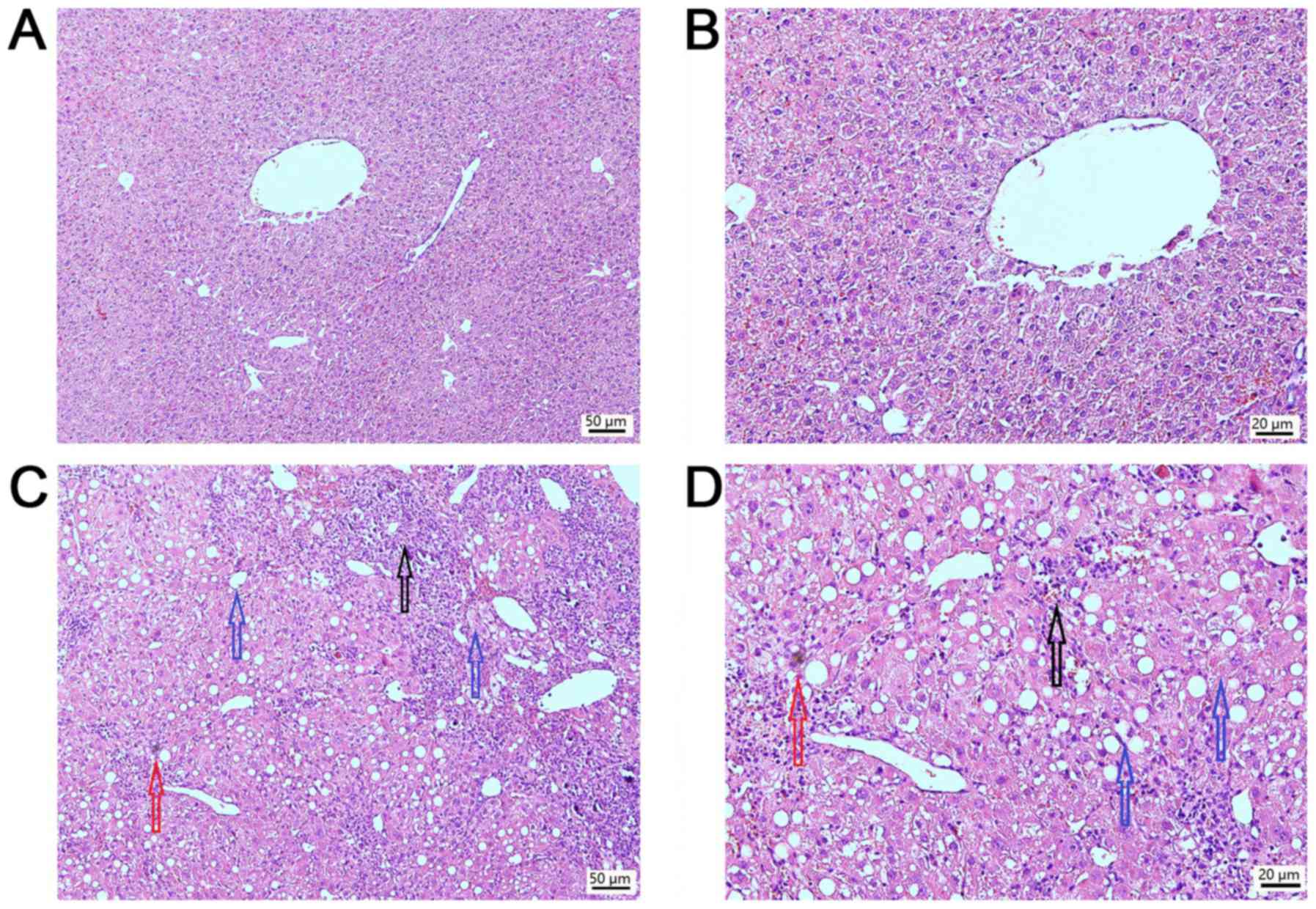
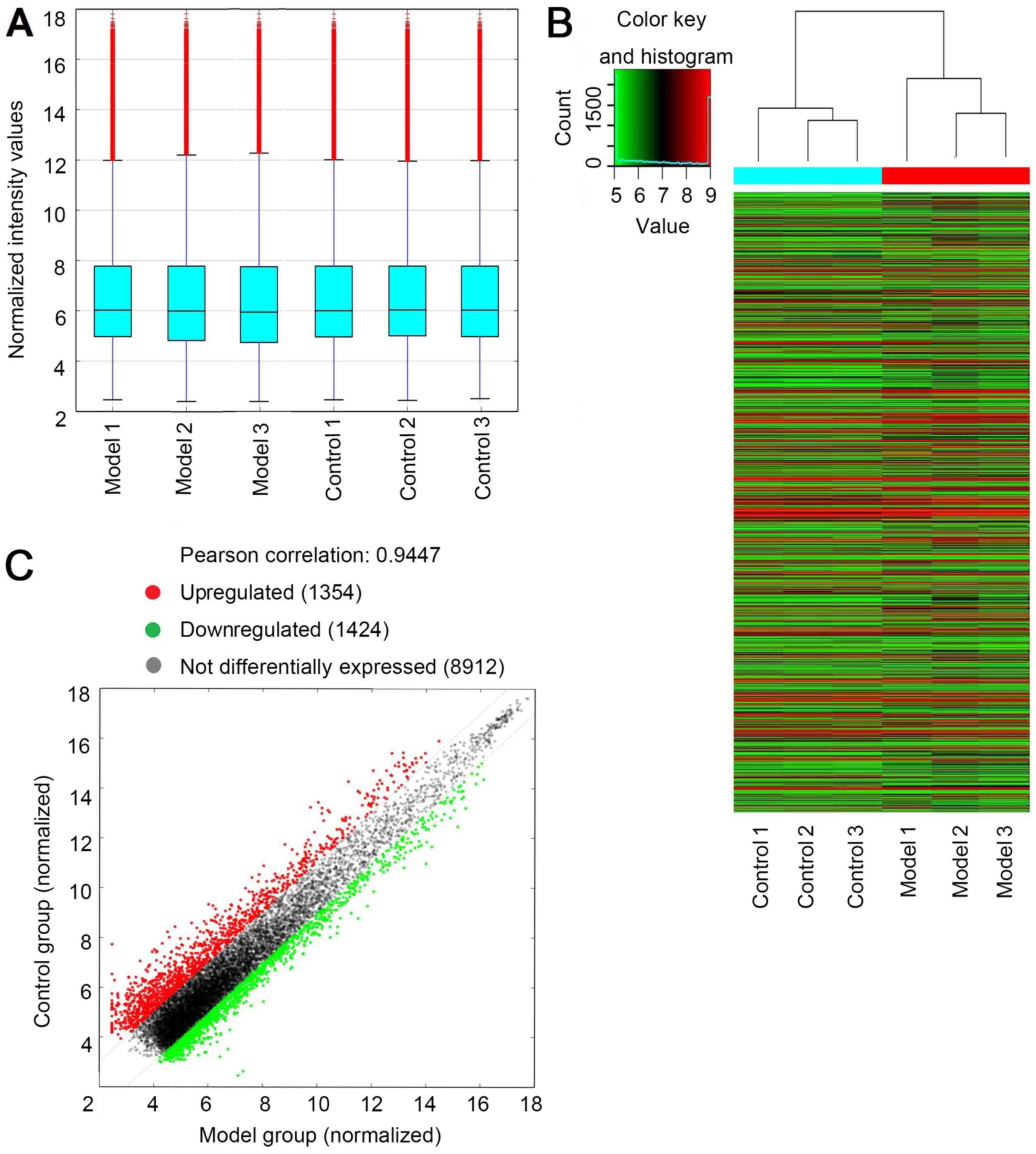
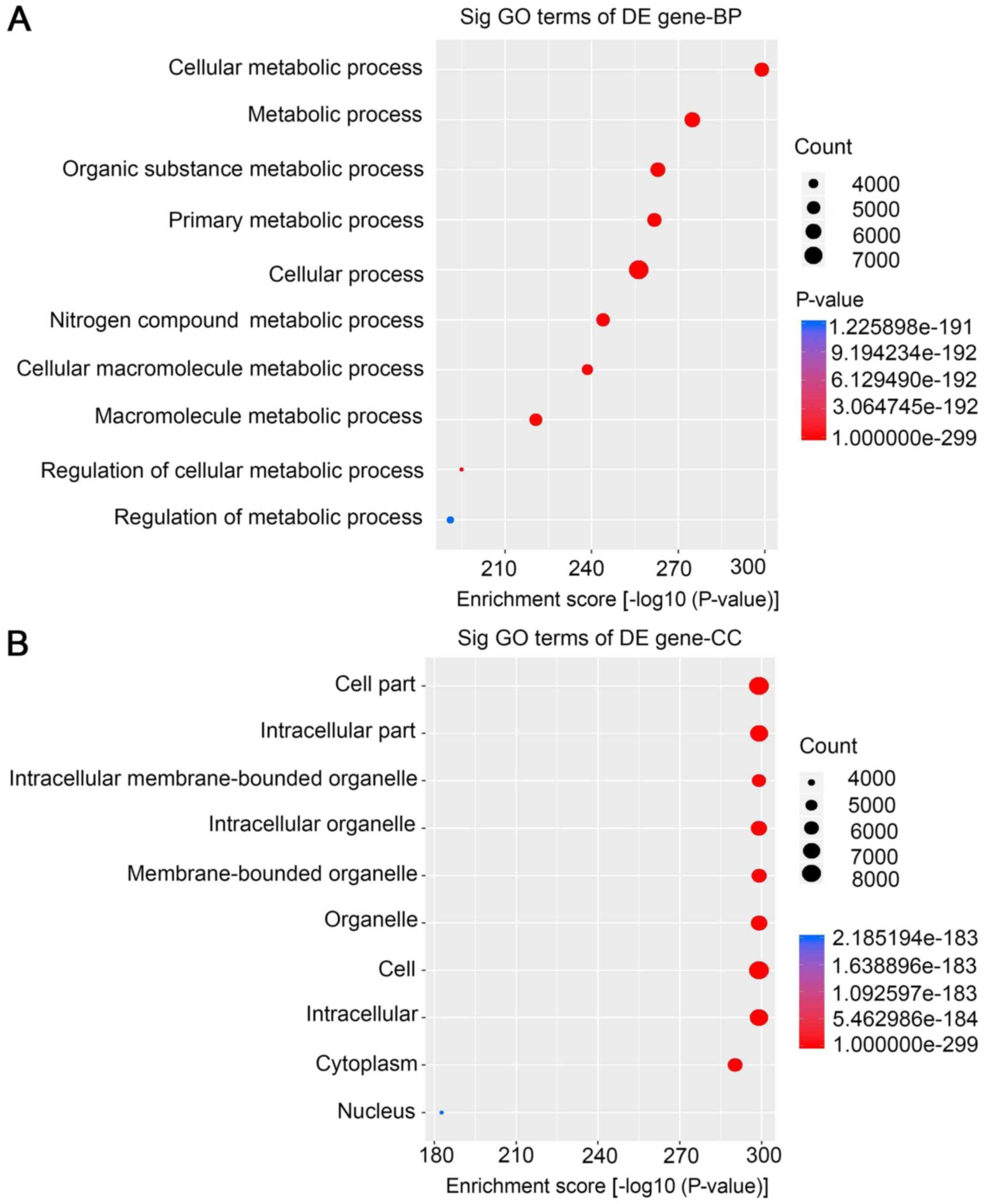
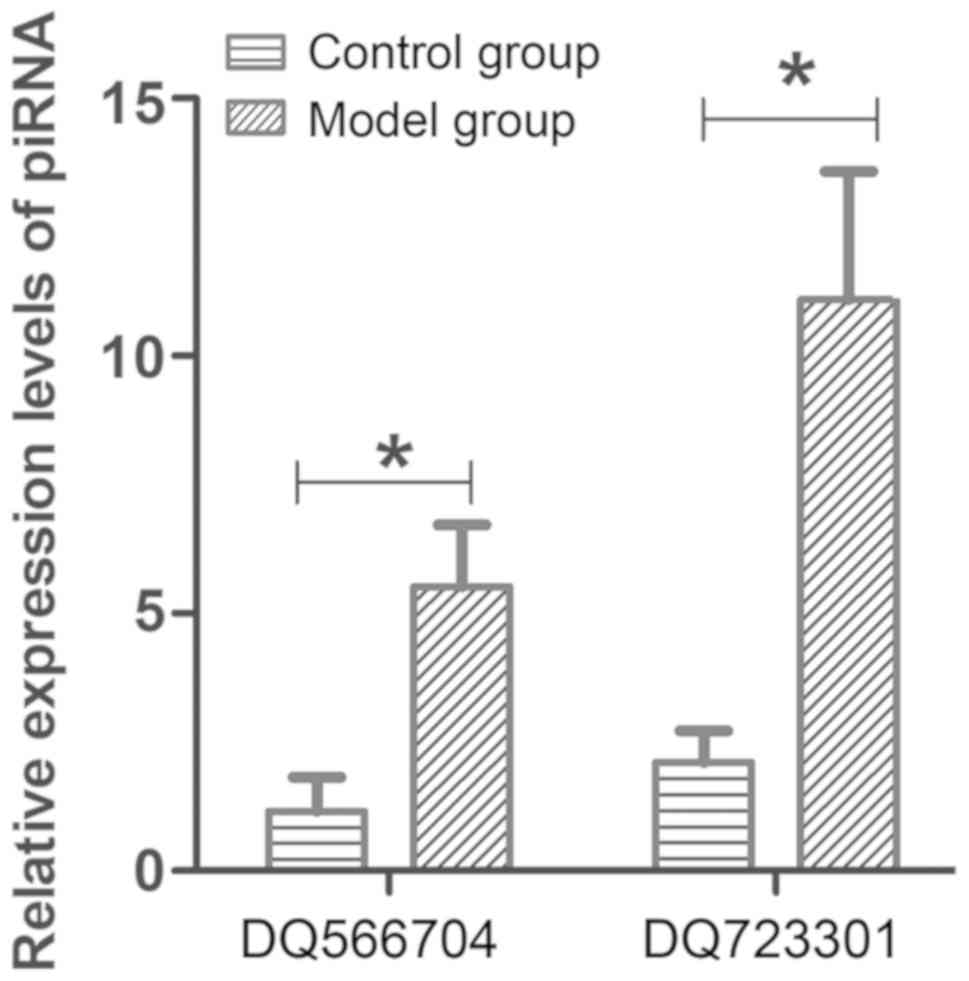
|
1
|
Ekstedt M, Nasr P and Kechagias S: Natural
history of NAFLD/NASH. Curr Hepatol Rep. 16:391–397.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Nakade Y, Sakamoto K, Yamauchi T, Inoue T,
Kobayashi Y, Yamamoto T, Ishii N, Ohashi T, Sumida Y, Ito K, et al:
Conophylline inhibits non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in mice. PLoS
One. 12(e0178436)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Spengler EK and Loomba R: Recommendations
for diagnosis, referral for liver biopsy, and treatment of
nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.
Mayo Clin Proc. 90:1233–1246. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Schuster S, Cabrera D, Arrese M and
