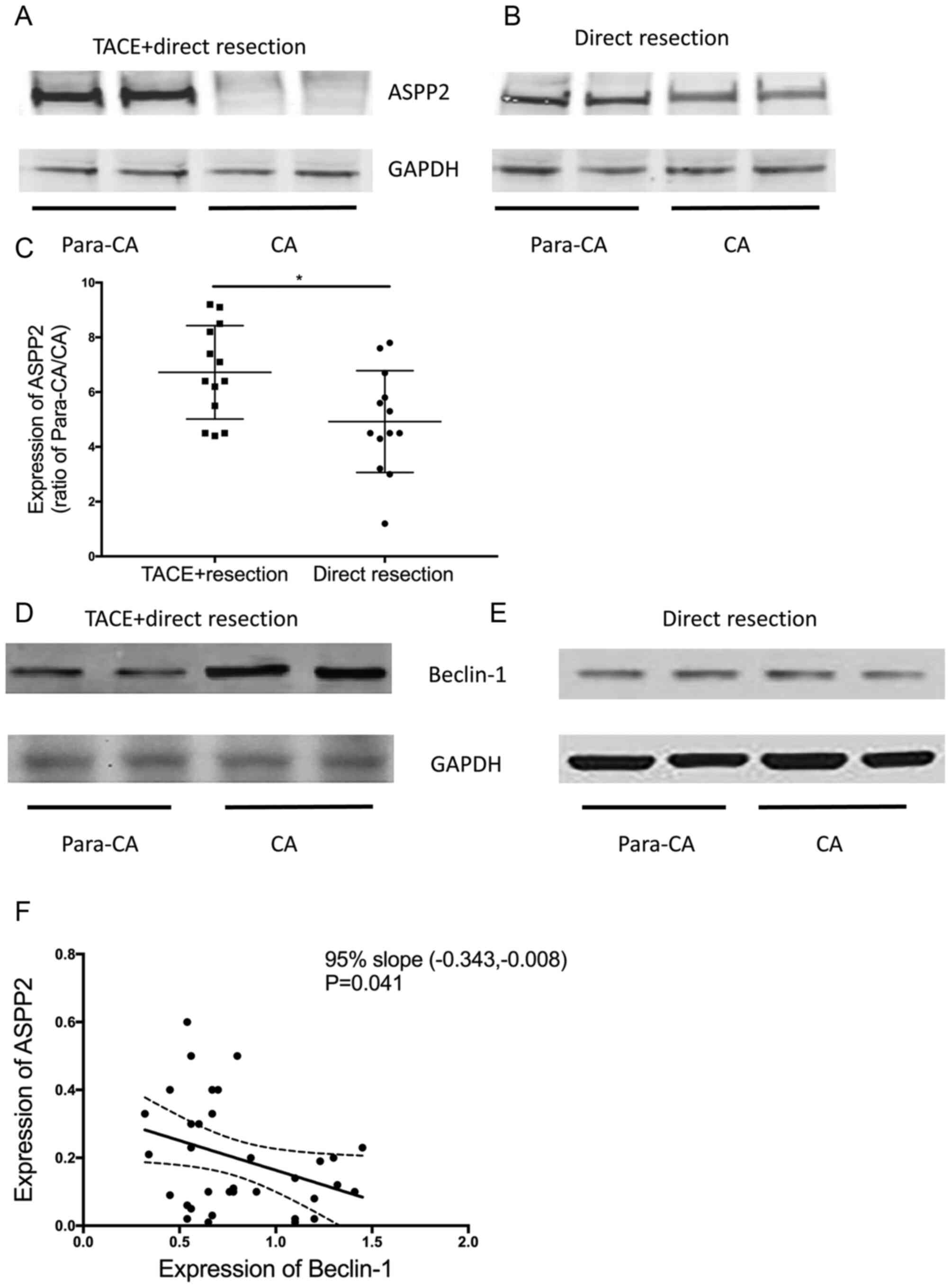
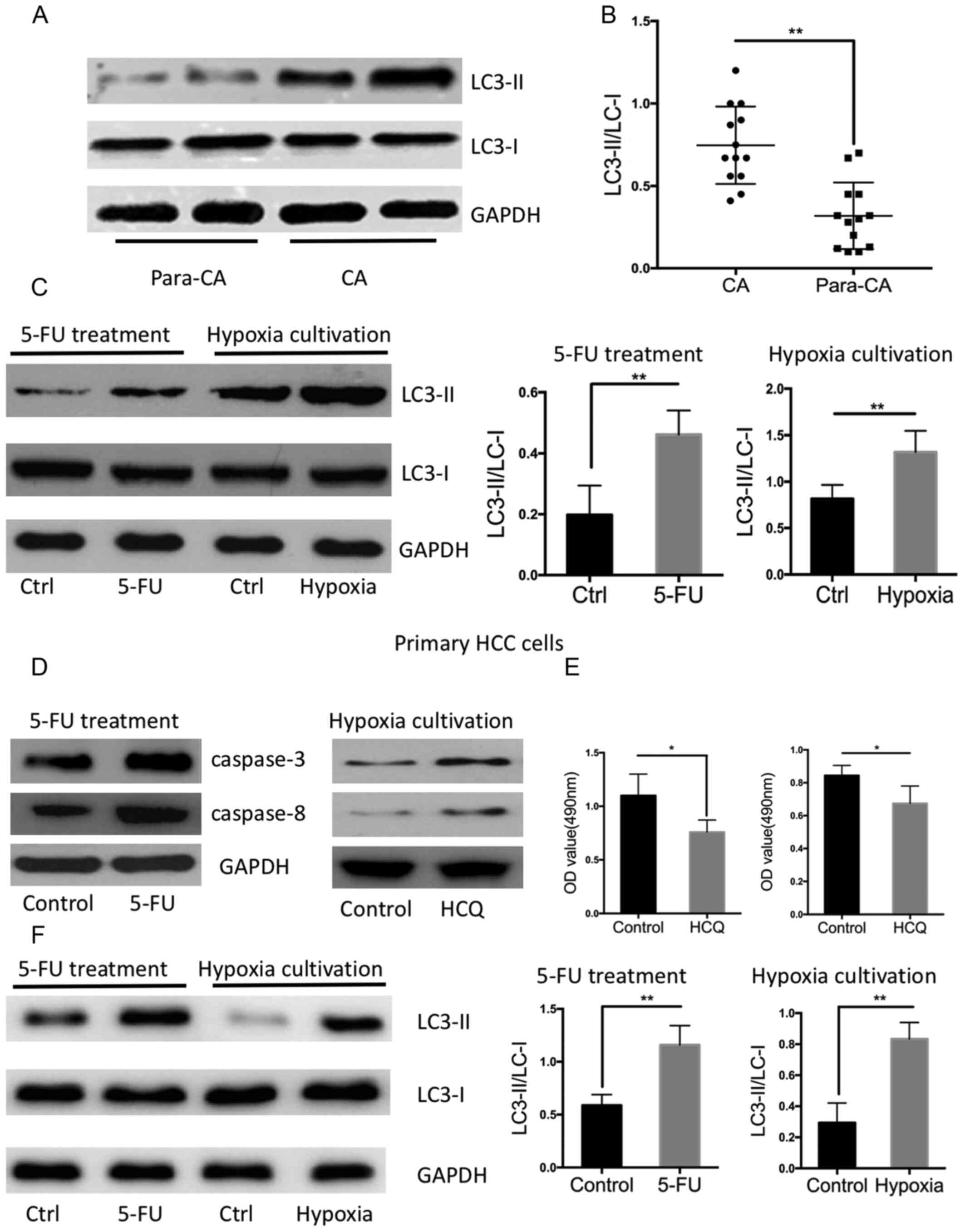
