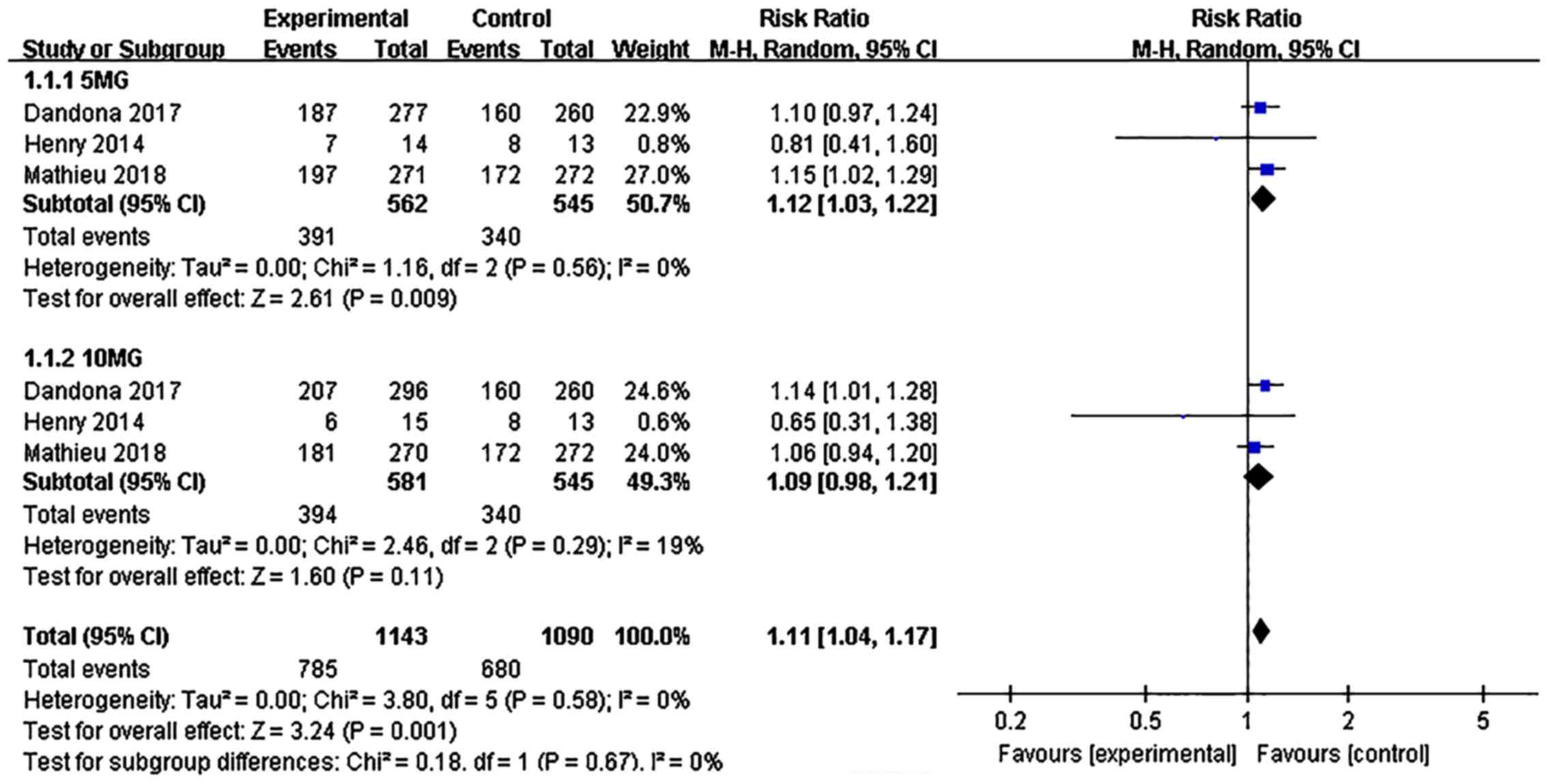
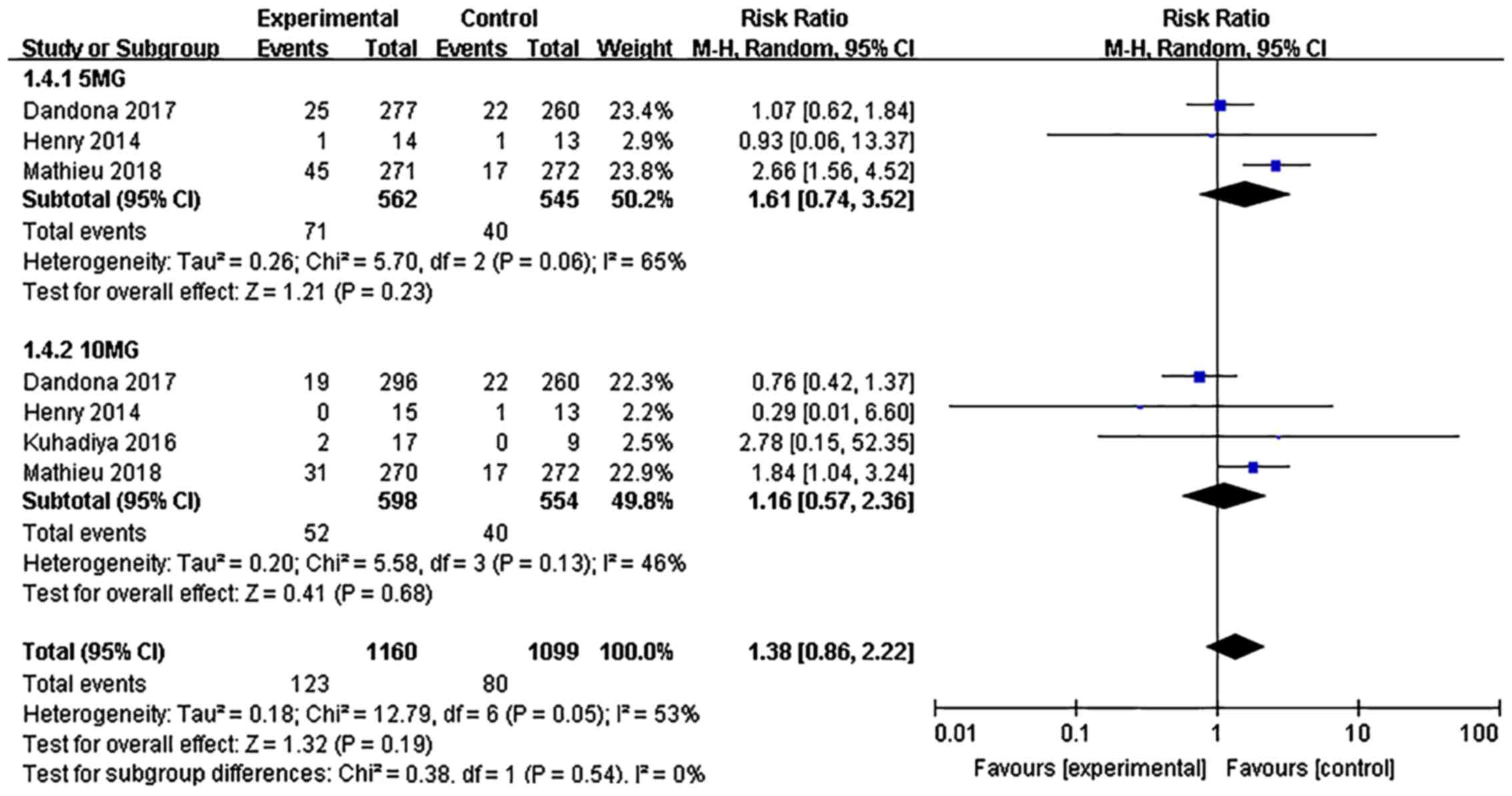
|
1
|
Chiang JL, Kirkman MS, Laffel LM and
Peters AL: Type 1 Diabetes Sourcebook Authors. Type 1 diabetes
through the life span: A position statement of the American
diabetes association. Diabetes Care. 37:2034–2054. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Aschner P, Horton E, Leiter LA, Munro N
and Skyler JS: Global Partnership For Effective Diabetes
Management. Practical steps to improving the management of type 1
diabetes: Recommendations from the Global partnership for effective
diabetes management. Int J Clin Pract. 64:305–315. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Miller KM, Foster NC, Beck RW, Bergenstal
RM, DuBose SN, DiMeglio LA, Maahs DM and Tamborlane WV: T1D
Exchange Clinic Network. Current state of type 1 diabetes treatment
in the U.S.: Updated data from the T1D exchange clinic registry.