Feldstein AE: Triggering and resolution of inflammation in NASH.
Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 15:349–364. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Marengo A, Jouness RIK and Bugianesi E:
Progression and natural history of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
in adults. Clin Liver Dis. 20:313–324. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Goh GB and McCullough AJ: Natural history
of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Dig Dis Sci. 61:1226–1233.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Koyama Y and Brenner DA: Liver
inflammation and fibrosis. J Clin Invest. 127:55–64.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Ma KL, Ruan XZ, Powis SH, Chen Y, Moorhead
JF and Varghese Z: Inflammatory stress exacerbates lipid
accumulation in hepatic cells and fatty livers of apolipoprotein E
knockout mice. Hepatology. 48:770–781. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Buzzetti E, Pinzani M and Tsochatzis EA:
The multiple-hit pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
(NAFLD). Metabolism. 65:1038–1048. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Hossain MA, Lee SJ, Park NH, Birhanu BT,
Mechesso AF, Park JY, Park EJ, Lee SP, Youn SJ and Park SC:
Enhancement of lipid metabolism and hepatic stability in
fat-induced obese mice by fermented Cucurbita moschata
extract. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine.
2018:1–11. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Litwin M, Szczepańska-Buda A, Piotrowska
A, Dzięgiel P and Witkiewicz W: The meaning of PIWI proteins in
cancer development. Oncol Lett. 13:3354–3362. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Han YN, Li Y, Xia SQ, Zhang YY, Zheng JH
and Li W: PIWI proteins and PIWI-Interacting RNA: Emerging roles in
cancer. Cell Physiol Biochem. 44:1–20. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Das B, Roy J, Jain N and Mallick B: Tumor
suppressive activity of PIWI-interacting RNA in human fibrosarcoma
mediated through repression of RRM2. Mol Carcinog. 58:344–357.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Pleštilová L, Neidhart M, Russo G,
Frank-Bertoncelj M, Ospelt C, Ciurea A, Kolling C, Gay RE, Michel
BA, Vencovský J, et al: Expression and regulation of PIWIL-proteins
and PIWI-interacting RNAs in rheumatoid arthritis. PLoS One.
