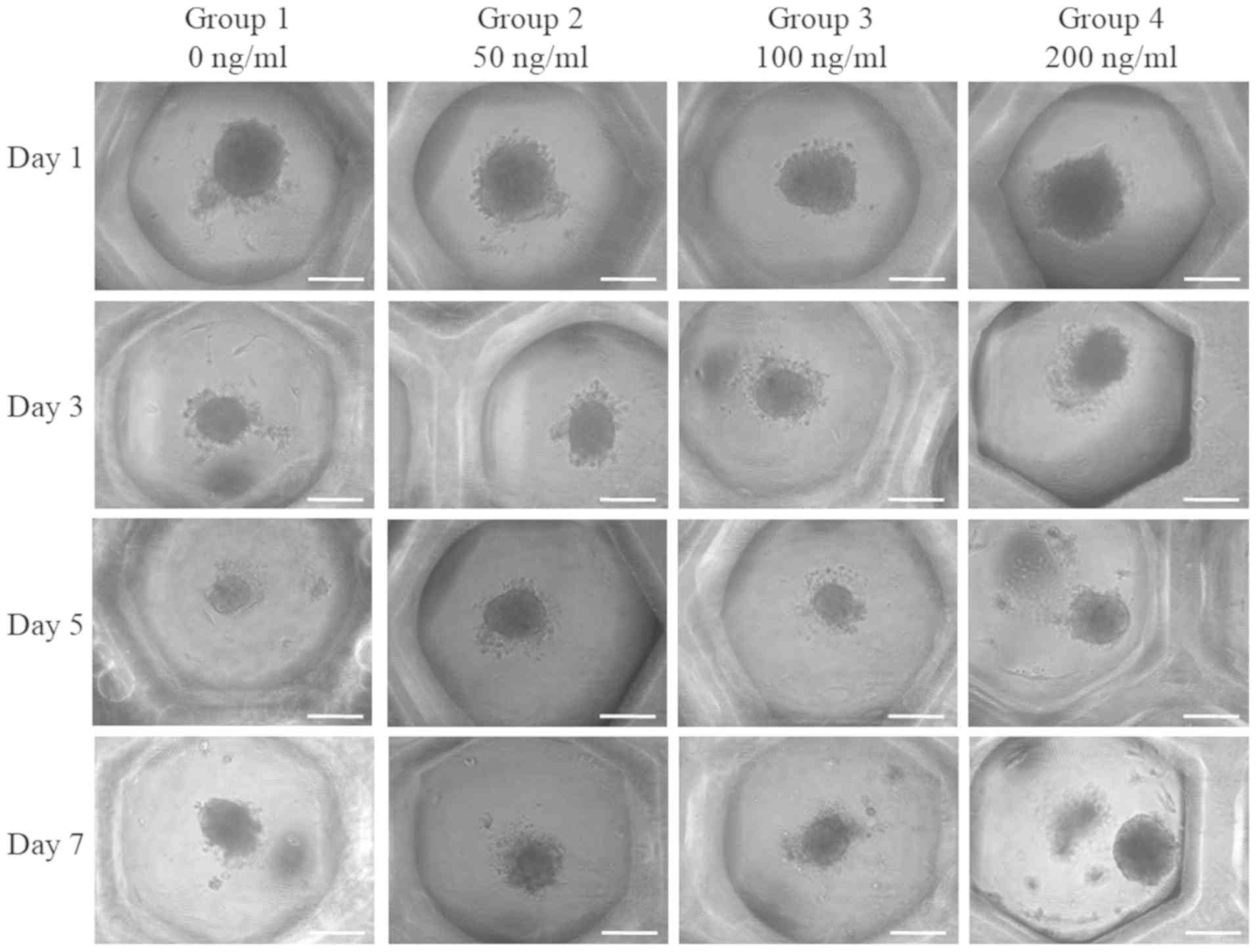
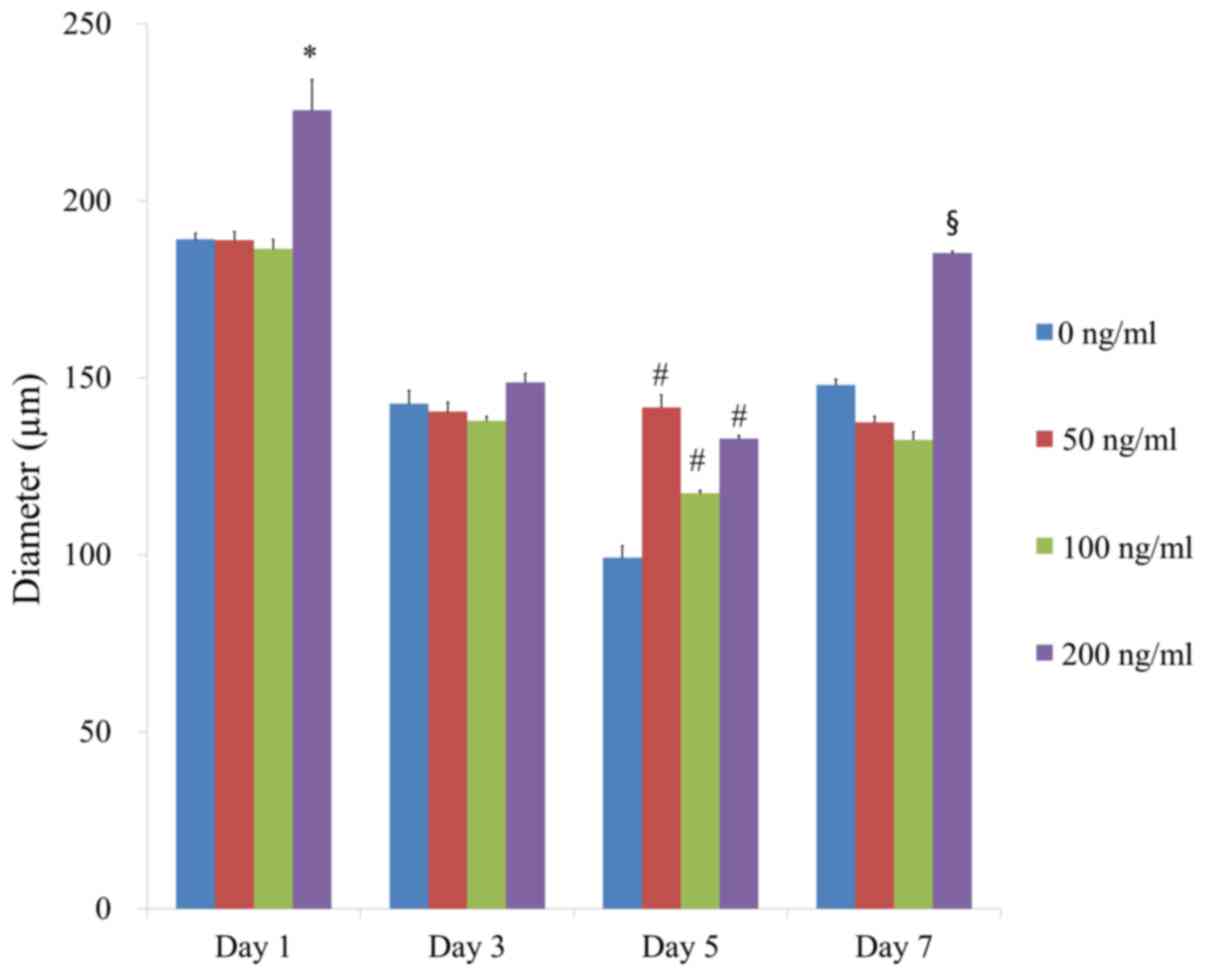
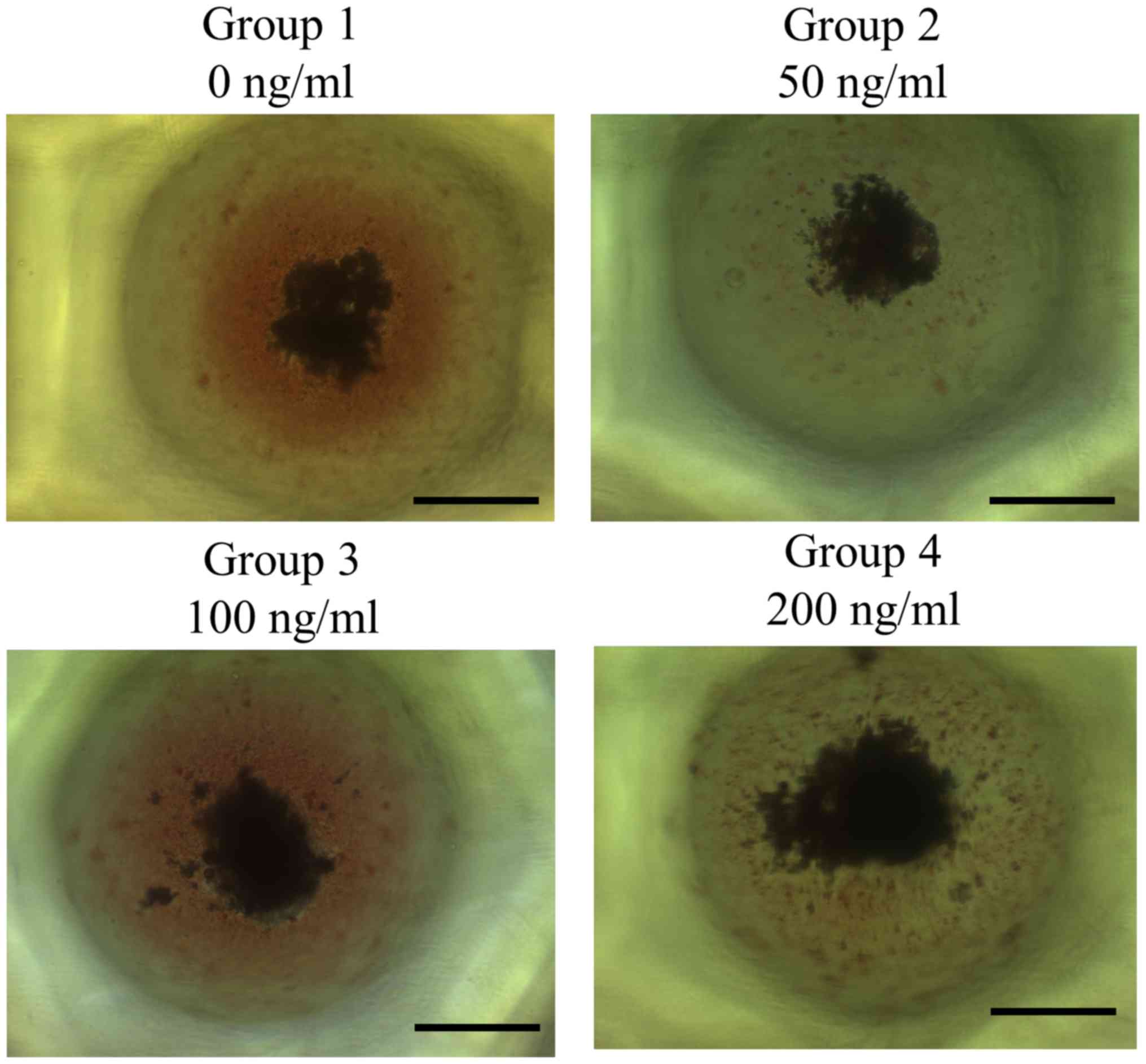
|
1
|
Sohn B, Hwang M, Kim S, Kim HI and Ku Y:
Ridge preservation using basic fibroblast growth factor-2 and
collagenated biphasic calcium phosphate in beagle dogs. J
Periodontal Implant Sci. 47:381–387. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Tiong KH, Mah LY and Leong CO: Functional
roles of fibroblast growth factor receptors (FGFRs) signaling in
human cancers. Apoptosis. 18:1447–1468. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Nunes QM, Li Y, Sun C, Kinnunen TK and
Fernig DG: Fibroblast growth factors as tissue repair and
regeneration therapeutics. PeerJ. 4(e1535)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Frese L, Dijkman PE and Hoerstrup SP:
Adipose tissue-derived stem cells in regenerative medicine.
Transfus Med Hemother. 43:268–274. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Chou YH, Pan SY, Yang CH and Lin SL: Stem
cells and kidney regeneration. J Formos Med Assoc. 113:201–209.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Coutu DL and Galipeau J: Roles of FGF
