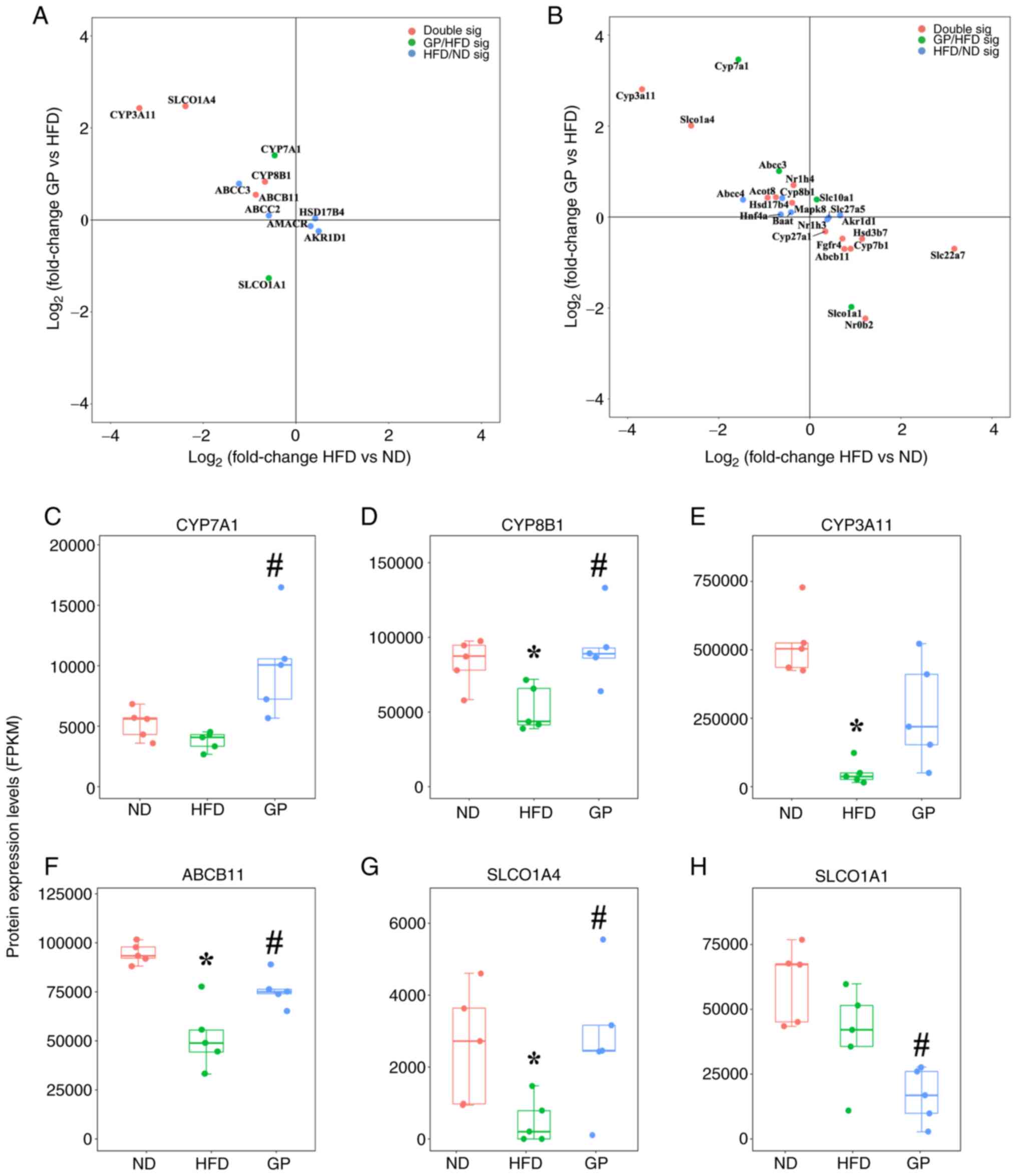
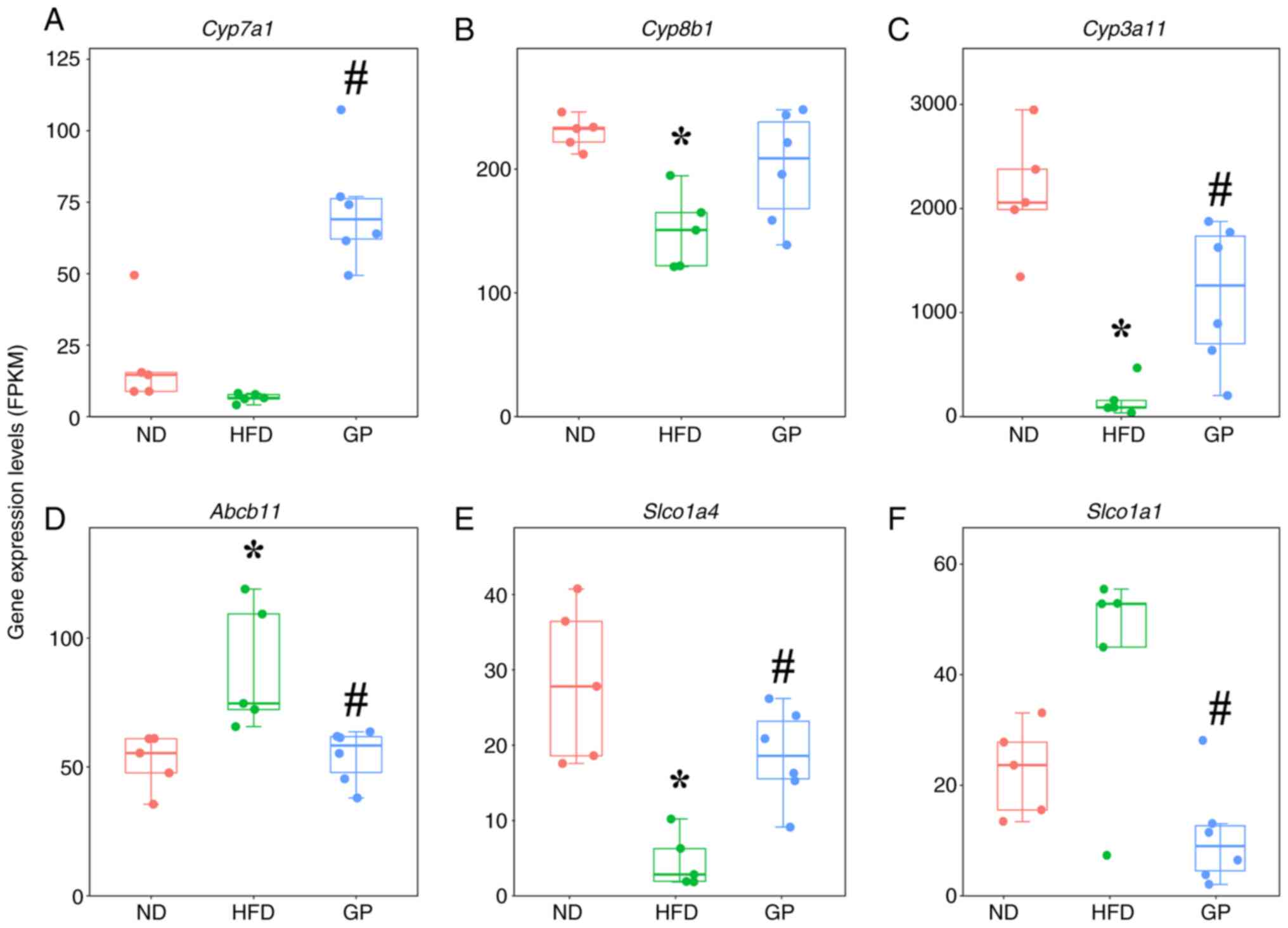
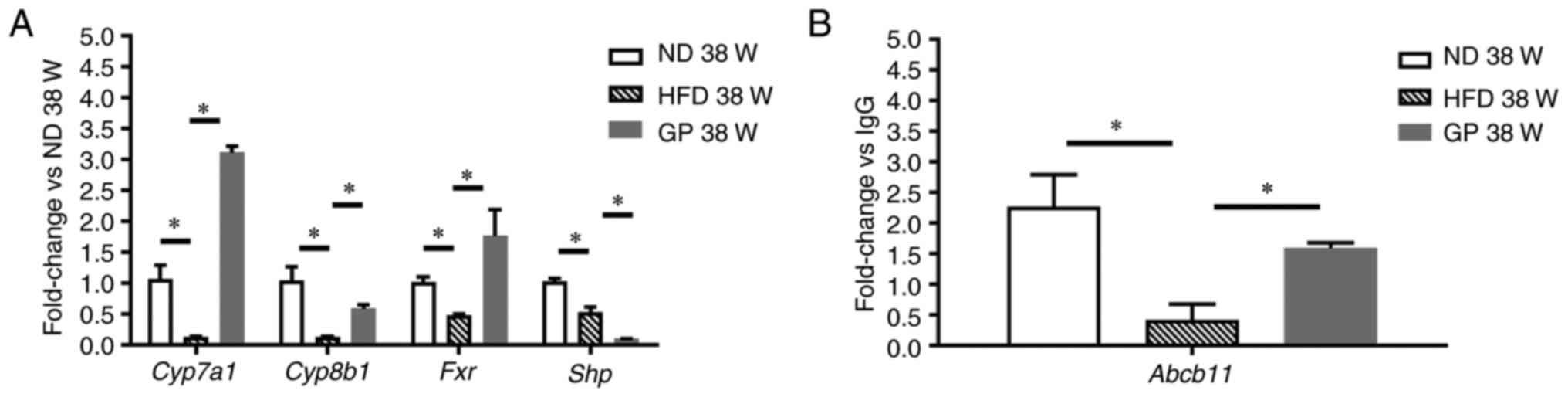
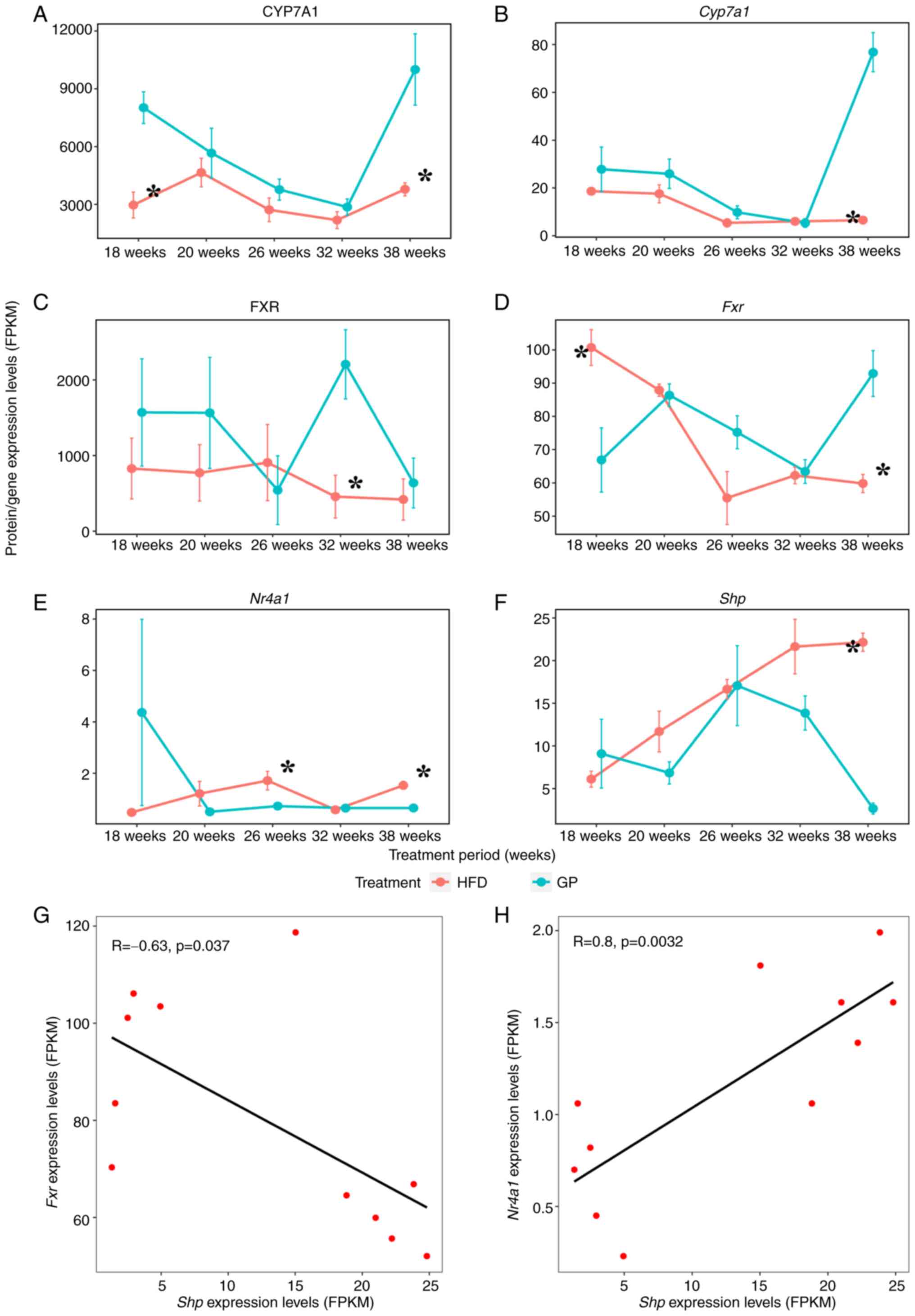
|
1
|
Yu JN, Cunningham SR, Thouin T, Gurvich D
and Liu D: Hyperlipidemia. Prim Care. 27:541–587. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Bunnoy A, Saenphet K, Lumyong S, Saenphet
S and Chomdej S: Monascus purpureus-fermented Thai glutinous rice
reduces blood and hepatic cholesterol and hepatic steatosis
concentrations in diet-induced hypercholesterolemic rats. BMC
