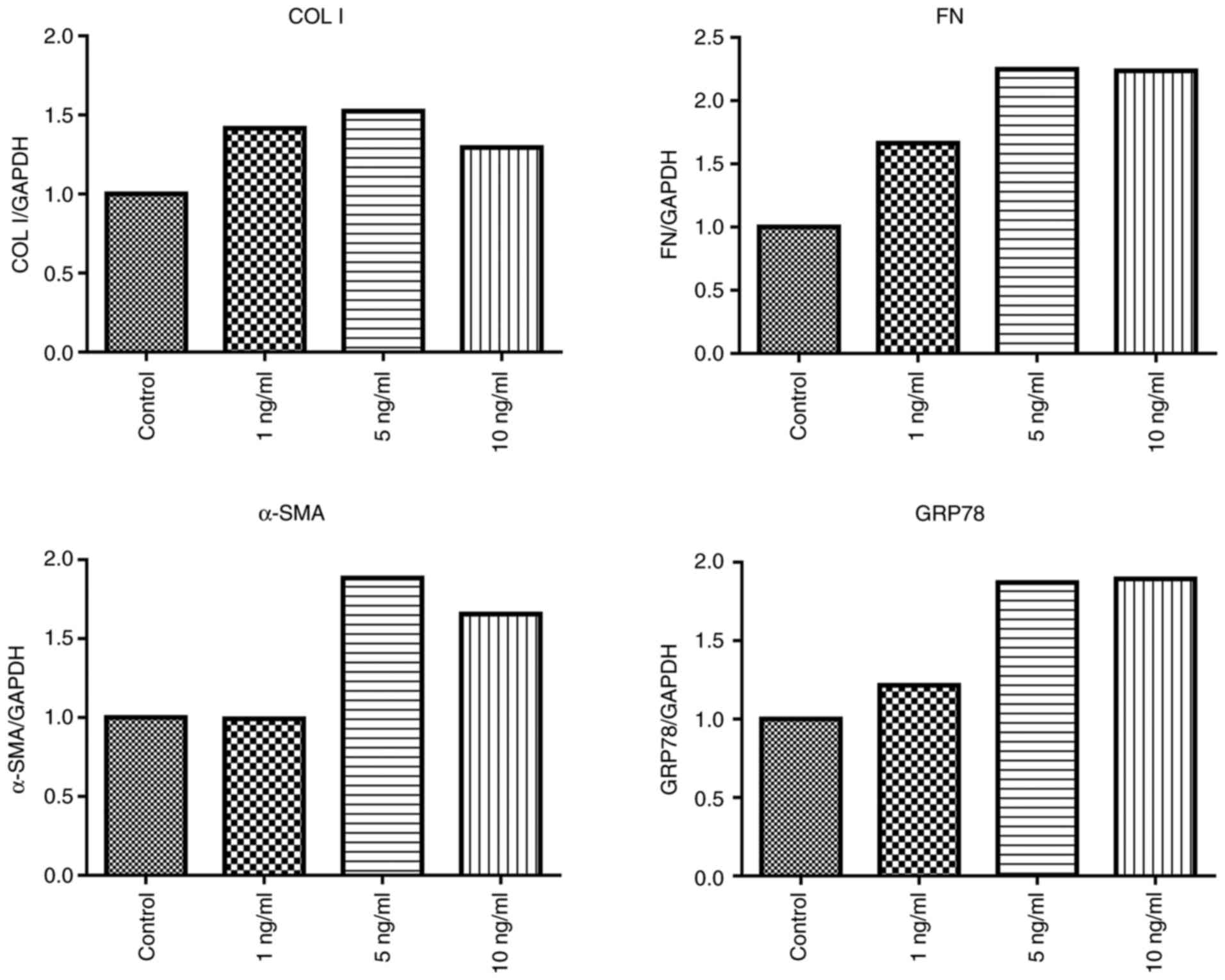
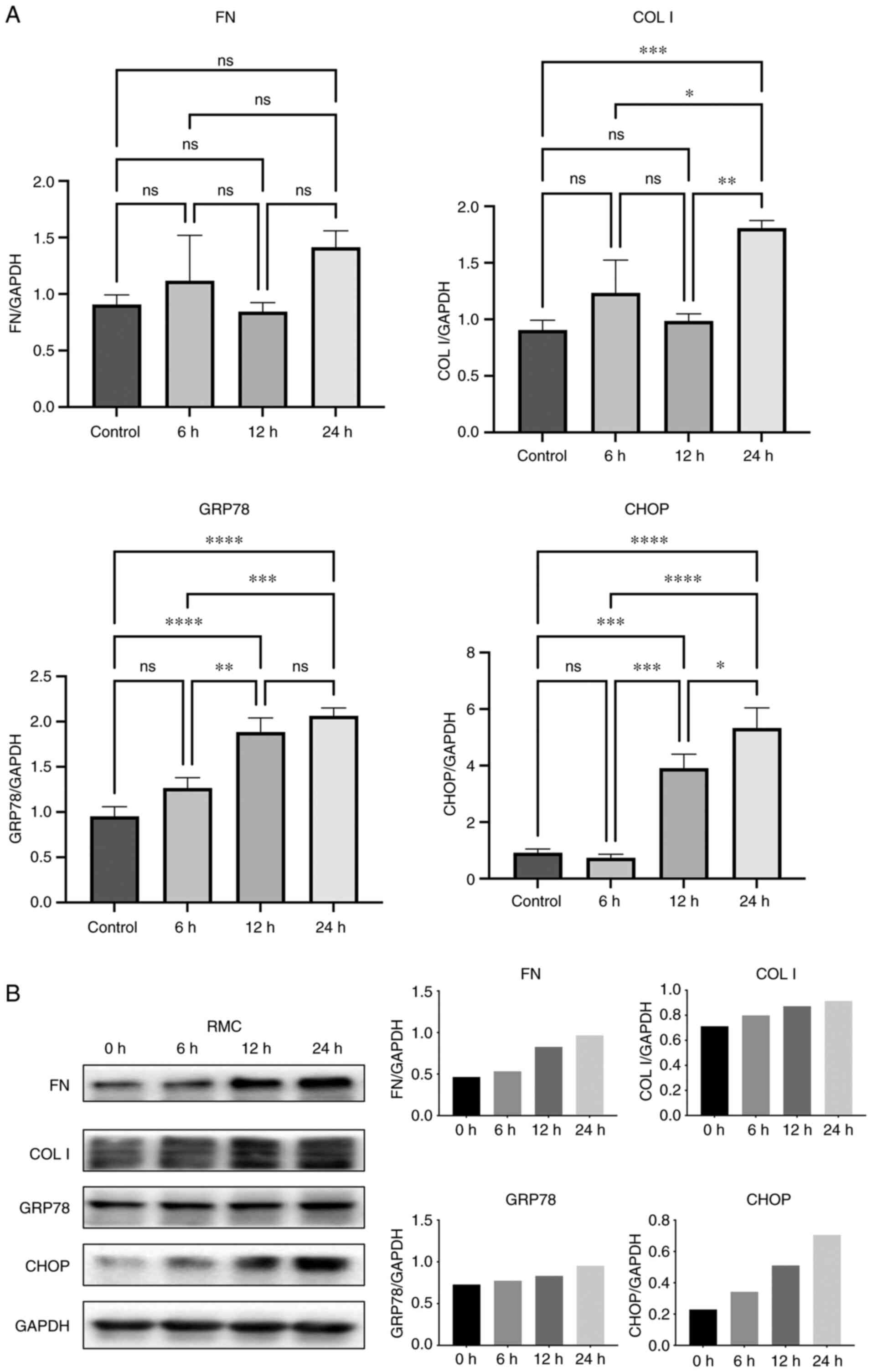
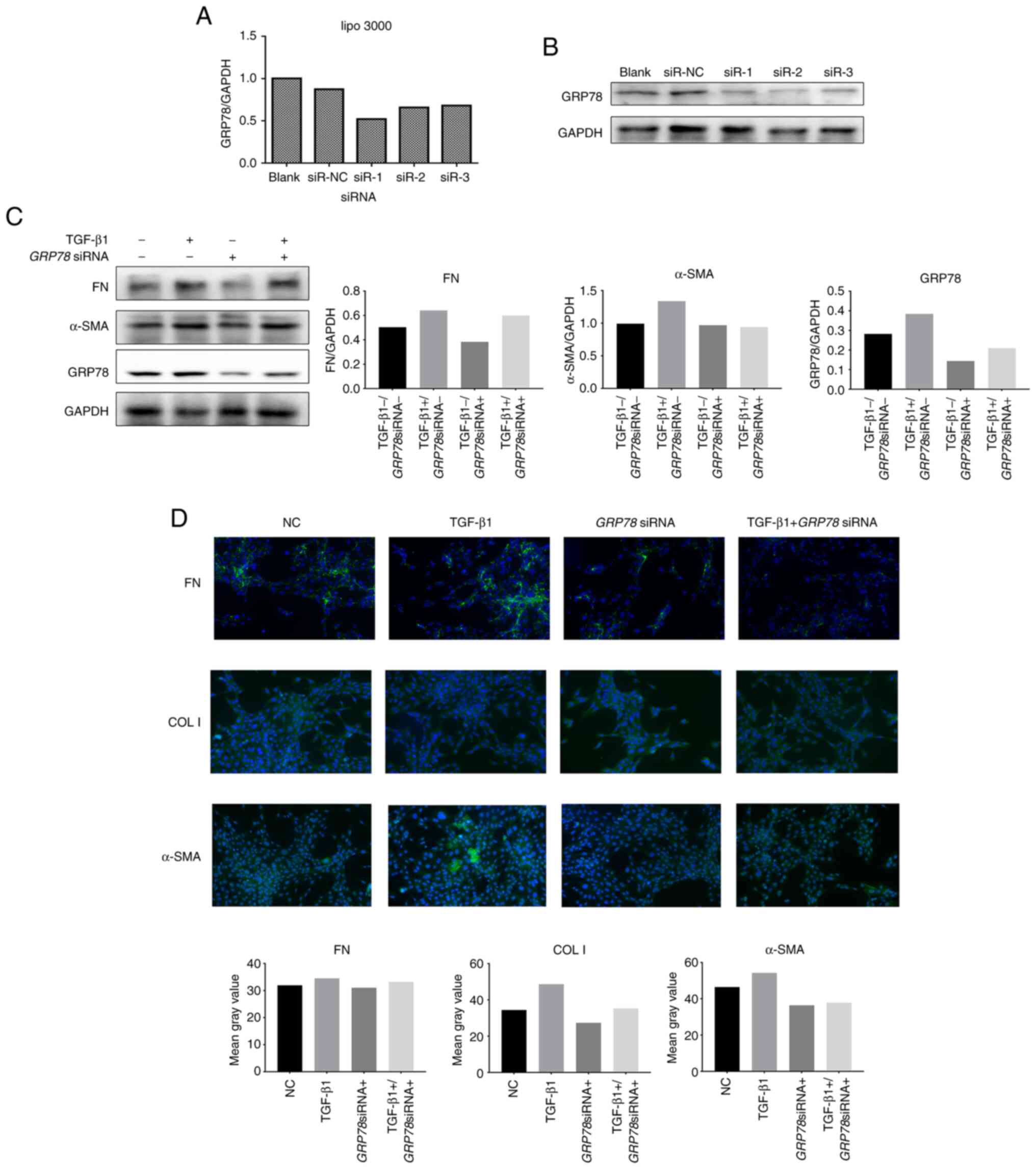
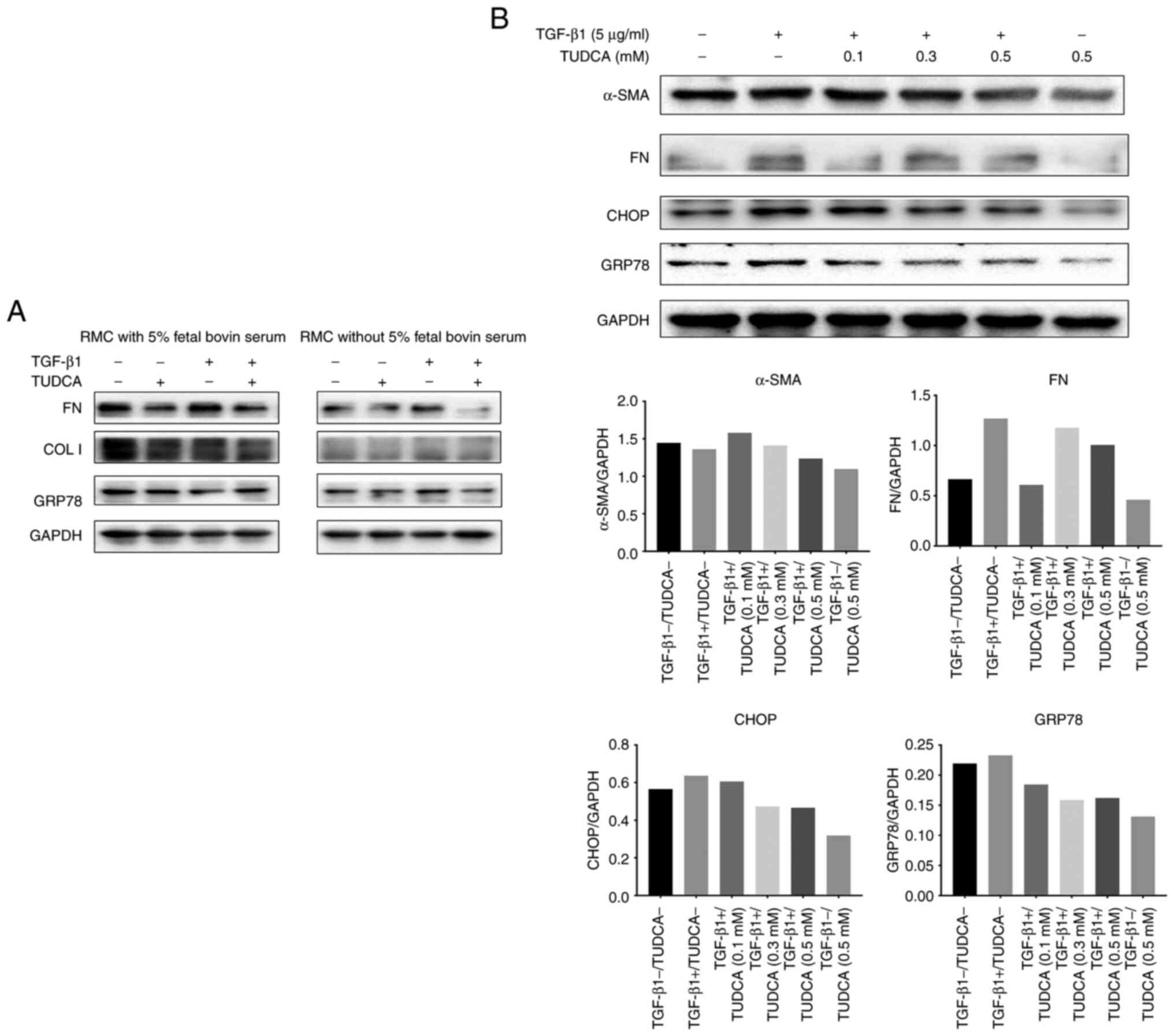
|
1
|
Webster AC, Nagler EV, Morton RL and
Masson P: Chronic kidney disease. Lancet. 389:1238–1252.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Djudjaj S and Boor P: Cellular and
molecular mechanisms of kidney fibrosis. Mol Aspects Med. 65:16–36.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Sun YB, Qu X, Caruana G and Li J: The
origin of renal fibroblasts/myofibroblasts and the signals that
trigger fibrosis. Differentiation. 92:102–107. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Hazzan AD, Halinski C, Agoritsas S,
Fishbane S and DeVita MV: Epidemiology and challenges to the
management of advanced CKD. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 23:217–221.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Fernández A, Ordóñez R, Reiter RJ,
González-Gallego J and Mauriz JL: Melatonin and endoplasmic
reticulum stress: Relation to autophagy and apoptosis. J Pineal
Res. 59:292–307. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Yoshida H: ER stress and diseases. FEBS J.