signaling in stem cell self-renewal, senescence and aging. Aging
(Albany NY). 3:920–933. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Boilly B, Vercoutter-Edouart AS,
Hondermarck H, Nurcombe V and Le Bourhis X: FGF signals for cell
proliferation and migration through different pathways. Cytokine
Growth Factor Rev. 11:295–302. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Henry TD, Grines CL, Watkins MW, Dib N,
Barbeau G, Moreadith R, Andrasfay T and Engler RL: Effects of
Ad5FGF-4 in patients with angina: An analysis of pooled data from
the AGENT-3 and AGENT-4 trials. J Am Coll Cardiol. 50:1038–1046.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Kapur NK and Rade JJ: Fibroblast growth
factor 4 gene therapy for chronic ischemic heart disease. Trends
Cardiovasc Med. 18:133–141. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Jung M, Kern FG, Jorgensen TJ, McLeskey
SW, Blair OC and Dritschilo A: Fibroblast growth factor-4 enhanced
G2 arrest and cell survival following ionizing radiation. Cancer
Res. 54:5194–5197. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Quito FL, Beh J, Bashayan O, Basilico C
and Basch RS: Effects of fibroblast growth factor-4 (k-FGF) on
long-term cultures of human bone marrow cells. Blood. 87:1282–1291.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wu SM, Chiu HC, Chin YT, Lin HY, Chiang
CY, Tu HP, Fu MM and Fu E: Effects of enamel matrix derivative on
the proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human gingival
mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 5(52)2014.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Choi SC, Kim SJ, Choi JH, Park CY, Shim WJ
and Lim DS: Fibroblast growth factor-2 and -4 promote the
proliferation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells by the
activation of the PI3K-Akt and ERK1/2 signaling pathways. Stem
Cells Dev. 17:725–736. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Lee SI, Yeo SI, Kim BB, Ko Y and Park JB:
Formation of size-controllable spheroids using gingiva-derived stem
cells and concave microwells: Morphology and viability tests.
