|
1
|
Sargent MA: What is the normal prevalence
of vesicoureteral reflux? Pediatr Radiol. 30:587–593.
2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Yeung CK, Godley ML, Dhillon HK, Gordon I,
Duffy PG and Ransley PG: The characteristics of primary
vesico-ureteric reflux in male and female infants with pre-natal
hydronephrosis. Br J Urol. 80:319–327. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Peters C and Rushton HG: Vesicoureteral
reflux associated renal damage: Congenital reflux nephropathy and
acquired renal scarring. J Urol. 184:265–273. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Noe HN, Wyatt RJ, Peeden JN Jr and Rivas
ML: The transmission of vesicoureteral reflux from parent to child.
J Urol. 148:1869–1871. 1992.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Jerkins GR and Noe HN: Familial
vesicoureteral reflux: A prospective study. J Urol. 128:774–778.
1982.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Wan J, Greenfield SP, Ng M, Zerin M,
Ritchey ML and Bloom D: Sibling reflux: A dual center retrospective
study. J Urol. 156:677–679. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Parekh DJ, Pope JC IV, Adams MC and Brock
JW III: Outcome of sibling vesicoureteral reflux. J Urol.
167:283–284. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chapman CJ, Bailey RR, Janus ED, Abbott GD
and Lynn KL: Vesicoureteric reflux: Segregation analysis. Am J Med
Genet. 20:577–584. 1985.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Feather SA, Malcolm S, Woolf AS, Wright V,
Blaydon D, Reid CJ, Flinter FA, Proesmans W, Devriendt K, Carter J,
et al: Primary, nonsyndromic vesicoureteric reflux and its
nephropathy is genetically heterogeneous, with a locus on
chromosome 1. Am J Hum Genet. 66:1420–1425. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Eccles MR and Jacobs GH: The genetics of
primary vesico-ureteric reflux. Ann Acad Med Singap. 29:337–345.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sanna-Cherchi S, Reese A, Hensle T, Caridi
G, Izzi C, Kim YY, Konka A, Murer L, Scolari F, Ravazzolo R, et al:
Familial vesicoureteral reflux: Testing replication of linkage in
seven new multigenerational kindreds. J Am Soc Nephrol.
16:1781–1787. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Lu W, van Eerde AM, Fan X, Quintero-River
F, Kulkarni S, Ferguson H, Kim HG, Fan Y, Xi Q, Li QG, et al:
Disruption of ROBO2 is associated with urinary tract anomalies and
confers risk of vesicoureteral reflux. Am J Hum Genet. 80:616–632.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Weng PL, Sanna-Cherchi S, Hensle T,
Shapiro E, Werzberger A, Caridi G, Izzi C, Konka A, Reese AC, Cheng
R, et al: A recessive gene for primary vesicoureteral reflux maps
to chromosome 12p11-q13. J Am Soc Nephrol. 20:1633–1640.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Naseri M, Ghiggeri GM, Caridi G and
Abbaszadegan MR: Five cases of severe vesico-ureteric reflux in a
family with an X-linked compatible trait. Pediatr Nephrol.
25:349–352. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Fillion ML, Watt CL and Gupta IR:
Vesicoureteric reflux and reflux nephropathy: From mouse models to
childhood disease. Pediatr Nephrol. 29:757–766. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Ichikawa I, Kuwayama F, Pope JC IV,
Stephens FD and Miyazaki Y: Paradigm shift from classic anatomic
theories to contemporary cell biological views of CAKUT. Kidney
Int. 61:889–898. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Nicolaou N, Pulit SL, Nijman IJ, Monroe
GR, Feitz WF, Schreuder MF, van Eerde AM, de Jong TP, Giltay JC,
van der Zwaag B, et al: Prioritization and burden analysis of rare
variants in 208 candidate genes suggest they do not play a major
role in CAKUT. Kidney Int. 89:476–486. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Hwang DY, Dworschak GC, Kohl S, Saisawat
P, Vivante A, Hilger AC, Reutter HM, Soliman NA, Bogdanovic R,
Kehinde EO, et al: Mutations in 12 known dominant disease-causing
genes clarify many congenital anomalies of the kidney and urinary
tract. Kidney Int. 85:1429–1433. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Kleinjan DA and van Heyningen V:
Long-range control of gene expression: Emerging mechanisms and
disruption in disease. Am J Hum Genet. 76:8–32. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Southard AE, Edelmann LJ and Gelb BD: Role
of copy number variants in structural birth defects. Pediatrics.