274:630–658. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Taniguchi M and Yoshida H: Endoplasmic
reticulum stress in kidney function and disease. Curr Opin Nephrol
Hypertens. 24:345–350. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Cybulsky AV: Endoplasmic reticulum stress,
the unfolded protein response and autophagy in kidney diseases. Nat
Rev Nephrol. 13:681–696. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Ke B, Zhu N, Luo F, Xu Y and Fang X:
Targeted inhibition of endoplasmic reticulum stress: New hope for
renal fibrosis (review). Mol Med Rep. 16:1014–1020. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Meng XM, Nikolic-Paterson DJ and Lan HY:
TGF-β: The master regulator of fibrosis. Nat Rev Nephrol.
12:325–338. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Bernales S, Papa FR and Walter P:
Intracellular signaling by the unfolded protein response. Annu Rev
Cell Dev Biol. 22:487–508. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Kaplan MM and Gershwin ME: Primary biliary
cirrhosis. N Engl J Med. 353:1261–1273. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Amaral JD, Viana RJ, Ramalho RM, Steer CJ
and Rodrigues CM: Bile acids: Regulation of apoptosis by
ursodeoxycholic acid. J Lipid Res. 50:1721–1734. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Malo A, Krüger B, Seyhun E, Schäfer C,
Hoffmann RT, Göke B and Kubisch CH: Tauroursodeoxycholic acid
reduces endoplasmic reticulum stress, trypsin activation, and
acinar cell apoptosis while increasing secretion in rat pancreatic
acini. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 299:G877–G886.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Chen Y, Liu CP, Xu KF, Mao XD, Lu YB, Fang
L, Yang JW and Liu C: Effect of taurine-conjugated ursodeoxycholic
acid on endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis induced by
advanced glycation end products in cultured mouse podocytes. Am J
Nephrol. 28:1014–1022. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Xiao W, Fan Y, Wang N, Chuang PY, Lee K
and He JC: Knockdown of RTN1A attenuates ER stress and kidney
injury in albumin overload-induced nephropathy. Am J Physiol Renal
Physiol. 310:F409–F415. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Ma TT and Meng XM: TGF-β/Smad and renal
fibrosis. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1165:347–364. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Ke B, Fan C, Yang L and Fang X: Matrix
metalloproteinases-7 and kidney fibrosis. Front Physiol.
8(21)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Zhao JH: Mesangial cells and renal
fibrosis. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1165:165–194. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Liu Y: Renal fibrosis: New insights into
the pathogenesis and therapeutics. Kidney Int. 69:213–217.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Baricos WH, Cortez SL, Deboisblanc M and
Xin S: Transforming growth factor-beta is a potent inhibitor of
extracellular matrix degradation by cultured human mesangial cells.
J Am Soc Nephrol. 10:790–795. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Hubchak SC, Sparks EE, Hayashida T and
Schnaper HW: Rac1 promotes TGF-beta-stimulated mesangial cell type
I collagen expression through a PI3K/Akt-dependent mechanism. Am J
Physiol Renal Physiol. 297:F1316–F1323. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Kassan M, Galán M, Partyka M, Saifudeen Z,
Henrion D, Trebak M and Matrougui K: Endoplasmic reticulum stress
is involved in cardiac damage and vascular endothelial dysfunction
in hypertensive mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 32:1652–1661.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Roberson EC, Tully JE, Guala AS, Reiss JN,
Godburn KE, Pociask DA, Alcorn JF, Riches DW, Dienz O,
Janssen-Heininger YM and Anathy V: Influenza induces endoplasmic
reticulum stress, caspase-12-dependent apoptosis, and c-Jun
N-terminal kinase-mediated transforming growth factor-β release in
lung epithelial cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 46:573–581.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Zhang M, Guo Y, Fu H, Hu S, Pan J, Wang Y,
Cheng J, Song J, Yu Q, Zhang S, et al: Chop deficiency prevents
UUO-induced renal fibrosis by attenuating fibrotic signals
originated from Hmgb1/TLR4/NFκB/IL-1β signaling. Cell Death Dis.
6(e1847)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Yang Y, Liu L, Naik I, Braunstein Z, Zhong
J and Ren B: Transcription factor C/EBP homologous protein in
health and diseases. Front Immunol. 8(1612)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|