|
1
|
China Pharmacopoeia Commission:
Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China. 2020 edition, Part
1. Chinese medicines and Technology Press, Beijing, 2020.
|
|
2
|
Dai RC, Nabil WNN and Xu HX: The history
of saffron in China: From its origin to applications. Chin Med
Cult. 4:228–234. 2021.
|
|
3
|
Huang WJ and Long CL: The medicinal
history and recent study of Crocus sativus. J Minzu Univ
China (Natural Sciences Edition). 24:55–58. 2015.
|
|
4
|
Samarghandian S and Borji A:
Anticarcinogenic effect of saffron (Crocus sativus L.) and
its ingredients. Pharmacognosy Res. 6:99–107. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Valle García-Rodríguez M, Serrano-Díaz J,
Tarantilis PA, López-Córcoles H, Carmona M and Alonso GL:
Determination of saffron quality by high-performance liquid
chromatography. J Agric Food Chem. 62:8068–8074. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Hatziagapiou K and Lambrou GI: The
protective role of Crocus sativus L. (saffron) against
ischemia-reperfusion injury, hyperlipidemia and atherosclerosis:
Nature opposing cardiovascular diseases. Curr Cardiol Rev.
14:272–289. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Thushara RM, Hemshekhar M, Santhosh MS,
Jnaneshwari S, Nayaka SC, Naveen S, Kemparaju K and Girish KS:
Crocin, a dietary additive protects platelets from oxidative
stress-induced apoptosis and inhibits platelet aggregation. Mol
Cell Biochem. 373:73–83. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Rahmani J, Manzari N, Thompson J, Clark
CCT, Villanueva G, Varkaneh HK and Mirmiran P: The effect of
saffron on weight and lipid profile: A systematic review,
meta-analysis, and dose-response of randomized clinical trials.
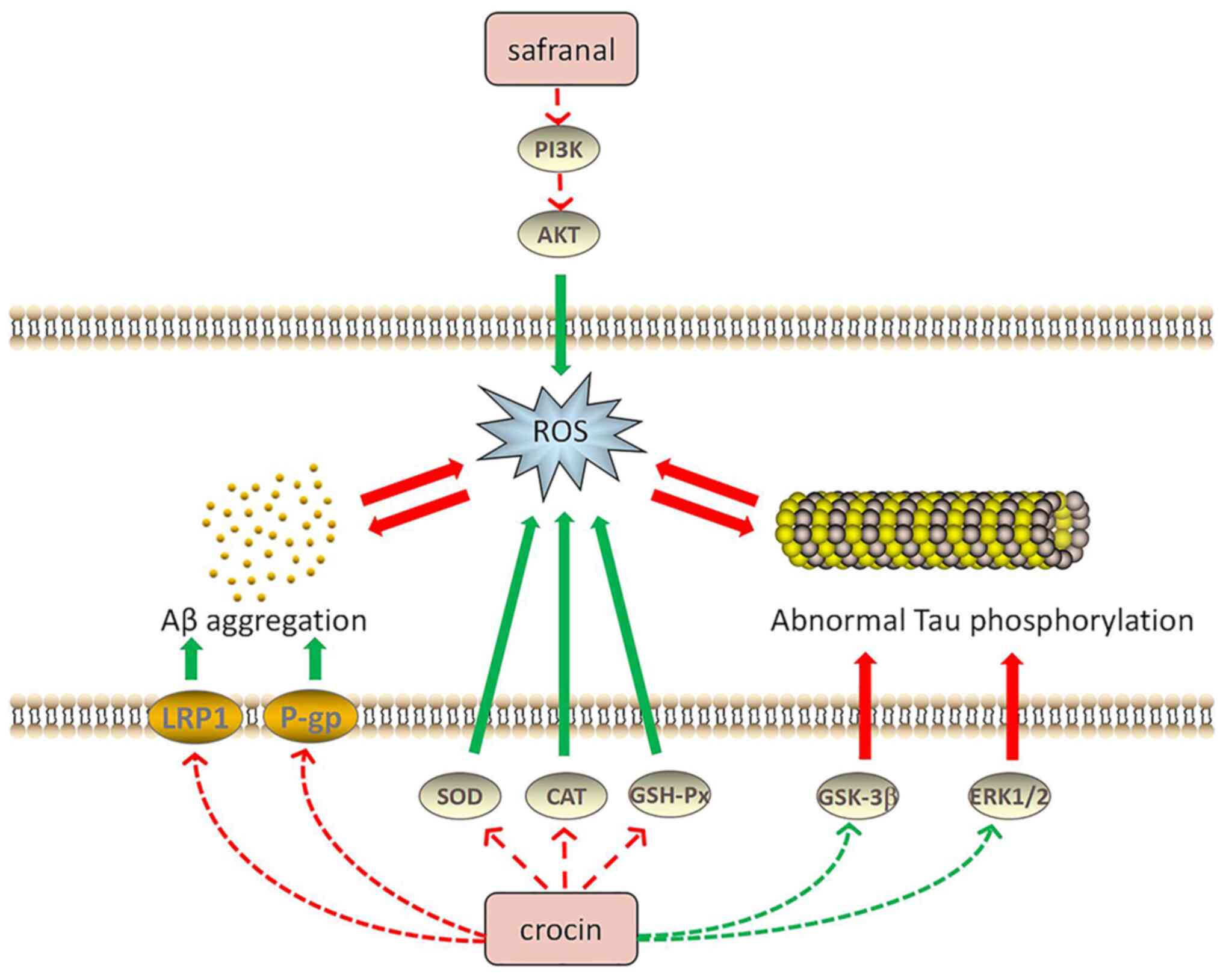
Phytother Res. 33:2244–2255. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Zhang A, Shen Y, Cen M, Hong X, Shao QS,
Chen Y and Zheng B: Polysaccharide and crocin contents, and
antioxidant activity of saffron from different origins. Ind Crop
Prod. 133:111–117. 2019.
