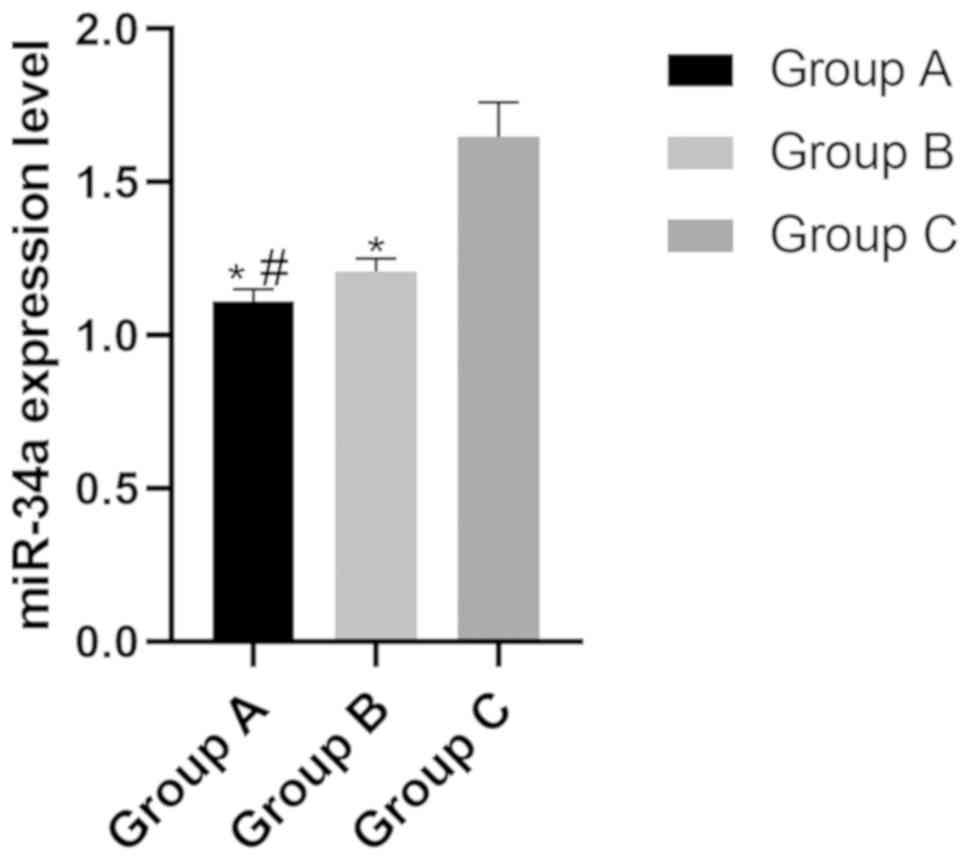
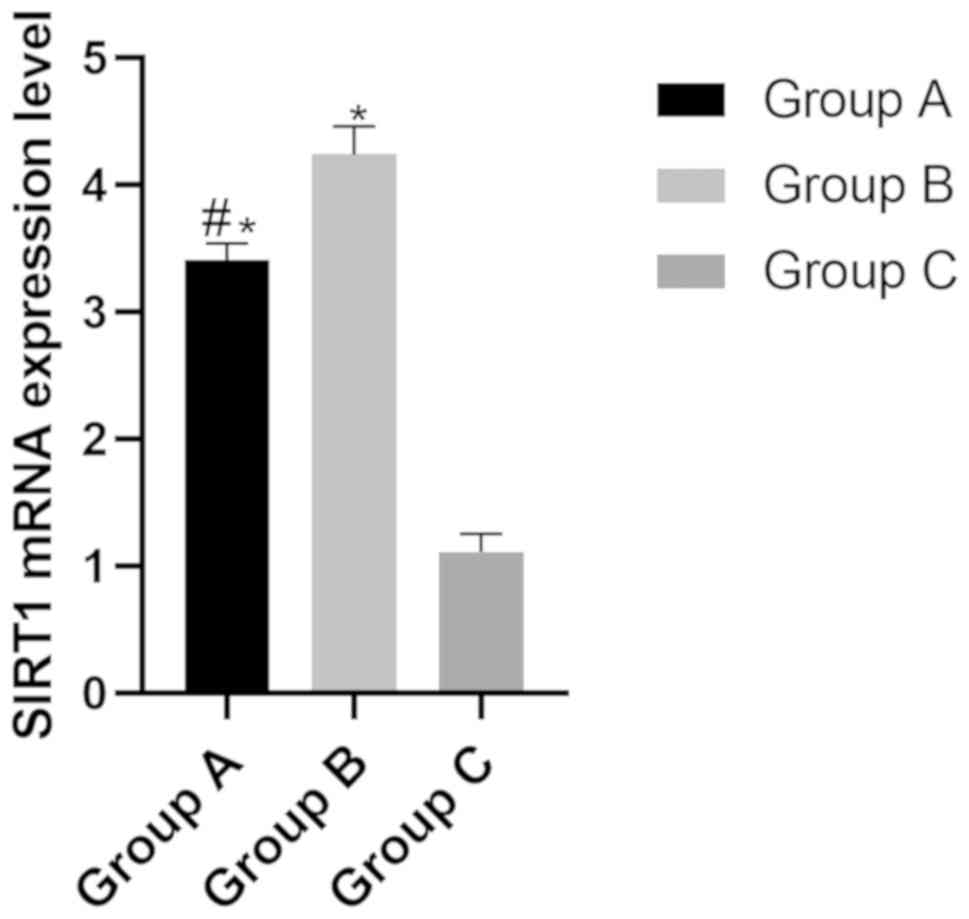
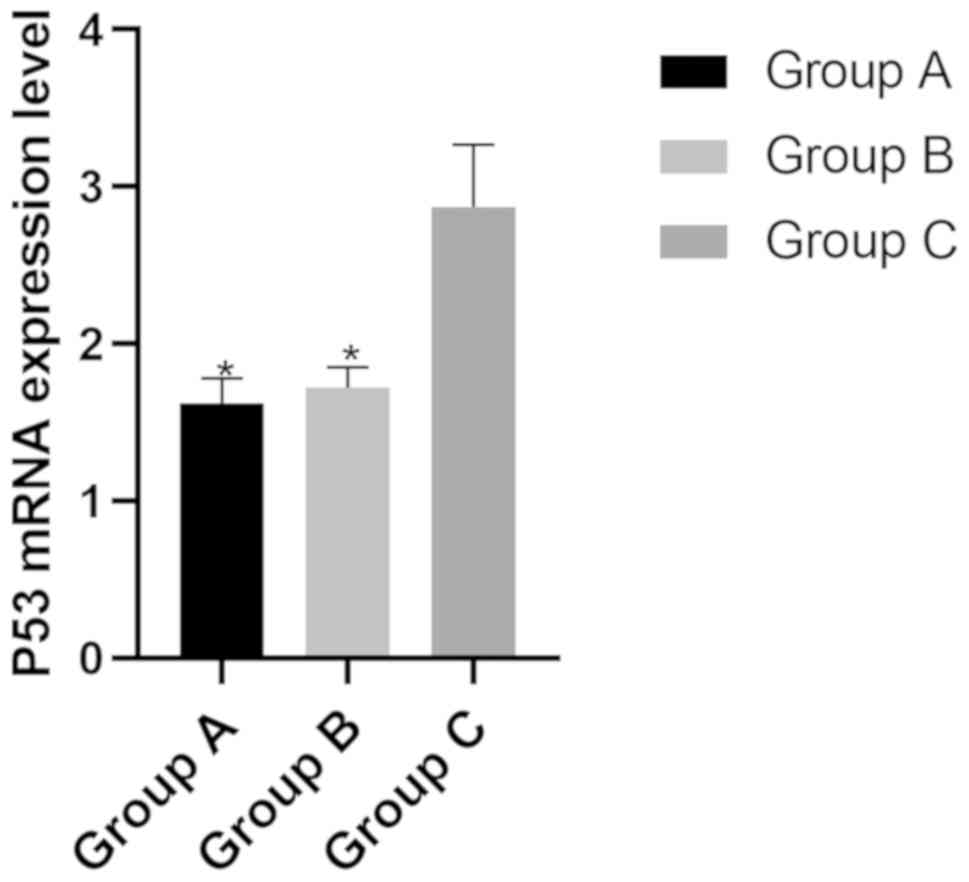
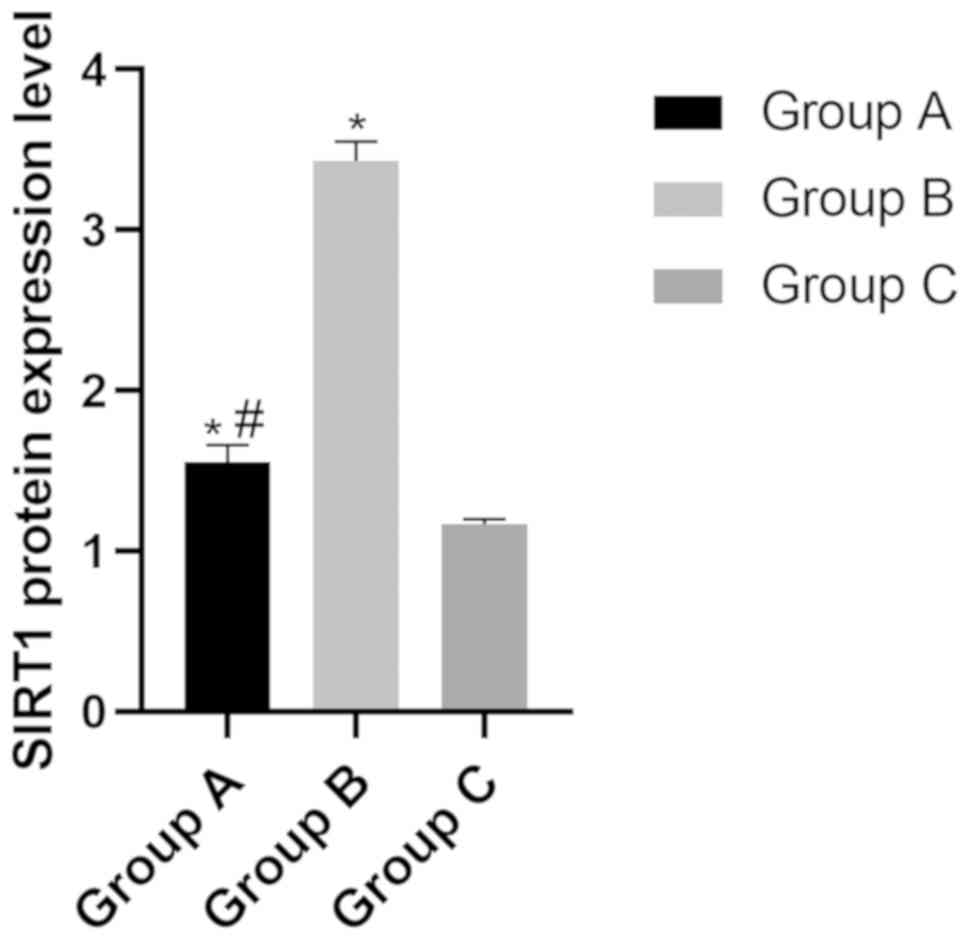
|
1
|
Chien KH, Chen SJ, Liu JH, Chang HM, Woung
LC, Liang CM, Chen JT, Lin TJ, Chiou SH and Peng CH: Correlation
between microRNA-34a levels and lens opacity severity in
age-related cataracts. Eye (Lond). 27:883–888. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Fan F, Zhuang J, Zhou P, Liu X and Luo Y:
MicroRNA-34a promotes mitochondrial dysfunction-induced apoptosis
in human lens epithelial cells by targeting Notch2. Oncotarget.
8:110209–110220. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Asuthkar S, Velpula KK, Chetty C, Gorantla
B and Rao JS: Epigenetic regulation of miRNA-211 by MMP-9 governs
