|
1
|
Ma X, Chen Z, Wang L, Wang G, Wang Z, Dong
X, Wen B and Zhang Z: The pathogenesis of diabetes mellitus by
oxidative stress and inflammation: Its inhibition by berberine.
Front Pharmacol. 9(782)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Pedersen AML, Sørensen CE, Proctor GB,
Carpenter GH and Ekström J: Salivary secretion in health and
disease. J Oral Rehabil. 45:730–746. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Bakianian Vaziri P, Vahedi M, Mortazavi H,
Abdollahzadeh SH and Hajilooi M: Evaluation of salivary glucose,
IgA and flow rate in diabetic patients: A case-control study. J
Dent (Tehran). 7:13–18. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
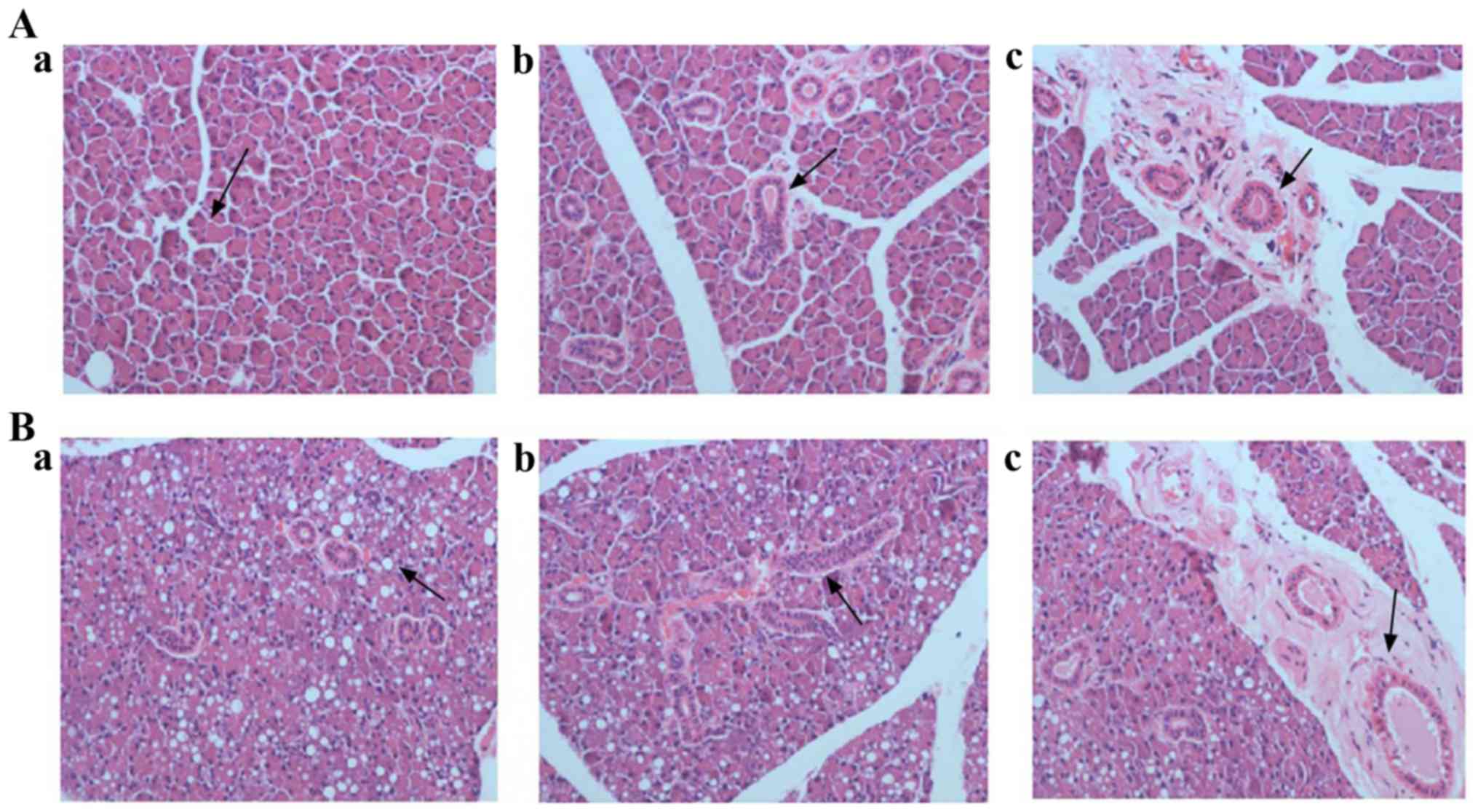
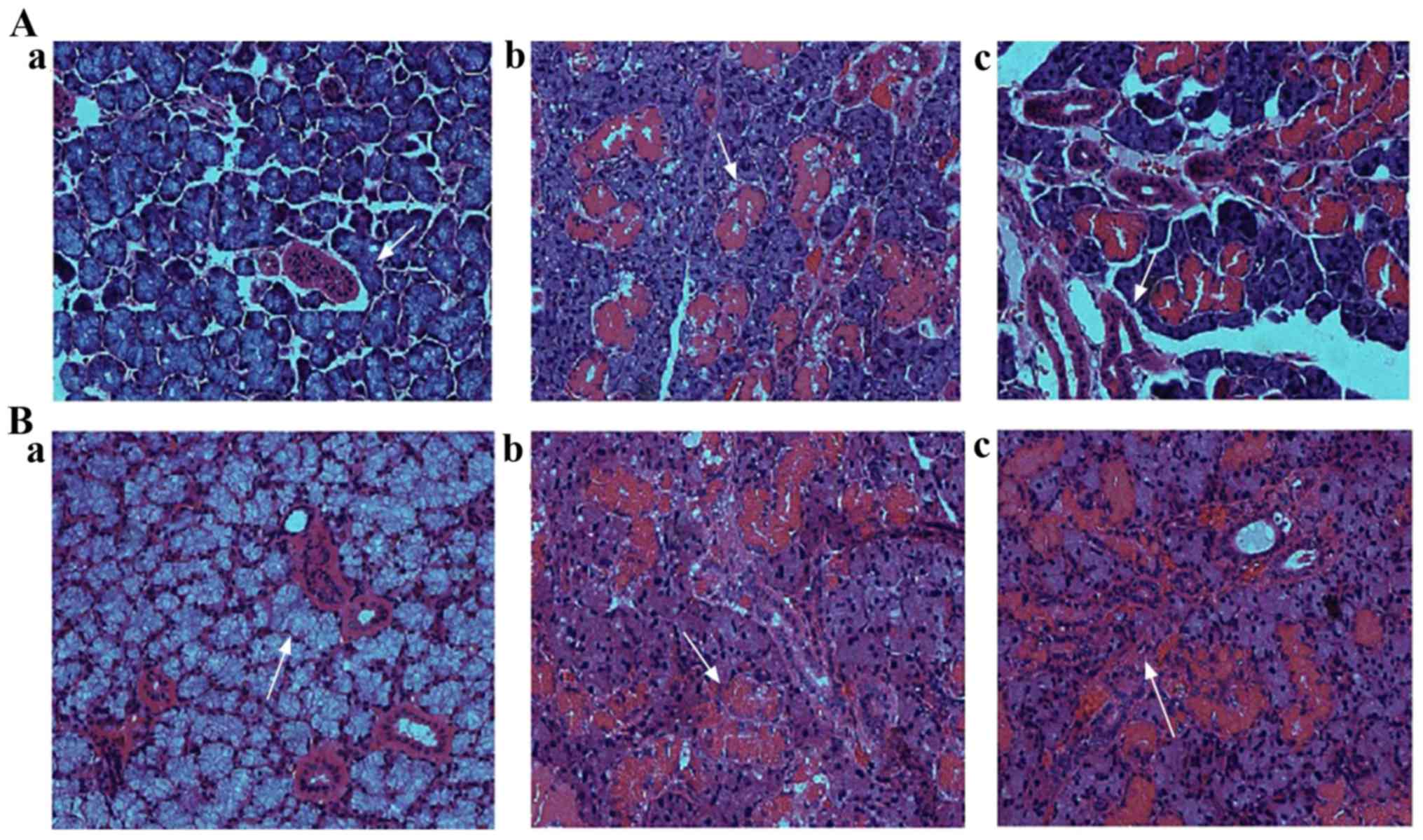
|
Indira M, Chandrashekar P, Kattappagari
KK, Chandra LP, Chitturi RT and BV RR: Evaluation of salivary
glucose, amylase, and total protein in type 2 diabetes mellitus
patients. Indian J Dent Res. 26:271–275. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Panchbhai AS, Degwekar SS and Bhowte RR:
Estimation of salivary glucose, salivary amylase, salivary total
protein and salivary flow rate in diabetics in India. J Oral Sci.
52:359–368. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Yin Z, Zhang YY and Cui LD: Clinical
significance of combined detection of serum tumor necrosis factor,
sialic acid and alpha-1 acid glycoprotein in type 2 diabetes
mellitus. J Chin Med University. 6:78–79. 2004.(In Chinese).
|
|
7
|
Marín Martínez L, Molino Pagán D and López
Jornet P: Trace elements in saliva as markers of type 2 diabetes
mellitus. Biol Trace Elem Res. 186:354–360. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Anderson LC, Garrett JR, Thulin A and
Proctor GB: Effects of streptozocin-induced diabetes on sympathetic
and parasympathetic stimulation of parotid salivary gland function
in rats. Diabetes. 38:1381–1389. 1989.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Stewart CR, Obi N, Epane EC, Akbari AA,
Halpern L, Southerland JH and Gangula PR: The effects of diabetes
on salivary gland protein expression of tetrahydrobiopterin and
nitric oxide synthesis and function. J Periodontol. 87:735–741.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Mori Y, Muratsu K, Nara Y and Morioka T:
The histopathological observation of the salivary gland in hamsters
with streptozotocin induced diabetes. Fukuoka Igaku Zasshi.