Complement Altern Med. 15(88)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Karr S: Epidemiology and management of
hyperlipidemia. Am J Manag Care. 23:139–148. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Collins R, Reith C, Emberson J, Armitage
J, Baigent C, Blackwell L, Blumenthal R, Danesh J, Smith GD, DeMets
D, et al: Interpretation of the evidence for the efficacy and
safety of statin therapy. Lancet. 19:2532–2561. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Sessa M, Rafaniello C, Scavone C, Mascolo
A, di Mauro G, Fucile A, Rossi F, Sportiello L and Capuano A:
Preventable statin adverse reactions and therapy discontinuation.
What can we learn from the spontaneous reporting system? Expert
Opin Drug Saf. 17:457–465. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Livingstone SJ, Looker HC, Akbar T,
Betteridge DJ, Durrington PN, Hitman GA, Neil HA, Fuller JH and
Colhoun HM: Effect of atorvastatin on glycaemia progression in
patients with diabetes: An analysis from the collaborative
atorvastatin in diabetes trial (CARDS). Diabetologia. 59:299–306.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Lu Y, Du Y, Qin L, Wu D, Wang W, Ling L,
Ma F, Ling H, Yang L, Wang C, et al: Gypenosides altered hepatic
bile acids homeostasis in mice treated with high fat diet. Evid
Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018(8098059)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Megalli S, Aktan F, Davies NM and
Roufogalis BD: Phytopreventative anti-hyperlipidemic effects of
gynostemma pentaphyllum in rats. J Pharm Pharm Sci. 8:507–515.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Attawish A, Chivapat S, Phadungpat S,
Bansiddhi J, Techadamrongsin Y, Mitrijit O, Chaorai B and
Chavalittumrong P: Chronic toxicity of Gynostemma pentaphyllum.
