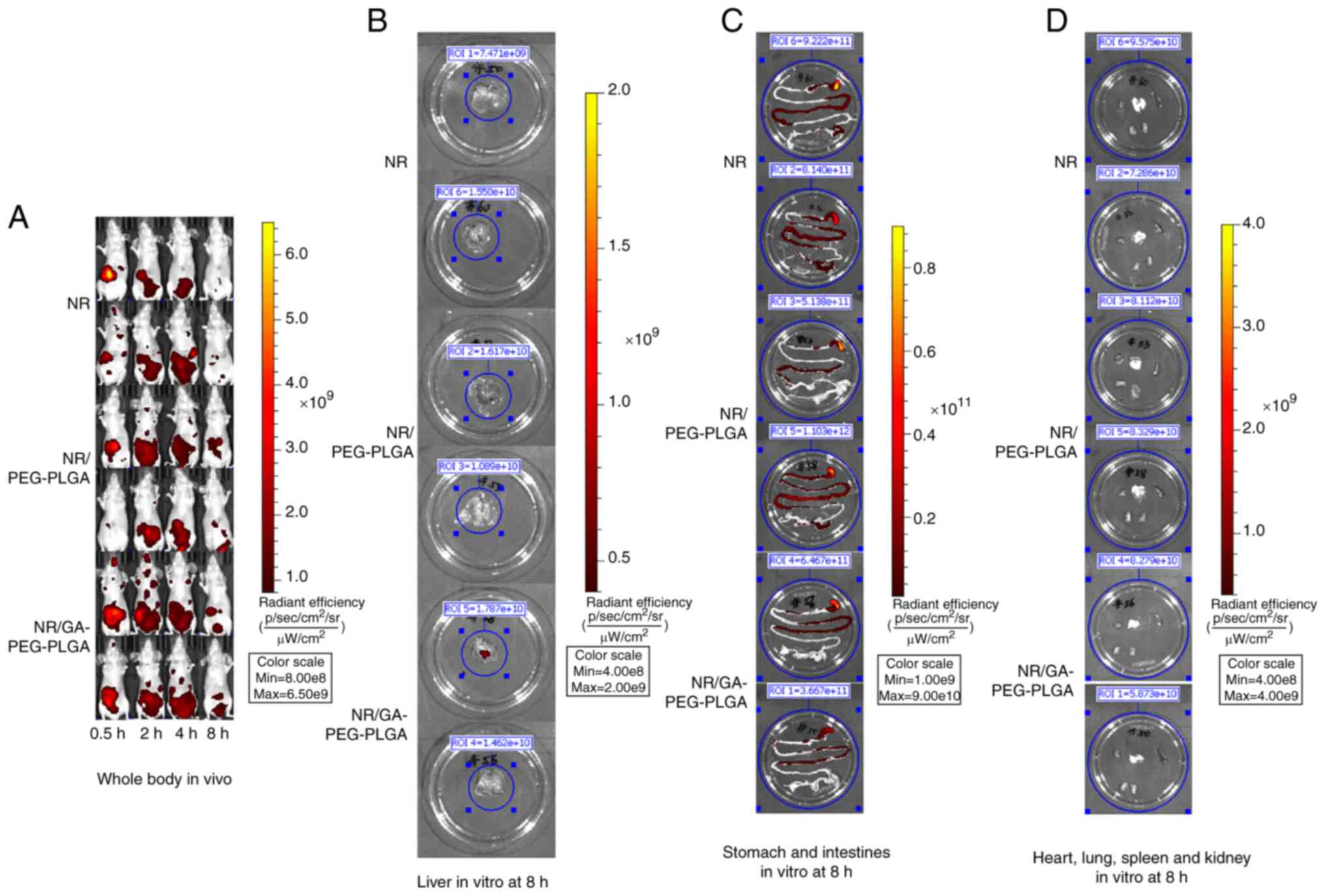
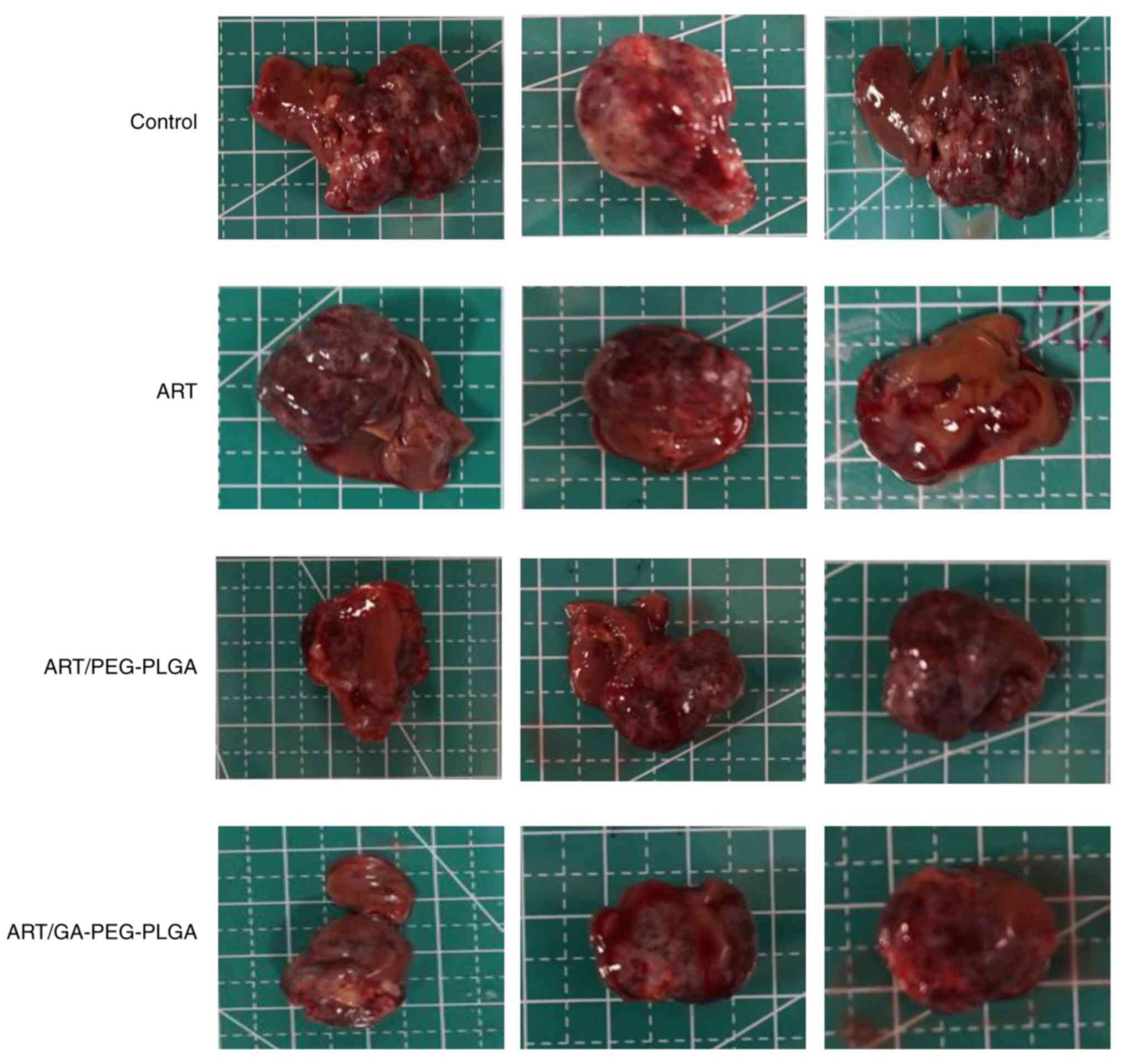
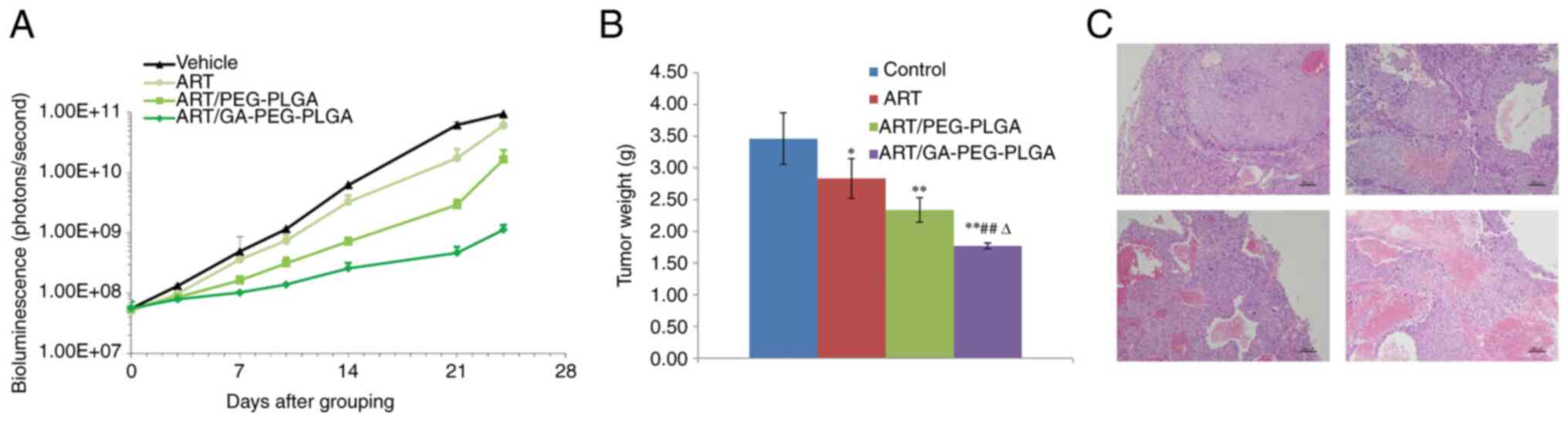
|
1
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Zhou M, Wang H, Zeng X, Yin P, Zhu J, Chen
W, Li X, Wang L, Wang L, Liu Y, et al: Mortality, morbidity, and
risk factors in China and its provinces, 1990-2017: A systematic
analysis for the global burden of disease study 2017. Lancet.