|
|
10
|
Xue Y, Jin W, Xue Y, Zhang Y, Wang H,
Zhang Y, Guan S, Chu X and Zhang J: Safranal, an active constituent
of saffron, ameliorates myocardial ischemia via reduction of
oxidative stress and regulation of Ca2+ homeostasis. J
Pharmacol Sci. 143:156–164. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
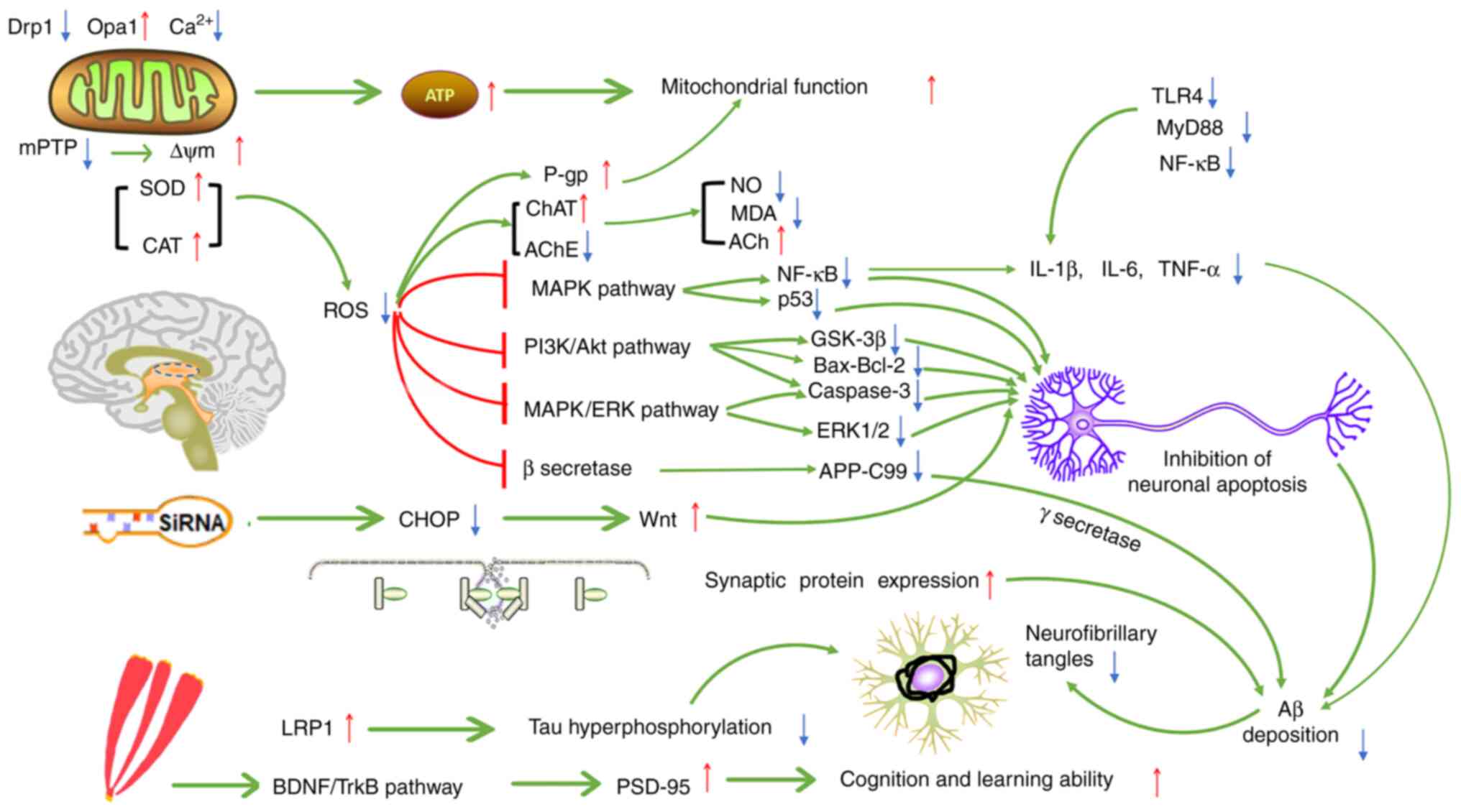
|
|
11
|
Poma A, Fontecchio G, Carlucci G and
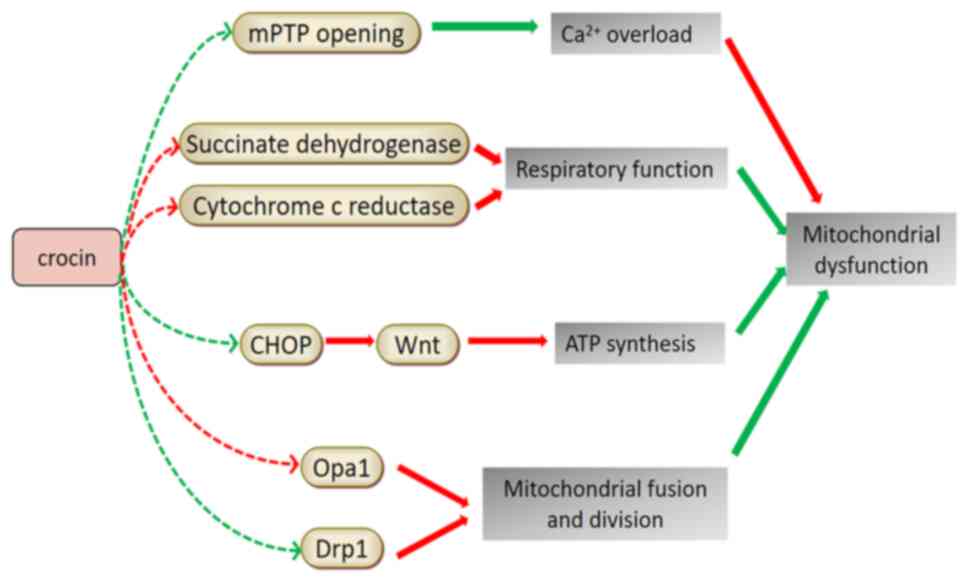
Chichiriccò G: Anti-inflammatory properties of drugs from saffron
crocus. Antiinflamm Antiallergy Agents Med Chem. 11:37–51.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Singh G, Haileselassie Y, Ji AR, Maecker
HT, Sinha SR, Brim H, Habtezion A and Ashktorab H: Protective
effect of saffron in mouse colitis models through immune
modulation. Digest Dis Sci. 67:2922–2935. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Lambrianidou A, Koutsougianni F,
Papapostolou I and Dimas K: Recent advances on the anticancer
properties of saffron (Crocus sativus L.) and its major
constituents. Molecules. 26(86)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Siddiqui SA, Ali Redha A, Snoeck ER, Singh
S, Simal-Gandara J, Ibrahim SA and Jafari SM: Anti-depressant
properties of crocin molecules in saffron. Molecules.
27(2076)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
José Bagur M, Alonso Salinas GL,
Jiménez-Monreal AM, Chaouqi S, Llorens S, Martínez-Tomé M and
Alonso GL: Saffron: An old medicinal plant and a potential novel
functional food. Molecules. 23(30)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Howes MR, Perry NSL, Vásquez-Londoño C and
Perry EK: Role of phytochemicals as nutraceuticals for cognitive
functions affected in ageing. Br J Pharmacol. 177:1294–1315.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Bathaie SZ: Saffron as a functional food
and a nutraceutical using saffron and its constituents as the
nutraceutics to protect against chronic diseases. Acta Hortic.
1200:201–204. 2018.
|
|
18
|
Hardy J: Pathways to primary
neurodegenerative disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 924:29–34.
2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Höglund K and Salter H: Molecular
biomarkers of neurodegeneration. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 13:845–861.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Sheikh S, Safia Haque E and Mir SS:
Neurodegenerative diseases: Multifactorial conformational diseases
and their therapeutic interventions. J Neurodegener Dis.
