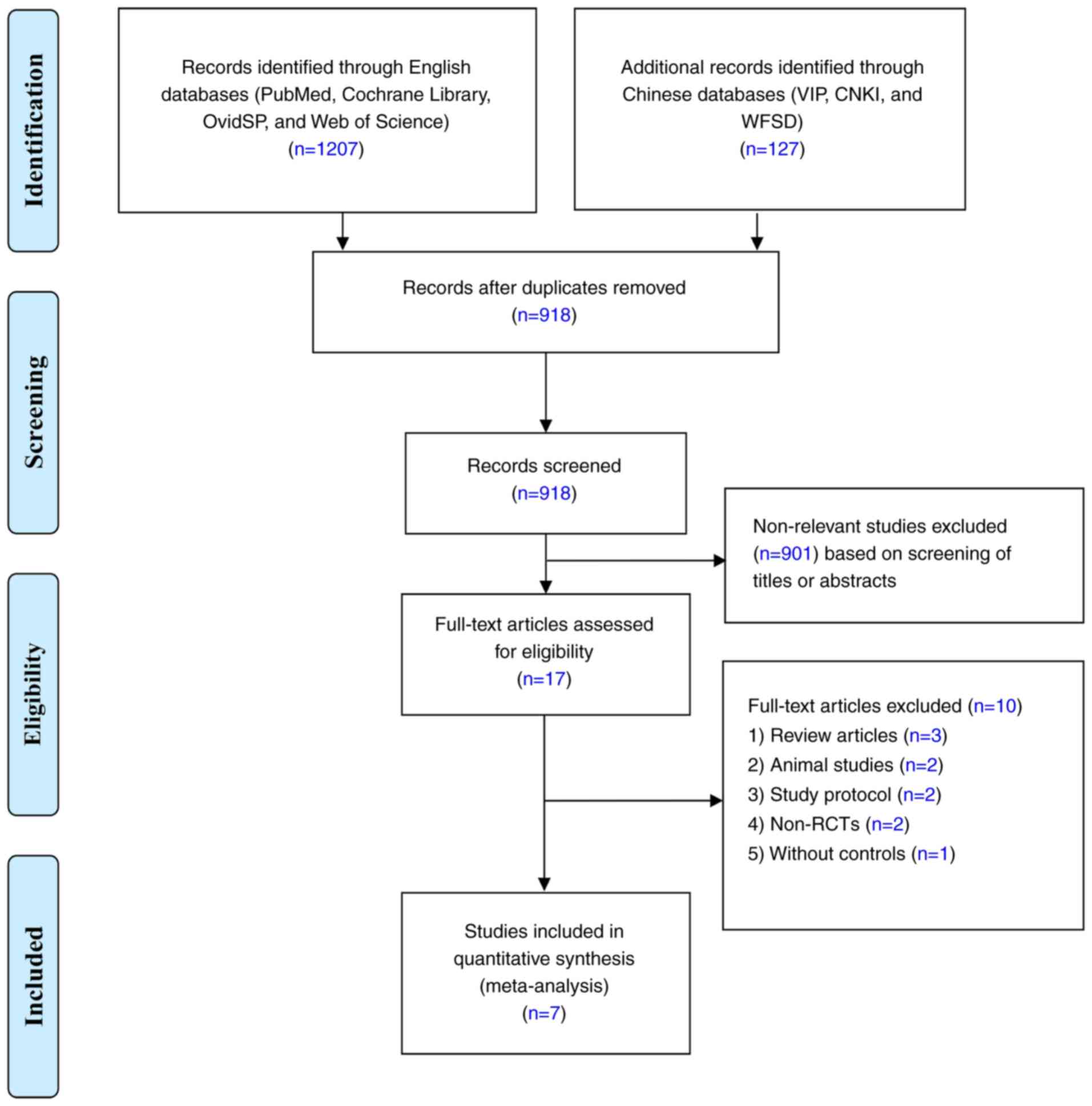
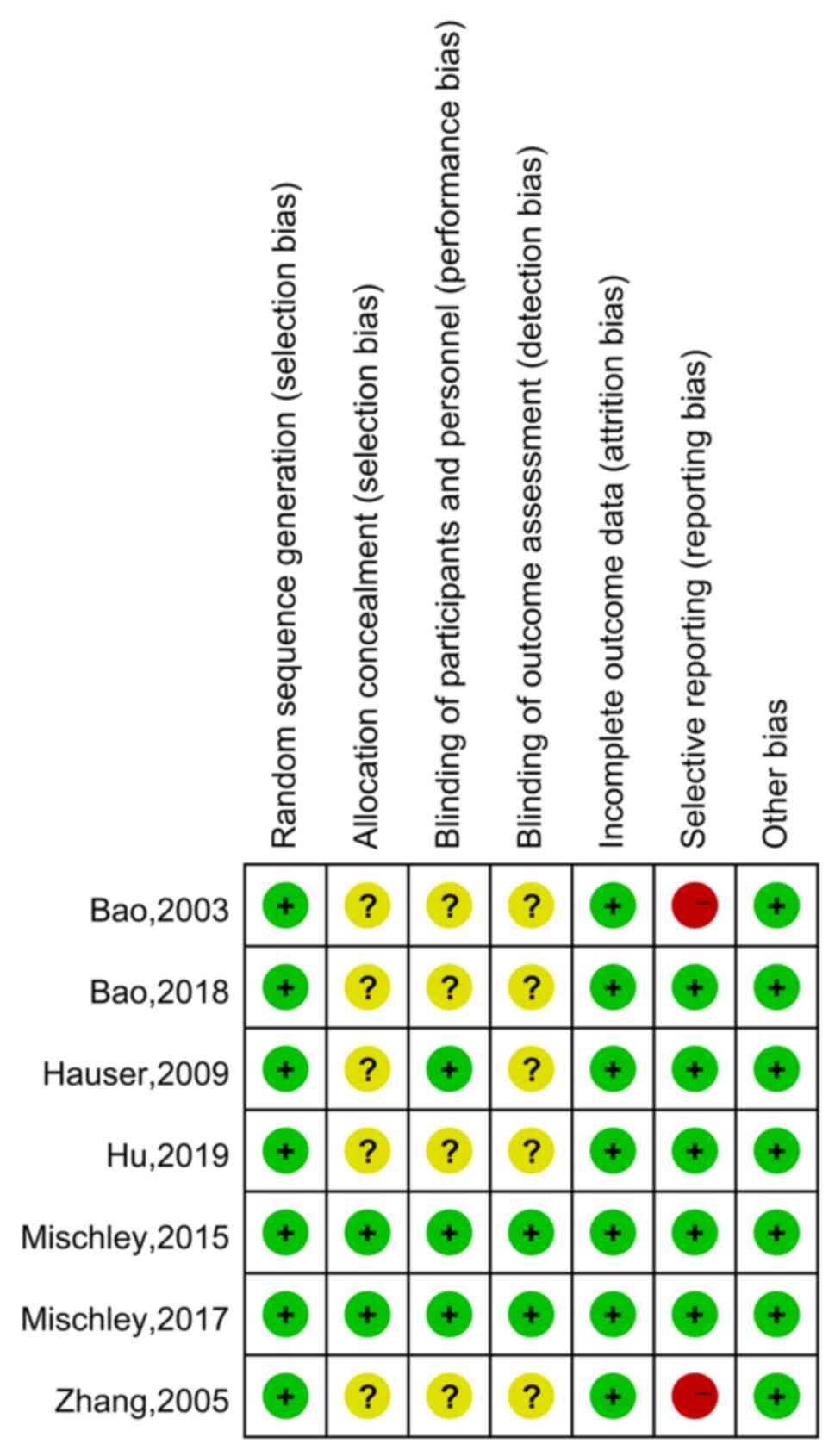
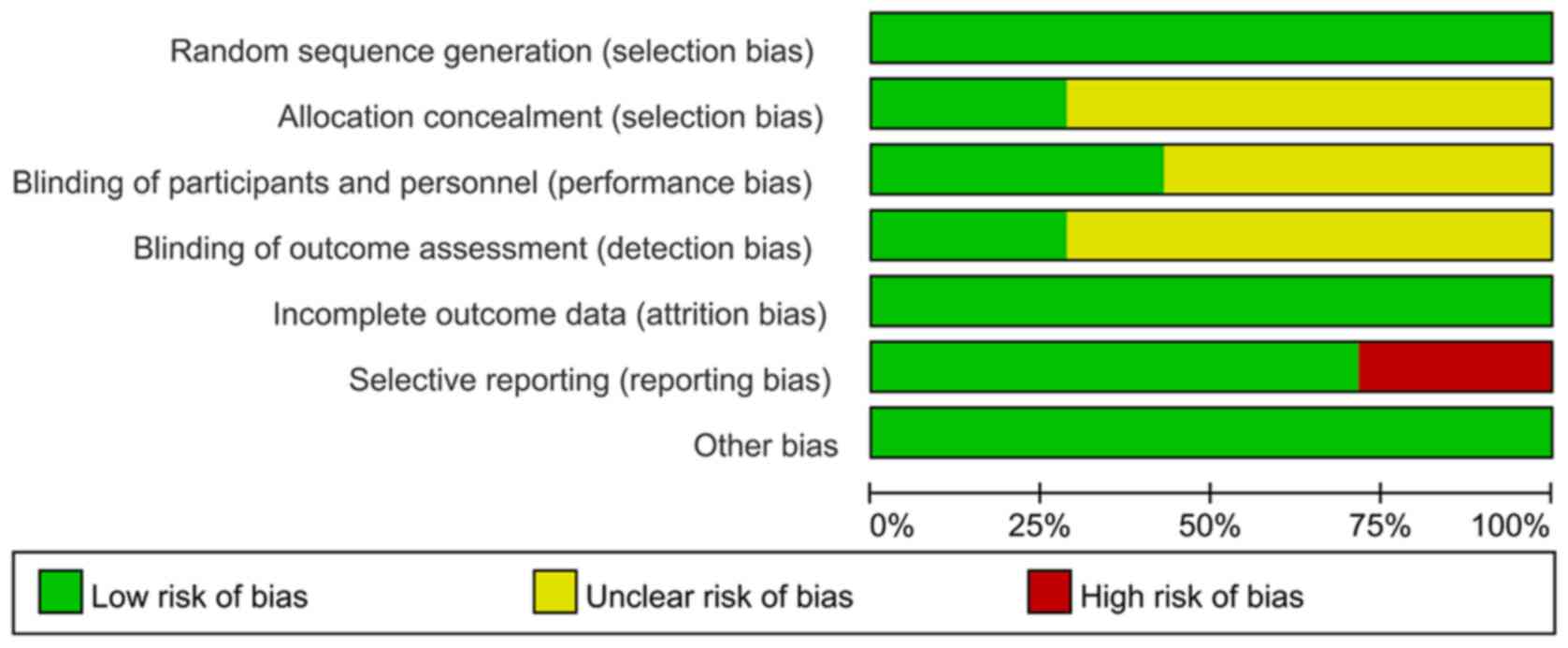
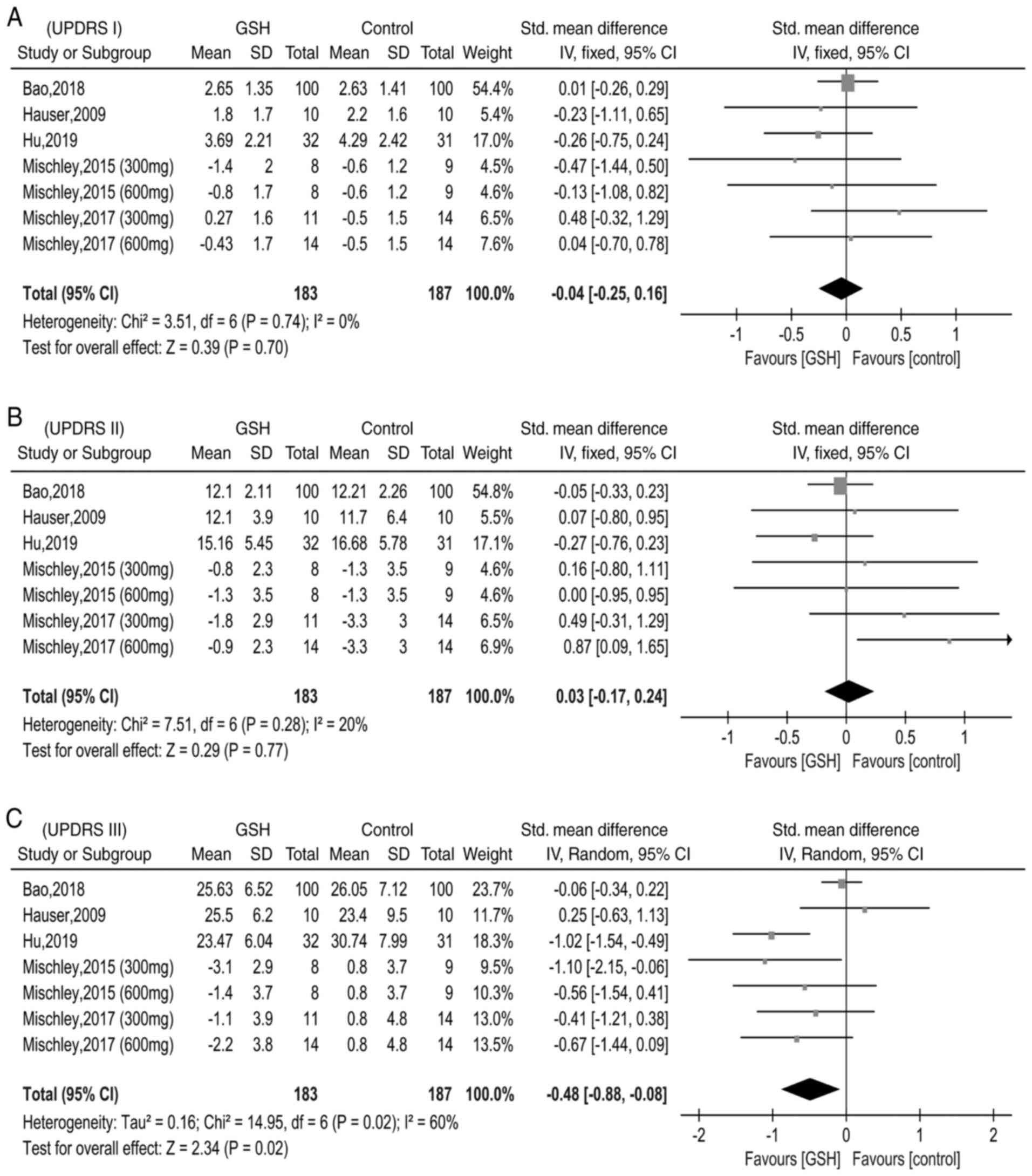
|
1
|
Panicker N, Kanthasamy A and Kanthasamy
AG: Fyn amplifies NLRP3 inflammasome signaling in Parkinson's
disease. Aging (Albany NY). 11:5871–5873. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Grespi F and Melino G: P73 and age-related
diseases: Is there any link with Parkinson disease? Aging (Albany
NY). 4:923–931. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Tamano H, Nishio R, Morioka H and Takeda
A: Extracellular Zn2+ influx into nigral dopaminergic