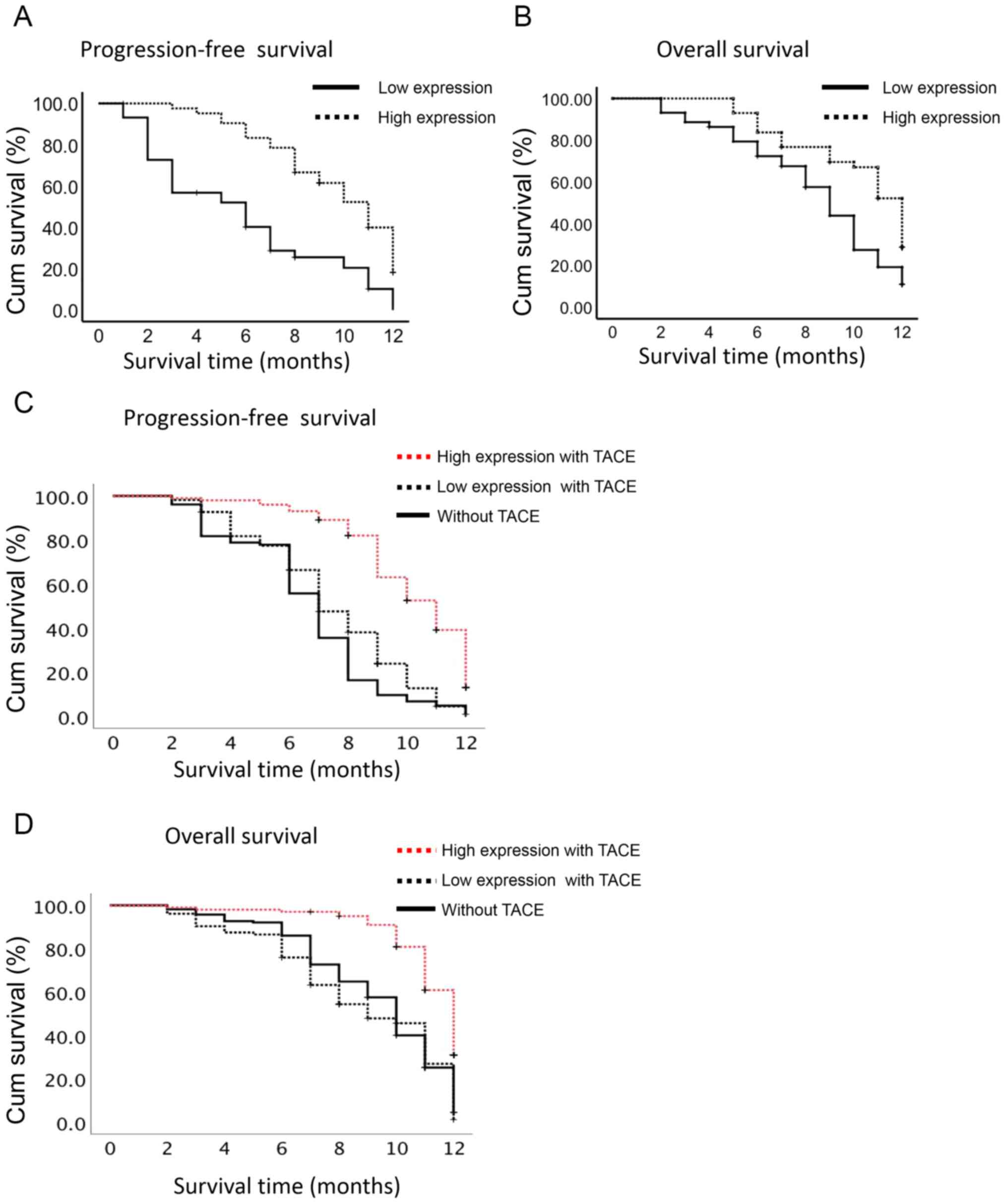
|
1
|
Galle PR, Tovoli F, Foerster F, Wörns MA,
Cucchetti A and Bolondi L: The treatment of intermediate stage
tumours beyond TACE: From surgery to systemic therapy. J Hepatol.