2013(563481)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Di Stefano A, Sozio P and Cerasa LS:
Antiparkinson prodrugs. Molecules. 13:46–68. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Klietz M, Greten S, Wegner F and Höglinger
GU: Safety and tolerability of pharmacotherapies for Parkinson's
disease in geriatric patients. Drugs Aging. 36:511–530.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Hosseinzadeh H and Sadeghnia HR: Safranal,
a constituent of Crocus sativus (saffron), attenuated
cerebral ischemia induced oxidative damage in rat hippocampus. J
Pharm Pharm Sci. 8:394–399. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Salem M, Shaheen M, Tabbara A and Borjac
J: Saffron extract and crocin exert anti-inflammatory and
anti-oxidative effects in a repetitive mild traumatic brain injury
mouse model. Sci Rep. 12(5004)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Saeedi M and Rashidy-Pour A: Association
between chronic stress and Alzheimer's disease: Therapeutic effects
of Saffron. Biomed Pharmacother. 133(110995)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Gregory J, Vengalasetti YV, Bredesen DE
and Rao RV: Neuroprotective herbs for the management of Alzheimer's
disease. Biomolecules. 11(543)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Hatziagapiou K, Kakouri E, Lambrou GI,
Bethanis K and Tarantilis PA: Antioxidant properties of Crocus
Sativus L. and its constituents and relevance to
neurodegenerative diseases; Focus on Alzheimer's and Parkinson's
disease. Curr Neuropharmacol. 17:377–402. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Ghasemi Sakha F, Azimi Saeen A, Moazzeni
SM, Etesam F and Vaezi G: A randomized, triple-blind
placebo-controlled trial to determine the effect of saffron on the
serum levels of MMP-9 and TIMP-1 in patients with multiple
sclerosis. Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol. 19:297–304.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Yuan Y, Shan X, Men W, Zhai H, Qiao X,
Geng L and Li C: The effect of crocin on memory, hippocampal
acetylcholine level, and apoptosis in a rat model of cerebral
ischemia. Biomed Pharmacother. 130(110543)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Jahromi GP, Khodadadi H, Fasihi-Ramandi M,
Esmaeili M and Shahriary A: Neuroprotective and antiapoptotic
effects of N-acetylcystein and Crocus sativus aqueous
extract on arsenic-induced neurotoxicity in SH-SY5Y human
dopaminergic neuroblastoma cells. Indian J Pharm Educ Res.