129:755–763. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Sanna-Cherchi S, Kiryluk K, Burgess KE,
Bodria M, Sampson MG, Hadley D, Nees SN, Verbitsky M, Perry BJ,
Sterken R, et al: Copy-number disorders are a common cause of
congenital kidney malformations. Am J Hum Genet. 91:987–997.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Caruana G, Wong MN, Walker A, Heloury Y,
Webb N, Johnstone L, James PA, Burgess T and Bertram JF:
Copy-number variation associated with congenital anomalies of the
kidney and urinary tract. Pediatr Nephrol. 30:487–495.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Ohlsson M, Hedberg C, Bradvik B, Lindberg
C, Tajsharghi H, Danielsson O, Melberg A, Udd B, Martinsson T and
Oldfors A: Hereditary myopathy with early respiratory failure
associated with a mutation in A-band titin. Brain. 135:1682–1694.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Östensson M: Statistical Methods for
Genome Wide Association Studies. PhD dissertation, University of
Gothenburg. ISBN, 9789173857420, 2012.
|
|
25
|
Piepsz A, Colarinha P, Gordon I, Hahn K,
Olivier P, Roca I, Sixt R and van Velzen J: Paediatric Committee of
the European Association of Nuclear Medicine. Guidelines for
99mTc-DMSA scintigraphy in children. Eur J Nucl Med. 28:BP37–BP41.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Schwartz GJ, Brion LP and Spitzer A: The
use of plasma creatinine concentration for estimating glomerular
filtration rate in infants, children, and adolescents. Pediatr Clin
North Am. 34:571–590. 1987.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Brochner-Mortensen J, Haahr J and
Christoffersen J: A simple method for accurate assessment of the
glomerular filtration rate in children. Scand J Clin Lab Invest.