Diabetes Care. 38:971–978. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Bode BW and Garg SK: The emerging role of
adjunctive noninsulin antihyperglycemic therapy in the management
of type 1 diabetes. Endocr Pract. 22:220–230. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Lyons SK, Hermann JM, Miller KM, Hofer SE,
Foster NC, Rami-Merhar BM, Aleppo G, Seufert J, DiMeglio LA, Danne
T, et al: Use of adjuvant pharmacotherapy in type 1 diabetes:
International comparison of 49,996 individuals in the prospective
diabetes follow-up and T1D exchange registries. Diabetes Care.
40:e139–e140. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Petrie JR, Chaturvedi N, Ford I, Brouwers
MC, Greenlaw N, Tillin T, Hramiak I, Hughes AD, Jenkins AJ, Klein
BE, et al: Cardiovascular and metabolic effects of metformin in
patients with type 1 diabetes (REMOVAL): A double-blind,
randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol.
5:597–609. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Garg S, Moser E, Bode B, Klaff L, Hiatt W,
Beatson C and Snell-Bergeon J: Effect of sitagliptin on
post-prandial glucagon and GLP-1 levels in patients with type 1
diabetes: Investigator initiated, double-blind, randomized, placebo
controlled trial. Endocr Pract. 19:19–28. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Ellis SL, Moser EG, Snell-Bergeon JK,
Rodionova AS, Hazenfield RM and Garg SK: Effect of sitagliptin on
glucose control in adult patients with type 1 diabetes: A pilot,
double-blind, randomized, crossover trial. Diabet Med.
28:1176–1181. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Mathieu C, Zinman B, Hemmingsson JU, Woo
V, Colman P, Christiansen E, Linder M and Bode B: ADJUNCT ONE
Investigators. Efficacy and safety of liraglutide added to insulin
treatment in type 1 diabetes: The ADJUNCT ONE treat to-target
randomized trial. Diabetes Care. 39:1702–1710. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Chen J, Williams S, Ho S, Loraine H, Hagan
D, Whaley JM and Feder JN: Quantitative PCR tissue expression
profiling of the human SGLT2 gene and related family members.
Diabetes Ther. 1:57–92. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Chao EC and Henry RR: SGLT2 inhibition-a
novel strategy for diabetes treatment. Nat Rev Drug Discov.
9:551–559. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Sun YN, Zhou Y, Chen X, Che WS and Leung
SW: The efficacy of dapagliflozin combined with hypoglycaemic drugs
in treating type 2 diabetes mellitus: Meta-analysis of randomised
controlled trials. BMJ Open. 4(e004619)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Zhang M, Zhang L, Wu B, Song H, An Z and
Li S: Dapagliflozin treatment for type 2 diabetes: A systematic
review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Diabetes
Metab Res Rev. 30:204–221. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Fioretto P, Giaccari A and Sesti G:
Efficacy and safety of dapagliflozin, a sodium glucose
cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor in diabetes mellitus. Cardiovasc
Diabetol. 14(142)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Weber MA, Mansfield TA, Cain VA, Iqbal N,
Parikh S and Ptaszynska A: Blood pressure and glycaemic effects of
dapagliflozin versus placebo in patients with type 2 diabetes on
combination antihypertensive therapy: A randomised, double blind,
placebo-controlled, phase 3 study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol.
