|
1
|
Engel CL, Sharima Rasanayagam M, Gray JM
and Rizzo J: Work and femalebreast cancer: The state of the
evidence, 2002-2017. New Solut. 28:55–78. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Jalilian H, Eeftens M, Ziaei M and Röösli
M: Public exposure to radiofrequency electromagnetic fields in
everyday microenvironments: An updated systematic review for
Europe. Environ Res. 176(108517)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Melnick RL: Commentary on the utility of
the national toxicology program study on cell phone radiofrequency
radiation data for assessing human health risks despite unfounded
criticisms aimed at minimizing the findings of adverse health
effects. Environ Res. 168:1–6. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Mokarram P, Sheikhi M, Mortazavi SMJ, Saeb
S and Shokrpour N: Effect of exposure to 900 MHz GSM mobile phone
radiofrequency radiation on estrogen receptor methylation status in
colon cells of male sprague dawley rats. J Biomed Phys Eng.
7:79–86. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of
Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. Non-ionizing radiation, Part 2:
Radiofrequency electromagnetic fields. IARC Monogr Eval Carcinog
Risks Hum. 102:1–460. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Belyaev I, Dean A, Eger H, Hubmann G,
Jandrisovits R, Kern M, Kundi M, Moshammer H, Lercher P, Müller K,
et al: EUROPAEM EMF Guideline 2016 for the prevention, diagnosis
and treatment of EMF-related health problems and illnesses. Rev
Environ Health. 31:363–397. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Kuo CN, Liao YM, Kuo LN, Tsai HJ, Chang WC
and Yen Y: Cancers in Taiwan: Practical insight from epidemiology,
treatments, biomarkers, and cost. J Formos Med Assoc, Sep 12, 2019
(Online ahead of print).
|
|
8
|
Lee KR, Hwang IC, Han KD, Jung J and Seo
MH: Waist circumference and risk of breast cancer in Korean women:
A nationwide cohort study. Int J Cancer. 142:1554–1559.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Groenendijk FH, Jager A, Cardoso F and van
Deurzen CHM: A nationwide registry-based cohort study of the
MammaPrint genomic risk classifier in invasive breast cancer.
Breast. 38:125–131. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Pop LA, Cojocneanu-Petric RM, Pileczki V,
Morar-Bolba G, Irimie A, Lazar V, Lombardo C, Paradiso A and
Berindan-Neagoe I: Genetic alterations in sporadic triple negative
breast cancer. Breast. 38:30–38. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Elwood PC, Whitmarsh A, Gallacher J, Bayer
A, Adams R, Heslop L, Pickering J, Morgan G, Galante J, Dolwani S,
et al: Healthy living and cancer: Evidence from UK Biobank.
Ecancermedicalscience. 12(792)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Zeinomar N, Thai A, Cloud AJ, McDonald JA,
Liao Y and Terry MB: Alcohol consumption and breast cancer-specific
and all-cause mortality in women diagnosed with breast cancer at
the New York site of the breast cancer family registry. PLoS One.
12(e0189118)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Larsen J, Wallace P, Sim F, Chick J,
Jarvis S, Lidington I, Neidle S, Ogden G and Owens L: Accuracy of
alcohol and breast cancer risk information on Drinkaware's website.
Drug Alcohol Rev. 37:304–306. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Takizawa Y, Kawai M, Kakugawa Y, Nishino
Y, Ohuchi N and Minami Y: Alcohol consumption and breast cancer
risk according to hormone receptor status in Japanese women: A
case-control study. Tohoku J Exp Med. 244:63–73. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Chen Q, Lang L, Wu W, Xu G, Zhang X, Li T
and Huang H: A meta-analysis on the relationship between exposure
to ELF-EMFs and the risk of female breast cancer. PLoS One.
