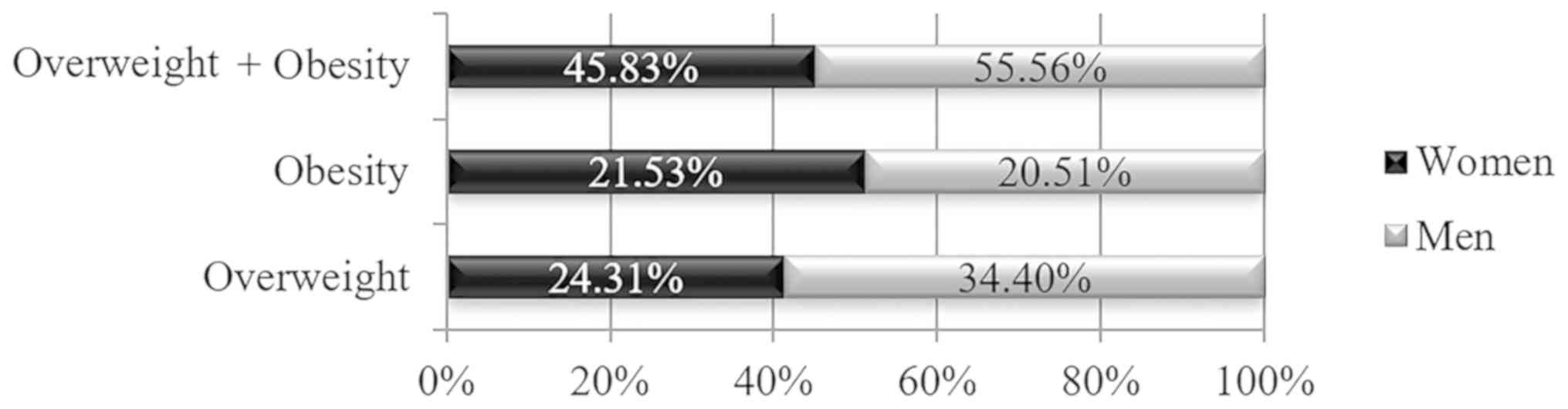
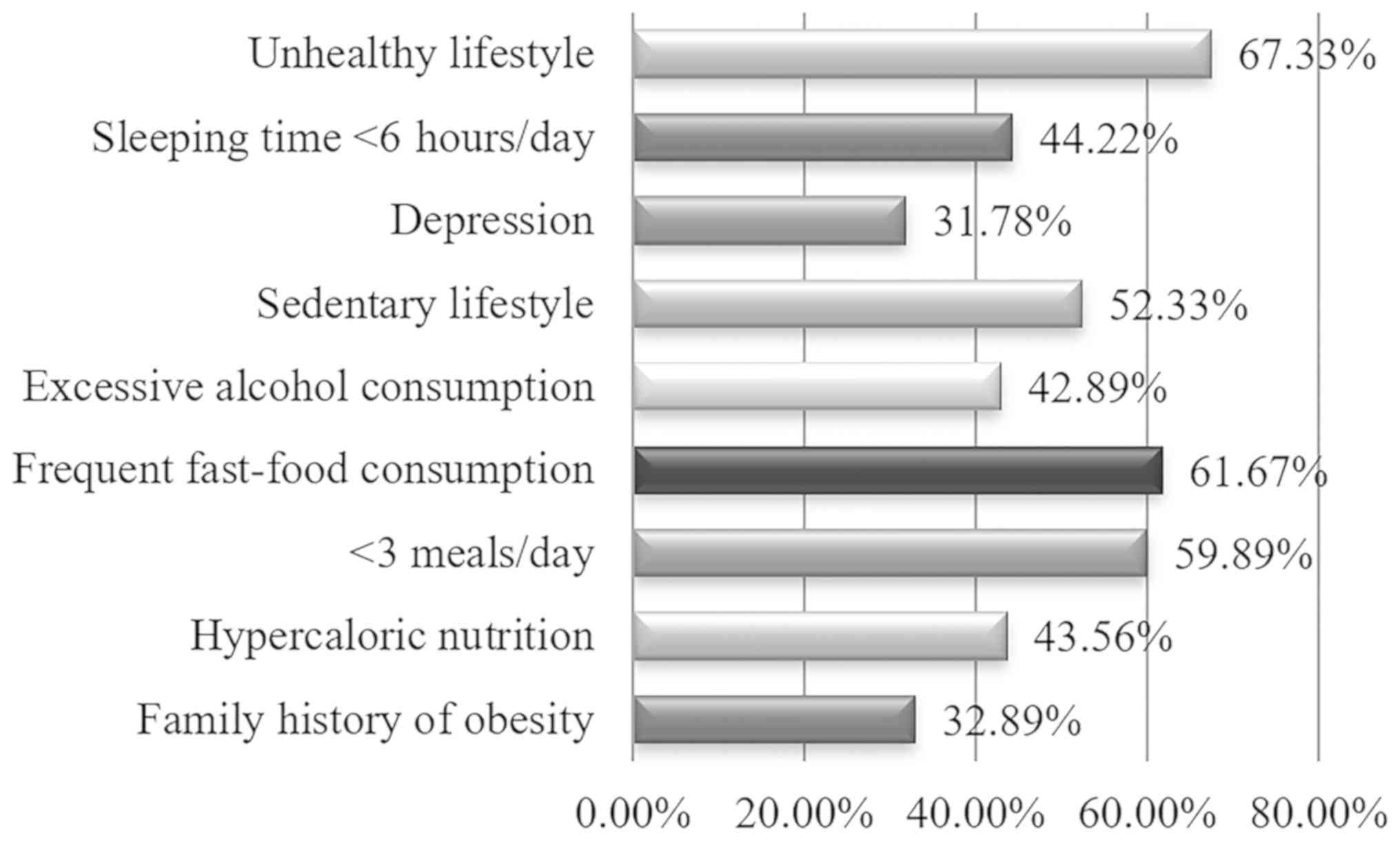
|
1
|
Kelly T, Yang W, Chen C-S, Reynolds K and
He J: Global burden of obesity in 2005 and projections to 2030. Int
J Obes. 32:1431–1437. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Popa S, Moţa M, Popa A, Moţa E,
Serafinceanu C, Guja C, Catrinoiu D, Hâncu N, Lichiardopol R, Bala
C, et al: Prevalence of overweight/obesity, abdominal obesity and
metabolic syndrome and atypical cardiometabolic phenotypes in the
adult Romanian population: PREDATORR study. J Endocrinol Invest.
