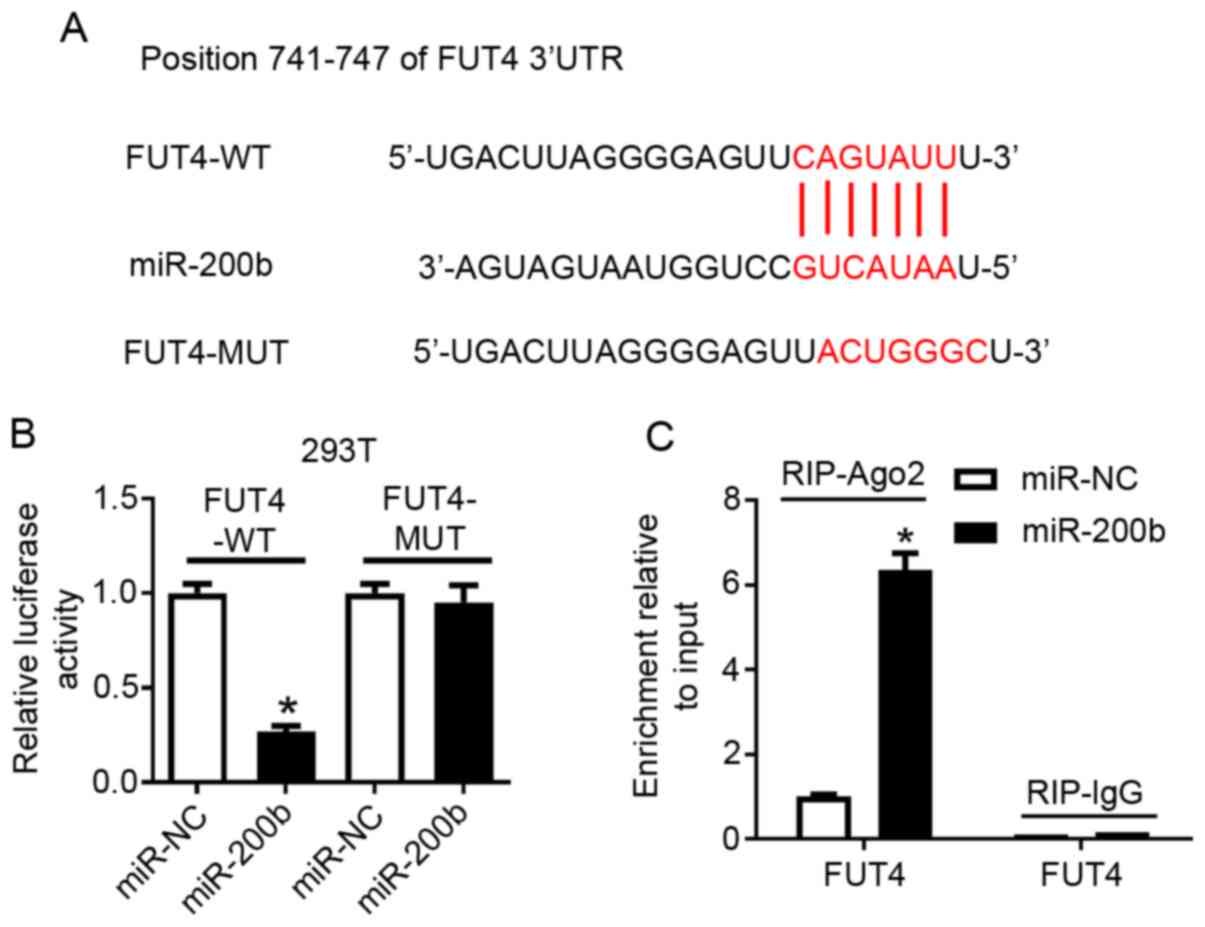
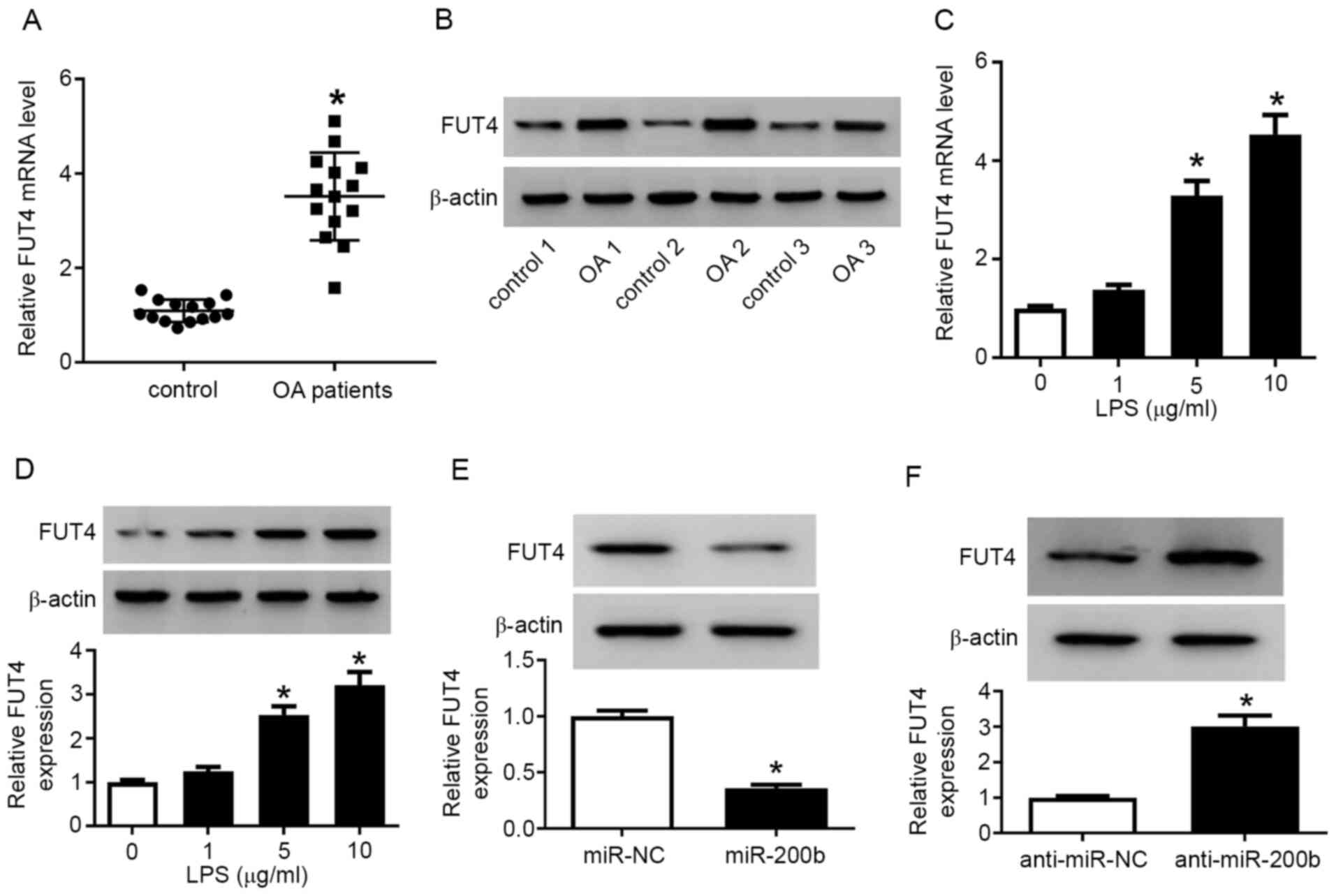
|
1
|
van den Bosch MHJ: Inflammation in
osteoarthritis: Is it time to dampen the alarm(in) in this
debilitating disease? Clin Exp Immunol. 195:153–166.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Loeser RF, Collins JA and Diekman BO:
Ageing and the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol.