8(e69272)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Balekouzou A, Yin P, Afewerky HK, Bekolo
C, Pamatika CM, Nambei SW, Djeintote M, Doui Doumgba A,
Mossoro-Kpinde CD, Shu C, et al: Behavioral risk factors of breast
cancer in Bangui of Central African Republic: A retrospective
case-control study. PLoS One. 12(e0171154)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Cig B and Naziroglu M: Investigation of
the effects of distance from sources on apoptosis, oxidative stress
and cytosolic calcium accumulation via TRPV1 channels induced by
mobile phones and Wi-Fi in breast cancer cells. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1848:2756–2765. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Esmekaya MA, Canseven AG, Kayhan H, Tuysuz
MZ, Sirav B and Seyhan N: Mitochondrial hyperpolarization and
cytochrome-c release in microwave-exposed MCF-7 cells. Gen Physiol
Biophys. 36:211–218. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Hallberg O: Cancer incidence vs. FM radio
transmitter density. Electromagn Biol Med. 35:343–347.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Alkan A, Kutuk T, Karci E, Yasar A,
Hicsonmez A and Utkan G: Radiation-induced tumor lysis syndrome in
chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Turk J Haematol. 33:248–250.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Wang P, Hou C, Li Y and Zhou D: Wireless
phone use and risk of adult glioma: Evidence from a meta-analysis.
World Neurosurg. 115:e629–e636. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Yang M, Guo W, Yang C, Tang J, Huang Q,
Feng S, Jiang A, Xu X and Jiang G: Mobile phone use and glioma
risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One.
12(e0175136)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Bortkiewicz A, Gadzicka E and Szymczak W:
Mobile phone use and risk for intracranial tumors and salivary
gland tumors-A meta-analysis. Int J Occup Med Environ Health.
30:27–43. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Fenga C: Occupational exposure and risk of