67:173–183. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Katsanos K, Kitrou P, Spiliopoulos S,
Maroulis I, Petsas T and Karnabatidis D: Comparative effectiveness
of different transarterial embolization therapies alone or in
combination with local ablative or adjuvant systemic treatments for
unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A network meta-analysis of
randomized controlled trials. PLoS One. 12(e0184597)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Ye JZ, Chen JZ, Li ZH, Bai T, Chen J, Zhu
SL, Li LQ and Wu FX: Efficacy of postoperative adjuvant
transcatheter arterial chemoembolization in hepatocellular
carcinoma patients with microvascular invasion. World J
Gastroenterol. 23:7415–7424. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Jianyong L, Jinjing Z, Lunan Y, Jingqiang
Z, Wentao W, Yong Z, Bo L, Tianfu W and Jiaying Y: Preoperative
adjuvant transarterial chemoembolization cannot improve the long
term outcome of radical therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma. Sci
Rep. 7(41624)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Ha TY, Hwang S, Lee YJ, Kim KH, Ko GY, Ii
Gwon D, Ahn CS, Moon DB, Song GW, Jung DH, et al: Absence of
benefit of transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) in
patients with resectable solitary hepatocellular carcinoma. World J
Surg. 40:1200–1210. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Wang W, Bai W, Wang E, Zhao Y, Liu L, Yang
M, Cai H, Xia D, Zhang L, Niu J, et al: mRECIST response combined
with sorafenib-related adverse events is superior to either
criterion alone in predicting survival in HCC patients treated with
TACE plus sorafenib. Int J Cancer. 140:390–399. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Shi HY, Wang SN, Wang SC, Chuang SC, Chen
CM and Lee KT: Preoperative transarterial chemoembolization and
resection for hepatocellular carcinoma: A nationwide Taiwan
database analysis of long-term outcome predictors. J Surg Oncol.
109:487–493. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Majno PE, Adam R, Bismuth H, Castaing D,
Ariche A, Krissat J, Perrin H and Azoulay D: Influence of
preoperative transarterial lipiodol chemoembolization on resection
and transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with
cirrhosis. Ann Surg. 226:688–703. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Liu K, Min XL, Peng J, Yang K, Yang L and
Zhang XM: The changes of HIF-1α and VEGF expression after TACE in
patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Med Res. 8:297–302.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Yuan G, Zeng CL, Zhu DD and Shi XJ:
Influences of RFA combined with TACE on the HIF-1α and EGR level of
patients with primary hepatic carcinoma. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
21:1738–1745. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Xu W, Kwon JH, Moon YH, Kim YB, Yu YS, Lee
N, Choi KY, Kim YS, Park YK, Kim BW and Wang HJ: Influence of
preoperative transcatheter arterial chemoembolization on gene
expression in the HIF-1α pathway in patients with hepatocellular
carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 140:1507–1515. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Pagotto A, Pilotto G, Mazzoldi EL,
Nicoletto MO, Frezzini S, Pastò A and Amadori A: Autophagy
inhibition reduces chemoresistance and tumorigenic potential of
human ovarian cancer stem cells. Cell Death Dis.
8(e2943)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Jawhari S, Ratinaud MH and Verdier M:
Glioblastoma, hypoxia and autophagy: A survival-prone
‘ménage-à-trois’. Cell Death Dis. 7(e2434)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Zhou C, Ma K, Gao R, Mu C, Chen L, Liu Q,
Luo Q, Feng D, Zhu Y and Chen Q: Regulation of mATG9 trafficking by
Src- and ULK1-mediated phosphorylation in basal and
starvation-induced autophagy. Cell Res. 27:184–201. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
White E, Mehnert JM and Chan CS:
Autophagy, metabolism, and cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 21:5037–5046.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Vives V, Slee EA and Lu X: ASPP2: A gene
that controls life and death in vivo. Cell Cycle. 5:2187–2190.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Sullivan A and Lu X: ASPP: A new family of
oncogenes and tumour suppressor genes. Br J Cancer. 96:196–200.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Yang T, Gao Y, Liu D, Wang Y, Wu J, Liu X,
Shi Y and Chen D: ASPP2 enhances chemotherapeutic sensitivity
through the down-regulation of XIAP expression in a p53 independent
manner in hepatocellular carcinoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
508:769–774. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Wu X, Feng X, Zhao X, Ma F, Liu N, Guo H,
Li C, Du H and Zhang B: Role of Beclin-1-mediated autophagy in the
survival of pediatric leukemia cells. Cell Physiol Biochem.
39:1827–1836. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Ueno T, Saji S, Sugimoto M, Masuda N,
Kuroi K, Sato N, Takei H, Yamamoto Y, Ohno S, Yamashita H, et al:
Clinical significance of the expression of autophagy-associated
marker, beclin 1, in breast cancer patients who received
neoadjuvant endocrine therapy. BMC Cancer. 16(230)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Amaral C, Borges M, Melo S, da Silva ET,
Correia-da-Silva G and Teixeira N: Apoptosis and autophagy in
breast cancer cells following exemestane treatment. PLoS One.