Biomed Rep. 4:97–101. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Lee H, Lee SI, Ko Y and Park JB:
Evaluation of the secretion and release of vascular endothelial
growth factor from two-dimensional culture and three-dimensional
cell spheroids formed with stem cells and osteoprecursor cells. Adv
Clin Exp Med. 27:971–977. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Lee SI, Ko Y and Park JB: Evaluation of
the maintenance of stemness, viability, and differentiation
potential of gingiva-derived stem-cell spheroids. Exp Ther Med.
13:1757–1764. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Jin SH, Lee JE, Yun JH, Kim I, Ko Y and
Park JB: Isolation and characterization of human mesenchymal stem
cells from gingival connective tissue. J Periodontal Res.
50:461–467. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Kim BB, Tae JY, Ko Y and Park JB:
Lovastatin increases the proliferation and osteoblastic
differentiation of human gingiva-derived stem cells in
three-dimensional cultures. Exp Ther Med. 18:3425–3430.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Lee H, Son J, Na CB, Yi G, Koo H and Park
JB: The effects of doxorubicin-loaded liposomes on viability, stem
cell surface marker expression and secretion of vascular
endothelial growth factor of three-dimensional stem cell spheroids.
Exp Ther Med. 15:4950–4960. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Huang X, Chen X, Chen H, Xu D, Lin C and
Peng B: Rho/Rho-associated protein kinase signaling
pathway-mediated downregulation of runt-related transcription
factor 2 expression promotes the differentiation of dental pulp
stem cells into odontoblasts. Exp Ther Med. 15:4457–4464.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Lee H, Lee H, Na CB and Park JB: The
effects of simvastatin on cellular viability, stemness and
osteogenic differentiation using 3-dimensional cultures of stem
cells and osteoblast-like cells. Adv Clin Exp Med. 28:699–706.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Kaur G, Valarmathi MT, Potts JD, Jabbari
E, Sabo-Attwood T and Wang Q: Regulation of osteogenic
differentiation of rat bone marrow stromal cells on 2D nanorod
substrates. Biomaterials. 31:1732–1741. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Mmethod. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Tae JY, Lee H, Lee H, Ko Y and Park JB:
Osteogenic potential of cell spheroids composed of varying ratios
of gingiva-derived and bone marrow stem cells using concave
microwells. Exp Ther Med. 16:2287–2294. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Gao F, Chiu SM, Motan DA, Zhang Z, Chen L,
Ji HL, Tse HF, Fu QL and Lian Q: Mesenchymal stem cells and
immunomodulation: Current status and future prospects. Cell Death
Dis. 7(e2062)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Mahla RS: Stem cells applications in
regenerative medicine and disease therapeutics. Int J Cell Biol.
2016(6940283)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Lee H, Son J, Yi G, Koo H and Park JB:
Cellular viability and osteogenic differentiation potential of
human gingiva-derived stem cells in 2D culture following treatment
with anionic, cationic, and neutral liposomes containing
doxorubicin. Exp Ther Med. 16:4457–4462. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Tomar GB, Srivastava RK, Gupta N,
Barhanpurkar AP, Pote ST, Jhaveri HM, Mishra GC and Wani MR: Human
gingiva-derived mesenchymal stem cells are superior to bone
marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells for cell therapy in
regenerative medicine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 393:377–383.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Zorin VL, Komlev VS, Zorina AI, Khromova
NV, Solovieva EV, Fedotov AY, Eremin II and Kopnin PB: Octacalcium
phosphate ceramics combined with gingiva-derived stromal cells for
engineered functional bone grafts. Biomed Mater.
