. 52:3573–3582. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Leao SC, Tortoli E, Viana-Niero C, Ueki
SY, Lima KV, Lopes ML, Yubero J, Menendez MC and Garcia MJ:
Characterization of mycobacteria from a major Brazilian outbreak
suggests that revision of the taxonomic status of members of the
Mycobacterium chelonae-M. abscessus group is needed. J Clin
Microbiol. 47:2691–2698. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tan JL, Khang TF, Ngeow YF and Choo SW: A
phylogenomic approach to bacterial subspecies classification: Proof
of concept in Mycobacterium abscessus. BMC Genomics.
14:8792013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kikuchi T, Watanabe A, Gomi K, Sakakibara
T, Nishimori K, Daito H, Fujimura S, Tazawa R, Inoue A, Ebina M, et
al: Association between mycobacterial genotypes and disease
progression in Mycobacterium avium pulmonary infection.
Thorax. 64:901–907. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wong YL, Ong CS and Ngeow YF: Molecular
typing of Mycobacterium abscessus based on tandem-repeat
polymorphism. J Clin Microbiol. 50:3084–3088. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Mougari F, Raskine L, Ferroni A, Marcon E,
Sermet-Gaudelus I, Veziris N, Heym B, Gaillard JL, Nassif X and
Cambau E: Clonal relationship and differentiation among
Mycobacterium abscessus isolates as determined using the
semiautomated repetitive extragenic palindromic sequence PCR-based
diversilab system. J Clin Microbiol. 52:1969–1977. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kim HY, Kook Y, Yun YJ, Park CG, Lee NY,
Shim TS, Kim BJ and Kook YH: Proportions of Mycobacterium
massiliense and Mycobacterium bolletii strains among
Korean Mycobacterium chelonae-Mycobacterium abscessus group
isolates. J Clin Microbiol. 46:3384–3390. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kim BJ, Kim GN, Kim BR, Shim TS, Kook YH
and Kim BJ: Phylogenetic analysis of Mycobacterium
massiliense strains having recombinant rpoB gene laterally
transferred from Mycobacterium abscessus. PLoS One.
12:e01792372017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Steindor M, Nkwouano V, Stefanski A,
Stuehler K, Loerger TR, Bogumil D, Jacobsen M, Mackenzie CR and
Kalscheuer R: A proteomics approach for the identification of
species-specific immunogenic proteins in the Mycobacterium
abscessus complex. Microbes Infect. Nov 13–2018.(Epub ahead of
print). doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2018.10.006. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lee SH, Yoo HK, Kim SH, Koh WJ, Kim CK,
Park YK and Kim HJ: Detection and assessment of clarithromycin
inducible resistant strains among Korean Mycobacterium
abscessus clinical strains: PCR methods. J Clin Lab Anal.
28:409–414. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Rubio M, March F, Garrigó M, Moreno C,
Español M and Coll P: Inducible and acquired clarithromycin
resistance in the Mycobacterium abscessus complex. PLoS One.
10:e01401662015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Bastian S, Veziris N, Roux AL, Brossier F,
Gaillard JL, Jarlier V and Cambau E: Assessment of clarithromycin
susceptibility in strains belonging to the Mycobacterium
abscessus group by erm(41) and rrl sequencing. Antimicrob
Agents Chemother. 55:775–781. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Mougari F, Bouziane F, Crockett F, Nessar
R, Chau F, Veziris N, Sapriel G, Raskine L and Cambau E: Selection
of resistance to clarithromycin in Mycobacterium abscessus
subspecies. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 61(pii): e00943–16.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kudoh S and Keicho N: Diffuse
panbronchiolitis. Clin Chest Med. 33:297–305. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kim SY, Shin SJ, Jeong BH and Koh WJ:
Successful antibiotic treatment of pulmonary disease caused by
Mycobacterium abscessus subsp. abscessus with C-to-T
mutation at position 19 in erm(41) gene: Case report. BMC Infect
Dis. 16:2072016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Shallom SJ, Gardina PJ, Myers TG,
Sebastian Y, Conville P, Calhoun LB, Tettelin H, Olivier KN, Uzal
G, Sampaio EP, et al: New rapid scheme for distinguishing the
subspecies of the Mycobacterium abscessus group and
identifying Mycobacterium massiliense isolates with
inducible clarithromycin resistance. J Clin Microbiol.
51:2943–2949. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Brown-Elliott BA, Vasireddy S, Vasireddy
R, Iakhiaeva E, Howard ST, Nash K, Parodi N, Strong A, Gee M, Smith
T and Wallace RJ Jr: Utility of sequencing the erm(41) gene in
isolates of Mycobacterium abscessus subsp. abscessus with
low and intermediate clarithromycin MICs. J Clin Microbiol.
53:1211–1215. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Yoshida S, Tsuyuguchi K, Suzuki K, Tomita
M, Okada M, Shimada R and Hayashi S: Rapid identification of
strains belonging to the Mycobacterium abscessus group
through erm(41) gene pyrosequencing. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis.
79:331–336. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Maurer FP, Rüegger V, Ritter C, Bloemberg
GV and Böttger EC: Acquisition of clarithromycin resistance
mutations in the 23S rRNA gene of Mycobacterium abscessus in
the presence of inducible erm(41). J Antimicrob Chemother.
67:2606–2611. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Miranda-CasoLuengo AA, Staunton PM, Dinan
AM, Lohan AJ and Loftus BJ: Functional characterization of the
Mycobacterium abscessus genome coupled with condition
specific transcriptomics reveals conserved molecular strategies for
host adaptation and persistence. BMC Genomics. 17:5532016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|