Fitoterapia. 75:539–551. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Chiranthanut N, Teekachunhatean S,
Panthong A, Khonsung P, Kanjanapothi D and Lertprasertsuk N:
Toxicity evaluation of standardized extract of Gynostemma
pentaphyllum Makino. J Ethnopharmacol. 149:228–234. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Lazarević S, Đanić M, Goločorbin-Kon S,
Al-Salami H and Mikov M: Semisynthetic bile acids: A new
therapeutic option for metabolic syndrome. Pharmacol Res.
146(104333)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Staley C, Weingarden AR, Khoruts A and
Sadowsky MJ: Interaction of gut microbiota with bile acid
metabolism and its influence on disease states. Appl Microbiol
Biotechnol. 101:47–64. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Vallim TQdA, Tarling EJ and Edwards PA:
Pleiotropic roles of bile acids in metabolism. Cell Metab.
17:657–669. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Malhi H and Camilleri M: Modulating bile
acid pathways and TGR5 receptors for treating liver and GI
diseases. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 37:80–86. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Trauner M, Fuchs D, Halilbasic E and
Paumgartner G: New therapeutic concepts in bile acid transport and
signaling for management of cholestasis. Hepatology. 65:1393–1404.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Zhang L, Wang Q, Liu W, Liu F, Ji A and Li
Y: The orphan nuclear receptor 4A1: A potential new therapeutic
target for metabolic diseases. J Diabetes Res.
2018(9363461)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Dawson PA and Oelkers P: Bile acid
transporters. Curr Opin Lipidol. 6:109–114. 1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Meier PJ, Eckhardt U, Schroeder A,
Hagenbuch B and Stieger B: Substrate specificity of sinusoidal bile
acid and organic anion uptake systems in rat and human liver.
Hepatology. 26:1667–1677. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Modica S, Gadaleta RM and Moschetta A:
Deciphering the nuclear bile acid receptor FXR paradigm. Nucl
Recept Signal. 8(e005)2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Goodwin B, Jones SA, Price RR, Watson MA,
McKee DD, Moore LB, Galardi C, Wilson JG, Lewis MC, Roth ME, et al:
A regulatory cascade of the nuclear receptors FXR, SHP-1, and LRH-1
represses bile acid biosynthesis. Mol Cell. 6:517–526.
2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Chiang JY, Kimmel R, Weinberger C and
Stroup D: Farnesoid X receptor responds to bile acids and represses
cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase gene (CYP7A1) transcription. J Biol
Chem. 275:10918–10924. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Hu YW, Zhang P, Yang JY, Huang JL, Ma X,
Li SF, Zhao JY, Hu YR, Wang YC, Gao JJ, et al: Nur77 decreases
atherosclerosis progression in apoE(-/-) mice fed a
high-fat/high-cholesterol diet. PLoS One. 9(e87313)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Jung YS, Lee HS, Cho HR, Kim KJ, Kim JH,
Safe S and Lee SO: Dual targeting of Nur77 and AMPKα by
isoalantolactone inhibits adipogenesis in vitro and decreases body
fat mass in vivo. Int J Obes (Lond). 43:952–962. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Kudo T, Nakayama E, Suzuki S, Akiyama M
and Shibata S: Cholesterol diet enhances daily rhythm of Pai-1 mRNA
in the mouse liver. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 287:E644–E651.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Abdou HS, Robert NM and Tremblay JJ:
Calcium-dependent Nr4a1 expression in mouse Leydig cells requires
distinct AP1/CRE and MEF2 elements. J Mol Endocrinol. 56:151–161.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
De Fabiani E, Mitro N, Anzulovich AC,
Pinelli A, Galli G and Crestani M: The negative effects of bile
acids and tumor necrosis factor-alpha on the transcription of
cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase gene (CYP7A1) converge to hepatic
nuclear factor-4: A novel mechanism of feedback regulation of bile
acid synthesis mediated by nuclear receptors. J Biol Chem.
