|
1
|
Flyvbjerg A: The role of the complement
system in diabetic nephropathy. Nat Rev Nephrol. 13:311–318.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Gu W, Liu Y, Chen Y, Deng W, Ran X, Chen
L, Zhu D, Yang J, Shin J, Lee SW, et al: Multicentre randomized
controlled trial with sensor-augmented pump vs multiple daily
injections in hospitalized patients with type 2 diabetes in China:
Time to reach target glucose. Diabetes Metab. 43:359–363.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Valencia WM and Florez H: How to prevent
the microvascular complications of type 2 diabetes beyond glucose
control. BMJ. 356(i6505)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Xiong Y and Zhou L: The Signaling of
Cellular Senescence in Diabetic Nephropathy. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2019(7495629)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Li J, Wu B, Hu H, Fang X, Liu Z and Wu S:
GdCl3 attenuates the glomerular sclerosis of streptozotocin (STZ)
induced diabetic rats via inhibiting TGF-β/Smads signal pathway. J
Pharmacol Sci. 142:41–49. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Sutariya B, Jhonsa D and Saraf MN: TGF-β:
The connecting link between nephropathy and fibrosis.
Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 38:39–49. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
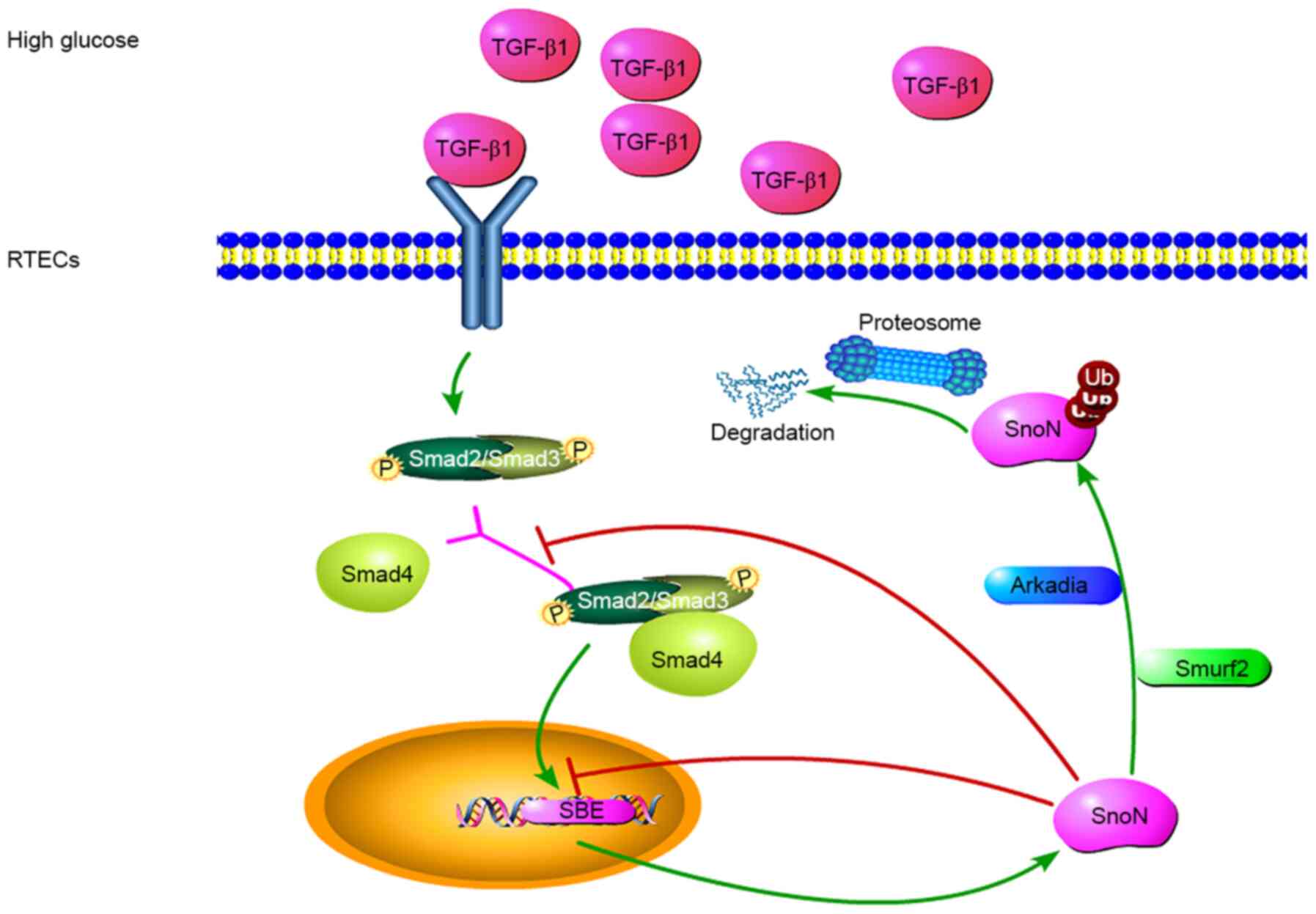
Zeglinski MR, Hnatowich M, Jassal DS and
Dixon IM: SnoN as a novel negative regulator of TGF-β/Smad
signaling: A target for tailoring organ fibrosis. Am J Physiol
Heart Circ Physiol. 308:H75–H82. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Liu R, Wang Y, Xiao Y, Shi M, Zhang G and
Guo B: SnoN as a key regulator of the high glucose-induced
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cells of the proximal tubule.