53:695–702. 2019.
|
|
31
|
Razavi BM and Hosseinzadeh H: Saffron as
an antidote or a protective agent against natural or chemical
toxicities. Daru. 23(31)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Chuquilín-Arista F, Álvarez-Avellón T and
Menéndez-González M: Prevalence of depression and anxiety in
Parkinson disease and impact on quality of life: A community-based
study in Spain. J Geriatr Psychiatry Neurol. 33:207–213.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Farkhondeh T, Samarghandian S, Shaterzadeh
Yazdi H and Samini F: The protective effects of crocin in the
management of neurodegenerative diseases: A review. Am J
Neurodegener Dis. 7:1–10. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Bian Y, Zhao C and Lee SMY:
Neuroprotective potency of saffron against neuropsychiatric
diseases, neurodegenerative diseases, and other brain disorders:
From bench to bedside. Front Pharmacol. 11(579052)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Uttara B, Singh AV, Zamboni P and Mahajan
RT: Oxidative stress and neurodegenerative diseases: A review of
upstream and downstream antioxidant therapeutic options. Curr
Neuropharmacol. 7:65–74. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Halliwell B: Oxidative stress and
neurodegeneration: Where are we now? J Neurochem. 97:1634–1658.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Praticò D: Oxidative stress hypothesis in
Alzheimer's disease: A reappraisal. Trends Pharmacol Sci.
29:609–615. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Reynolds A, Laurie C, Mosley RL and
Gendelman HE: Oxidative stress and the pathogenesis of
neurodegenerative disorders. Int Rev Neurobiol. 82:297–325.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Wojsiat J, Zoltowska KM, Laskowska-Kaszub
K and Wojda U: Oxidant/antioxidant imbalance in Alzheimer's
disease: Therapeutic and diagnostic prospects. Oxid Med Cell
Longev. 2018(6435861)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Danielson SR and Andersen JK: Oxidative
and nitrative protein modifications in Parkinson's disease. Free
Radical Bio Med. 44:1787–1794. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Yamamoto A, Shin RW, Hasegawa K, Naiki H,
Sato H, Yoshimasu F and Kitamoto T: Iron (III) induces aggregation
of hyperphosphorylated tau and its reduction to iron (II) reverses
the aggregation: Implications in the formation of neurofibrillary
tangles of Alzheimer's disease. J Neurochem. 82:1137–1147.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Su B, Wang X, Lee HG, Tabaton M, Perry G,
Smith MA and Zhu X: Chronic oxidative stress causes increased tau
phosphorylation in M17 neuroblastoma cells. Neurosci Lett.
468:267–271. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Kumar V and Gill KD: Oxidative stress and
mitochondrial dysfunction in aluminium neurotoxicity and its
amelioration: A review. Neurotoxicology. 41:154–166.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Lim J and Yue Z: Neuronal aggregates:
Formation, clearance, and spreading. Dev Cell. 32:491–501.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Sabayan B, Namazi MR, Mowla A and Moniri
SA: Are patients with Darier and Haily-Haily diseases susceptible
to Alzheimer's disease? A theory based on abnormal intraneuronal
Ca2+ homeostasis. J Alzheimers Dis. 16:521–523. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Singh N, Haldar S, Tripathi AK, McElwee
MK, Horback K and Beserra A: Iron in neurodegenerative disorders of
protein misfolding: A case of prion disorders and Parkinson's
disease. Antioxid Redox Signal. 21:471–484. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Hare DJ and Double KL: Iron and dopamine:
A toxic couple. Brain. 139:1026–1035. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Batarseh YS, Bharate SS, Kumar V, Kumar A,
Vishwakarma RA, Bharate SB and Kaddoumi A: Crocus sativus
extract tightens the blood-brain barrier, reduces Amyloid β load
and related toxicity in 5XFAD mice. ACS Chem Neurosci. 8:1756–1766.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Papandreou MA, Kanakis CD, Polissiou MG,
Efthimiopoulos S, Cordopatis P, Margarity M and Lamari FN:
Inhibitory activity on amyloid-beta aggregation and antioxidant
properties of Crocus sativus stigmas extract and its crocin
constituents. J Agric Food Chem. 54:8762–8768. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Shati AA, Elsaid FG and Hafez EE:
Biochemical and molecular aspects of aluminium chloride-induced
neurotoxicity in mice and the protective role of Crocus
sativus L. extraction and honey syrup. Neuroscience. 175:66–74.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Reeta KH, Singh D and Gupta YK: Chronic
treatment with taurine after intracerebroventricular streptozotocin
injection improves cognitive dysfunction in rats by modulating
oxidative stress, cholinergic functions and neuroinflammation.
