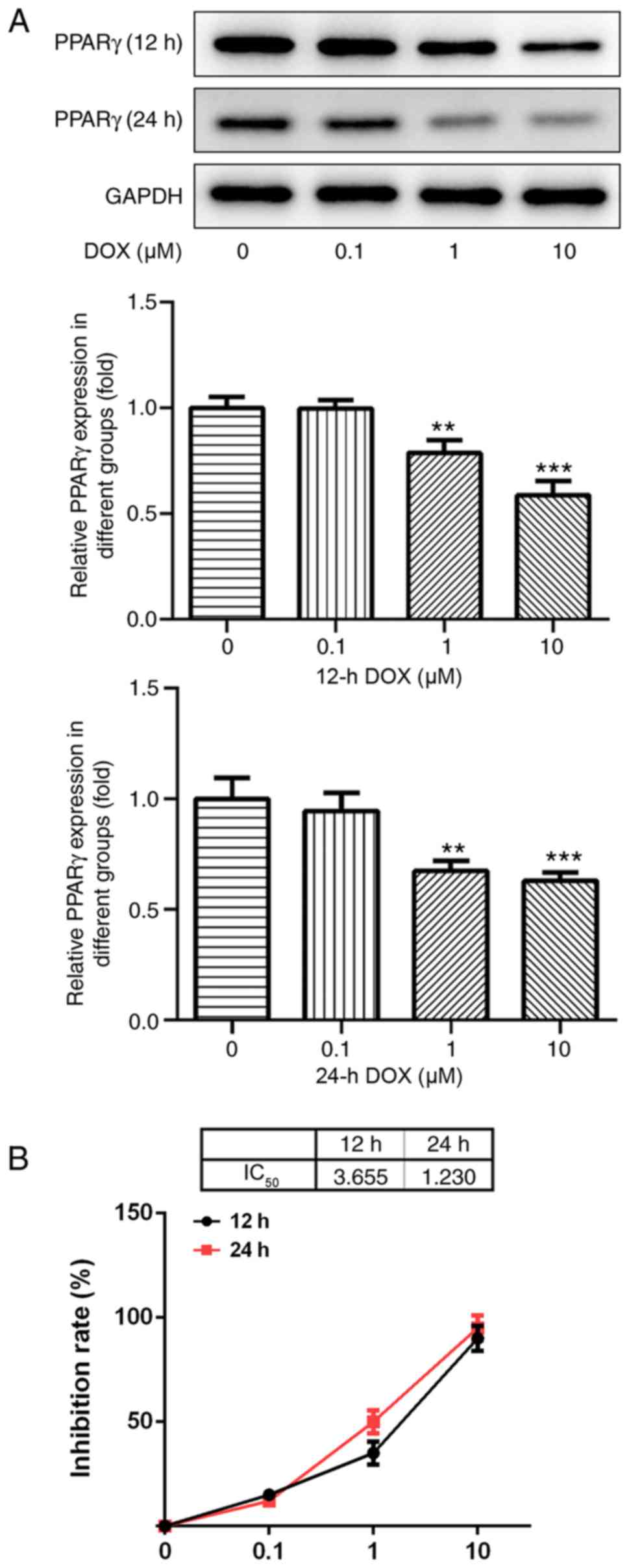
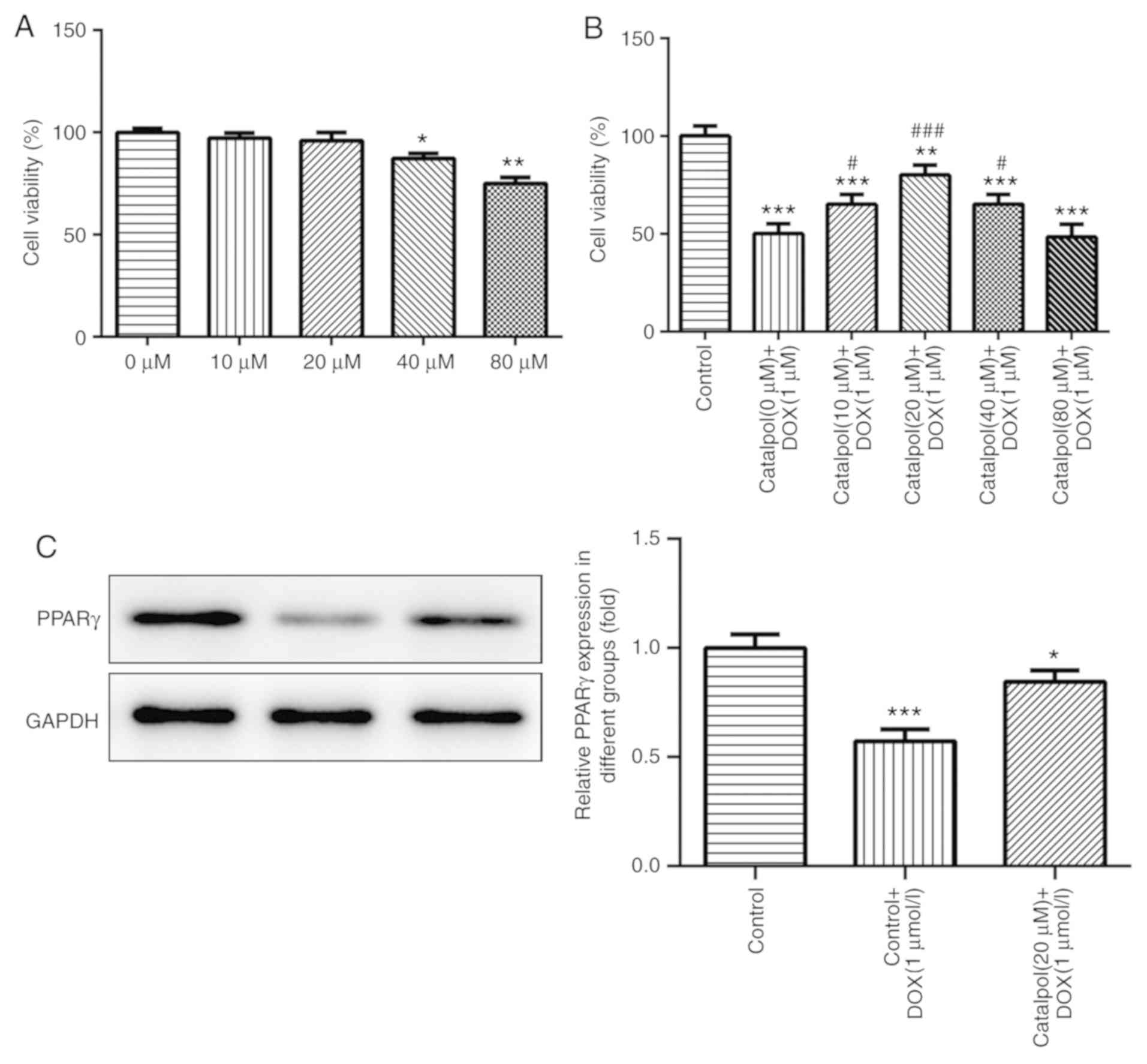
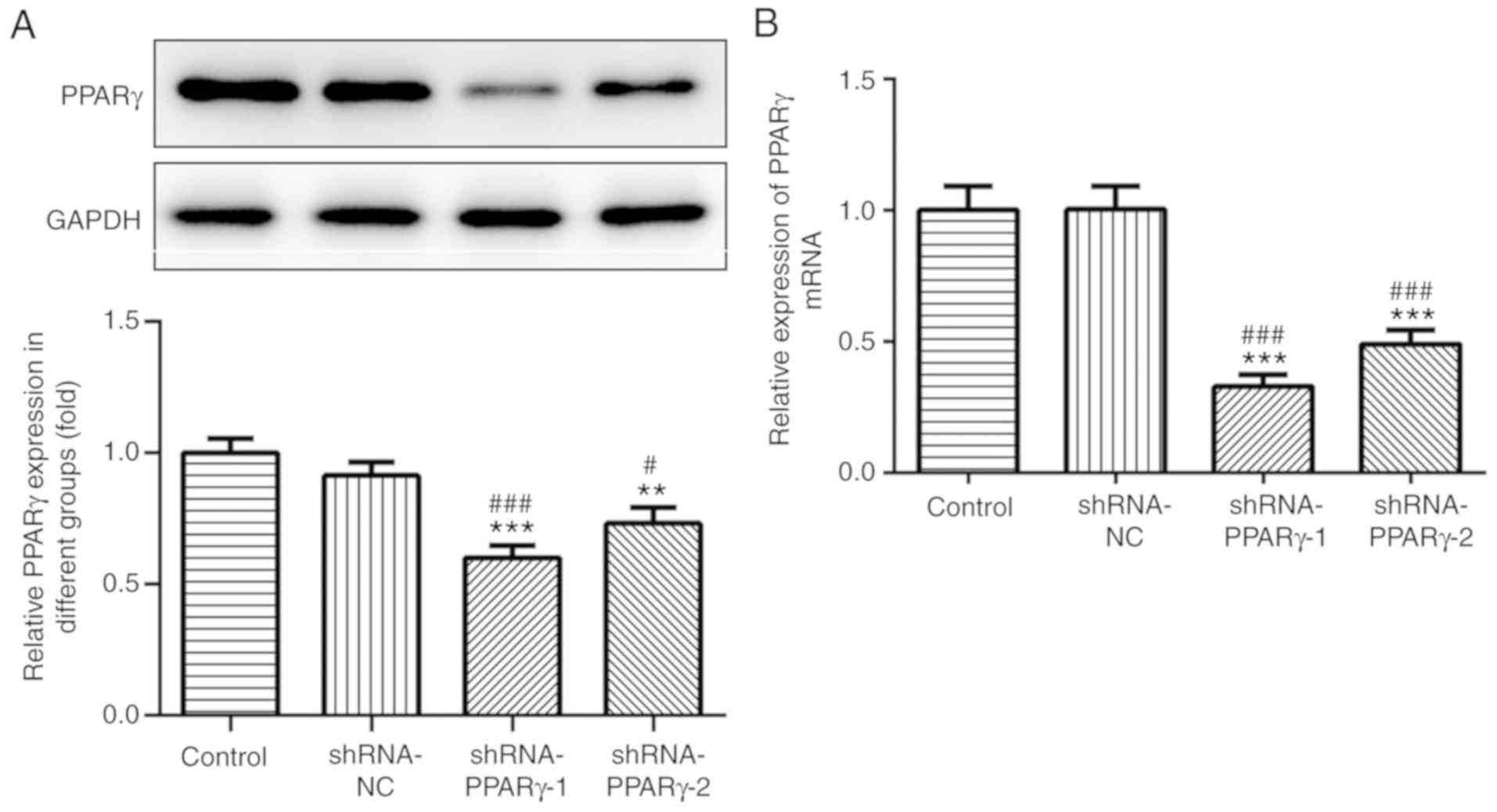
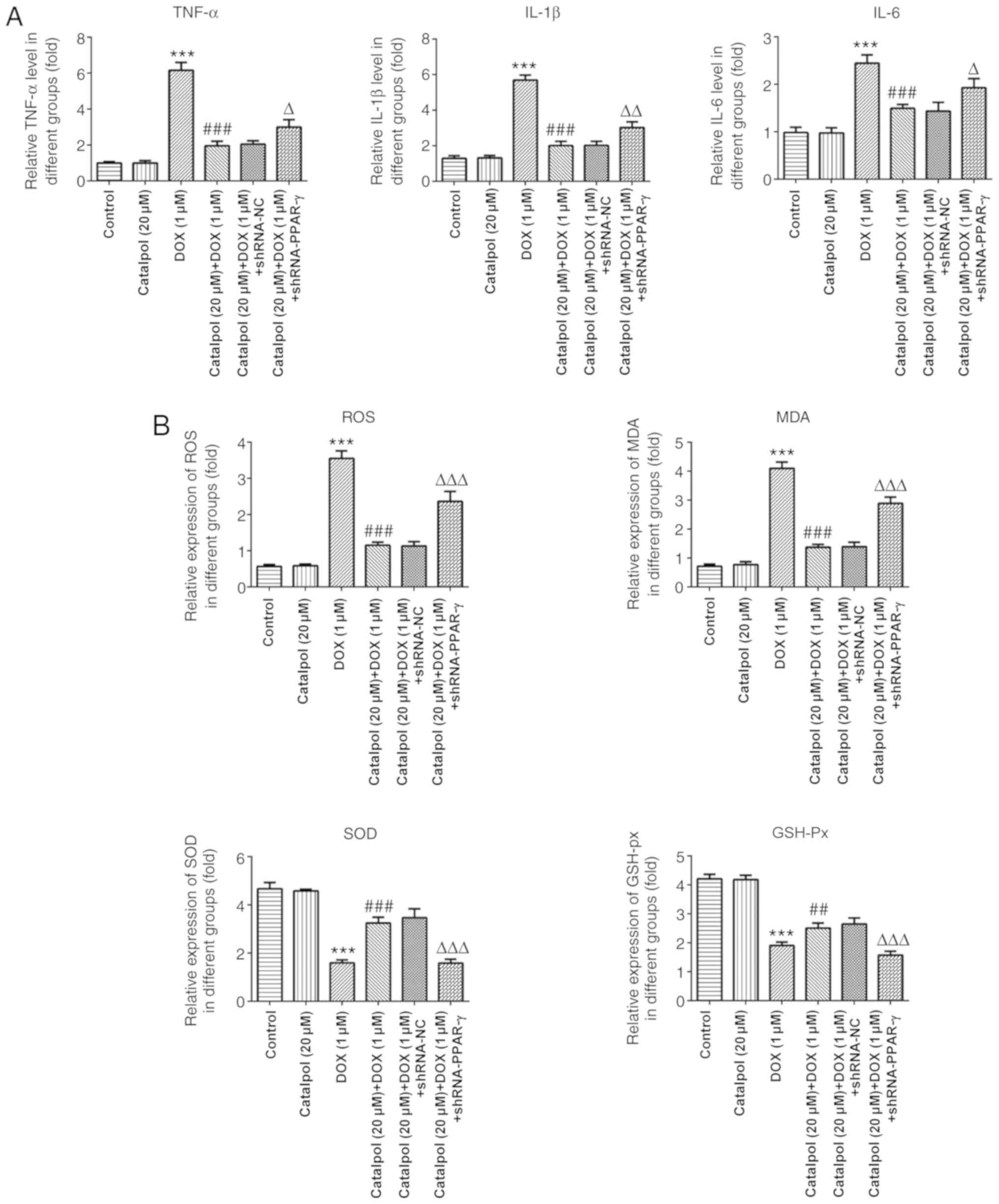
|
1
|
Rochette L, Guenancia C, Gudjoncik A,
Hachet O, Zeller M, Cottin Y and Vergely C:
Anthracyclines/trastuzumab: New aspects of cardiotoxicity and
molecular mechanisms. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 36:326–348.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Smith LA, Cornelius VR, Plummer CJ, Levitt
G, Verrill M, Canney P and Jones A: Cardiotoxicity of anthracycline
agents for the treatment of cancer: Systematic review and
meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. BMC Cancer.
10(337)2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Zhang YW, Shi J, Li YJ and Wei L:
Cardiomyocyte death in doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Arch
Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 57:435–445. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Cardinale D, Colombo A, Bacchiani G,
Tedeschi I, Meroni CA, Veglia F, Civelli M, Lamantia G, Colombo N,
Curigliano G, et al: Early detection of anthracycline
cardiotoxicity and improvement with heart failure therapy.