neurons plays a key role for pathogenesis of
6-hydroxydopamine-induced Parkinson's disease in rats. Mol
Neurobiol. 56:435–443. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Dorsey ER, Constantinescu R, Thompson JP,
Biglan KM, Holloway RG, Kieburtz K, Marshall FJ, Ravina BM,
Schifitto G, Siderowf A and Tanner CM: Projected number of people
with Parkinson disease in the most populous nations, 2005 through
2030. Neurology. 68:384–386. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Smeyne M and Smeyne RJ: Glutathione
metabolism and Parkinson's disease. Free Radic Biol Med. 62:13–25.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Soukup SF, Vanhauwaert R and Verstreken P:
Parkinson's disease: Convergence on synaptic homeostasis. EMBO J.
37(e98960)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Gaki GS and Papavassiliou AG: Oxidative
stress-induced signaling pathways implicated in the pathogenesis of
Parkinson's disease. Neuromolecular Med. 16:217–230.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Bisaglia M, Soriano ME, Arduini I, Mammi S
and Bubacco L: Molecular characterization of dopamine-derived
quinones reactivity toward NADH and glutathione: Implications for
mitochondrial dysfunction in Parkinson disease. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1802:699–706. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Díaz-Hung ML, Yglesias-Rivera A,
Hernández-Zimbrón LF, Orozco-Suárez S, Ruiz-Fuentes JL, Díaz-García
A, León-Martínez R, Blanco-Lezcano L, Pavón-Fuentes N and
Lorigados-Pedre L: Transient glutathione depletion in the
substantia nigra compacta is associated with neuroinflammation in
rats. Neuroscience. 335:207–220. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Hauser RA, Lyons KE, McClain T, Carter S
and Perlmutter D: Randomized, double-blind, pilot evaluation of
intravenous glutathione in Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord.