11(e0166920)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Shen S, Yu H, Liu X, Liu Y, Zheng J, Wang
P, Gong W, Chen J, Zhao L and Xue Y: PIWIL1/piRNA-DQ593109
regulates the permeability of the blood-tumor barrier via the
MEG3/miR-330-5p/RUNX3 axis. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 10:412–425.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Sturm Á, Perczel A, Ivics Z and Vellai T:
The Piwi-piRNA pathway: Road to immortality. Aging Cell.
16:906–911. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Phay M, Kim HH and Yoo S: Analysis of
piRNA-like small non-coding RNAs present in axons of adult sensory
neurons. Mol Neurobiol. 55:483–494. 2016.
|
|
18
|
Wang Y, Gable T, Ma MZ, Clark D, Zhao J,
Zhang Y, Liu W, Mao L and Mei Y: A piRNA-like small RNA induces
chemoresistance to cisplatin-based therapy by inhibiting apoptosis
in lung squamous cell carcinoma. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 6:269–278.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Mahamid M, Mahroum N, Bragazzi N, Shalaata
K, Yavne Y, Adawi M, Amital H and Watad A: Folate and B12 levels
correlate with histological severity in NASH patients. Nutrients.
10(E440)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Ishikawa H: Evolution of ribosomal RNA.
Comp Biochem Physiol B. 58:1–7. 1977.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Pasquinelli AE: MicroRNAs and their
targets: Recognition, regulation and an emerging reciprocal
relationship. Nat Rev Genet. 13:271–282. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Garcia DM, Baek D, Shin C, Bell GW,
Grimson A and Bartel DP: Weak seed-pairing stability and high
target-site abundance decrease the proficiency of lsy-6 and other
microRNAs. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 18:1139–1146. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Watanabe T, Cheng EC, Zhong M and Lin H:
Retrotransposons and pseudogenes regulate mRNAs and lncRNAs via the
piRNA pathway in the germline. Genome Res. 25:368–380.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Wang S, Song K, Srivastava R, Dong C, Go
GW, Li N, Iwakiri Y and Mani A: Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
induced by noncanonical Wnt and its rescue by Wnt3a. FASEB J.
29:3436–3445. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Tian Y, Mok MTS, Yang P and Cheng AS:
Epigenetic activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in
NAFLD-associated hepatocarcinogenesis. Cancers (Basel).
8(E76)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Wu YK, Hu LF, Lou DS, Wang BC and Tan J:
Targeting DUSP16/TAK1 signaling alleviates hepatic dyslipidemia and
inflammation in high fat diet (HFD)-challenged mice through
suppressing JNK MAPK. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 524:142–149.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Lau JK, Zhang X and Yu J: Animal models of
non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Current perspectives and recent
advances. J Pathol. 241:36–44. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Matsumoto M, Hada N, Sakamaki Y, Uno A,
Shiga T, Tanaka C, Ito T, Katsume A and Sudoh M: An improved mouse
model that rapidly develops fibrosis in non-alcoholic
steatohepatitis. Int J Exp Pathol. 94:93–103. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Matsuzawa N, Takamura T, Kurita S, Misu H,
Ota T, Ando H, Yokoyama M, Honda M, Zen Y, Nakanuma Y, et al:
Lipid-induced oxidative stress causes steatohepatitis in mice fed
an atherogenic diet. Hepatology. 46:1392–1403. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Van Herck MA, Vonghia L and Francque SM:
Animal models of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-a starter's
guide. Nutrients. 9(E1072)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Mamikutty N, Thent ZC and Haji Suhaimi F:
Fructose-drinking water induced nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
and ultrastructural alteration of hepatocyte mitochondria in male
wistar rat. Biomed Res Int. 2015(895961)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Ogasawara M, Hirose A, Ono M, Aritake K,
Nozaki Y, Takahashi M, Okamoto N, Sakamoto S, Iwasaki S, Asanuma T,
et al: A novel and comprehensive mouse model of human non-alcoholic
steatohepatitis with the full range of dysmetabolic and
histological abnormalities induced by gold thioglucose and a
high-fat diet. Liver Int. 31:542–551. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Charlton M, Krishnan A, Viker K, Sanderson
S, Cazanave S, McConico A, Masuoko H and Gores G: Fast food diet
mouse: Novel small animal model of NASH with ballooning,
progressive fibrosis, and high physiological fidelity to the human
condition. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 301:G825–G834.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Tanaka N, Takahashi S, Fang ZZ, Matsubara
T, Krausz KW, Qu A and Gonzalez FJ: Role of white adipose lipolysis
in the development of NASH induced by methionine- and
choline-deficient diet. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1841:1596–1607.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Fisher-Wellman KH, Ryan TE, Smith CD,
Gilliam LA, Lin CT, Reese LR, Torres MJ and Neufer PD: A direct
comparison of metabolic responses to high-fat diet in C57BL/6J and
C57BL/6NJ mice. Diabetes. 65:3249–3261. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Li MY, Feng GP, Wang H, Yang RL, Xu Z and
Sun YM: Deacetylated konjac glucomannan is less effective in
reducing dietary-induced hyperlipidemia and hepatic steatosis in
C57BL/6 mice. J Agric Food Chem. 65:1556–1565. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Ghosh SS, Wang J, Yannie PJ, Sandhu YK,
Korzun WJ and Ghosh S: Dietary supplementation with
galactooligosaccharides attenuates high-fat, high-cholesterol
diet-induced glucose intolerance and disruption of colonic mucin
layer in C57BL/6 mice and reduces atherosclerosis in Ldlr-/- mice.