394:1145–1158. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Kulik L and El-Serag HB: Epidemiology and
management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology.
156:477–491.e1. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Sugawara Y and Hibi T: Surgical treatment
of hepatocellular carcinoma. Biosci Trends. 15:138–141.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Piñero F, Silva M and Iavarone M:
Sequencing of systemic treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma:
Second line competitors. World J Gastroenterol. 26:1888–1900.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Colquhoun SD and Wan YY: Hepatocellular
carcinoma diagnosis and treatment: An overview. Liver Res.
4:159–160. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Yang JD and Heimbach JK: New advances in
the diagnosis and management of hepatocellular carcinoma. BMJ.
371(m3544)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Malla RR, Kumari S, Kgk D, Momin S and
Nagaraju GP: Nanotheranostics: Their role in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 151(102968)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Wiwatchaitawee K, Quarterman JC, Geary SM
and Salem AK: Enhancement of therapies for glioblastoma (GBM) using
nanoparticle-based delivery systems. AAPS PharmSciTech.
22(71)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Kalyane D, Raval N, Maheshwari R, Tambe V,
Kalia K and Tekade RK: Employment of enhanced permeability and
retention effect (EPR): Nanoparticle-based precision tools for
targeting of therapeutic and diagnostic agent in cancer. Mater Sci
Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 98:1252–1276. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Yang C, Tan Y, Qi H, Zhou J, Long L, Zhan
Q, Wang Y, Yuan X and Kang C: Boosting of the enhanced permeability
and retention effect with nanocapsules improves the therapeutic
effects of cetuximab. Cancer Biol Med. 17:433–443. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Yang M, Li J, Gu P and Fan X: The
application of nanoparticles in cancer immunotherapy: Targeting
tumor microenvironment. Bioact Mater. 6:1973–1987. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Baker A and Khan MS, Iqbal MZ and Khan MS:
Tumor-targeted drug delivery by nanocomposites. Curr Drug Metab.
21:599–613. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Hu X, Zhang J, Deng L, Hu H, Hu J and
Zheng G: Galactose-modified pH-sensitive niosomes for controlled
release and hepatocellular carcinoma target delivery of tanshinone
IIA. AAPS PharmSciTech. 22(96)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Severino P, da Silva CF, Andrade LN, de
Lima Oliveira D, Campos J and Souto EB: Alginate nanoparticles for
drug delivery and targeting. Curr Pharm Des. 25:1312–1334.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Wathoni N, Rusdin A, Motoyama K, Joni IM,
Lesmana R and Muchtaridi M: Nanoparticle drug delivery systems for
α-mangostin. Nanotechnol Sci Appl. 13:23–36. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Essa D, Kondiah PPD, Choonara YE and
Pillay V: The design of poly (lactide-co-glycolide) nanocarriers
for medical applications. Front Bioeng Biotechnol.
8(48)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Begines B, Ortiz T, Pérez-Aranda M,
Martínez G, Merinero M, Argüelles-Arias F and Alcudia A: Polymeric
nanoparticles for drug delivery: Recent developments and future
prospects. Nanomaterials (Basel). 10(1403)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Du M, Ouyang Y, Meng F, Zhang X, Ma Q,
Zhuang Y, Liu H, Pang M, Cai T and Cai Y: Polymer-lipid hybrid
nanoparticles: A novel drug delivery system for enhancing the
activity of Psoralen against breast cancer. Int J Pharm.