33:140–143. 1974.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bengtsson H, Wirapati P and Speed TP: A
single-array preprocessing method for estimating full-resolution
raw copy numbers from all Affymetrix genotyping arrays including
GenomeWideSNP 5 & 6. Bioinformatics. 25:2149–2156.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Olshen AB, Venkatraman ES, Lucito R and
Wigler M: Circular binary segmentation for the analysis of
array-based DNA copy number data. Biostatistics. 5:557–572.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
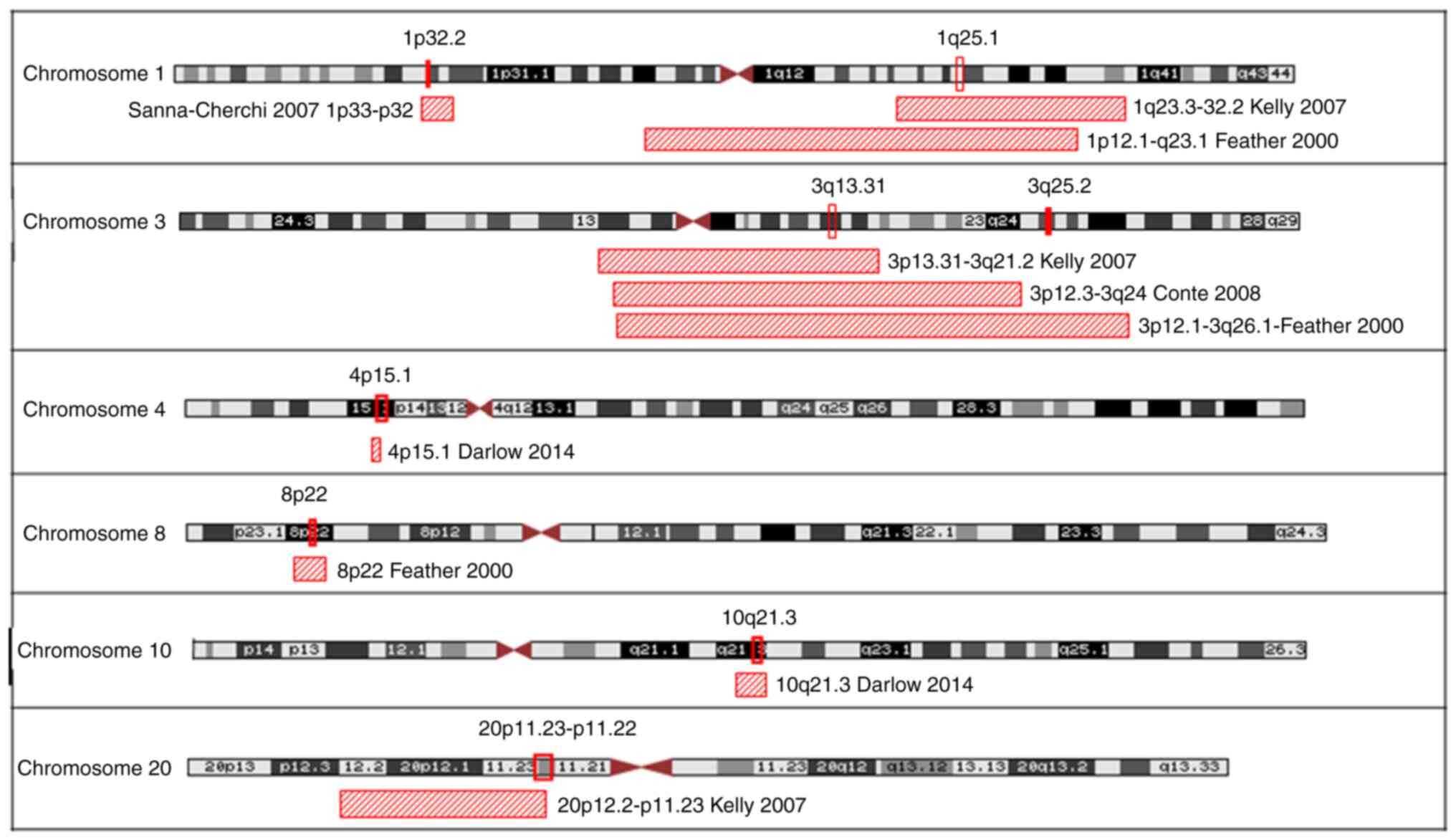
Kelly H, Molony CM, Darlow JM, Pirker ME,
Yoneda A, Green AJ, Puri P and Barton DE: A genome-wide scan for
genes involved in primary vesicoureteric reflux. J Med Genet.
44:710–717. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Darlow JM, Dobson MG, Darlay R, Molony CM,
Hunziker M, Green AJ, Cordell HJ, Puri P and Barton DE: A new
genome scan for primary nonsyndromic vesicoureteric reflux
emphasizes high genetic heterogeneity and shows linkage and
association with various genes already implicated in urinary tract
development. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2:7–29. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Marchini GS, Onal B, Guo CY, Rowe CK,
Kunkel L, Bauer SB, Retik AB and Nguyen HT: Genome gender diversity
in affected sib-pairs with familial vesico-ureteric reflux
identified by single nucleotide polymorphism linkage analysis. BJU
Int. 109:1709–1714. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Cordell HJ, Darlay R, Charoen P, Stewart
A, Gullett AM, Lambert HJ, Malcolm S, Feather SA, Goodship TH,
Woolf AS, et al: Whole-genome linkage and association scan in
primary, nonsyndromic vesicoureteric reflux. J Am Soc Nephrol.