breast cancer. Biomed Rep. 4:282–292. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Sagar S, Dongus S, Schoeni A, Roser K,
Eeftens M, Struchen B, Foerster M, Meier N, Adem S and Röösli M:
Radiofrequency electromagnetic field exposure in everyday
microenvironments in Europe: A systematic literature review. J Expo
Sci Environ Epidemiol. 28:147–160. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Stang A: Critical evaluation of the
Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of
nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur J Epidemiol.
25:603–605. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Pagano M and Gauvreau K: Principles of
biostatistics (2nd edition). Duxbury Press, 2000.
|
|
28
|
Ioannidis JP, Patsopoulos NA and Evangelou
E: Uncertainty in heterogeneity estimates in meta-analyses. BMJ.
335:914–916. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M and
Minder C: Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical
test. BMJ. 315:629–634. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Shi L and Lin L: The trim-and-fill method
for publication bias: Practical guidelines and recommendations
based on a large database of meta-analyses. Medicine (Baltimore).
98(e15987)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J and Altman
DG: PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews
and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Med.
6(e1000097)2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
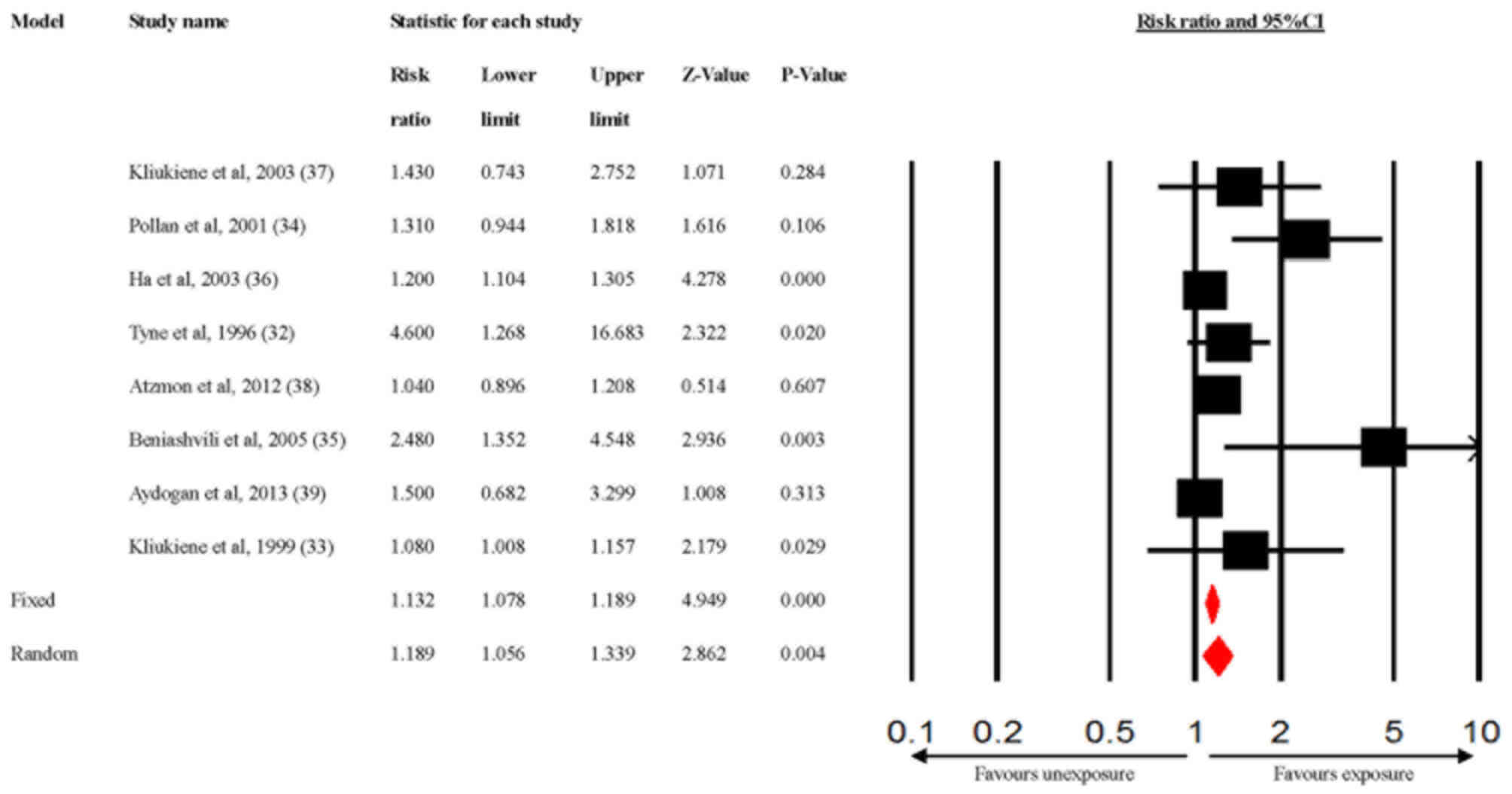
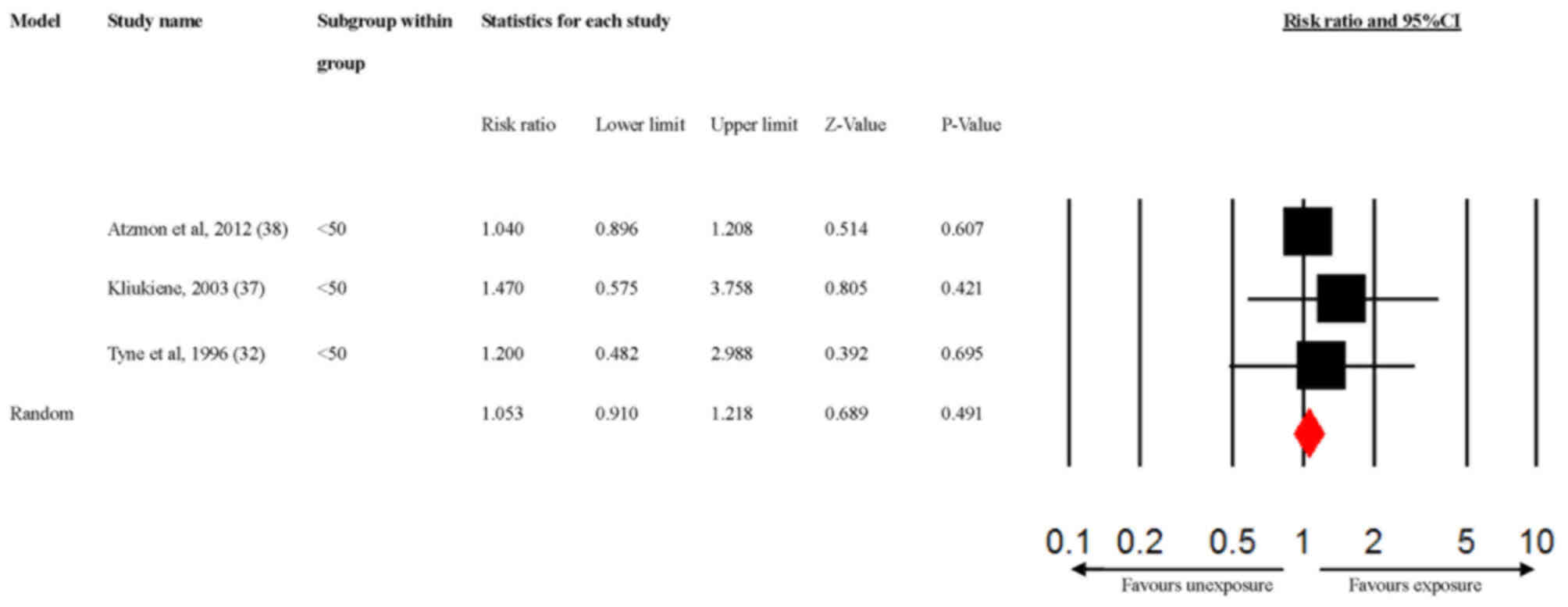
32
|
Tynes T, Hannevik M, Andersen A, Vistnes
AI and Haldorsen T: Incidence of breast cancer in Norwegian female
radio and telegraph operators. Cancer Causes Control. 7:197–204.
1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Kliukiene J, Tynes T, Martinsen JI,
Blaasaas KG and Andersen A: Incidence of breast cancer in a
Norwegian cohort of women with potential workplace exposure to 50