276:30708–30716. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
He Y, Yang T, Du Y, Qin L, Ma F, Wu Z,
Ling H, Yang L, Wang Z, Zhou Q, et al: High fat diet significantly
changed the global gene expression profile involved in hepatic drug
metabolism and pharmacokinetic system in mice. Nutr Metab (Lond).
17(37)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Zhang Y and Klaassen CD: Effects of
feeding bile acids and a bile acid sequestrant on hepatic bile acid
composition in mice. J Lipid Res. 51:3230–3242. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Kakiyama G, Pandak WM, Gillevet PM,
Hylemon PB, Heuman DM, Daita K, Takei H, Muto A, Nittono H, Ridlon
JM, et al: Modulation of the fecal bile acid profile by gut
microbiota in cirrhosis. J Hepatol. 58:949–955. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Wood M, Ananthanarayanan M, Jones B,
Wooton-Kee R, Hoffman T, Suchy FJ and Vore M: Hormonal regulation
of hepatic organic anion transporting polypeptides. Mol Pharmacol.
68:218–225. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Miyazaki H, Sekine T and Endou H: The
multispecific organic anion transporter family: Properties and
pharmacological significance. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 25:654–662.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Zhang H, Chen X, Zong B, Yuan H, Wang Z,
Wei Y, Wang X, Liu G, Zhang J, Li S, et al: Gypenosides improve
diabetic cardiomyopathy by inhibiting ROS-mediated NLRP3
inflammasome activation. J Cell Mol Med. 22:4437–4448.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
He X, Zheng N, He J, Liu C, Feng J, Jia W
and Li H: Gut microbiota modulation attenuated the hypolipidemic
effect of simvastatin in High-Fat/cholesterol-diet fed mice. J
Proteome Res. 16:1900–1910. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Yu L, Lu H, Yang X, Li R, Shi J, Yu Y, Ma
C, Sun F, Zhang S and Zhang F: Diosgenin alleviates
hypercholesterolemia via SRB1/CES-1/CYP7A1/FXR pathway in high-fat
diet-fed rats. Toxicol App Pharmacol. 412(115388)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Gillard J, Clerbaux LA, Nachit M, Sempoux
C, Staels B, Bindels LB, Tailleux A and Leclercq IA: Bile acids
contribute to the development of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in
mice. JHEP Rep. 4(100387)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Gryn SE and Hegele RA: Ezetimibe plus
simvastatin for the treatment of hypercholesterolemia. Expert Opin
Pharmacother. 16:1255–1262. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Ren T, Pang L, Dai W, Wu S and Kong J:
Regulatory mechanisms of the bile salt export pump (BSEP/ABCB11)
and its role in related diseases. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol.
45(101641)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Okushin K, Tsutsumi T, Ikeuchi K, Kado A,
Enooku K, Fujinaga H, Yamauchi N, Ushiku T, Moriya K, Yotsuyanagi H
and Koike K: Heterozygous knockout of Bile salt export pump
ameliorates liver steatosis in mice fed a high-fat diet. PLoS One.
15(e0234750)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Okushin K, Tsutsumi T, Enooku K, Fujinaga
H, Kado A, Shibahara J, Fukayama M, Moriya K, Yotsuyanagi H and
Koike K: The intrahepatic expression levels of bile acid
transporters are inversely correlated with the histological
progression of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Gastroenterol.
51:808–818. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Kalliokoski A and Niemi M: Impact of OATP
transporters on pharmacokinetics. Br J Pharmacol. 158:693–705.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Herrema H, Meissner M, Dijk TH, Brufa G,
Boverhof R, Oosterveer MH, Reijngoud DJ, Müller M, Stellaard F,
Groen AK and Kuipers F: Bile salt sequestration induces hepatic de
novo lipogenesis through farnesoid X receptor- and liver X receptor
alpha-controlled metabolic pathways in mice. Hepatology.
