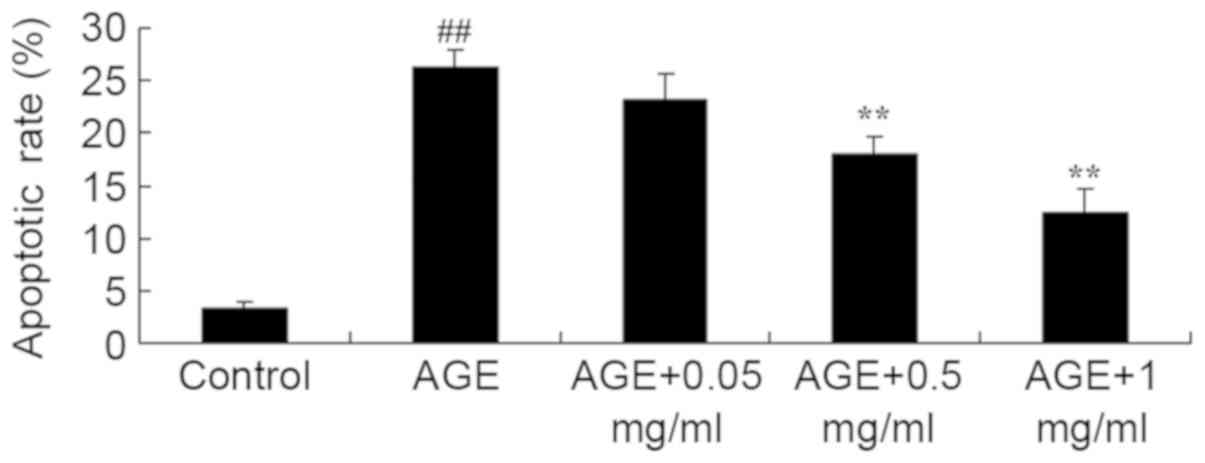
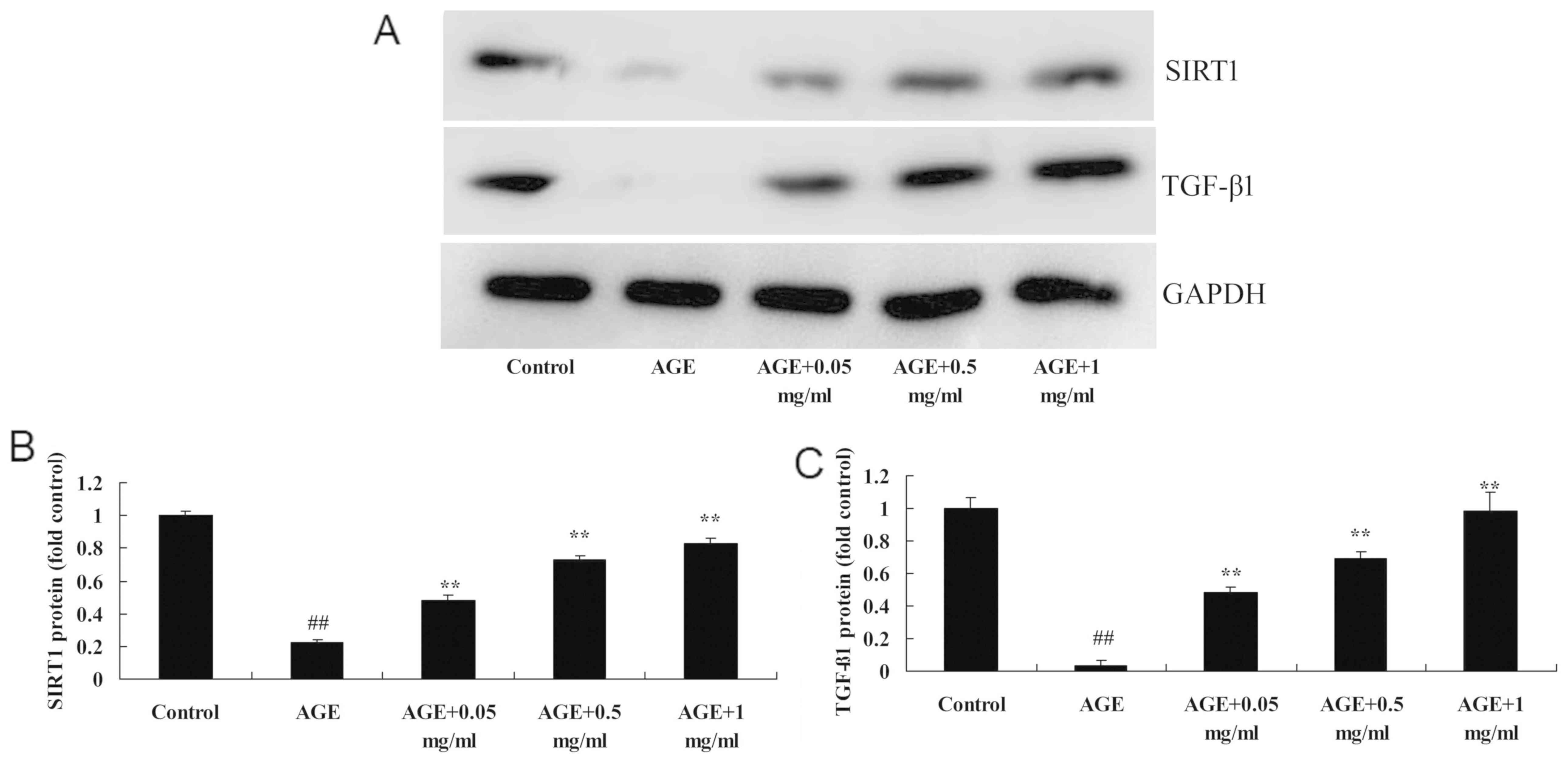
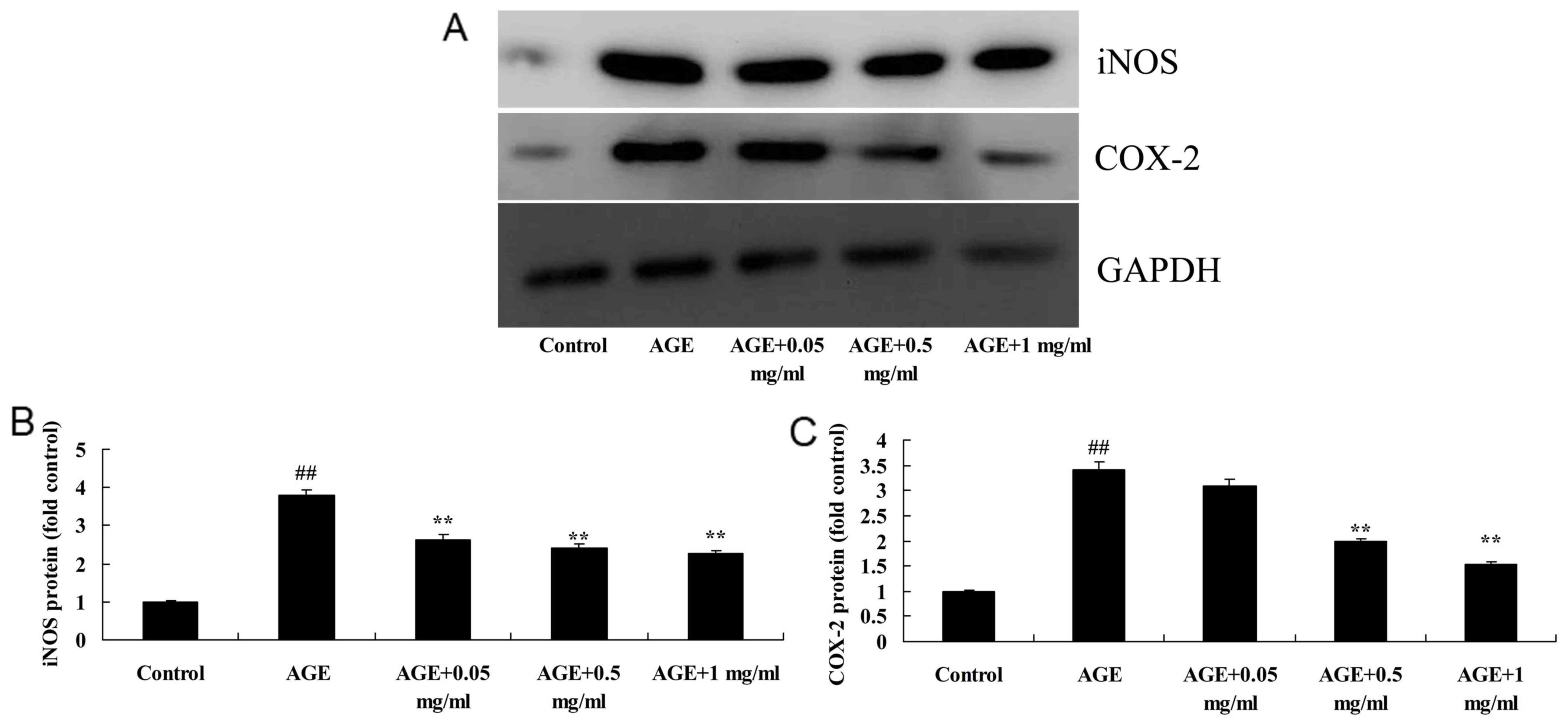
|
1
|
Writing Committee for the Diabetic
Retinopathy Clinical Research Network. Gross JG, Glassman AR,
Jampol LM, Inusah S, Aiello LP, Antoszyk AN, Baker CW, Berger BB,
Bressler NM, et alPanretinal photocoagulation vs intravitreous
ranibizumab for proliferative diabetic retinopathy: A randomized
clinical trial. JAMA. 314:2137–2146. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
de Franciscis S, Gallelli L, Battaglia L,
Molinari V, Montemurro R, Stillitano DM, Buffone G and Serra R:
Cilostazol prevents foot ulcers in diabetic patients with
peripheral vascular disease. Int Wound J. 12:250–253.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Davis KE, Prasad C, Vijayagopal P, Juma S,
Adams-Huet B and Imrhan V: Contribution of dietary advanced
glycation end products (AGE) to circulating AGE: Role of dietary
fat. Br J Nutr. 114:1797–1806. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Komosinska-Vassev K, Olczyk P,
Winsz-Szczotka K, Klimek K and Olczyk K: Plasma biomarkers of
oxidative and AGE-mediated damage of proteins and
glycosaminoglycans during healthy ageing: A possible association
with ECM metabolism. Mech Ageing Dev. 133:538–548. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Calfee CS, Ware LB, Eisner MD, Parsons PE,
Thompson BT, Wickersham N and Matthay MA: NHLBI ARDS Network.
Plasma receptor for advanced glycation end products and clinical