4:211–220. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
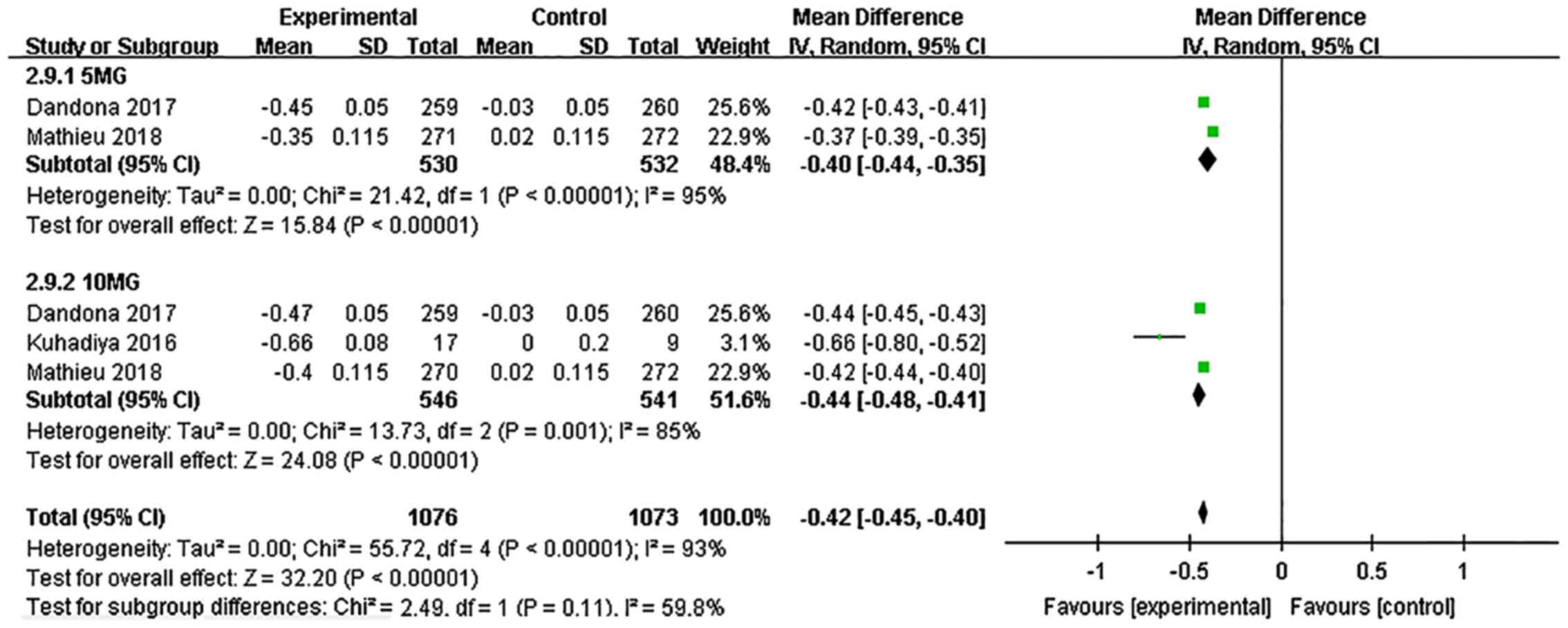
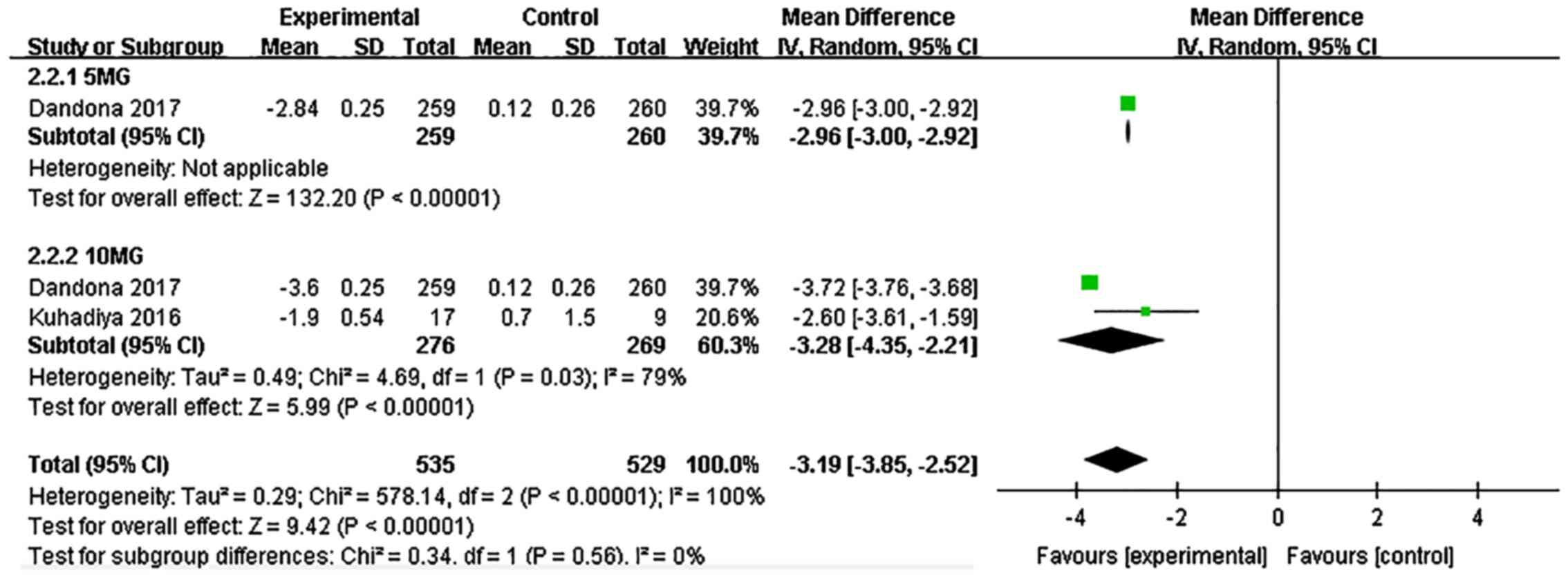
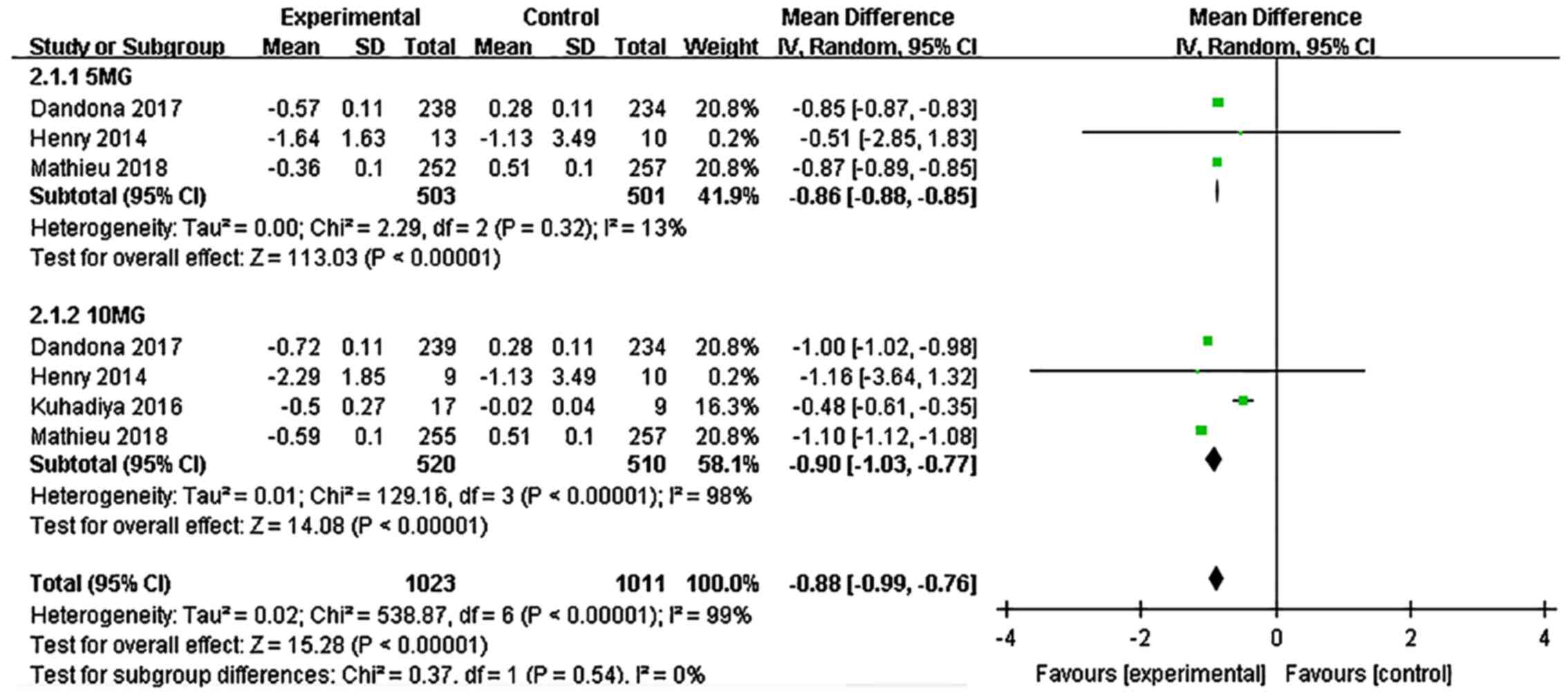
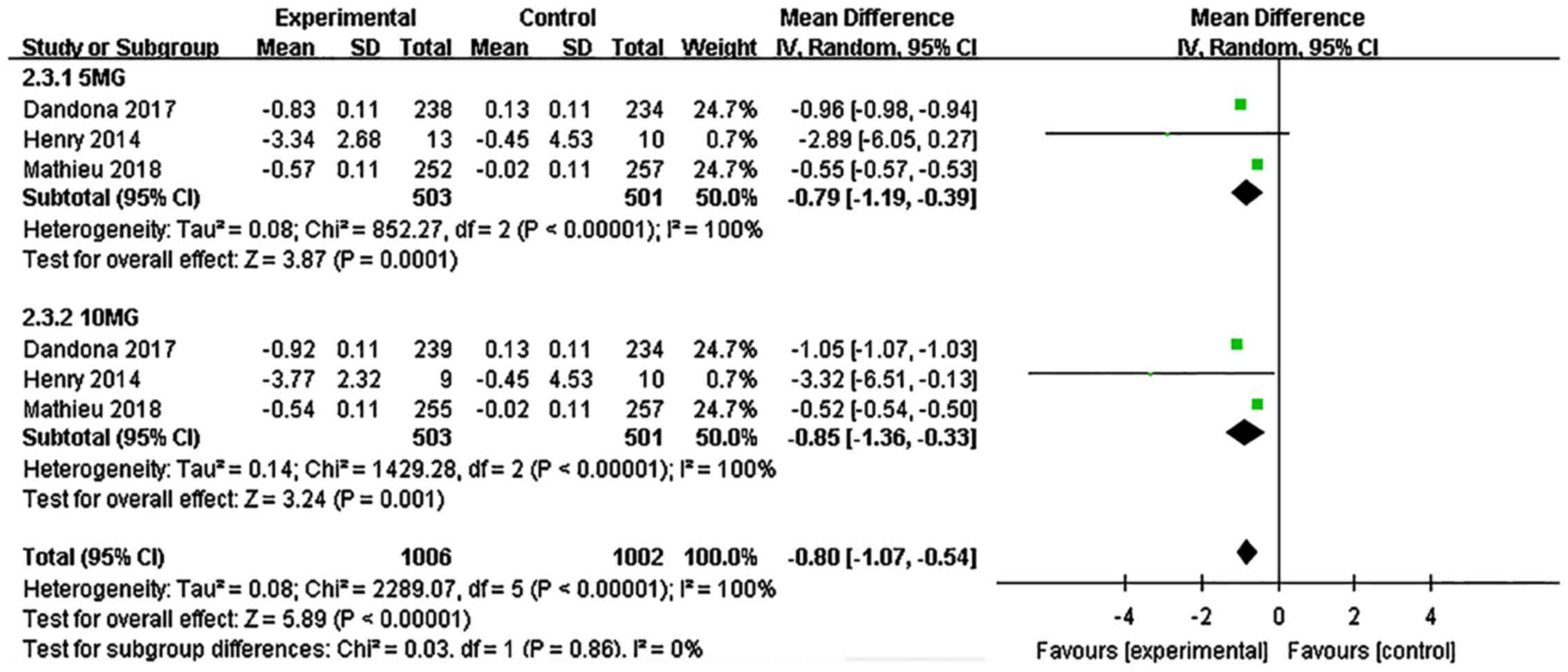
Dandona P, Mathieu C, Phillip M, Hansen L,
Griffen SC, Tschöpe D, Thorén F, Xu J and Langkilde AM: DEPICT-1
Investigators. Efficacy and safety of dapagliflozin in patients
with inadequately controlled type 1 diabetes (DEPICT-1): 24 week
results from a multicentre, double-blind, phase 3, randomised
controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 5:864–876.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Dandona P, Mathieu C, Phillip M, Hansen L,