Hz magnetic fields. Am J Ind Med. 36:147–154. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Pollán M, Gustavsson P and Floderus B:
Breast cancer, occupation, and exposure to electromagnetic fields
among Swedish men. Am J Ind Med. 39:276–285. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Beniashvili D, Avinoach I, Baazov D and
Zusman I: Household electromagnetic fields and breast cancer in
elderly women. In Vivo. 19:563–566. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ha M, Lim HJ, Cho SH, Choi HD and Cho KY:
Incidence of cancer in the vicinity of Korean AM radio
transmitters. Arch Environ Health. 58:756–762. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Kliukiene J, Tynes T and Andersen A:
Follow-up of radio and telegraph operators with exposure to
electromagnetic fields and risk of breast cancer. Eur J Cancer
Prev. 12:301–307. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Atzmon I, Linn S, Richter E and Portnov
BA: Cancer risks in the druze isifya village: Reasons and RF/MW
antennas. Pathophysiology. 19:21–28. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Aydoǧan T, Cakcak E, Şimşek O, Erginöz E,
Aydogan F, Hatipoglu S and Kapan S: The effect of current
environmental risk factors on breast cancer. Med J Bakirkoy.
9:176–182. 2013.
|
|
40
|
Bartsch H, Bartsch C, Seebald E, Deerberg
F, Dietz K, Vollrath L and Mecke D: Chronic exposure to a GSM-like
signal (mobile phone) does not stimulate the development of
DMBA-induced mammary tumors in rats: Results of three consecutive
studies. Radiat Res. 157:183–190. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Shih YW, Yang SF, Chien MH, Chang CW,
Chang VHS and Tsai HT: Significant effect of acupressure in
elevating blood stem cell factor during chemotherapy in patients
with gynecologic cancer. J Nurs Res. 26:411–419. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Miah T and Kamat D: Current understanding
of the health effects of electromagnetic fields. Pediatr Ann.