outcomes in acute lung injury. Thorax. 63:1083–1089.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Hipps D, Ausania F, Manas DM, Rose JD and
French JJ: Selective interarterial radiation therapy (SIRT) in
colorectal liver metastases: How do we monitor response? HPB Surg.
2013(570808)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Mortuza R, Chen S, Feng B, Sen S and
Chakrabarti S: High glucose induced alteration of SIRTs in
endothelial cells causes rapid aging in a p300 and FOXO regulated
pathway. PLoS One. 8(e54514)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Donato AJ, Morgan RG, Walker AE and
Lesniewski LA: Cellular and molecular biology of aging endothelial
cells. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 89:122–135. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Roy A, Zhang M, Saad Y and Kolattukudy PE:
Antidicer RNAse activity of monocyte chemotactic protein-induced
protein-1 is critical for inducing angiogenesis. Am J Physiol Cell
Physiol. 305:C1021–C1032. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Marampon F, Gravina GL, Scarsella L,
Festuccia C, Lovat F, Ciccarelli C, Zani BM, Polidoro L, Grassi D,
Desideri G, et al: Angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibition
counteracts angiotensin II-mediated endothelial cell dysfunction by
modulating the p38/SirT1 axis. J Hypertens. 31:1972–1983.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Madani Z, Malaisse WJ and Ait-Yahia D: A
