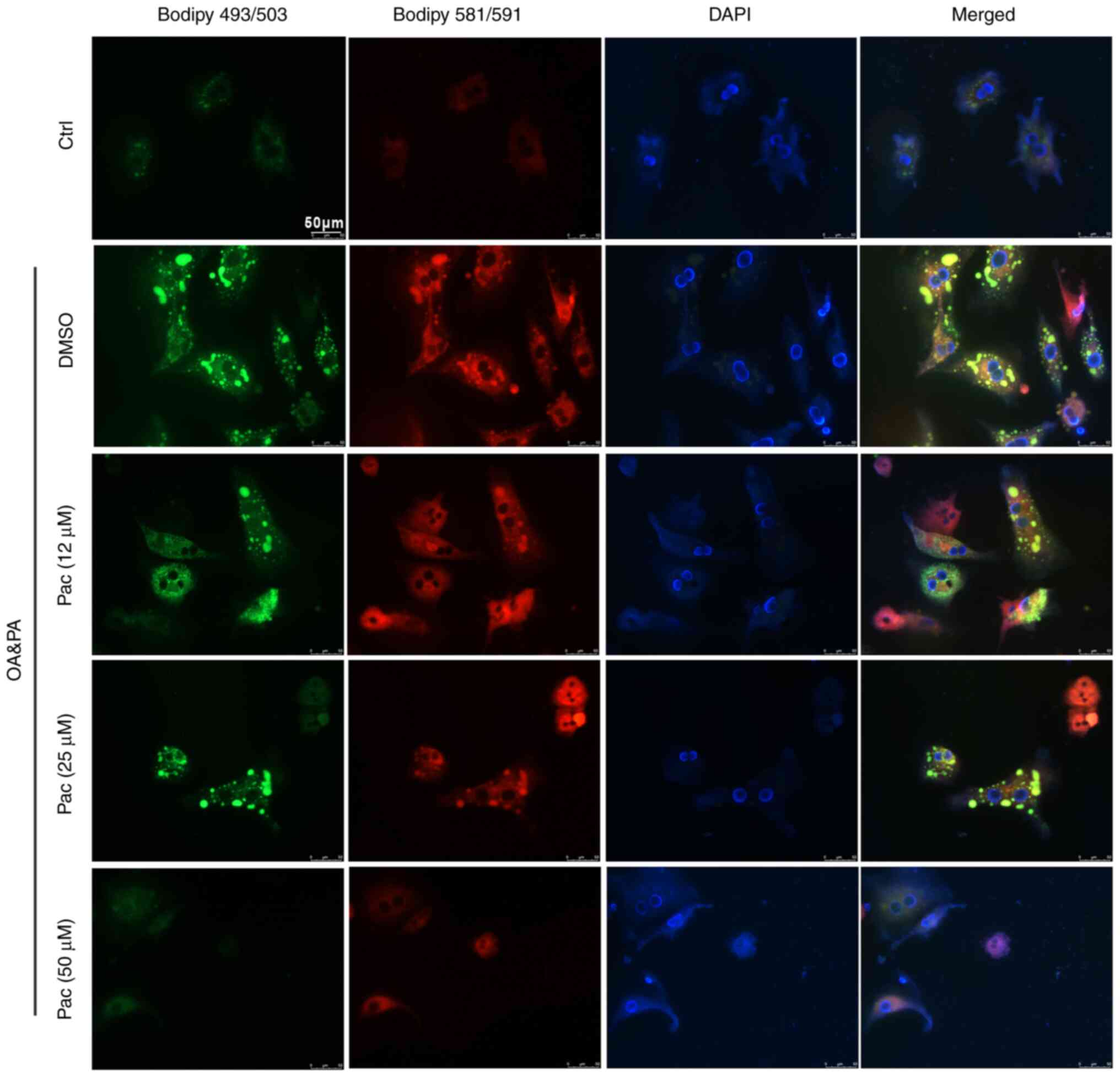
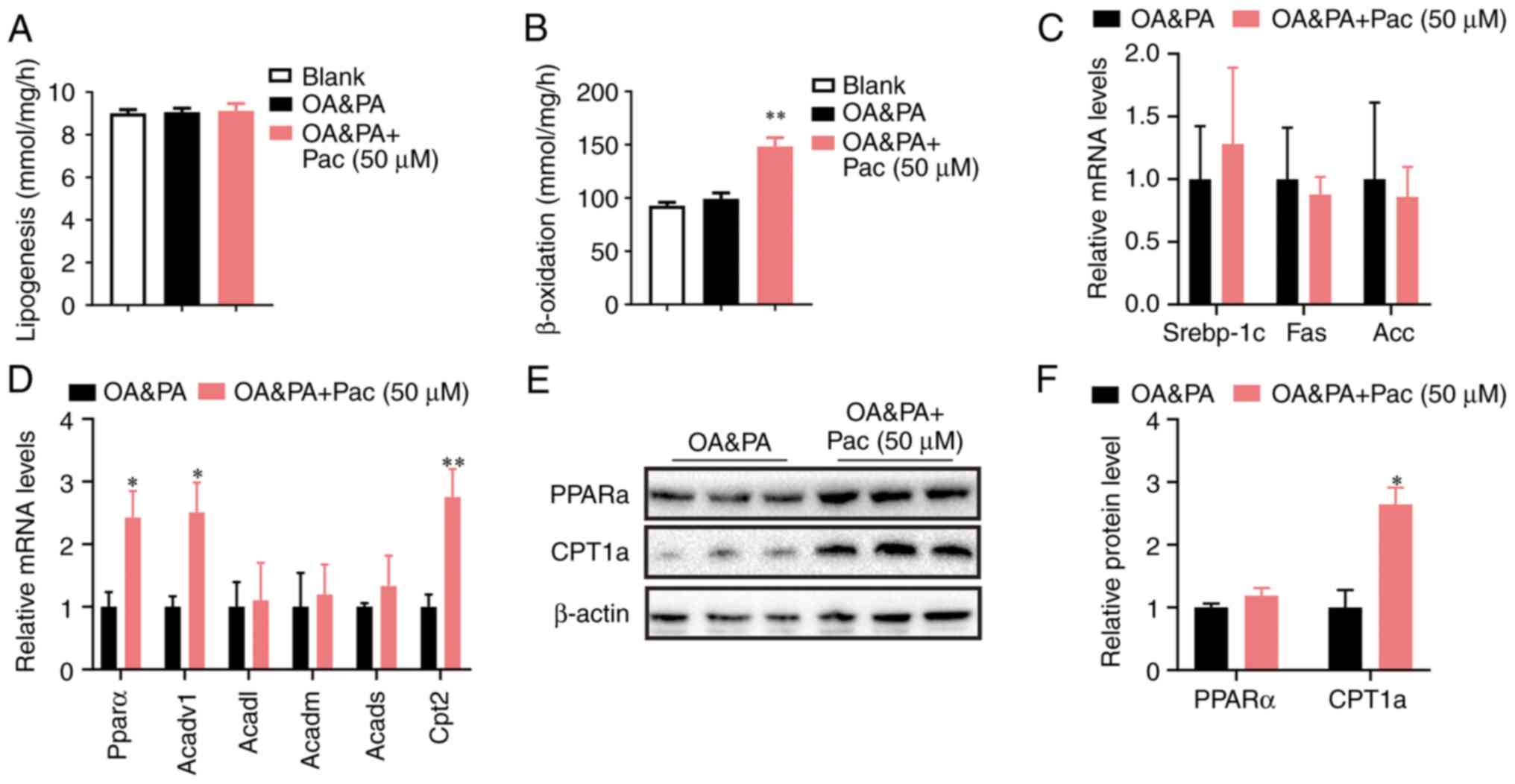
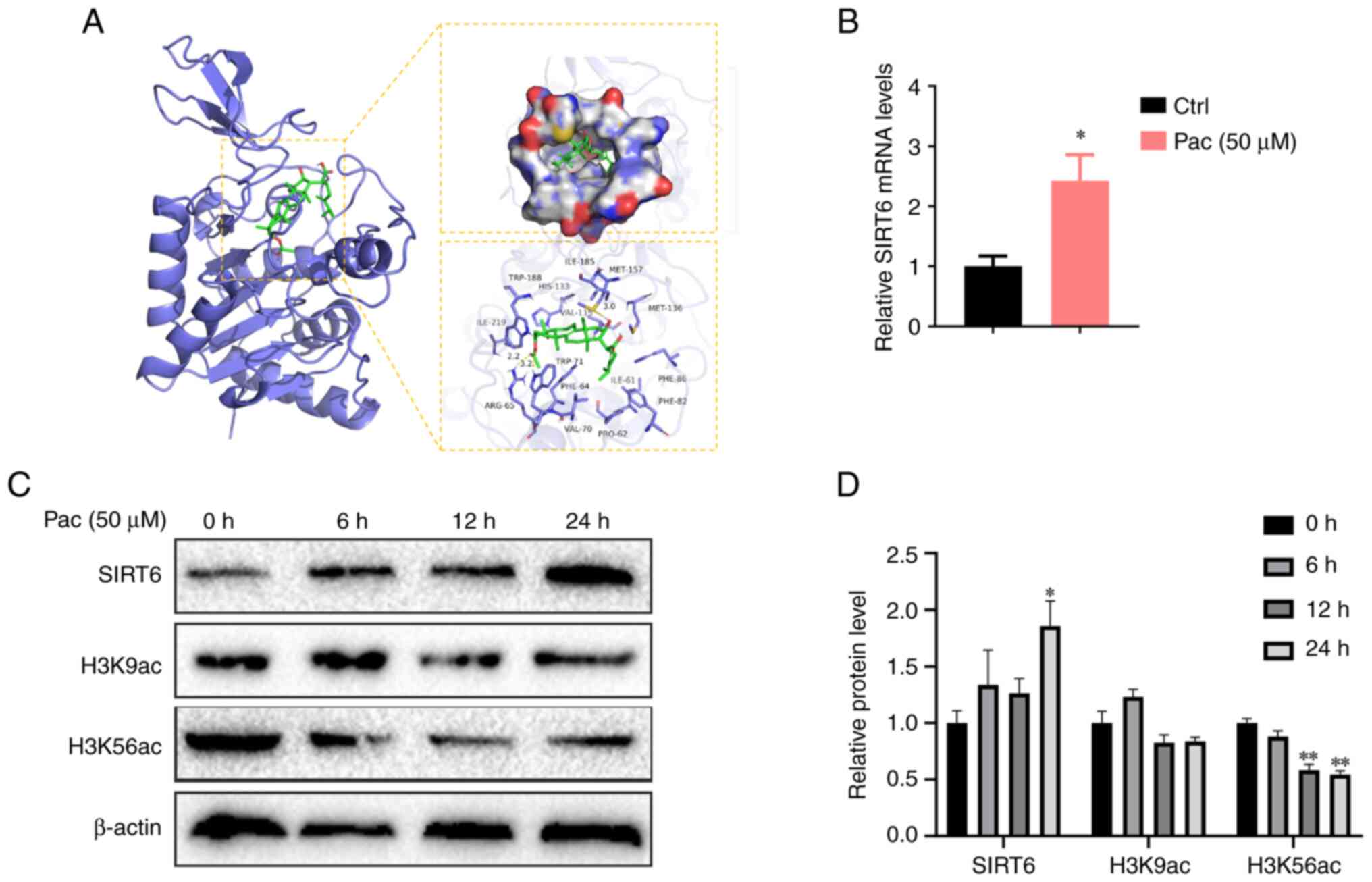
|
1
|
Juanola O, Martinez-Lopez S, Frances R and
Gomez-Hurtado I: Non-Alcoholic fatty liver disease: Metabolic,
genetic, epigenetic and environmental risk factors. Int J Environ
Res Public Health. 18(5227)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Byun S, Seok S, Kim YC, Zhang Y, Yau P,
Iwamori N, Xu HE, Ma J, Kemper B and Kemper JK: Fasting-induced
FGF21 signaling activates hepatic autophagy and lipid degradation
via JMJD3 histone demethylase. Nat Commun. 11(807)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Alves-Bezerra M and Cohen DE: Triglyceride
metabolism in the liver. Compr Physiol. 8:1–8. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Secor JD, Fligor SC, Tsikis ST, Yu LJ and
Puder M: Free fatty acid receptors as mediators and therapeutic
targets in liver disease. Front Physiol. 12(656441)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Jiang G, Chen D, Li W, Liu C, Liu J and