glioma cell apoptosis, chemosensitivity and radiosensitivity.
Oncotarget. 3:1439–1454. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Leung AK and Sharp PA: MicroRNA functions
in stress responses. Mol Cell. 40:205–215. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Noguchi S, Mori T, Otsuka Y, Yamada N,
Yasui Y, Iwasaki J, Kumazaki M, Maruo K and Akao Y: Anti-oncogenic
microRNA-203 induces senescence by targeting E2F3 protein in human
melanoma cells. J Biol Chem. 287:11769–11777. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wu C, Lin H, Wang Q, Chen W, Luo H, Chen W
and Zhang H: Discrepant expression of microRNAs in transparent and
cataractous human lenses. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 53:3906–3912.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chen Q, Yang F, Guo M, Wen G, Zhang C,
Luong A, Zhu J, Xiao Q and Zhang L: miRNA-34a reduces neointima
formation through inhibiting smooth muscle cell proliferation and
migration. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 89A:75–86. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Hu Y, Pu Q, Cui B and Lin J: MicroRNA-34a
inhibits tumor invasion and metastasis in gastric cancer by
targeting Tgif2. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:8921–8928.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang B, Li D and Kovalchuk O: p53 Ser15
phosphorylation and histone modifications contribute to IR-induced
miR-34a transcription in mammary epithelial cells. Cell Cycle.