46:e172–e174. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Taheri M, Mortazavi SM, Moradi M, Mansouri
S, Hatam GR and Nouri F: Evaluation of the effect of radiofrequency
radiation emitted from Wi-Fi router and mobile phone simulator on
the antibacterial susceptibility of pathogenic bacteria listeria
monocytogenes and escherichia coli. Dose Response.
15(1559325816688527)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Havas M: When theory and observation
collide: Can non-ionizing radiation cause cancer? Environ Pollut.
221:501–505. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Lodi M, Scheer L, Reix N, Heitz D, Carin
AJ, Thiébaut N, Neuberger K, Tomasetto C and Mathelin C: Breast
cancer in elderly women and altered clinico-pathological
characteristics: A systematic review. Breast cancer res Treat.
166:657–668. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Dugue PA, Bassett JK, Joo JE, Jung CH,
Ming Wong E, Moreno-Betancur M, Schmidt D, Makalic E, Li S, Severi
G, et al: DNA methylation-based biological aging and cancer risk
and survival: Pooled analysis of seven prospective studies. Int J
Cancer. 142:1611–1619. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Hernandez L, Terradas M, Camps J, Martin
M, Tusell L and Genesca A: Aging and radiation: Bad companions.
Aging Cell. 14:153–161. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Ameziane-El-Hassani R and Dupuy C:
Detection of reactive oxygen species in cells undergoing
oncogene-induced senescence. Methods Mol Biol. 1534:139–145.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Lee WJ, Choi Y, Ko S, Cha ES, Kim J, Kim
YM, Kong KA, Seo S, Bang YJ and Ha YW: Projected lifetime cancer
risks from occupational radiation exposure among diagnostic medical
radiation workers in South Korea. BMC Cancer.
18(1206)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
West JG, Kapoor NS, Liao SY, Chen JW,
Bailey L and Nagourney RA: Multifocal breast cancer in young women
with prolonged contact between their breasts and their cellular
phones. Case Rep Med. 2013(354682)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Richter ED, Berman T, Ben-Michael E,
Laster R and Westin JB: Cancer in radar technicians exposed to
radiofrequency/microwave radiation: Sentinel episodes. Int J Occup
Environ Health. 6:187–193. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Warille AA, Altun G, Elamin AA, Kaplan AA,
Mohamed H, Yurt KK and El Elhaj A: Skeptical approaches concerning
the effect of exposure to electromagnetic fields on brain hormones
and enzyme activities. J Microsc Ultrastruct. 5:177–184.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Chang AM, Aeschbach D, Duffy JF and
Czeisler CA: Evening use of light-emitting eReaders negatively
affects sleep, circadian timing, and next-morning alertness. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 112:1232–1237. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Kim J, Seo S, Lee DN, Park S, Im KJ, Park
S and Jin YW: Occupational exposure characteristics and factors
associated with radiation doses among Korean radiation workers.
Radiat Prot Dosimetry, Feb 22, 2020 (Online ahead of print).
|
|
55
|
Koeman T, van den Brandt PA, Slottje P,
Schouten LJ, Goldbohm RA, Kromhout H and Vermeulen R: Occupational
extremely low-frequency magnetic field exposure and selected cancer
outcomes in a prospective Dutch cohort. Cancer Causes Control.
25:203–214. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
McElroy JA, Egan KM, Titus-Ernstoff L,
Anderson HA, Trentham-Dietz A, Hampton JM and Newcomb PA:
Occupational exposure to electromagnetic field and breast cancer
risk in a large, population-based, case-control study in the United
States. J Occup Environ Med. 49:266–274. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Rodgers KM, Udesky JO, Rudel RA and Brody
JG: Environmental chemicals and breast cancer: An updated review of
epidemiological literature informed by biological mechanisms.
Environ Res. 160:152–182. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|