Guo Y: Effects of wogonoside on the inflammatory response and
oxidative stress in mice with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
Pharm Biol. 58:1177–1183. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Kersten S and Stienstra R: The role and
regulation of the peroxisome proliferator activated receptor alpha
in human liver. Biochimie. 136:75–84. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Sun N, Shen C, Zhang L, Wu X, Yu Y, Yang
X, Yang C, Zhong C, Gao Z, Miao W, et al: Hepatic Kruppel-like
factor 16 (KLF16) targets PPARα to improve steatohepatitis and
insulin resistance. Gut. 70:2183–2195. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Wahli W and Michalik L: PPARs at the
crossroads of lipid signaling and inflammation. Trends Endocrinol
Metab. 23:351–363. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Montagner A, Polizzi A, Fouche E, Ducheix
S, Lippi Y, Lasserre F, Barquissau V, Régnier M, Lukowicz C,
Benhamed F, et al: Liver PPARα is crucial for whole-body fatty acid
homeostasis and is protective against NAFLD. Gut. 65:1202–1214.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Yang DK and Jo DG: Mulberry fruit extract
ameliorates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) through
inhibition of mitochondrial oxidative stress in rats. Evid Based
Complement Alternat Med. 2018(8165716)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Wu W, Peng G, Yang F, Zhang Y, Mu Z and
Han X: Sulforaphane has a therapeutic effect in an atopic
dermatitis murine model and activates the Nrf2/HO1 axis. Mol Med
Rep. 20:1761–1771. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Yan C, Sun W, Wang X, Long J, Liu X, Feng
Z and Liu J: Punicalagin attenuates palmitate-induced lipotoxicity
in HepG2 cells by activating the Keap1-Nrf2 antioxidant defense
system. Mol Nutr Food Res. 60:1139–1149. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Van Gool F, Galli M, Gueydan C, Kruys V,
Prevot PP, Bedalov A, Mostoslavsky R, Alt FW, De Smedt T and Leo O:
Intracellular NAD levels regulate tumor necrosis factor protein
synthesis in a sirtuin-dependent manner. Nat Med. 15:206–210.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Naiman S, Huynh FK, Gil R, Glick Y, Shahar
Y, Touitou N, Nahum L, Avivi MY, Roichman A, Kanfi Y, et al: SIRT6
promotes hepatic beta-oxidation via activation of PPARα. Cell Rep.
29:4127–4143 e8. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Kim HS, Xiao C, Wang RH, Lahusen T, Xu X,
Vassilopoulos A, Vazquez-Ortiz G, Jeong WI, Park O, Ki SH, et al:
Hepatic-specific disruption of SIRT6 in mice results in fatty liver
formation due to enhanced glycolysis and triglyceride synthesis.
Cell Metab. 12:224–236. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Kuang J, Chen L, Tang Q, Zhang J, Li Y and
He J: The role of Sirt6 in obesity and diabetes. Front Physiol.
9(135)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Kanfi Y, Peshti V, Gil R, Naiman S, Nahum
L, Levin E, Kronfeld-Schor N and Cohen HY: SIRT6 protects against
pathological damage caused by diet-induced obesity. Aging Cell.