12:2073–2083. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lin TJ, Peng CH, Chiou SH, Liu JH, Lin
C-W, Tsai CY, Chuang JH and Chen SJ: Severity of lens opacity, age,
and correlation of the level of silent information regulator T1
expression in age-related cataract. J Cataract Refract Surg.
37:1270–1274. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yu X, Zheng H, Chan MT and Wu WKK:
MicroRNAs: New players in cataract. Am J Transl Res. 9:3896–3903.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chylack LT Jr, Wolfe JK, Singer DM, Leske
MC, Bullimore MA, Bailey IL, Friend J, McCarthy D and Wu SY; The
Longitudinal Study of Cataract Study Group, : The lens opacities
classification system III. Arch Ophthalmol. 111:831–836. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xiang W, Lin H, Wang Q and Chen W, Liu Z,
Chen H, Zhang H and Chen W: miR-34a suppresses proliferation and
induces apoptosis of human lens epithelial cells by targeting E2F3.
Mol Med Rep. 14:5049–5056. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mimura T, Kaji Y, Noma H, Funatsu H and
Okamoto S: The role of SIRT1 in ocular aging. Exp Eye Res.
116:17–26. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li QL, Zhang HY, Qin YJ, Meng QL, Yao XL
and Guo HK: MicroRNA-34a promoting apoptosis of human lens
epithelial cells through down-regulation of B-cell lymphoma-2 and
silent information regulator. Int J Ophthalmol. 9:1555–1560.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Huang K, Huang J, Xie X, Wang S, Chen C,
Shen X, Liu P and Huang H: Sirt1 resists advanced glycation end
products-induced expressions of fibronectin and TGF-β1 by
activating the Nrf2/ARE pathway in glomerular mesangial cells. Free
Radic Biol Med. 65:528–540. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yamakuchi M, Ferlito M and Lowenstein CJ:
miR-34a repression of SIRT1 regulates apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 105:13421–13426. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
López Valverde G, Garcia Martin E, Larrosa
Povés JM, Polo Llorens V, Fernández Mateos J, Pablo Júlvez LE and
González Sarmiento R: Study of association between pre-senile
cataracts and the polymorphisms rs2228000 in XPC and rs1042522 in
p53 in Spanish population. PLoS One. 11:e01563172016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Volker M, Moné MJ, Karmakar P, van Hoffen
A, Schul W, Vermeulen W, Hoeijmakers JH, van Driel R, van Zeeland
AA and Mullenders LH: Sequential assembly of the nucleotide
excision repair factors in vivo. Mol Cell. 8:213–224. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ji WK, Tang XC, Yi M, Chen PQ, Liu FY, Hu
XH, Hu WF, Fu SJ, Liu JF, Wu KL, et al: p53 directly regulates αA-
and βA3/A1-crystallin genes to modulate lens differentiation. Curr
Mol Med. 13:968–978. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kondo A, Goto M, Mimura T and Matsubara M:
Silent information regulator T1 in aqueous humor of patients with
cataract. Clin Ophthalmol. 10:307–312. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lu B, Christensen IT, Ma LW, Wang XL,
Jiang LF, Wang CX, Feng L, Zhang JS and Yan QC: miR-24-p53 pathway
evoked by oxidative stress promotes lens epithelial cell apoptosis
in age-related cataracts. Mol Med Rep. 17:5021–5028.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zheng T and Lu Y: Upregulation of Sirt1
protects lens epithelial cells in oxidative conditions and cataract
formation in humans. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 52:5291. 2011.
|
|
24
|
Yan S, Wang M, Zhao J, Zhang H, Zhou C,
Jin L, Zhang Y, Qiu X, Ma B and Fan Q: MicroRNA-34a affects
chondrocyte apoptosis and proliferation by targeting the SIRT1/p53
signaling pathway during the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Int J
Mol Med. 38:201–209. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|