Neurochem Int. 108:146–156. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Bharate SS, Kumar V, Singh G, Singh A,
Gupta M, Singh D, Kumar A, Vishwakarma RA and Bharate SB:
Preclinical development of Crocus sativus-based botanical
lead IIIM-141 for Alzheimer's disease: Chemical standardization,
efficacy, formulation development, pharmacokinetics, and safety
pharmacology. ACS Omega. 3:9572–9585. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Kapucu A: Crocin ameliorates oxidative
stress and suppresses renal damage in streptozotocin induced
diabetic male rats. Biotech Histochem. 96:153–160. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Naghizadeh B, Mansouri MT, Ghorbanzadeh B,
Farbood Y and Sarkaki A: Protective effects of oral crocin against
intracerebroventricular streptozotocin-induced spatial memory
deficit and oxidative stress in rats. Phytomedicine. 20:537–542.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Asadi F, Jamshidi AH, Khodagholi F, Yans
A, Azimi L, Faizi M, Vali L, Abdollahi M and Ghahremani MH:
Reversal effects of crocin on amyloid β-induced memory deficit:
Modification of autophagy or apoptosis markers. Pharmacol Biochem
Behav. 139:47–58. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Wang C, Cai X, Hu W, Li Z, Kong F, Chen X
and Wang D: Investigation of the neuroprotective effects of crocin
via antioxidant activities in HT22 cells and in mice with
Alzheimer's disease. Int J Mol Med. 43:956–966. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Osaki LH and Gama P: MAPKs and signal
transduction in the control of gastrointestinal epithelial cell
proliferation and differentiation. Int J Mol Sci. 14:10143–10161.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Kim EK and Choi EJ: Pathological roles of
MAPK signaling pathways in human diseases. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1802:396–405. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Shehzad A and Lee YS: Molecular mechanisms
of curcumin action: Signal transduction. Biofactors. 39:27–36.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Vriz S, Reiter S and Galliot B: Cell
death: A program to regenerate. Curr Top Dev Biol. 108:121–151.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Rafieipour F, Hadipour E, Emami SA, Asili
J and Tayarani-Najaran Z: Safranal protects against beta-amyloid
peptide-induced cell toxicity in PC12 cells via MAPK and PI3K
pathways. Metab Brain Dis. 34:165–172. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Baluchnejadmojarad T, Mohamadi-Zarch SM
and Roghani M: Safranal, an active ingredient of saffron,
attenuates cognitive deficits in amyloid β-induced rat model of
Alzheimer's disease: Underlying mechanisms. Metab Brain Dis.
34:1747–1759. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Alonso AC, Zaidi T, Grundke-Iqbal I and
Iqbal K: Role of abnormally phosphorylated tau in the breakdown of
microtubules in Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
91:5562–5566. 1994.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Chalatsa I, Arvanitis DA, Koulakiotis NS,
Giagini A, Skaltsounis AL, Papadopoulou-Daifoti Z, Tsarbopoulos A
and Sanoudou D: The Crocus sativus compounds trans-crocin 4
and trans-crocetin modulate the amyloidogenic pathway and tau
misprocessing in Alzheimer disease neuronal cell culture models.
Front Neurosci. 13(249)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Rashedinia M, Lari P, Abnous K and
Hosseinzadeh H: Protective effect of crocin on acrolein-induced tau
phosphorylation in the rat brain. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars).
75:208–219. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Koulakiotis NS, Purhonen P, Gikas E,
Hebert H and Tsarbopoulos A: Crocus-derived compounds alter the
aggregation pathway of Alzheimer's disease: Associated beta amyloid
protein. Sci Rep. 10(18150)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Haeri P, Mohammadipour A, Heidari Z and
Ebrahimzadeh-Bideskan A: Neuroprotective effect of crocin on
substantia nigra in MPTP-induced Parkinson's disease model of mice.
Anat Sci Int. 94:119–127. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Rao SV, Muralidhara Yenisetti SC and
Rajini PS: Evidence of neuroprotective effects of saffron and
crocin in a Drosophila model of parkinsonism. Neurotoxicology.