Circulation. 131:1981–1988. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Gallucci G and Simeon V: Letter by
Gallucci and Simeon regarding article, ‘early detection of
anthracycline cardiotoxicity and improvement with heart failure
therapy’. Circulation. 133(e362)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Chen Y, Liu Q, Shan Z, Zhao Y, Li M, Wang
B, Zheng X and Feng W: The protective effect and mechanism of
catalpol on high glucose-induced podocyte injury. BMC Complement
Altern Med. 19(244)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Zhang X, Jin C, Li Y, Guan S, Han F and
Zhang S: Catalpol improves cholinergic function and reduces
inflammatory cytokines in the senescent mice induced by
D-galactose. Food Chem Toxicol. 58:50–55. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Fu Q, Zhou Z, Li X, Guo H, Fan X, Chen J,
Zhuang J, Zheng S and Zhu P: Protective effect of adenosine
preconditioning against spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury in
rats. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 34:92–95. 2014.PubMed/NCBI(In Chinese).
|
|
9
|
Bi J, Jiang B, Zorn A, Zhao RG, Liu P and
An LJ: Catalpol inhibits LPS plus IFN-γ-induced inflammatory
response in astrocytes primary cultures. Toxicol In Vitro.
27:543–550. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Zhang Z, Liu Y, Xue B and Wei L:
Protective effects of catalpol against
H2O2-induced oxidative damage in astrocytes.
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 34:1955–1958. 2009.PubMed/NCBI(In Chinese).
|
|
11
|
Mao YR, Jiang L, Duan YL, An LJ and Jiang
B: Efficacy of catalpol as protectant against oxidative stress and
mitochondrial dysfunction on rotenone-induced toxicity in mice
brain. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 23:314–318. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Hu L, Sun Y and Hu J: Catalpol inhibits
apoptosis in hydrogen peroxide-induced endothelium by activating
the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway and modulating expression of Bcl-2
and Bax. Eur J Pharmacol. 628:155–163. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Li DQ, Bao YM, Li Y, Wang CF, Liu Y and An
LJ: Catalpol modulates the expressions of Bcl-2 and Bax and
attenuates apoptosis in gerbils after ischemic injury. Brain Res.
1115:179–185. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Huang WJ, Niu HS, Lin MH, Cheng JT and Hsu
FL: Antihyperglycemic effect of catalpol in streptozotocin-induced
diabetic rats. J Nat Prod. 73:1170–1172. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Wang CF, Li DQ, Xue HY and Hu B: Oral
supplementation of catalpol ameliorates diabetic encephalopathy in
rats. Brain Res. 1307:158–165. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Yuan H, Ni X, Zheng M, Han X, Song Y and
Yu M: Effect of catalpol on behavior and neurodevelopment in an
ADHD rat model. Biomed Pharmacother. 118(109033)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Li Q, Yang T, Guo AC and Fan YP: Role of
catalpol in ameliorating the pathogenesis of experimental
autoimmune encephalomyelitis by increasing the level of
noradrenaline in the locus coeruleus. Mol Med Rep. 17:4163–4172.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Zou G, Zhong W, Wu F, Wang X and Liu L:
Inhibition of lncRNA Neat1 by catalpol via suppressing
transcriptional activity of NF-κB attenuates cardiomyocyte
apoptosis. Cell Cycle. 18:3432–3441. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Liu YR, Li PW, Suo JJ, Sun Y, Zhang BA, Lu
H, Zhu HC and Zhang GB: Catalpol provides protective effects
against cerebral ischaemia/reperfusion injury in gerbils. J Pharm
Pharmacol. 66:1265–1270. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Cai Q, Yao Z and Li H: Catalpol promotes
oligodendrocyte survival and oligodendrocyte progenitor
differentiation via the Akt signaling pathway in rats with chronic
cerebral hypoperfusion. Brain Res. 1560:27–35. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Youssef J and Badr M: Role of peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptors in inflammation control. J Biomed
Biotechnol. 2004:156–166. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Morgan MJ and Liu ZG: Crosstalk of
reactive oxygen species and NF-κB signaling. Cell Res. 21:103–115.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Bishop-Bailey D: Peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptors in the cardiovascular system. Br J
Pharmacol. 129:823–834. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Geng DF, Wu W, Jin DM, Wang JF and Wu YM:
Effect of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma ligand.