12:412–420. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Greene MA and Loeser RF: Aging-related
inflammation in osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.
23:1966–1971. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Jia J, Wang J, Zhang J, Cui M, Sun X, Li Q
and Zhao B: MiR-125b inhibits LPS-induced inflammatory injury via
targeting MIP-1α in chondrogenic cell ATDC5. Cell Physiol Biochem.
45:2305–2316. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Kourtis A, Adamopoulos PG, Papalois A,
Iliopoulos DC, Babis GC and Scorilas A: Quantitative analysis and
study of the mRNA expression levels of apoptotic genes BCL2, BAX
and BCL2L12 in the articular cartilage of an animal model of
osteoarthritis. Ann Transl Med. 6(243)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Chen Y, Sun Y, Pan X, Ho K and Li G: Joint
distraction attenuates osteoarthritis by reducing secondary
inflammation, cartilage degeneration and subchondral bone aberrant
change. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 23:1728–1735. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Cong L, Zhu Y and Tu G: A bioinformatic
analysis of microRNAs role in osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis
Cartilage. 25:1362–1371. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Jeffries MA, Donica M, Baker LW, Stevenson
ME, Annan AC, Humphrey MB, James JA and Sawalha AH: Genome-wide DNA
methylation study identifies significant epigenomic changes in
osteoarthritic cartilage. Arthritis Rheumatol. 66:2804–2815.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Li B, Bai L, Shen P, Sun Y, Chen Z and Wen
Y: Identification of differentially expressed microRNAs in knee
anterior cruciate ligament tissues surgically removed from patients
with osteoarthritis. Int J Mol Med. 40:1105–1113. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Song J, Ahn C, Chun CH and Jin EJ: A long
non-coding RNA, GAS5, plays a critical role in the regulation of
miR-21 during osteoarthritis. J Orthop Res. 32:1628–1635.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Yang R, Zhang D, Yu K, Sun L, Yang J, Zhao
C, Li X and Chen Y: Detection of miR-22, miR-140 and bone
morphogenetic proteins (BMP)-2 expression levels in synovial fluid
of osteoarthritis patients before and after arthroscopic
debridement. Med Sci Monit. 24:863–868. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Zhang HX, Sun C, Yu HC, Song B and Pan ZX:
Targeted inhibition of β-catenin by miR-320 and decreased MMP-13
expression in suppressing chondrocyte collagen degradation. Eur Rev
Med Pharmacol Sci. 22:5828–5835. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Feng B, Wang R and Chen L: Review of
miR-200b and cancer chemosensitivity. Biomed Pharmacother.
66:397–402. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Zeng F, Xue M, Xiao T, Li Y, Xiao S, Jiang
B and Ren C: MiR-200b promotes the cell proliferation and
metastasis of cervical cancer by inhibiting FOXG1. Biomed
Pharmacother. 79:294–301. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Zheng Q, Cui X, Zhang D, Yang Y, Yan X,
Liu M, Niang B, Aziz F, Liu S, Yan Q and Liu J: miR-200b inhibits
proliferation and metastasis of breast cancer by targeting
fucosyltransferase IV and α1,3-fucosylated glycans. Oncogenesis.
6(e358)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Wu J, Tao Y, Shang A, Wang W, Zhang Y, Hu
L, Wang J, Wang Y and Guo N: Effect of the interaction between
MiR-200b-3p and DNMT3A on cartilage cells of osteoarthritis
patients. J Cell Mol Med. 21:2308–2316. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Keeley TS, Yang S and Lau E: The diverse
contributions of fucose linkages in cancer. Cancers (Basel).