comparison between the impact of two types of dietary protein on
brain glucose concentrations and oxidative stress in high
fructose-induced metabolic syndrome rats. Biomed Rep. 3:731–735.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Mooradian AD, Onstead-Haas L and Haas MJ:
Asymmetrical cross-talk between the endoplasmic reticulum stress
and oxidative stress caused by dextrose. Life Sci. 144:37–48.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Bone DB, Antic M, Vilas G and Hammond JR:
Oxidative stress modulates nucleobase transport in microvascular
endothelial cells. Microvasc Res. 95:68–75. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Nagar H, Jung SB, Kwon SK, Park JB, Shong
M, Song HJ, Jeon BH, Irani K and Kim CS: CRIF1 deficiency induces
p66shc-mediated oxidative stress and endothelial activation. PLoS
One. 9(e98670)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Roy A and Kolattukudy PE: Monocyte
chemotactic protein-induced protein (MCPIP) promotes inflammatory
angiogenesis via sequential induction of oxidative stress,
endoplasmic reticulum stress and autophagy. Cell Signal.
24:2123–2131. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Ding RB, Tian K, Cao YW, Bao JL, Wang M,
He C, Hu Y, Su H and Wan JB: Protective effect of panax
notoginseng saponins on acute ethanol-induced liver injury is
associated with ameliorating hepatic lipid accumulation and
reducing ethanol-mediated oxidative stress. J Agric Food Chem.