52:230–242. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Finley JW and Gao S: A Perspective on
Crocus sativus L. (saffron) constituent crocin: A potent
water-soluble antioxidant and potential therapy for Alzheimer's
disease. J Agric Food Chem. 65:1005–1020. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Chen WW, Zhang X and Huang WJ: Role of
neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative diseases (Review). Mol Med
Rep. 13:3391–3396. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Spencer JP, Vafeiadou K, Williams RJ and
Vauzour D: Neuroinflammation: Modulation by flavonoids and
mechanisms of action. Mol Aspects Med. 33:83–97. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
McManus RM and Heneka MT: Role of
neuroinflammation in neurodegeneration: New insights. Alzheimers
Res Ther. 9(14)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Simpson DSA and Oliver PL: ROS Generation
in microglia: Understanding oxidative stress and inflammation in
neurodegenerative disease. Antioxidants (Basel).
9(743)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Spagnuolo C, Moccia S and Russo GL:
Anti-inflammatory effects of flavonoids in neurodegenerative
disorders. Eur J Med Chem. 153:105–115. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Korani S, Korani M, Sathyapalan T and
Sahebkar A: Therapeutic effects of crocin in autoimmune diseases: A
review. Biofactors. 45:835–843. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Zhang J, Wang Y, Dong X and Liu J:
Crocetin attenuates inflammation and amyloid-β accumulation in
APPsw transgenic mice. Immun Ageing. 15(24)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Jurcau A and Simion A: Neuroinflammation
in cerebral ischemia and ischemia/reperfusion injuries: From
pathophysiology to therapeutic strategies. Int J Mol Sci.
23(14)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Das J and G K R: Post stroke depression:
The sequelae of cerebral stroke. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 90:104–114.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Wang SH, Zhang ZJ, Guo YJ, Sui YX and Sun
Y: Involvement of serotonin neurotransmission in hippocampal
neurogenesis and behavioral responses in a rat model of post-stroke
depression. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 95:129–137. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Xu QQ, Qian XD, Sun F, Liu H, Dou ZJ, Gong
J and Zhang XR: Effects of crocin on inflammatory response and
TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway in post-stroke depression rats.
Chin J Immunol. 37:179–185. 2021.
|
|
81
|
Johannsen DL and Ravussin E: The role of
mitochondria in health and disease. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 9:780–786.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Hernández-Reséndiz S, Buelna-Chontal M,
Correa F and Zazueta C: Targeting mitochondria for cardiac
protection. Curr Drug Targets. 14:586–600. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Lin MT and Beal MF: Mitochondrial
dysfunction and oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases.
Nature. 443:787–795. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Shults CW: Mitochondrial dysfunction and
possible treatments in Parkinson's disease-a review. Mitochondrion.
4:641–648. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Zhang GF, Zhang Y and Zhao G: Crocin
protects PC12 cells against MPP(+)-induced injury through
inhibition of mitochondrial dysfunction and ER stress. Neurochem
Int. 89:101–110. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Vongsfak J, Pratchayasakul W, Apaijai N,
Vaniyapong T, Chattipakorn N and Chattipakorn SC: The alterations
in mitochondrial dynamics following cerebral ischemia/reperfusion
injury. Antioxidants (Basel). 10(1384)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Wen B: Study on the protective effect of
crocin pretreatment on hippocampal mitochondria in the rats with
ischemic brain injury. Mod J Integr Tradit Chin West Med.
29(6)2020.
|
|
88
|
Zhang YH, Cong WH and Liu JX: Effect of
crocin on mitochondrial dynamics in SH-SY5Y cells against injury
induced by oxygen-glucose deprivation. Chin Pharmacol Bull.
32:986–990. 2016.
|
|
89
|
Zhang YH, Yao MJ, Cong WH and Liu JX:
Effect of extraction of saffron crocus on mitochondrial dynamics in
ischemia/reperfusion rats. Chin Pharmacol Bull. 34:770–775.
2018.
|
|
90
|
Reddy PH: Abnormal tau, mitochondrial
dysfunction, impaired axonal transport of mitochondria, and
synaptic deprivation in Alzheimer's disease. Brain Res.
1415:136–148. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
91
|
Lin L, Liu G and Yang L: Crocin improves
cognitive behavior in rats with Alzheimer's disease by regulating
endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis. Biomed Res Int.
2019(9454913)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Hadipour M, Kaka G, Bahrami F, Meftahi GH,
Pirzad Jahromi G, Mohammadi A and Sahraei H: Crocin improved
amyloid beta induced long-term potentiation and memory deficits in
the hippocampal CA1 neurons in freely moving rats. Synapse.
72(e22026)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
93
|
Naghibi SM, Hosseini M, Khani F, Rahimi M,
Vafaee F, Rakhshandeh H and Aghaie A: Effect of aqueous extract of
Crocus sativus L. on morphine-induced memory impairment. Adv
Pharmacol Sci. 2012(494367)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
94
|
Mazumder AG, Sharma P, Patial V and Singh
D: Crocin attenuates kindling development and associated cognitive
impairments in mice via inhibiting reactive oxygen species-mediated
NF-κB activation. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 120:426–433.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
95
|
Canal CE, Chang Q and Gold PE: Amnesia
produced by altered release of neurotransmitters after
intraamygdala injections of a protein synthesis inhibitor. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:12500–12505. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
96
|
D'Amato RJ, Zweig RM, Whitehouse PJ, Wenk
GL, Singer HS, Mayeux R, Price DL and Snyder SH: Aminergic systems
in Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease. Ann Neurol.