11(1241)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Cheng L, Luo S, Jin C, Ma H, Zhou H and
Jia L: FUT family mediates the multidrug resistance of human
hepatocellular carcinoma via the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Cell
Death Dis. 4(e923)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
De Benedetti F, Pignatti P, Biffi M, Bono
E, Wahid S, Ingegnoli F, Chang SY, Alexander H, Massa M, Pistorio
A, et al: Increased expression of alpha(1,3)-fucosyltransferase-VII
and P-selectin binding of synovial fluid T cells in juvenile
idiopathic arthritis. J Rheumatol. 30:1611–1615. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Isozaki T, Ruth JH, Amin MA, Campbell PL,
Tsou PS, Ha CM, Haines GK, Edhayan G and Koch AE:
Fucosyltransferase 1 mediates angiogenesis, cell adhesion and
rheumatoid arthritis synovial tissue fibroblast proliferation.
Arthritis Res Ther. 16(R28)2014.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Hu J, Wang Z, Pan Y, Ma J, Miao X, Qi X,
Zhou H and Jia L: MiR-26a and miR-26b mediate osteoarthritis
progression by targeting FUT4 via NF-κB signaling pathway. Int J
Biochem Cell Biol. 94:79–88. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Chaby R: Lipopolysaccharide-binding
molecules: Transporters, blockers and sensors. Cell Mol Life Sci.
61:1697–1713. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Huang ZY, Stabler T, Pei FX and Kraus VB:
Both systemic and local lipopolysaccharide (LPS) burden are
associated with knee OA severity and inflammation. Osteoarthritis
Cartilage. 24:1769–1775. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Sun T, Li X, Song H, Gao F, Zhou G, Li X,
Chen Z and Chen L: MiR-146a aggravates LPS-induced inflammatory
injury by targeting CXCR4 in the articular chondrocytes. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 44:1282–1294. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Wang Y and Kong D: MicroRNA-136 promotes
lipopolysaccharide-induced ATDC5 cell injury and inflammatory
cytokine expression by targeting myeloid cell leukemia 1. J Cell
Biochem. 119:9316–9326. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Hubertsson J, Petersson IF, Thorstensson
CA and Englund M: Risk of sick leave and disability pension in
working-age women and men with knee osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis.
72:401–405. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
van Middelkoop M, Arden NK, Atchia I,
Birrell F, Chao J, Rezende MU, Lambert RG, Ravaud P, Bijlsma JW,
Doherty M, et al: The OA Trial Bank: meta-analysis of individual
patient data from knee and hip osteoarthritis trials show that
patients with severe pain exhibit greater benefit from
intra-articular glucocorticoids. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.
24:1143–1152. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Hwang HS and Kim HA: Chondrocyte apoptosis
in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Int J Mol Sci.
16:26035–2654. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Feldmann M: Pathogenesis of arthritis:
Recent research progress. Nat Immunol. 2:771–773. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Li F, Sun J, Huang S, Su G and Pi G:
LncRNA GAS5 overexpression reverses LPS-induced inflammatory injury
and apoptosis through up-regulating KLF2 expression in ATDC5
chondrocytes. Cell Physiol Biochem. 45:1241–1251. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Pan L, Liu D, Zhao L, Wang L, Xin M and Li
X: Long noncoding RNA MALAT1 alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced
inflammatory injury by upregulating microRNA-19b in murine
chondrogenic ATDC5 cells. J Cell Biochem. 119:10165–10175.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Wu J, Cui H, Zhu Z and Wang L:
MicroRNA-200b-3p suppresses epithelial-mesenchymal transition and
inhibits tumor growth of glioma through down-regulation of ERK5.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 478:1158–1164. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
He M, Liu Y, Deng X, Qi S, Sun X, Liu G,
Liu Y, Liu Y and Zhao M: Down-regulation of miR-200b-3p by low p73
contributes to the androgen-independence of prostate cancer cells.
Prostate. 73:1048–1056. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Gwam CU, Etcheson JI, George NE, Mistry
JB, Mohamed N, Patel A, Gwam PN, Piuzzi NS and Delanois RE:
Presentation of knee osteoarthritis in the emergency department: A
problem worth mentioning? Surg Technol Int. 31:277–284.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|