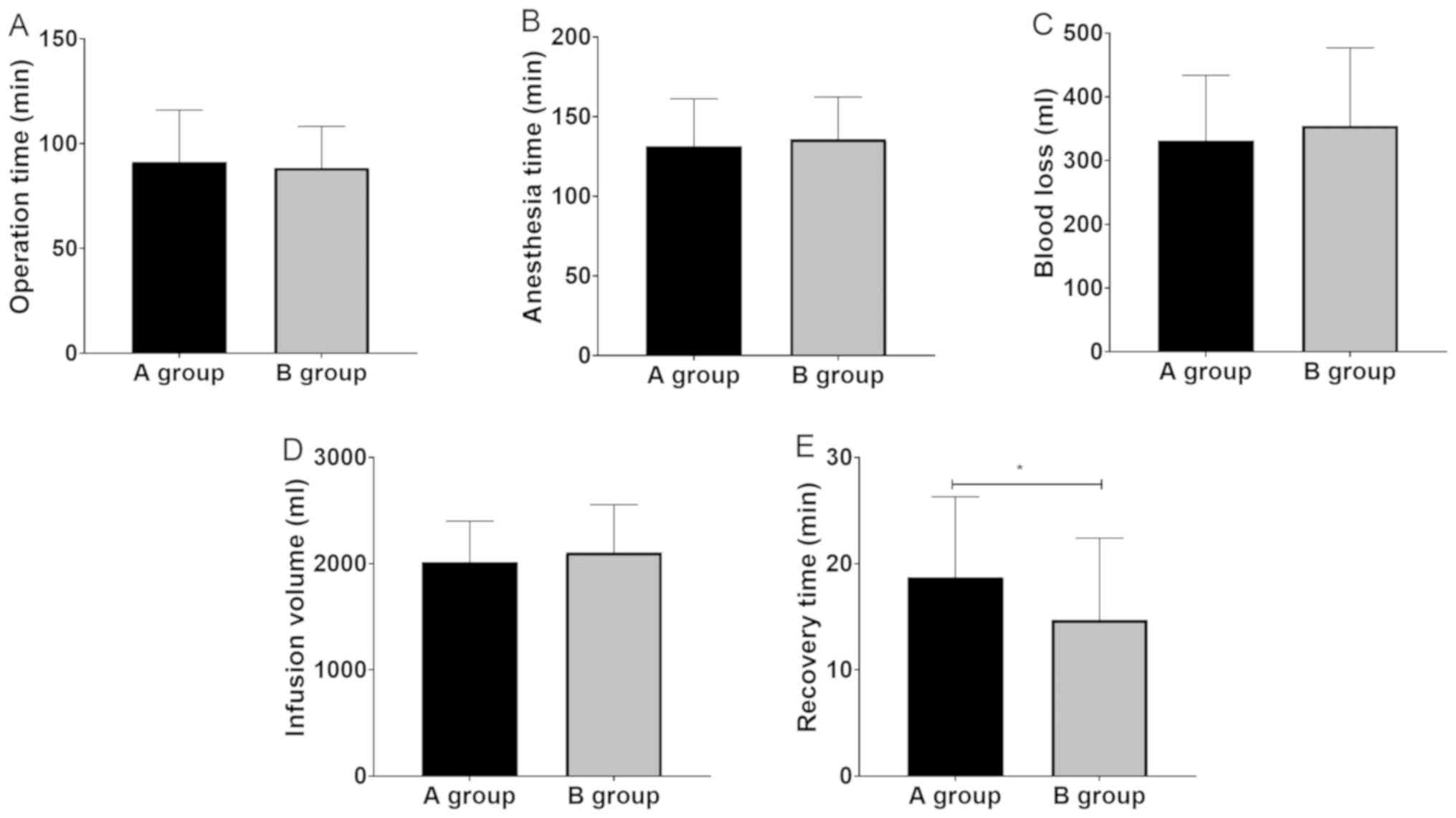
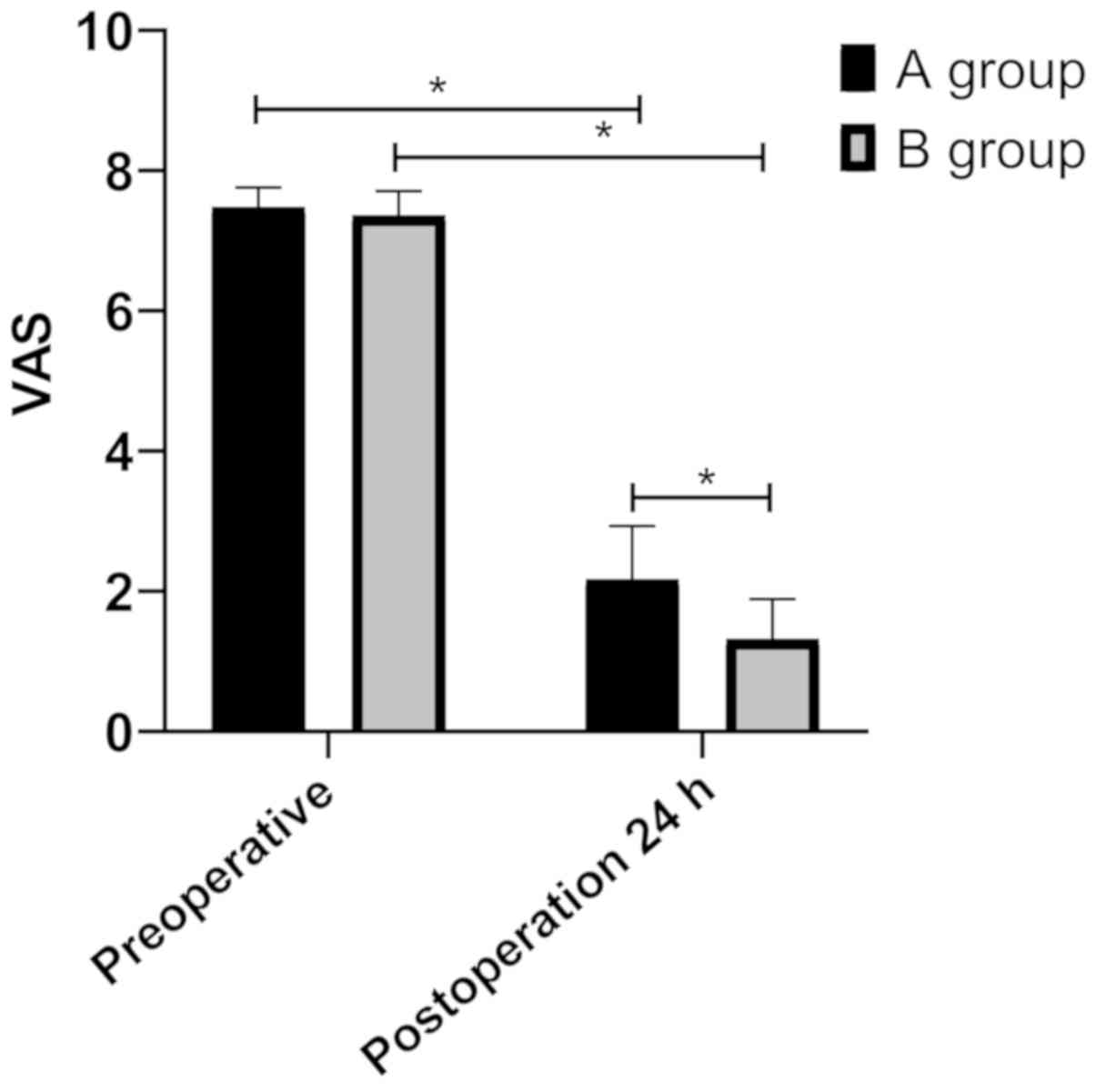
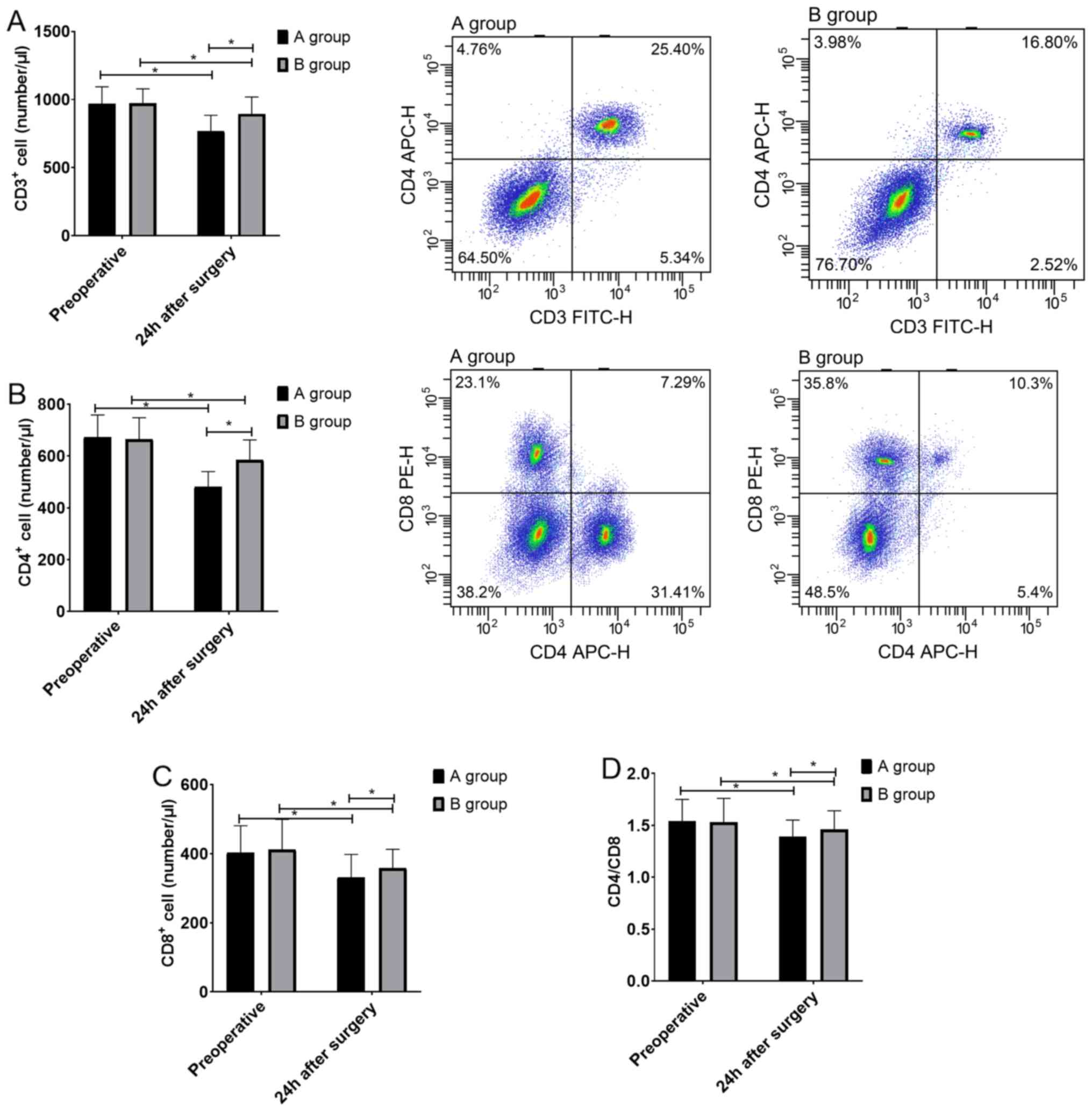
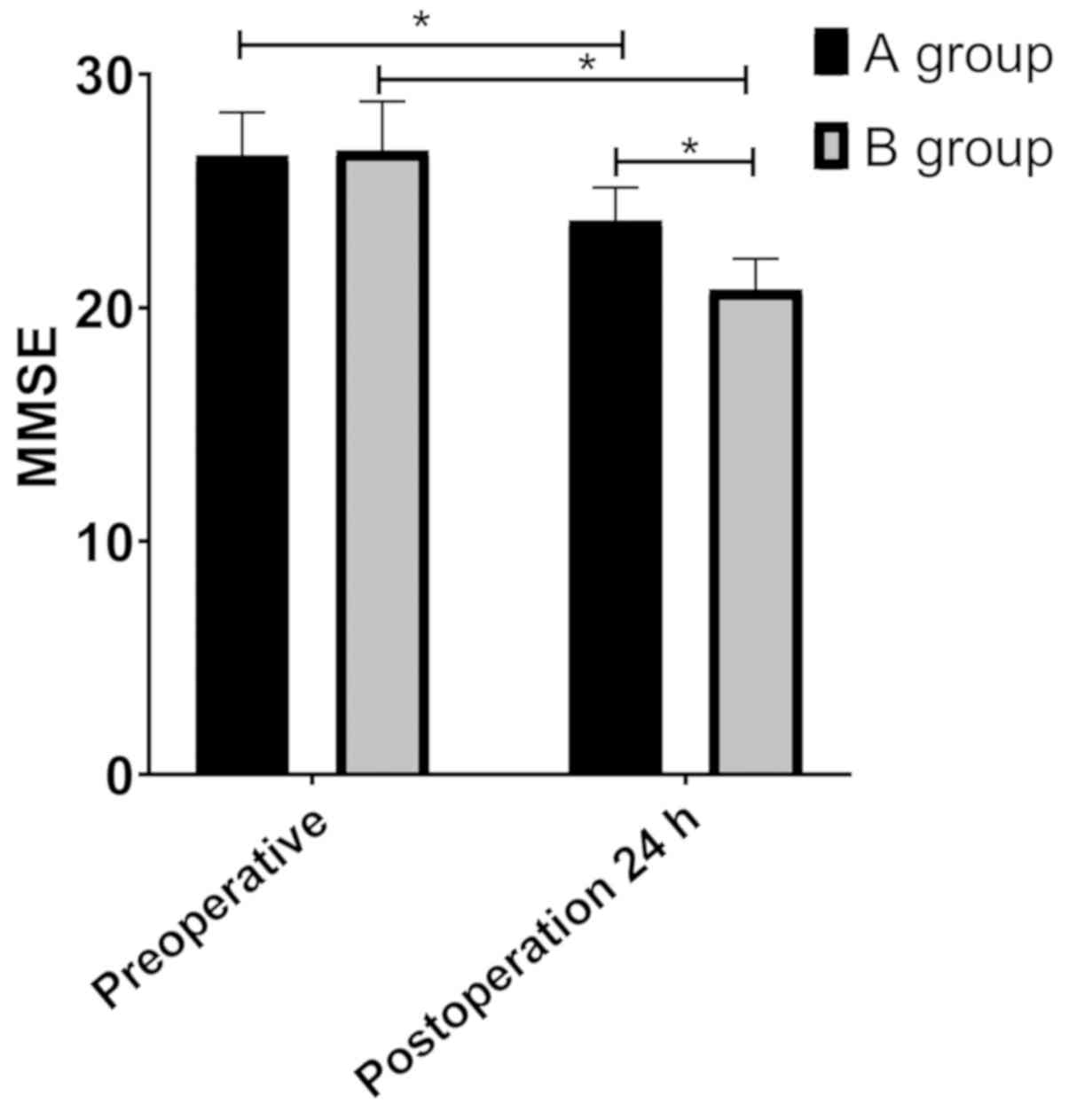
|
1
|
Kremers HM, Larson DR, Crowson CS, Kremers
WK, Washington RE, Steiner CA, Jiranek WA and Berry DJ: Prevalence
of total hip and knee replacement in the United States. J Bone
Joint Surg Am. 97:1386–1397. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Kurtz SM, Lau E, Ong K, Zhao K, Kelly M
and Bozic KJ: Future young patient demand for primary and revision
joint replacement: National projections from 2010 to 2030. Clin
Orthop Relat Res. 467:2606–2612. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Liu XW, Zi Y, Xiang LB and Wang Y: Total
hip arthroplasty: Areview of advances, advantages and limitations.