9(055005)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Futrega K, Mosaad E, Chambers K, Lott WB,
Clements J and Doran MR: Bone marrow-derived stem/stromal cells
(BMSC) 3D microtissues cultured in BMP-2 supplemented osteogenic
induction medium are prone to adipogenesis. Cell Tissue Res.
374:541–553. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Kang SH, Park JB, Kim I, Lee W and Kim H:
Assessment of stem cell viability in the initial healing period in
rabbits with a cranial bone defect according to the type and form
of scaffold. J Periodontal Implant Sci. 49:258–267. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Zhang ZZ, Zhang HZ and Zhang ZY: 3D
printed poly(ε-caprolactone) scaffolds function with
simvastatin-loaded poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) microspheres to
repair load-bearing segmental bone defects. Exp Ther Med. 17:79–90.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Vahabi S, Amirizadeh N, Shokrgozar MA,
Mofeed R, Mashhadi A, Aghaloo M, Sharifi D and Jabbareh L: A
comparison between the efficacy of Bio-Oss, hydroxyapatite
tricalcium phosphate and combination of mesenchymal stem cells in
inducing bone regeneration. Chang Gung Med J. 35:28–37.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Navarro-Tableros V, Gai C, Gomez Y, Giunti
S, Pasquino C, Deregibus MC, Tapparo M, Pitino A, Tetta C, Brizzi
MF, et al: Islet-like structures generated in vitro from adult
human liver stem cells revert hyperglycemia in diabetic SCID mice.
Stem Cell Rev Rep. 15:93–111. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Rao N, Grover GN, Vincent LG, Evans SC,
Choi YS, Spencer KH, Hui EE, Engler AJ and Christman KL: A
co-culture device with a tunable stiffness to understand
combinatorial cell-cell and cell-matrix interactions. Integr Biol.
5:1344–1354. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Lawrence LM, Cottrill A, Valluri A,
Marenzi G, Denning KL, Valluri J, Claudio PP and Day JB: Minimally
manipulative method for the expansion of human bone marrow
mesenchymal stem cells to treat osseous defects. Int J Mol Sci.
20(20)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Moritani Y, Usui M, Sano K, Nakazawa K,
Hanatani T, Nakatomi M, Iwata T, Sato T, Ariyoshi W, Nishihara T,
et al: Spheroid culture enhances osteogenic potential of
periodontal ligament mesenchymal stem cells. J Periodontal Res.
53:870–882. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Žigon-Branc S, Markovic M, Van Hoorick J,
Van Vlierberghe S, Dubruel P, Zerobin E, Baudis S and Ovsianikov A:
Impact of hydrogel stiffness on differentiation of human
adipose-derived stem cell microspheroids. Tissue Eng Part A.
25:1369–1380. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Mraz M, Bartlova M, Lacinova Z, Michalsky
D, Kasalicky M, Haluzikova D, Matoulek M, Dostalova I, Humenanska V
and Haluzik M: Serum concentrations and tissue expression of a
novel endocrine regulator fibroblast growth factor-21 in patients
with type 2 diabetes and obesity. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf).
71:369–375. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Kuroda S, Kasugai S, Oida S, Iimura T,
Ohya K and Ohyama T: Anabolic effect of aminoterminally truncated
fibroblast growth factor 4 (FGF4) on bone. Bone. 25:431–437.
1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Kubota K, Iseki S, Kuroda S, Oida S,
Iimura T, Duarte WR, Ohya K, Ishikawa I and Kasugai S: Synergistic
effect of fibroblast growth factor-4 in ectopic bone formation
induced by bone morphogenetic protein-2. Bone. 31:465–471.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Franke Stenport V, Johansson CB, Sawase T,
Yamasaki Y and Oida S: FGF-4 and titanium implants: A pilot study
in rabbit bone. Clin Oral Implants Res. 14:363–368. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Rath B, Nam J, Knobloch TJ, Lannutti JJ
and Agarwal S: Compressive forces induce osteogenic gene expression
in calvarial osteoblasts. J Biomech. 41:1095–1103. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Salasznyk RM, Williams WA, Boskey A,
Batorsky A and Plopper GE: Adhesion to vitronectin and collagen I
promotes osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem
cells. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2004:24–34. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Guan M, Yao W, Liu R, Lam KS, Nolta J, Jia
J, Panganiban B, Meng L, Zhou P, Shahnazari M, et al: Directing
mesenchymal stem cells to bone to augment bone formation and
increase bone mass. Nat Med. 18:456–462. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Lee H, Min SK and Park JB: Effects of
demographic factors on adipogenic and chondrogenic differentiation
in bone marrow-derived stem cells. Exp Ther Med. 17:3548–3554.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|