39:1045–1053. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Hamulka J, Wadolowska L, Hoffmann M,
Kowalkowska J and Gutkowska K: Effect of an education program on
nutrition knowledge, attitudes toward nutrition, diet quality,
lifestyle, and body composition in Polish teenagers. The ABC of
healthy eating project: Design, protocol, and methodology.
Nutrients. 10(1439)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Speliotes EK, Willer CJ, Berndt SI, Monda
KL, Thorleifsson G, Jackson AU, Lango Allen H, Lindgren CM, Luan J,
Mägi R, et al: Procardis Consortium: Association analyses of
249,796 individuals reveal 18 new loci associated with body mass
index. Nat Genet. 42:937–948. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Wadden TA, Webb VL, Moran CH and Bailer
BA: Lifestyle modification for obesity: New developments in diet,
physical activity, and behavior therapy. Circulation.
125:1157–1170. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Donnelly JE, Blair SN, Jakicic JM, Manore
MM, Rankin JW and Smith BK: American College of Sports Medicine.
American College of Sports Medicine Position Stand. Appropriate
physical activity intervention strategies for weight loss and
prevention of weight regain for adults. Med Sci Sports Exerc.
41:459–471. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Cercato C and Fonseca FA: Cardiovascular
risk and obesity. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 11(74)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
WHO: Overweight and obesity. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight.
Accessed December 6, 2019.
|
|
9
|
Fryar CD, Carroll MD and Ogden CL:
Prevalence of overweight, obesity, and extreme obesity among adults
aged 20 and over: United States, 1960-1962 through 2015-2016.
National Center for Health Statistics Data, Health E-Stats, July
2016. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/hestat/obesity_adult_13_14/obesity_adult_13_14.htm.
Accessed December 6, 2019.
|
|
10
|
Bahadoran Z, Mirmiran P and Azizi F: Fast
food pattern and cardiometabolic disorders: A review of current
studies. Health Promot Perspect. 5:231–240. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Popa AR, Vesa CM, Uivarosan D, Jurca CM,
Isvoranu G, Socea B, Stanescu AMA, Iancu MA, Scarneciu I and Zaha
DC: Cross-sectional study regarding the association between
sweetened beverages intake, fast-food products, body mass index,
fasting blood glucose and blood pressure in the young adults from
North-western Romania. Rev Chim-Bucharest. 70:156–160. 2019.
|
|
12
|
Popa AR, Bungau S, Vesa CM, Bondar AC,
Pantis C, Maghiar O, Dimulescu (Nica) IA, Nistor Cseppento DC and
Rus M: Evaluating the efficacy of the treatment with benfotiamine
and alpha-lipoic acid in distal symmetric painful diabetic
polyneuropathy. Rev Chim. 70:3108–3114. 2019.
|
|
13
|
Lua PL and Wan Putri Elena WD: The impact
of nutrition education interventions on the dietary habits of
college students in developed nations: A brief review. Malays J Med
Sci. 19:4–14. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Abdel-Daim MM, El-Tawil OS, Bungau SG and
Atanasov AG: Applications of antioxidants in metabolic disorders
and degenerative diseases: Mechanistic approach. Oxid Med Cell
Longev. 2019(4179676)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Glevitzky I, Dumitrel GA, Glevitzky M,
Pasca B, Otrisal P, Bungau S, Cioca G, Pantis C and Popa M:
Statistical analysis of the relationship between antioxidant
activity and the structure of flavonoid compounds. Rev
Chim-Bucharest. 70:3103–3107. 2019.
|
|
16
|
Heinonen I, Helajärvi H and Pahkala K:
Sedentary behaviours and obesity: in adults: the cardiovascular
risk in young Finns study. BMJ Open. (3e002901)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
González K, Fuentes J and Márquez JL:
Physical inactivity, sedentary behavior and chronic diseases.
Korean J Fam Med. 38:111–115. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Mulugeta A, Zhou A, Power C and Hyppönen
E: Obesity and depressive symptoms in mid-life: A population-based
cohort study. BMC Psychiatry. 18(297)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Beccuti G and Pannain S: Sleep and
obesity. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 14:402–412.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Spiegel K, Tasali E, Penev P and Van
Cauter E: Brief communication: Sleep curtailment in healthy young
men is associated with decreased leptin levels, elevated ghrelin
levels, and increased hunger and appetite. Ann Intern Med.
141:846–850. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Chaput JP, Després JP, Bouchard C and
Tremblay A: The association between sleep duration and weight gain
in adults: A 6-year prospective study from the Quebec Family Study.
Sleep. 31:517–523. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Lagerros YT and Rössner S: Obesity
management: What brings success? Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 6:77–88.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Kumar S and Kelly AS: Review of childhood
obesity: From epidemiology, etiology, and comorbidities to clinical
assessment and Treatment. Mayo Clin Proc. 92:251–265.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|