7(e42398)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Han K and Kim JH: Transarterial
chemoembolization in hepatocellular carcinoma treatment: Barcelona
clinic liver cancer staging system. World J Gastroenterol.
21:10327–10335. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Seymour L, Bogaerts J, Perrone A, Ford R,
Schwartz LH, Mandrekar S, Lin NU, Litière S, Dancey J, Chen A, et
al: iRECIST: Guidelines for response criteria for use in trials
testing immunotherapeutics. Lancet Oncol. 18:e143–e152.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
European Association for the Study of the
Liver; European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer.
EASL-EORTC clinical practice guidelines: Management of
hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol 56: 908-943, 2012.
|
|
25
|
Chen J, Huang J, Chen M, Yang K, Chen J,
Wang J, Xu L, Zhou Z and Zhang Y: Transcatheter arterial
chemoembolization (TACE) versus hepatectomy in hepatocellular
carcinoma with macrovascular invasion: A meta-analysis of 1,683
patients. J Cancer. 8:2984–2991. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Sacco R, Tapete G, Simonetti N, Sellitri
R, Natali V, Melissari S, Cabibbo G, Biscaglia L, Bresci G and
Giacomelli L: Transarterial chemoembolization for the treatment of
hepatocellular carcinoma: A review. J Hepatocell Carcinoma.
4:105–110. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Kudo M, Matsui O, Izumi N, Kadoya M,
Okusaka T, Miyayama S, Yamakado K, Tsuchiya K, Ueshima K, Hiraoka
A, et al: Transarterial chemoembolization failure/refractoriness:
JSH-LCSGJ criteria 2014 update. Oncology. 87 (Suppl 1):S22–S31.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Li Z, Xue TQ and Chen XY: Predictive
values of serum VEGF and CRP levels combined with contrast enhanced
MRI in hepatocellular carcinoma patients after TACE. Am J Cancer
Res. 6:2375–2385. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Guo LY, Zhu P and Jin XP: Association
between the expression of HIF-1α and VEGF and prognostic
implications in primary liver cancer. Genet Mol Res.
15(15)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Waked I, Berhane S, Toyoda H, Chan SL,
Stern N, Palmer D, Tada T, Yeo W, Mo F, Bettinger D, et al:
Transarterial chemo-embolisation of hepatocellular carcinoma:
Impact of liver function and vascular invasion. Br J Cancer.
116:448–454. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Bettinger D, Spode R, Glaser N, Buettner
N, Boettler T, Neumann-Haefelin C, Brunner TB, Gkika E, Maruschke
L, Thimme R and Schultheiss M: Survival benefit of transarterial
chemoembolization in patients with metastatic hepatocellular
carcinoma: A single center experience. BMC Gastroenterol.
17(98)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Dodson M, Redmann M, Rajasekaran NS,
Darley-Usmar V and Zhang J: KEAP1-NRF2 signalling and autophagy in
protection against oxidative and reductive proteotoxicity. Biochem
J. 469:347–355. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Zhou Y, Wang Y, Wang X, Tian X, Zhang S,
Yang F, Guo H, Fan R, Feng N, Jia M, et al: The protective effects
of Κ-opioid receptor stimulation in hypoxic pulmonary hypertension
involve inhibition of autophagy through the AMPK-MTOR pathway. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 44:1965–1979. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Endo S, Nakata K, Ohuchida K, Takesue S,
Nakayama H, Abe T, Koikawa K, Okumura T, Sada M, Horioka K, et al:
Autophagy is required for activation of pancreatic stellate cells,
associated with pancreatic cancer progression and promotes growth
of pancreatic tumors in mice. Gastroenterology. 152:1492–1506 e24.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Auberger P and Puissant A: Autophagy, a
key mechanism of oncogenesis and resistance in leukemia. Blood.
129:547–552. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Levy JMM, Towers CG and Thorburn A:
Targeting autophagy in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 17:528–542.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Chen R, Wang H, Liang B, Liu G, Tang M,
Jia R, Fan X, Jing W, Zhou X, Wang H, et al: Downregulation of
ASPP2 improves hepatocellular carcinoma cells survival via
promoting BECN1-dependent autophagy initiation. Cell Death Dis.
7(e2512)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|