Kidney Blood Press Res. 35:517–528. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Liu L, Wang Y, Yan R, Li S, Shi M, Xiao Y
and Guo B: Oxymatrine Inhibits Renal Tubular EMT Induced by High
Glucose via Upregulation of SnoN and Inhibition of TGF-β1/Smad
Signaling Pathway. PLoS One. 11(e0151986)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Luo DD, Phillips A and Fraser D: Bone
morphogenetic protein-7 inhibits proximal tubular epithelial cell
Smad3 signaling via increased SnoN expression. Am J Pathol.
176:1139–1147. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Jahchan NS and Luo K: SnoN in mammalian
development, function and diseases. Curr Opin Pharmacol.
10:670–675. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Liu S, Yu N, Zhang XL, Chen XQ and Tang
LQ: Regulatory effect of berberine on unbalanced expressions of
renal tissue TGF-beta1/SnoN and smad signaling pathway in rats with
early diabetic nephropathy. Zhongguo Zhongyao Zazhi. 37:3604–3610.
2012.PubMed/NCBI(In Chinese).
|
|
13
|
Sakairi T, Hiromura K, Takahashi S,
Hamatani H, Takeuchi S, Tomioka M, Maeshima A, Kuroiwa T and Nojima
Y: Effects of proteasome inhibitors on rat renal fibrosis in vitro
and in vivo. Nephrology (Carlton). 16:76–86. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Wang Y, Zhang X, Mao Y, Liang L, Liu L,
Peng W, Liu H, Xiao Y, Zhang Y, Zhang F, et al: Smad2 and Smad3
play antagonistic roles in high glucose-induced renal tubular
fibrosis via the regulation of SnoN. Exp Mol Pathol.
113(104375)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Wang Y, Mao Y, Zhang X, Liu H, Peng W,
Liang L, Shi M, Xiao Y, Zhang Y, Zhang F, et al: TAK1 may promote
the development of diabetic nephropathy by reducing the stability
of SnoN protein. Life Sci. 228:1–10. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Kajino T, Omori E, Ishii S, Matsumoto K
and Ninomiya-Tsuji J: TAK1 MAPK kinase kinase mediates transforming
growth factor-beta signaling by targeting SnoN oncoprotein for
degradation. J Biol Chem. 282:9475–9481. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Satirapoj B and Adler SG: Prevalence and
Management of Diabetic Nephropathy in Western Countries. Kidney
Dis. 1:61–70. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Zhang Q, Li Y and Chen L: Effect of
berberine in treating type 2 diabetes mellitus and complications
and its relevant mechanisms. Zhongguo Zhongyao Zazhi. 40:1660–1665.
2015.PubMed/NCBI(In Chinese).
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Mise K, Ueno T, Hoshino J, Hazue R, Sumida
K, Yamanouchi M, Hayami N, Suwabe T, Hiramatsu R, Hasegawa E, et
al: Nodular lesions in diabetic nephropathy: Collagen staining and
renal prognosis. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 127:187–197.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Kato M, Park JT and Natarajan R: MicroRNAs
and the glomerulus. Exp Cell Res. 318:993–1000. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Loboda A, Sobczak M, Jozkowicz A and Dulak
J: TGF-β1/Smads and miR-21 in Renal Fibrosis and Inflammation.
Mediators Inflamm. 2016(8319283)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Sun Z, Ma Y, Chen F, Wang S, Chen B and
Shi J: miR-133b and miR-199b knockdown attenuate TGF-β1-induced
epithelial to mesenchymal transition and renal fibrosis by
targeting SIRT1 in diabetic nephropathy. Eur J Pharmacol.
837:96–104. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Deheuninck J and Luo K: Ski and SnoN,
potent negative regulators of TGF-β signaling. Cell Res. 19:47–57.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Ma T-T and Meng XM: TGF-β/Smad and Renal
Fibrosis. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1165:347–364. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Stroschein SL, Wang W, Zhou S, Zhou Q and
Luo K: Negative feedback regulation of TGF-beta signaling by the
SnoN oncoprotein. Science. 286:771–774. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Ciechanover A, Orian A and Schwartz AL:
The ubiquitin-mediated proteolytic pathway: Mode of action and
clinical implications. J Cell Biochem Suppl. 34:40–51.
2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Inoue Y and Imamura T: Regulation of
TGF-beta family signaling by E3 ubiquitin ligases. Cancer Sci.
99:2107–2112. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Li XZ, Feng JT, Hu CP, Chen ZQ, Gu QH and
Nie HP: Effects of Arkadia on airway remodeling through enhancing
TGF-beta signaling in allergic rats. Lab Invest. 90:997–1003.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Briones-Orta MA, Levy L, Madsen CD, Das D,
Erker Y, Sahai E and Hill CS: Arkadia regulates tumor metastasis by
modulation of the TGF-β pathway. Cancer Res. 73:1800–1810.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Levy L, Howell M, Das D, Harkin S,
Episkopou V and Hill CS: Arkadia activates Smad3/Smad4-dependent
transcription by triggering signal-induced SnoN degradation. Mol
Cell Biol. 27:6068–6083. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Tan R, He W, Lin X, Kiss LP and Liu Y:
Smad ubiquitination regulatory factor-2 in the fibrotic kidney:
Regulation, target specificity, and functional implication. Am J
Physiol Renal Physiol. 294:F1076–F1083. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|