22:229–236. 1987.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
97
|
Müller ML and Bohnen NI: Cholinergic
dysfunction in Parkinson's disease. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep.
13(377)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
98
|
Hall H, Reyes S, Landeck N, Bye C, Leanza
G, Double K, Thompson L, Halliday G and Kirik D: Hippocampal Lewy
pathology and cholinergic dysfunction are associated with dementia
in Parkinson's disease. Brain. 137:2493–2508. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
99
|
Geromichalos GD, Lamari FN, Papandreou MA,
Trafalis DT, Margarity M, Papageorgiou A and Sinakos Z: Saffron as
a source of novel acetylcholinesterase inhibitors: Molecular
docking and in vitro enzymatic studies. J Agric Food Chem.
60:6131–6138. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
100
|
Pitsikas N and Sakellaridis N: Crocus
sativus L. extracts antagonize memory impairments in different
behavioural tasks in the rat. Behav Brain Res. 173:112–115.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
101
|
Pitsikas N, Zisopoulou S, Tarantilis PA,
Kanakis CD, Polissiou MG and Sakellaridis N: Effects of the active
constituents of Crocus sativus L., crocins on recognition
and spatial rats' memory. Behav Brain Res. 183:141–146.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
102
|
White LD, Cory-Slechta DA, Gilbert ME,
Tiffany-Castiglioni E, Zawia NH, Virgolini M, Rossi-George A,
Lasley SM, Qian YC and Basha MR: New and evolving concepts in the
neurotoxicology of lead. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 225:1–27.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
103
|
Bakulski KM, Seo YA, Hickman RC, Brandt D,
Vadari HS, Hu H and Park SK: Heavy metals exposure and Alzheimer's
disease and related dementias. J Alzheimers Dis. 76:1215–1242.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
104
|
Butnariu M, Quispe C, Herrera-Bravo J,
Sharifi-Rad J, Singh L, Aborehab NM, Bouyahya A, Venditti A, Sen S,
Acharya K, et al: The pharmacological activities of Crocus
sativus L.: A review based on the mechanisms and therapeutic
opportunities of its phytoconstituents. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2022(8214821)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
105
|
Tamegart L, Abbaoui A, Makbal R, Zroudi M,
Bouizgarne B, Bouyatas MM and Gamrani H: Crocus sativus
restores dopaminergic and noradrenergic damages induced by lead in
Meriones shawi: A possible link with Parkinson's disease. Acta
Histochem. 121:171–181. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
106
|
Sartori E and Edan G: Assessment of
cognitive dysfunction in multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Sci.
245:169–175. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
107
|
Glanz BI, Healy BC, Hviid LE, Chitnis T
and Weiner HL: Cognitive deterioration in patients with early
multiple sclerosis: A 5-year study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry.
83:38–43. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
108
|
Ziehn MO, Avedisian AA, Tiwari-Woodruff S
and Voskuhl RR: Hippocampal CA1 atrophy and synaptic loss during
experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis, EAE. Lab Invest.
90:774–786. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
109
|
Ghaffari S, Hatami H and Dehghan G:
Saffron ethanolic extract attenuates oxidative stress, spatial
learning, and memory impairments induced by local injection of
ethidium bromide. Res Pharm Sci. 10:222–232. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Bonuccelli U, Meco G, Fabbrini G,
Tessitore A, Pierantozzi M, Stocchi F, Ceravolo R, Caltagirone C,
Silvestrini M, Morgante F, et al: A non-comparative assessment of
tolerability and efficacy of duloxetine in the treatment of
depressed patients with Parkinson's disease. Expert Opin
Pharmacother. 13:2269–2280. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
111
|
Dobkin RD, Menza M, Bienfait KL, Gara M,
Marin H, Mark MH, Dicke A and Friedman J: Depression in Parkinson's
disease: Symptom improvement and residual symptoms after acute
pharmacologic management. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 19:222–229.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
112
|
Lozupone M, La Montagna M, D'Urso F,
Piccininni C, Sardone R, Dibello V, Giannelli G, Solfrizzi V, Greco
A, Daniele A, et al: Pharmacotherapy for the treatment of
depression in patients with alzheimer's disease: A
treatment-resistant depressive disorder. Expert Opin Pharmacother.
19:823–842. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
113
|
Novais F and Starkstein S: Phenomenology
of depression in Alzheimer's disease. J Alzheimers Dis. 47:845–855.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
114
|
Pålhagen S, Qi H, Mårtensson B, Wålinder
J, Granérus AK and Svenningsson P: Monoamines, BDNF, IL-6 and
corticosterone in CSF in patients with Parkinson's disease and
major depression. J Neurol. 257:524–532. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
115
|
Schrag A and Taddei RN: Depression and
anxiety in Parkinson's disease. Int Rev Neurobiol. 133:623–655.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
116
|
Xiao Q, Xiong Z, Yu C, Zhou J, Shen Q,
Wang L, Xie X and Fu Z: Antidepressant activity of crocin-I is
associated with amelioration of neuroinflammation and attenuates
oxidative damage induced by corticosterone in mice. Physiol Behav.