Tschöpe D, Thorén F, Xu J and Langkilde AM: DEPICT-1 Investigators.
Efficacy and safety of dapagliflozin in patients with inadequately
controlled type 1 diabetes: The DEPICT-1 52-Week Study. Diabetes
Care. 41:2552–2559. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Henry RR, Dandona P, Pettus J, Mudaliar S,
Xu J and Hansen L: Dapagliflozin in patients with type 1 diabetes:
A post hoc analysis of the effect of insulin dose adjustments on
24-hour continuously monitored mean glucose and fasting
β-hydroxybutyrate levels in a phase IIa pilot study. Diabetes Obes
Metab. 19:814–821. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Kuhadiya ND, Ghanim H, Mehta A, Garg M,
Khan S, Hejna J, Torre B, Makdissi A, Chaudhuri A, Batra M and
Dandona P: Dapagliflozin as additional treatment to liraglutide and
insulin in patients with type 1 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
101:3506–3515. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Mathieu C, Dandona P, Gillard P, Senior P,
Hasslacher C, Araki E, Lind M, Bain SC, Jabbour S, Arya N, et al:
Efficacy and safety of dapagliflozin in patients with inadequately
controlled type 1 diabetes (the DEPICT-2 Study): 24-week results
from a randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Care. 41:1938–1946.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Aguillo'n AR, Mascarello A, Segretti ND,
de Azevedo HF, Guimaraes CR, Miranda LS and de Souza RO: Synthetic
strategies toward SGLT2 inhibitors. Org Process Res Dev.
22:467–488. 2018.
|
|
22
|
NIA Adverse Event and Serious Adverse
Event Guidelines. National Institutes on Aging, National Institutes
of Health, 2011.
|
|
23
|
Higgins J and Green S (eds): Cochrane
Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions, version 5.1.0,
March 2011. The Cochrane Collaboration. John Wiley & Sons,
Ltd., New Jersey, 2014.
|
|
24
|
Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, Mulrow
C, Gøtzsche PC, Ioannidis JPA, Clarke M, Devereaux PJ, Kleijnen J
and Moher D: The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews
and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate healthcare
interventions: Explanation and elaboration. BMJ.