Rosiglitazone on left ventricular remodeling in rats with
myocardial infarction. Int J Cardiol. 113:86–91. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Singh AP, Singh N, Pathak D and Bedi PMS:
Estradiol attenuates ischemia reperfusion-induced acute kidney
injury through PPAR-γ stimulated eNOS activation in rats. Mol Cell
Biochem. 453:1–9. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Otero-Losada M, LC Udovin L, Kobiec T,
Toro-Urrego N, A KR and Capani F: Long-term effects of
hypoxia-reoxygenation on thioredoxins in rat central nervous
system. Curr Pharm Des. 25:4791–4798. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Messinis DE, Melas IN, Hur J, Varshney N,
Alexopoulos LG and Bai JPF: Translational systems
pharmacology-based predictive assessment of drug-induced
cardiomyopathy. CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol. 7:166–174.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Yanagimoto K, Okamoto Y, Kodama Y,
Nishikawa T, Tanabe T and Kawano Y: Decrease of cardiac base
rotation in 2D speckle tracking indicates drug-induced
cardiomyopathy after chemotherapy in children with cancer. J
Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 39:10–14. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Helbock HJ, Beckman KB and Ames BN:
8-Hydroxydeoxyguanosine and 8-hydroxyguanine as biomarkers of
oxidative DNA damage. Methods Enzymol. 300:156–166. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Rasheed S, Hashim R and Yan JS: Possible
biomarkers for the early detection of HIV-associated heart
diseases: A proteomics and bioinformatics prediction. Comput Struct
Biotechnol J. 13:145–152. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Bizino MB, Jazet IM, Westenberg JJM, van
Eyk HJ, Paiman EHM, Smit JWA and Lamb HJ: Effect of liraglutide on
cardiac function in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus:
Randomized placebo-controlled trial. Cardiovasc Diabetol.
18(55)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Xin YF, Wan LL, Peng JL and Guo C:
Alleviation of the acute doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by
Lycium barbarum polysaccharides through the suppression of
oxidative stress. Food Chem Toxicol. 49:259–264. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Hu J, Wu Q, Wang Z, Hong J, Chen R, Li B,
Hu Z, Hu X and Zhang M: Inhibition of CACNA1H attenuates
doxorubicin-induced acute cardiotoxicity by affecting endoplasmic
reticulum stress. Biomed Pharmacother. 120(109475)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Riba A, Deres L, Eros K, Szabo A, Magyar
K, Sumegi B, Toth K, Halmosi R and Szabados E: Doxycycline protects
against ROS-induced mitochondrial fragmentation and ISO-induced
heart failure. PLoS One. 12(e0175195)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Chaudhari U, Nemade H, Gaspar JA,
Hescheler J, Hengstler JG and Sachinidis A: MicroRNAs as early
toxicity signatures of doxorubicin in human-induced pluripotent
stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes. Arch Toxicol. 90:3087–3098.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Mjos KD, Cawthray JF, Jamieson G, Fox JA
and Orvig C: Iron (III)-binding of the anticancer agents
doxorubicin and vosaroxin. Dalton Trans. 44:2348–2358.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Medeiros-Lima DJM, Carvalho JJ, Tibirica
E, Borges JP and Matsuura C: Time course of cardiomyopathy induced
by doxorubicin in rats. Pharmacol Rep. 71:583–590. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Xu L, Zhang W, Zeng L and Jin JO:
Rehmannia glutinosa polysaccharide induced an anti-cancer effect by
activating natural killer cells. Int J Biol Macromol. 105:680–685.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Choi EM, Suh KS, Jung WW, Yun S, Park SY,
Chin SO, Rhee SY and Chon S: Catalpol protects against
2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin-induced cytotoxicity in
osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells. J Appl Toxicol. 39:1710–1719.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Zou G, Zhong W, Wu F, Wang X and Liu L:
Catalpol attenuates cardiomyocyte apoptosis in diabetic
cardiomyopathy via Neat1/miR-140-5p/HDAC4 axis. Biochimie.