212(112699)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
117
|
Ghadrdoost B, Vafaei AA, Rashidy-Pour A,
Hajisoltani R, Bandegi AR, Motamedi F, Haghighi S, Sameni HR and
Pahlvan S: Protective effects of saffron extract and its active
constituent crocin against oxidative stress and spatial learning
and memory deficits induced by chronic stress in rats. Eur J
Pharmacol. 667:222–229. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
118
|
Halataei BAS, Khosravi M, Arbabian S,
Sahraei H, Golmanesh L, Zardooz H, Jalili C and Ghoshooni H:
Saffron (Crocus sativus) aqueous extract and its constituent
crocin reduces stress-induced anorexia in mice. Phytother Res.
25:1833–1838. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
119
|
Ghasemi T, Abnous K, Vahdati F, Mehri S,
Razavi BM and Hosseinzadeh H: Antidepressant effect of Crocus
sativus aqueous extract and its effect on CREB, BDNF, and VGF
transcript and protein levels in rat hippocampus. Drug Res
(Stuttg). 65:337–343. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
120
|
Vahdati Hassani F, Naseri V, Razavi BM,
Mehri S, Abnous K and Hosseinzadeh H: Antidepressant effects of
crocin and its effects on transcript and protein levels of CREB,
BDNF, and VGF in rat hippocampus. Daru. 22(16)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
121
|
Cano A, Fonseca E, Ettcheto M,
Sánchez-López E, de Rojas I, Alonso-Lana S, Morató X, Souto EB,
Toledo M, Boada M, et al: Epilepsy in neurodegenerative diseases:
Related drugs and molecular pathways. Pharmaceuticals (Basel).
14(1057)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
122
|
Vezzani A, French J, Bartfai T and Baram
TZ: The role of inflammation in epilepsy. Nat Rev Neurol. 7:31–40.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
123
|
Filippini A, D'Amore A and D'Alessio A:
Calcium mobilization in endothelial cell functions. Int J Mol Sci.
20(4525)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
124
|
Maklad A, Sharma A and Azimi I: Calcium
signaling in brain cancers: Roles and therapeutic targeting.
Cancers (Basel). 11(145)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
125
|
Schrank S, Barrington N and Stutzmann GE:
Calcium-handling defects and neurodegenerative disease. Cold Spring
Harb Perspect Biol. 12(a035212)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
126
|
Xing B, Li S, Yang J, Lin D, Feng Y, Lu J
and Shao Q: Phytochemistry, pharmacology, and potential clinical
applications of saffron: A review. J Ethnopharmacol.
281(114555)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
127
|
Zhao Z, Zheng B, Li J, Wei Z, Chu S, Han
X, Chu L, Wang H and Chu X: Influence of crocetin, a natural
carotenoid dicarboxylic acid in saffron, on L-type Ca2+
current, intracellular Ca2+ handling and contraction of
isolated rat cardiomyocytes. Biol Pharm Bull. 43:1367–1374.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
128
|
Moshiri M, Vahabzadeh M and Hosseinzadeh
H: Clinical Applications of saffron (Crocus sativus) and its
constituents: A review. Drug Res (Stuttg). 65:287–295.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
129
|
Omidkhoda SF and Hosseinzadeh H: Saffron
and its active ingredients against human disorders: A literature
review on existing clinical evidence. Iran J Basic Med Sci.
25:913–933. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
130
|
Foster ER: Themes from the special issue
on neurodegenerative diseases: What have we learned, and where can
we go from here? Am J Occup Ther. 68:6–8. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
131
|
Akhondzadeh S, Shafiee Sabet M, Harirchian
MH, Togha M, Cheraghmakani H, Razeghi S, Hejazi SS, Yousefi MH,
Alimardani R, Jamshidi A, et al: A 22-week, multicenter,
randomized, double-blind controlled trial of Crocus sativus
in the treatment of mild-to-moderate Alzheimer's disease.
Psychopharmacology (Berl). 207:637–643. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
132
|
Asadollahi M, Nikdokht P, Hatef B, Sadr
SS, Sahraei H, Assarzadegan F and Pirzad Jahromi G: Protective
properties of the aqueous extract of saffron (Crocus sativus
L.) in ischemic stroke, randomized clinical trial. J
Ethnopharmacol. 238(111833)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
133
|
Zandi N, Pazoki B, Momeni Roudsari N,
Lashgari NA, Jamshidi V, Momtaz S, Abdolghaffari AH and Akhondzadeh
S: Prospects of saffron and its derivatives in Alzheimer's disease.
Arch Iran Med. 24:233–252. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
134
|
Marzabadi LR, Fazljou SMB, Araj-Khodaei M,
Sadigh-Eteghad S, Naseri A and Talebi M: Saffron reduces some
inflammation and oxidative stress markers in donepezil-treated
mild-to-moderate Alzheimer's disease patients: A randomized
double-blind placebo-control trial. J Herb Med. 34(100574)2022.
|