Int J Clin Exp Med. 8:27–36. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bilsel K, Erdil M, Gulabi D, Elmadag M,
Cengiz O and Sen C: Factors affecting mortality after hip fracture
surgery: A retrospective analysis of 578 patients. Eur J Orthop
Surg Traumatol. 23:895–900. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Kadry B, Feaster WW, Macario A and
Ehrenfeld JM: Anesthesia information management systems: Past,
present, and future of anesthesia records. Mt Sinai J Med.
79:154–165. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Flack S and Anderson C: Ultrasound guided
lower extremity blocks. Paediatr Anaesth. 22:72–80. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Karaca S, Ayhan E, Kesmezacar H and Uysal
O: Hip fracture mortality: Is it affected by anesthesia techniques?
Anesthesiol Res Pract. 2012(708754)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Shi ZY, Jiang CN and Shao G: Application
of lower limb nerve block combined with slow induction of light
general anesthesia and tracheal induction in elderly hip surgery.
Medicine (Baltimore). 97(e12581)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Gu CY, Zhang J, Qian YN and Tang QF:
Effects of epidural anesthesia and postoperative epidural analgesia
on immune function in esophageal carcinoma patients undergoing
thoracic surgery. Mol Clin Oncol. 3:190–196. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Suthar O, Sethi P and Sharma UD:
Comparison of dexmedetomidine and clonidine as an adjuvant to
intrathecal bupivacaine in lower limb surgery: A randomised,
double-blind, placebo controlled trial. Anaesth Pain Intensive
Care. 18:149–154. 2015.
|
|
11
|
Wang Y, Xu X, Liu H and Ji F: Effects of
dexmedetomidine on patients undergoing radical gastrectomy. J Surg
Res. 194:147–153. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Jang Y, Yeom MY, Kang ES, Kang JW and Song
HK: The antinociceptive effect of dexmedetomidine modulates spleen
cell immunity in mice. Int J Med Sci. 11:226–233. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Zhou J, Wang J and Meng F: The use of
dexmedetomidine in aged patients with total hip replacement surgery
under general anesthesia: Changes in hemodynamics, cerebral state
index and wakening quality. Afr J Pharm Pharmacol. 6:1833–1836.
2012.
|
|
14
|
Nayagam HA, Singh NR and Singh HS: A
prospective randomised double blind study of intrathecal fentanyl
and dexmedetomidine added to low dose bupivacaine for spinal
anesthesia for lower abdominal surgeries. Indian J Anaesth.
58:430–435. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Park SH, Kim AR and Lee HS: Effects of
short-term corrective exercise on pain, hip joint range of motion
and trunk muscle strength of a patient with anterior pelvic tilt: A
case study. Off J Korean Acad Kinesiol. 18:85–93. 2016.
|
|
16
|
Iidaka T, Muraki S, Oka H, Kodama R,
Tanaka S, Kawaguchi H, Nakamura K, Akune T and Yoshimura N:
Radiographic measurements of the hip joint and their associations
with hip pain in Japanese men and women: The Research on
Osteoarthritis/osteoporosis Against Disability (ROAD) study.
Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 25:2072–2079. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Wylde V, Sayers A, Lenguerrand E,
Gooberman-Hill R, Pyke M, Beswick AD, Dieppe P and Blom AW:
Preoperative widespread pain sensitization and chronic pain after
hip and knee replacement: a cohort analysis. Pain. 156:47–54.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Hua X, Hu Y, Chen D, Xiao Y and Luo L:
Efficacy and safety of ultrasound-guided fascia iliaca compartment
block using dexmedetomidine combined with ropivacaine in aged
patients undergoing hip replacement. Int J Clin Exp Med.
10:16484–16491. 2017.
|
|
19
|
Wu ZL, Zhou ZF, Xu LX and She SZ: Effect
of dexmedetomidine on patient-controlled intravenous analgesia with
fentanyl in elderly patients after total hip replacement. Nan Fang
Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 31:701–704. 2011.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Peng K, Liu HY, Wu SR, Cheng H and Ji FH:
Effects of combining dexmedetomidine and opioids for postoperative
intravenous patient-controlled analgesia. Clin J Pain.
31:1097–1104. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Reddi D: Preventing chronic postoperative
pain. Anaesthesia. 71 (Suppl 1):64–71. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Zhang Z, Xu H, Zhang Y, Li W, Yang Y, Han
T, Wei Z, Xu X and Gao J: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for
postoperative pain control after lumbar spine surgery: A
meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Clin Anesth.
43:84–89. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Li B, Li Y, Tian S, Wang H, Wu H, Zhang A
and Gao C: Anti-inflammatory effects of perioperative
dexmedetomidine administered as an adjunct to general anesthesia: A
meta-analysis. Sci Rep. 5(12342)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Li S, Yang Y, Yu C, Yao Y, Wu Y, Qian L
and Cheung CW: Dexmedetomidine analgesia effects in patients
undergoing dental implant surgery and its impact on postoperative
inflammatory and oxidative stress. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2015(186736)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Beilin B, Shavit Y, Trabekin E, Mordashev
B, Mayburd E, Zeidel A and Bessler H: The effects of postoperative
pain management on immune response to surgery. Anesth Analg.
97:822–827. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Yang XH, Bai Q, Lv MM, Fu HG, Dong TL and
Zhou Z: Effect of dexmedetomidine on immune function of patients
undergoing radical mastectomy: A double blind and placebo control
study. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 21:1112–1116. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Mei B, Meng G, Xu G, Cheng X, Chen S,
Zhang Y, Zhang M, Liu X and Gu E: Intraoperative sedation with
dexmedetomidine is superior to propofol for elderly patients
undergoing hip arthroplasty. Clin J Pain. 34:811–817.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Liu Y, Ma L, Gao M, Guo W and Ma Y:
Dexmedetomidine reduces postoperative delirium after joint
replacement in elderly patients with mild cognitive impairment.
Aging Clin Exp Res. 28:729–736. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Li Y, He R, Chen S and Qu Y: Effect of
dexmedetomidine on early postoperative cognitive dysfunction and
peri-operative inflammation in elderly patients undergoing
laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Exp Ther Med. 10:1635–1642.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Chen W, Liu B, Zhang F, Xue P, Cui R and
Lei W: The effects of dexmedetomidine on post-operative cognitive
dysfunction and inflammatory factors in senile patients. Int J Clin
Exp Med. 8:4601–4605. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Liu X, Yu Y and Zhu S: Inflammatory
markers in postoperative delirium (POD) and cognitive dysfunction
(POCD): A meta-analysis of observational studies. PLoS One.
13(e0195659)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Jang M, Jung T, Kim SH and Noh J: Sex
differential effect of dexmedetomidine on fear memory extinction
and anxiety behavior in adolescent rats. Neurosci Res. 149:29–37.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Li YY, Ge DJ, Li JY and Qi B: Sex
differences in the morphine-sparing effects of intraoperative
dexmedetomidine in patient-controlled analgesia following general
anesthesia: A consort-prospective, randomized, controlled clinical
trial. Medicine (Baltimore). 95(e3619)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|