81:298–302. 1990.(In Japanese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
High AS, Sutton J and Hopper AH: A
morphometric study of submandibular salivary gland changes in
streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Arch Oral Biol. 30:667–671.
1985.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Widjaja J, Dolo PR, Zhang Q, Yao L, Li C,
Hong J, Wang H, Meng S, Shao Y and Zhu X: Bypassed and preserved
stomach resulted in superior glucose control in sprague-dawley rats
with streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Sci Rep.
9(9981)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Lin J, Lu Q and Yang ZM: Evaluation of
saliva collection method in rat model of spleen-deficiency by using
salivary alpha-amylase activity index. J Basic Chin Med.
22:909–911+924. 2016.(In Chinese).
|
|
14
|
Lin J, Yang ZM and Lu Q: Evaluation on the
methods for collecting saliva before and after acid stimulation by
salivary flow rate and sAA activity in rats. J Guangdong Pharm
University. 30:753–757. 2014.(In Chinese).
|
|
15
|
Mandel AL and Breslin PA: High endogenous
salivary amylase activity is associated with improved glycemic
homeostasis following starch ingestion in adults. J Nutr.
142:853–858. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Elder PJD, Ramsden DB, Burnett D, Weickert
MO and Barber TM: Human amylase gene copy number variation as a
determinant of metabolic state. Expert Rev Endocrinol Metab.
13:193–205. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Chen LH, Yang ZM, Chen WW, Lin J, Zhang M,
Yang XR and Zhao LB: Attenuated acute salivary α-amylase responses
to gustatory stimulation with citric acid in thin children. Br J
Nutr. 113:1078–1085. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Kołodziej U, Maciejczyk M, Miąsko A,
Matczuk J, Knaś M, Żukowski P, Żendzian-Piotrowska M, Borys J and
Zalewska A: Oxidative modification in the salivary glands of high
fat-diet induced insulin resistant rats. Front Physiol.
8(20)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Silva MF, Barbosa KG, Pereira JV, Bento
PM, Godoy GP and Gomes DQ: Prevalence of oral mucosal lesions among
patients with diabetes mellitus types 1 and 2. An Bras Dermatol.
90:49–53. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Aydin S: A comparison of ghrelin, glucose,
alpha-amylase and protein levels in saliva from diabetics. J
Biochem Mol Biol. 40:29–35. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Hamed M, Mina J, Maryam B and Hamidreza A:
Salivary alpha-amylase alteration as a possible indicator for
diabetes. J Basic Appl Sci Res. 4:284–288. 2014.
|
|
22
|
Rohleder N and Nater UM: Determinants of
salivary α-amylase in humans and methodological considerations.
Psychoneuroendocrinology. 34:469–485. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Carda C, Mosquera-Lloreda N, Salom L,
Gomez de Ferraris ME and Peydró A: Structural and functional
salivary disorders in type 2 diabetic patients. Med Oral Patol Oral
Cir Bucal. 11:E309–E314. 2006.(In English, Spanish). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Xia DS, Liu Y, Zhang CM, Yang SH and Wang
SL: Observation of salivary flow rate and oral bacterial changes in
small pigs after bilateral parotid atrophy. Chin J Stomatol.
42:737–740. 2007.(In Chinese).
|
|
25
|
Teng YJ, Chen P, Zhao HT, Yang XF, Nian H
and Dong DW: The effect of ginkgo biloba extract on morphological
character of parotid gland and submandibular gland of diabetic
rats. Acta Chin Med Pharmacol. 39:21–23. 2011.(In Chinese).
|
|
26
|
Malicka B, Kaczmarek U and
Skośkiewicz-Malinowska K: Prevalence of xerostomia and the salivary
flow rate in diabetic patients. Adv Clin Exp Med. 23:225–233.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Zalewska A, Knaś M, Zendzian-Piotrowska M,
Waszkiewicz N, Szulimowska J, Prokopiuk S, Waszkiel D and Car H:
Antioxidant profile of salivary glands in high fat diet-induced
insulin resistance rats. Oral Dis. 20:560–566. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Proctor GB and Carpenter GH: Regulation of
salivary gland function by autonomic nerves. Auton Neurosci.
133:3–18. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Ishikawa Y, Cho G, Yuan Z, Skowronski MT,
Pan Y and Ishida H: Water channels and zymogen granules in salivary
glands. J Pharmacol Sci. 100:495–512. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Murdiastuti K, Purwanti N, Karabasil MR,
Li X, Yao C, Akamatsu T, Kanamori N and Hosoi K: A naturally
occurring point mutation in the rat aquaporin 5 gene, influencing
its protein production by and secretion of water from salivary
glands. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 291:G1081–G1088.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Ma T, Song Y, Gillespie A, Carlson EJ,
Epstein CJ and Verkman AS: Defective secretion of saliva in
transgenic mice lacking aquaporin-5 water channels. J Biol Chem.
274:20071–20074. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Solinas G and Karin M: JNK1 and IKKbeta:
Molecular links between obesity and metabolic dysfunction. FASEB J.
24:2596–2611. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|