51:806–816. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Out C, Hageman J, Bloks VW, Gerrits H,
Gelpke MDS, Bos T, Smit MJ, Kuipers F and Groen AK: Liver receptor
homolog-1 is critical for adequate up-regulation of Cyp7a1 gene
transcription and bile salt synthesis during bile salt
sequestration. Hepatology. 53:2075–2085. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Chen J, Zhao KN and Chen C: The role of
CYP3A4 in the biotransformation of bile acids and therapeutic
implication for cholestasis. Ann Transl Med. 2(7)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Cao K, Zhang K, Ma M, Ma J, Tian J and Jin
Y: Lactobacillus mediates the expression of NPC1L1, CYP7A1, and
ABCG5 genes to regulate cholesterol. Food Sci Nutr. 9:6882–6891.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Maekawa M: Domain 4 (D4) of perfringolysin
O to visualize cholesterol in cellular membranes-the update.
Sensors (Basel). 17:504–518. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Lorbek G, Lewinska M and Rozman D:
Cytochrome P450s in the synthesis of cholesterol and bile
acids-from mouse models to human diseases. FEBS J. 279:1516–1533.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Chiang JYL: Bile acids: Regulation of
synthesis. J Lipid Res. 50:1955–1966. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Makishima M, Okamoto AY, Repa JJ, Tu H,
Learned RM, Luk A, Hull MV, Lustig KD, Mangelsdorf DJ and Shan B:
Identification of a nuclear receptor for bile acids. Science.
284:1362–1365. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Li G and Guo GL: Farnesoid X receptor, the
bile acid sensing nuclear receptor, in liver regeneration. Acta
Pharm Sin B. 5:93–98. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Xiang D, Yang J, Liu Y, He W, Zhang S, Li
X, Zhang C and Liu D: Calculus bovis sativus improves bile acid
homeostasis via Farnesoid X receptor-mediated signaling in rats
with estrogen-induced cholestasis. Front Pharmacol.
10(48)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Zhang Y, Jackson JP, St Claire RL III,
Freeman K, Brouwer KR and Edwards JE: Obeticholic acid, a selective
farnesoid X receptor agonist, regulates bile acid homeostasis in
sandwich-cultured human hepatocytes. Pharmacol Res Perspect.
5:329–340. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Miao L, Yang Y, Liu Y, Lai L, Wang L, Zhan
Y, Yin R, Yu M, Li C, Yang X and Ge C: Glycerol kinase interacts
with nuclear receptor NR4A1 and regulates glucose metabolism in the
liver. FASEB J. 33:6736–6747. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Wahlström A, Sayin SI, Marschall HU and
Bäckhed F: Intestinal crosstalk between bile acids and microbiota
and its impact on host metabolism. Cell Metab. 24:41–50.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Begley M, Hill C and Gahan CG: Bile salt
hydrolase activity in probiotics. App Environs Microbiol.
72:1729–1738. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Tanaka H, Hashiba H, Kok J and Mierau I:
Bile salt hydrolase of Bifidobacterium longum-biochemical and
genetic characterization. App Environ Microbiol. 66:2502–2512.
2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Kim GB, Miyamoto CM, Meighen EA and Lee
BH: Cloning and characterization of the bile salt hydrolase genes
(bsh) from Bifidobacterium bifidum strains. App Environ Microbiol.
70:5603–5612. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Yang T, Shu T, Liu G, Mei H, Zhu X, Huang
X, Zhang L and Jiang Z: Quantitative profiling of 19 bile acids in
rat plasma, liver, bile and different intestinal section contents
to investigate bile acid homeostasis and the application of
temporal variation of endogenous bile acids. J Steroid Biochem Mol
Biol. 172:69–78. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|