24:979–983. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Mischley LK, Lau RC, Shankland EG, Wilbur
TK and Padowski JM: Phase IIb study of intranasal glutathione in
Parkinson's disease. J Parkinsons Dis. 7:289–299. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Mischley LK, Leverenz JB, Lau RC, Polissar
NL, Neradilek MB, Samii A and Standish LJ: A randomized,
double-blind phase I/IIa study of intranasal glutathione in
Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord. 30:1696–1701. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Higgins JPT and Green S (eds): Cochrane
Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions, version 5.1.0
(updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. urihttp://training.cochrane.org/handbooksimplehttp://training.cochrane.org/handbook.
|
|
14
|
Bao H: Clinical effect of reduced
glutathione on Parkinson's disease. Chin J Clin Ration Drug Use.
11:44–45. 2018.(In Chinese).
|
|
15
|
Bao Y, Wang H, Chen H, Zhang B, Wang X, Xu
G, Tong J, Wang Y and Yang X: An observation of 30 cases of
Parkinson's disease treated with glutathiono. Anhui Med
Pharmaceutical J. 7:22–24. 2003.(In Chinese).
|
|
16
|
Hu Y and Yang W: Clinical study of reduced
glutathione in the treatment of Parkinsons disease. Chin J Pract
Nervous Dis. 22:720–724. 2019.(In Chinese).
|
|
17
|
Zhang Y, Cao X, Hu H and Sun S:
Therapeutic effect of reduced glutathione for Parkinson disease.
Chin J Rehabil. 20:29–30. 2005.(In Chinese).
|
|
18
|
Aquilano K, Baldelli S and Ciriolo MR:
Glutathione: New roles inredox signaling for an old antioxidant.
Front Pharmacol. 5(196)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Fitzmaurice PS, Ang L, Guttman M, Rajput
AH, Furukawa Y and Kish SJ: Nigral glutathione deficiency is not
specific for idiopathic Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord.
18:969–976. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Pearce RK, Owen A, Daniel S, Jenner P and
Marsden CD: Alterations in the distribution of glutathione in the
substantia nigra in Parkinson's disease. J Neural Transm (Vienna).
104:661–677. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Liddell JR and White AR: Nexus between
mitochondrial function, iron, copper and glutathione in Parkinson's
disease. eurochem Int. 117:126–138. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Mischley LK, Standish LJ, Weiss NS,
Padowski JM, Kavanagh TJ, White CC and Rosenfeld ME: Glutathione as
a biomarker in Parkinson's disease: Associations with aging and
disease severity. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2016(9409363)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Chinta SJ and Andersen JK: Reversible
inhibition of mitochondrial complex I activity following chronic
dopaminergic glutathione depletion in vitro: Implications for
Parkinson's disease. Free Radic Biol Med. 41:1442–1448.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Sechi G, Deeden MG, Bua G, Satta WM,
Deiana GA, Pes GM and Rosati G: Reduced intraveous glutathione in
the treatment of ealy Parkinson's disease. Prog
Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 20:1159–1170. 1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Mischley LK: Glutathione deficiency in
Parkinson's disease: Intranasal administration as a method of
augmentation. J Orthomol Med. 26:32–36. 2011.
|
|
26
|
Zhou GH, Pao YC and Lu JM: The effect of
glutathione on oxidation stress of Parkinson's disease rat. Chin J
Behav Med Sci. 13:267–268. 2004.(In Chinese).
|
|
27
|
Bharath S, Hsu M, Kaur D, Rajagopalan S
and Andersen JK: Glutathione,iron and Parkinson's disease. Biochem
Pharmacol. 64:1037–1048. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Klivenyi P, Andreassen OA, Ferrante RJ,
Dedeoglu A, Mueller G, Lancelot E, Bogdanov M, Andersen JK, Jiang D
and Beal MF: Mice deficient in cellular glutathione peroxidase show
increased vulnerability to malonate, 3-nitropropionic acid, and
1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,5,6-tetrahydropyridine. J Neurosci. 20:1–7.
2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Dalhoff K, Ranek L, Mantoni M and Poulsen
HE: Glutathione treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver.
12:342–343. 1992.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Tedeschi M, De Cesare A, Oriana S, Perego
P, Silva A, Venturino P and Zunino F: The role of glutathione in
combination with cisplatin in the treatment of ovarian cancer.
Cancer Treat Rev. 18:253–259. 1991.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|