9:162–173. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Ding B, Ji X, Sun X, Zhang T and Mu S: In
vitro effect of pachymic acid on the activity of Cytochrome P450
enzymes. Xenobiotica. 50:913–918. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Akihisa T, Nakamura Y, Tokuda H, Uchiyama
E, Suzuki T, Kimura Y, Uchikura K and Nishino H: Triterpene acids
from Poria cocos and their anti-tumor-promoting effects. J Nat
Prod. 70:948–953. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Kim TG, Lee YH, Lee NH, Bhattarai G, Lee
IK, Yun BS and Yi HK: The antioxidant property of pachymic acid
improves bone disturbance against AH plus-induced inflammation in
MC-3T3 E1 cells. J Endod. 39:461–466. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Lee YH, Lee NH, Bhattarai G, Kim GE, Lee
IK, Yun BS, Hwang PH and Yi HK: Anti-inflammatory effect of
pachymic acid promotes odontoblastic differentiation via HO-1 in
dental pulp cells. Oral Dis. 19:193–199. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Lu C, Ma J and Cai D: Pachymic acid
inhibits the tumorigenicity of gastric cancer cells by the
mitochondrial pathway. Anticancer Drugs. 28:170–179.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Kim JH, Sim HA, Jung DY, Lim EY, Kim YT,
Kim BJ and Jung MH: Poria cocus Wolf extract ameliorates hepatic
steatosis through regulation of lipid metabolism, inhibition of ER
stress, and activation of autophagy via AMPK activation. Int J Mol
Sci. 20(4801)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Chen L, Liu Q, Tang Q, Kuang J, Li H, Pu
S, Wu T, Yang X, Li R, Zhang J, et al: Hepatocyte-specific Sirt6
deficiency impairs ketogenesis. J Biol Chem. 294:1579–1589.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Friesner RA, Banks JL, Murphy RB, Halgren
TA, Klicic JJ, Mainz DT, Repasky MP, Knoll EH, Shelley M, Perry JK,
et al: Glide: A new approach for rapid, accurate docking and
scoring. 1. Method and assessment of docking accuracy. J Med Chem.
47:1739–1749. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Fazi R, Tintori C, Brai A, Botta L,
Selvaraj M, Garbelli A, Maga G and Botta M: Homology model-based
virtual screening for the identification of human helicase DDX3
inhibitors. J Chem Inf Model. 55:2443–2454. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Chen Z, Tian R, She Z, Cai J and Li H:
Role of oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of nonalcoholic fatty
liver disease. Free Radic Biol Med. 152:116–141. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Zhou Y, Fan X, Jiao T, Li W, Chen P, Jiang
Y, Sun J, Chen Y, Chen P, Guan L, et al: SIRT6 as a key event
linking P53 and NRF2 counteracts APAP-induced hepatotoxicity
through inhibiting oxidative stress and promoting hepatocyte
proliferation. Acta Pharm Sin B. 11:89–99. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Rives C, Fougerat A, Ellero-Simatos S,
Loiseau N, Guillou H, Gamet-Payrastre L and Wahli W: Oxidative
stress in NAFLD: Role of nutrients and food contaminants.
Biomolecules. 10(1702)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Fang YL, Chen H, Wang CL and Liang L:
Pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in children and
adolescence: From ‘two hit theory’ to ‘multiple hit model’. World J
Gastroenterol. 24:2974–2983. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Buzzetti E, Pinzani M and Tsochatzis EA:
The multiple-hit pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
(NAFLD). Metabolism. 65:1038–1048. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Pawlak M, Lefebvre P and Staels B:
Molecular mechanism of PPARalpha action and its impact on lipid
metabolism, inflammation and fibrosis in non-alcoholic fatty liver
disease. J Hepatol. 62:720–733. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Ferramosca A and Zara V: Modulation of
hepatic steatosis by dietary fatty acids. World J Gastroenterol.
20:1746–1755. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Kawahara TL, Michishita E, Adler AS,
Damian M, Berber E, Lin M, McCord RA, Ongaigui KC, Boxer LD, Chang
HY and Chua KF: SIRT6 links histone H3 lysine 9 deacetylation to
NF-kappaB-dependent gene expression and organismal life Span. Cell.
136:62–74. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Li Z, Xu K, Guo Y, Ping L, Gao Y, Qiu Y,
Ni J, Liu Q and Wang Z: A high-fat diet reverses metabolic
disorders and premature aging by modulating insulin and IGF1
signaling in SIRT6 knockout mice. Aging Cell.
19(e13104)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|