339(b2700)2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
McKnight J, Wild S, Lamb M, Cooper M,
Jones T, Davis E, Hofer S, Fritsch M, Schober E, Svensson J, et al:
Glycaemic control of type 1 diabetes in clinical practice early in
the 21st century: An international comparison. Diabet Med.
32:1036–1050. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Weinstock RS, Schutz-Fuhrmann I, Connor
CG, Hermann JM, Maahs DM, Schütt M, Agarwal S, Hofer SE, Beck RW
and Holl RW: T1D Exchange Clinic Network; DPV Initiative. T1D
exchange clinic network; DPV initiative. Type 1 diabetes in older
adults: Comparing treatments and chronic complications in the
United States T1D exchange and the German/Austrian DPV registries.
Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 122:28–37. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Chao EC: SGLT-2 inhibitors: A new
mechanism for glycemic control. Clin Diabetes. 32:4–11.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Bolinder J, Ljunggren O, Kullberg J,
Johansson L, Wilding J, Langkilde AM, Sugg J and Parikh S: Effects
of dapagliflozin on body weight, total fat mass, and regional
adipose tissue distribution in patients with type 2 diabetes
mellitus with inadequate glycemic control on metformin. J Clin
Endocrinol Metab. 97:1020–1031. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Wing RR, Lang W, Wadden TA, Safford M,
Knowler WC, Bertoni AG, Hill JO, Brancati FL, Peters A and
Wagenknecht L: Look AHEAD Research Group. Benefits of modest weight
loss in improving cardiovascular risk factors in overweight and
obese individuals with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care.
34:1481–1486. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Van Gaal LF, Wauters MA and De Leeuw IH:
The beneficial effects of modest weight loss on cardiovascular risk
factors. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 21 (Suppl 1):S5–S9.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Evans M, Hicks D, Patel D, Patel V, McEwan
P and Dashora U: Optimising the benefits of SGLT2 inhibitors for
type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Ther. 11:37–52. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
McCrimmon RJ and Henry RR: SGLT inhibitor
adjunct therapy in type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia. 61:2126–2133.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Li K and Xu G: Safety and efficacy of
sodium glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors combined with insulin in
adults with type 1 diabetes: A meta-analysis of randomized
controlled trials. J Diabetes. 11:645–655. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
El Masri D, Ghosh S and Jaber LA: Safety
and efficacy of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors
in type 1 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes
Res Clin Pract. 137:83–92. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Yamada T, Shojima N, Noma H, Yamauchi T
and Kadowaki T: Sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors as
add-on therapy to insulin for type 1 diabetes mellitus: Systematic
review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Diabetes
Obes Metab. 20:1755–1761. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Baker C, Wason S, Banks P, Sawhney S,
Chang A, Danne T, Gesty-Palmer D, Kushner JA, McGuire DK, Mikell F,
et al: Dose-dependent glycometabolic effects of sotagliflozin on
type 1 diabetes over 12 weeks: The inTandem4 trial. Diabetes Obes
Metab. 21:2440–2449. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Boeder S and Edelman SV: Sodium-glucose
co-transporter inhibitors as adjunctive treatment to insulin in
type 1 diabetes: A review of randomized controlled trials. Diabetes
Obes Metab. 21 (Suppl 2):S62–S77. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Yang Y, Pan H, Wang B, Chen S and Zhu H:
Efficacy and safety of SGLT2 inhibitors in patients with type 1
diabetes: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Chin Med
Sci J. 32:22–27. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Peters AL, Henry RR, Thakkar P, Tong C and
Alba M: Diabetic ketoacidosis with canagliflozin, a sodium-glucose
cotransporter 2 inhibitor, in patients with type 1 diabetes.
Diabetes Care. 39:532–538. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Peters AL, Buschur EO, Buse JB, Cohan P,
Diner JC and Hirsch IB: Euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis: A
potential complication of treatment with sodium-glucose
cotransporter 2 inhibition. Diabetes Care. 38:1687–1693.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|