165:90–99. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Fu K, Piao T, Wang M, Zhang J, Jiang J,
Wang X and Liu H: Protective effect of catalpol on
lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice. Int
Immunopharmacol. 23:400–406. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Stěrba M, Popelová O, Vávrová A, Jirkovský
E, Kovaříková P, Geršl V and Simůnek T: Oxidative stress, redox
signaling, and metal chelation in anthracycline cardiotoxicity and
pharmacological cardioprotection. Antioxid Redox Signal.
18:899–929. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Yu X, Cui L, Zhang Z, Zhao Q and Li S:
α-Linolenic acid attenuates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in
rats through suppression of oxidative stress and apoptosis. Acta
Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 45:817–826. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Zhao X, Jin Y, Li L, Xu L, Tang Z, Qi Y,
Yin L and Peng J: MicroRNA-128-3p aggravates doxorubicin-induced
liver injury by promoting oxidative stress via targeting Sirtuin-1.
Pharmacol Res. 146(104276)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Wu S, Lu Q, Ding Y, Wu Y, Qiu Y, Wang P,
Mao X, Huang K, Xie Z and Zou MH: Hyperglycemia-driven inhibition
of AMP-activated protein kinase α2 induces diabetic cardiomyopathy
by promoting mitochondria-associated endoplasmic reticulum
membranes in vivo. Circulation. 139:1913–1936. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Li Y, Bao Y, Jiang B, Wang Z, Liu Y, Zhang
C and An L: Catalpol protects primary cultured astrocytes from in
vitro ischemia-induced damage. Int J Dev Neurosci. 26:309–317.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Chakraborty RK and Burns B: Systemic
inflammatory response syndrome. In: StatPearls, Treasure Island
(FL), 2020.
|
|
49
|
Ramadori P, Ahmad G and Ramadori G:
Cellular and molecular mechanisms regulating the hepatic
erythropoietin expression during acute-phase response: A role for
IL-6. Lab Invest. 90:1306–1324. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Hu L, Mauro TM, Dang E, Man G, Zhang J,
Lee D, Wang G, Feingold KR, Elias PM and Man MQ: Epidermal
dysfunction leads to an age-associated increase in levels of serum
inflammatory cytokines. J Invest Dermatol. 137:1277–1285.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Yamashita M and Passegue E: TNF-α
coordinates hematopoietic stem cell survival and myeloid
regeneration. Cell Stem Cell. 25:357–372, e357. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Faridvand Y, Haddadi P, Vahedian V, Nozari
S, Nejabati HR, Pezeshkian M, Afrasiabi A, Safaie N, Jodati A and
Nouri M: Human amnion membrane proteins prevent doxorubicin-induced
oxidative stress injury and apoptosis in rat H9c2 cardiomyocytes.
Cardiovasc Toxicol: Feb 21, 2020 doi: 10.1007/s12012-020-09564-8
(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
53
|
Han MS, White A, Perry RJ, Camporez JP,
Hidalgo J, Shulman GI and Davis RJ: Regulation of adipose tissue
inflammation by interleukin 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
117:2751–2760. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Cen W, Chen Z, Gu N and Hoppe R:
Prevention of AMI induced ventricular remodeling: Inhibitory
effects of heart-protecting musk pill on IL-6 and TNF-alpha. Evid
Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017(3217395)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Terrasi M, Bazan V, Caruso S, Insalaco L,
Amodeo V, Fanale D, Corsini LR, Contaldo C, Mercanti A, Fiorio E,
et al: Effects of PPARγ agonists on the expression of leptin and
vascular endothelial growth factor in breast cancer cells. J Cell
Physiol. 228:1368–1374. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Tan NS, Michalik L, Desvergne B and Wahli
W: Multiple expression control mechanisms of peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptors and their target genes. J Steroid
Biochem Mol Biol. 93:99–105. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Choo J, Lee Y, Yan XJ, Noh TH, Kim SJ, Son
S, Pothoulakis C, Moon HR, Jung JH and Im E: A novel peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR)γ agonist 2-hydroxyethyl
5-chloro-4,5-didehydrojasmonate exerts anti-inflammatory effects in
colitis. J Biol Chem. 290:25609–25619. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|