J Nutr. 150:285–293. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Mentis AA, Dardiotis E, Romas NA and
Papavassiliou AG: PIWI family proteins as prognostic markers in
cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cell Mol Life Sci:
Dec 9, 2019 (Epub ahead of print).
|
|
40
|
Ross RJ, Weiner MM and Lin H: PIWI
proteins and PIWI-interacting RNAs in the soma. Nature.
505:353–359. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Wang Y and Li J, Zhuge L, Su D, Yang M,
Tao S and Li J: Comparison between the efficacies of curcumin and
puerarin in C57BL/6 mice with steatohepatitis induced by a
methionine- and choline-deficient diet. Exp Ther Med. 7:663–668.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Ji G, Wang Y, Deng Y, Li X and Jiang Z:
Resveratrol ameliorates hepatic steatosis and inflammation in
methionine/choline-deficient diet-induced steatohepatitis through
regulating autophagy. Lipids Health Dis. 14(134)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Ye Y, Yin DT, Chen L, Zhou Q, Shen R, He
G, Yan Q, Tong Z, Issekutz AC, Shapiro CL, et al: Identification of
Piwil2-like (PL2L) proteins that promote tumorigenesis. PLoS One.
5(e13406)2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Jiang F, Parsons CJ and Stefanovic B: Gene
expression profile of quiescent and activated rat hepatic stellate
cells implicates Wnt signaling pathway in activation. J Hepatol.
45:401–409. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Hino M, Kamo M, Saito D, Kyakumoto S,
Shibata T, Mizuki H and Ishisaki A: Transforming growth factor-β1
induces invasion ability of HSC-4 human oral squamous cell
carcinoma cells through the Slug/Wnt-5b/MMP-10 signalling axis. J
Biochem. 159:631–640. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Behari J: The Wnt/β-catenin signaling
pathway in liver biology and disease. Expert Rev Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 4:745–756. 2014.
|
|
47
|
Menendez JA, Vazquez-Martin A, Ortega FJ
and Fernandez-Real JM: Fatty acid synthase: Association with
insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, and cancer. Clin Chem.
55:425–438. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
McPherson R and Gauthier A: Molecular
regulation of SREBP function: The Insig-SCAP connection and
isoform-specific modulation of lipid synthesis. Biochem Cell Biol.
82:201–211. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Ide T, Shimano H, Yahagi N, Matsuzaka T,
Nakakuki M, Yamamoto T, Nakagawa Y, Takahashi A, Suzuki H, Sone H,
et al: SREBPs suppress IRS-2-mediated insulin signalling in the
liver. Nat Cell Biol. 6:351–357. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Lee DH, Park DB, Lee YK, An CS, Oh YS,
Kang JS, Kang SH and Chung MY: The effects of thiazolidinedione
treatment on the regulations of aquaglyceroporins and glycerol
kinase in OLETF rats. Metabolism. 54:1282–1289. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Ji RR, Gereau RW IV, Malcangio M and
Strichartz GR: MAP kinase and pain. Brain Res Rev. 60:135–148.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Gao W, Du X, Lei L, Wang H, Zhang M, Wang
Z and Li X, Liu G and Li X: NEFA-induced ROS impaired insulin
signalling through the JNK and p38MAPK pathways in non-alcoholic
steatohepatitis. J Cell Mol Med. 22:3408–3422. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Seki E and Schwabe RF: Hepatic
inflammation and fibrosis: Functional links and key pathways.
Hepatology. 61:1066–1079. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|