63:2413–2422. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Lopes-Virella MF, Baker NL, Hunt KJ, Lyons
TJ, Jenkins AJ and Virella G: DCCT/EDIC Study Group. High
concentrations of AGE-LDL and oxidized LDL in circulating immune
complexes are associated with progression of retinopathy in type 1
diabetes. Diabetes Care. 35:1333–1340. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Ng ZX, Chua KH, Iqbal T and Kuppusamy UR:
Soluble receptor for advanced glycation end-product
(sRAGE)/pentosidine ratio: A potential risk factor determinant for
type 2 diabetic retinopathy. Int J Mol Sci. 14:7480–7491.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Stróżecki P, Kurowski R, Flisiński M,
Stefańska A, Odrowąż-Sypniewska G and Manitius J: Advanced
glycation end products and arterial stiffness in patients with
diabetic nephropathy and patients with chronic kidney disease
without diabetes. Pol Arch Med Wewn. 123:609–616. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
You WH, Wang P, Li MQ, Zhang Y, Peng YL
and Zhang FL: Therapeutic effects of modified Danggui Sini
Decoction on plasma level of advanced glycation end products in
patients with Wagner grade 0 diabetic foot: A randomized controlled
trial. Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Xue Bao. 7:622–628. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Peng XX, Zhang SH, Wang XL, Ye TJ, Li H,
Yan XF, Wei L, Wu ZP, Hu J, Zou CP, et al: Panax notoginseng
flower saponins (PNFS) inhibit LPS-stimulated NO overproduction and
iNOS gene overexpression via the suppression of TLR4-mediated
MAPK/NF-kappa B signaling pathways in RAW264.7 macrophages. Chin
Med. 10(15)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Eiselein L, Nyunt T, Lamé MW, Ng KF,
Wilson DW, Rutledge JC and Aung HH: TGRL lipolysis products induce
stress protein ATF3 via the TGF-β receptor pathway in human aortic
endothelial cells. PLoS One. 10(e0145523)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Star GP, Giovinazzo M and Langleben D:
Effects of bone morphogenic proteins and transforming growth
factor-beta on In-vitro production of endothelin-1 by human
pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells. Vascul Pharmacol.
50:45–50. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Ferrari G, Terushkin V, Wolff MJ, Zhang X,
Valacca C, Poggio P, Pintucci G and Mignatti P: TGF-β1 induces
endothelial cell apoptosis by shifting VEGF activation of p38(MAPK)
from the prosurvival p38β to proapoptotic p38α. Mol Cancer Res.
10:605–614. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Hu W, Zhang Y and Sigdel KR: The effects
of Panax notoginseng saponins on the cytokines and
peritoneal function in rats with peritoneal fibrosis. Ren Fail.
37:1507–1513. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Gao R, Wang Y, Pan Q, Huang G, Li N, Mou J
and Wang D: Fuzhisan, a chinese herbal medicine, suppresses
beta-secretase gene transcription via upregulation of SIRT1
expression in N2a-APP695 cells. Int J Clin Exp Med. 8:7231–7240.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Takizawa Y, Kosuge Y, Awaji H, Tamura E,
Takai A, Yanai T, Yamamoto R, Kokame K, Miyata T, Nakata R and
Inoue H: Up-regulation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS),
silent mating type information regulation 2 homologue 1 (SIRT1) and
autophagy-related genes by repeated treatments with resveratrol in
human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Br J Nutr. 110:2150–2155.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Ota H, Eto M, Kano MR, Kahyo T, Setou M,
Ogawa S, Iijima K, Akishita M and Ouchi Y: Induction of endothelial
nitric oxide synthase, SIRT1, and catalase by statins inhibits
endothelial senescence through the Akt pathway. Arterioscler Thromb
Vasc Biol. 30:2205–2211. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Suo R, Zhao ZZ, Tang ZH, Ren Z, Liu X, Liu
LS, Wang Z, Tang CK, Wei DH and Jiang ZS: Hydrogen sulfide prevents
H2O2-induced senescence in human umbilical
vein endothelial cells through SIRT1 activation. Mol Med Rep.
7:1865–1870. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Du YG, Wang LP, Qian JW, Zhang KN and Chai
KF: Panax notoginseng saponins protect kidney from diabetes
by up-regulating silent information regulator 1 and activating
antioxidant proteins in rats. Chin J Integr Med. 22:910–917.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|