21:113–123. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Briggs CE, Guo CY, Schoettler C, Rosoklija
I, Silva A, Bauer SB, Retik AB, Kunkel L and Nguyen HT: A genome
scan in affected sib-pairs with familial vesicoureteral reflux
identifies a locus on chromosome 5. Eur J Hum Genet. 18:245–250.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Sanna-Cherchi S, Caridi G, Weng PL,
Dagnino M, Seri M, Konka A, Somenzi D, Carrea A, Izzi C, Casu D, et
al: Localization of a gene for nonsyndromic renal hypodysplasia to
chromosome 1p32-33. Am J Hum Genet. 80:539–549. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Casas KA, Mononen TK, Mikail CN, Hassed
SJ, Li S, Mulvihill JJ, Lin HJ and Falk RE: Chromosome 2q terminal
deletion: Report of 6 new patients and review of
phenotype-breakpoint correlations in 66 individuals. Am J Med Genet
A. 130A:331–339. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Conte ML, Bertoli-Avella AM, de Graaf BM,
Lama G, La Manna A, Grassia C, Rambaldi PF, Oostra BA, Perrotta S
and Punzo F: A genome search for primary vesicoureteral reflux
shows further evidence for genetic heterogeneity. Pediatr Nephrol.
23:587–595. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Williams G, Fletcher JT, Alexander SI and
Craig JC: Vesicoureteral reflux. J Am Soc Nephrol. 19:847–862.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Carvas F, Silva A and Nguyen HT: The
genetics of primary, nonsyndromic vesicoureteral reflux. Curr Opin
Urol. 20:336–342. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Vukicevic S, Helder MN and Luyten FP:
Developing human lung and kidney are major sites for synthesis of
bone morphogenetic protein-3 (osteogenin). J Histochem Cytochem.
42:869–875. 1994.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Takahashi H and Ikeda T: Transcripts for
two members of the transforming growth factor-beta superfamily
BMP-3 and BMP-7 are expressed in developing rat embryos. Dev Dyn.
207:439–449. 1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Cancilla B, Ford-Perriss MD and Bertram
JF: Expression and localization of fibroblast growth factors and
fibroblast growth factor receptors in the developing rat kidney.
Kidney Int. 56:2025–2039. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Dudley AT, Godin RE and Robertson EJ:
Interaction between FGF and BMP signaling pathways regulates
development of metanephric mesenchyme. Genes Dev. 13:1601–1613.
1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Cirillo E, Giardino G, Gallo V, Galasso G,
Romano R, D'Assante R, Scalia G, Del Vecchio L, Nitsch L, Genesio R
and Pignata C: DiGeorge-like syndrome in a child with a 3p12.3
deletion involving MIR4273 gene born to a mother with gestational
diabetes mellitus. Am J Med Genet A. 173:1913–1918. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Kohl S, Hwang DY, Dworschak GC, Hilger AC,
Saisawat P, Vivante A, Stajic N, Bogdanovic R, Reutter HM, Kehinde
EO, et al: Mild recessive mutations in six Fraser syndrome-related
genes cause isolated congenital anomalies of the kidney and urinary
tract. J Am Soc Nephrol. 25:1917–1922. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Bernardo GM and Keri RA: FOXA1: A
transcription factor with parallel functions in development and
cancer. Biosci Rep. 32:113–130. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Kaestner KH: The FoxA factors in
organogenesis and differentiation. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 20:527–532.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Siomou E, Mitsioni AG, Giapros V, Bouba I,
Noutsopoulos D and Georgiou I: Copy-number variation analysis in
familial nonsyndromic congenital anomalies of the kidney and
urinary tract: Evidence for the causative role of a transposable
element-associated genomic rearrangement. Mol Med Rep.
15:3631–3636. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|