561:274–282. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Anderson CF, Grimmett ME, Domalewski CJ
and Cui H: Inhalable nanotherapeutics to improve treatment efficacy
for common lung diseases. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed
Nanobiotechnol. 12(e1586)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Carter P, Narasimhan B and Wang Q:
Biocompatible nanoparticles and vesicular systems in transdermal
drug delivery for various skin diseases. Int J Pharm. 555:49–62.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Wei T, Cheng Q, Min YL, Olson EN and
Siegwart DJ: Systemic nanoparticle delivery of CRISPR-Cas9
ribonucleoproteins for effective tissue specific genome editing.
Nat Commun. 11(3232)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Anselmo AC and Mitragotri S: Nanoparticles
in the clinic: An update. Bioeng Transl Med.
4(e10143)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Krauss AC, Gao X, Li L, Manning ML, Patel
P, Fu W, Janoria KG, Gieser G, Bateman DA, Przepiorka D, et al: FDA
approval summary: (Daunorubicin and Cytarabine) Liposome for
injection for the treatment of adults with high-risk acute myeloid
leukemia. Clin Cancer Res. 25:2685–2690. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Naqvi S, Panghal A and Flora SJS:
Nanotechnology: A promising approach for delivery of
neuroprotective drugs. Front Neurosci. 14(494)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Gu Z, Wang Q, Shi Y, Huang Y, Zhang J,
Zhang X and Lin G: Nanotechnology-mediated immunochemotherapy
combined with docetaxel and PD-L1 antibody increase therapeutic
effects and decrease systemic toxicity. J Control Release.
286:369–380. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Chen B, Dai W, He B, Zhang H, Wang X, Wang
Y and Zhang Q: Current multistage drug delivery systems based on
the tumor microenvironment. Theranostics. 7:538–558.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Zhang YR, Lin R, Li HJ, He WL, Du JZ and
Wang J: Strategies to improve tumor penetration of nanomedicines
through nanoparticle design. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed
Nanobiotechnol. 11(e1519)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Niu Y, Zhu J, Li Y, Shi H, Gong Y, Li R,
Huo Q, Ma T and Liu Y: Size shrinkable drug delivery nanosystems
and priming the tumor microenvironment for deep intratumoral
penetration of nanoparticles. J Control Release. 277:35–47.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Lim S, Park J, Shim MK, Um W, Yoon HY, Ryu
JH, Lim DK and Kim K: Recent advances and challenges of repurposing
nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems to enhance cancer
immunotherapy. Theranostics. 9:7906–7923. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Gonda A, Zhao N, Shah JV, Calvelli HR,
Kantamneni H, Francis NL and Ganapathy V: Engineering
tumor-targeting nanoparticles as vehicles for precision
nanomedicine. Med One. 4(e190021)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Negishi M, Irie A, Nagata N and Ichikawa
A: Specific binding of glycyrrhetinic acid to the rat liver
membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1066:77–82. 1991.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Sun Y, Dai C, Yin M, Lu J, Hu H and Chen
D: Hepatocellular carcinoma-targeted effect of configurations and
groups of glycyrrhetinic acid by evaluation of its
derivative-modified liposomes. Int J Nanomedicine. 13:1621–1632.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Wu F, Li X, Jiang B, Yan J, Zhang Z, Qin
J, Yu W and Gao Z: Glycyrrhetinic acid functionalized nanoparticles
for drug delivery to liver cancer. J Biomed Nanotechnol.
14:1837–1852. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Li YL, Zhu XM, Liang H, Orvig C and Chen
ZF: Recent advances in asialoglycoprotein receptor and
glycyrrhetinic acid receptor-mediated and/or pH-responsive
hepatocellular carcinoma-targeted drug delivery. Curr Med Chem.
28:1508–534. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Stecanella LA, Bitencourt APR, Vaz GR,
Quarta E, Silva Júnior JOC and Rossi A: Glycyrrhizic acid and its
hydrolyzed metabolite 18β-glycyrrhetinic acid as specific ligands
for targeting nanosystems in the treatment of liver cancer.
Pharmaceutics. 13(1792)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Kim J, Lee S and Na K: Glycyrrhetinic
acid-modified silicon phthalocyanine for liver cancer-targeted
photodynamic therapy. Biomacromolecules. 22:811–822.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Li L, Han S, Yang C, Liu L, Zhao S, Wang
X, Liu B, Pan H and Liu Y: Glycyrrhetinic acid modified MOFs for
the treatment of liver cancer. Nanotechnology.
31(325602)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Huang S, Ren D, Wu X, Li M, Yu X, Nie X
and Wang Y and Wang Y: Glycyrrhetinic acid and TAT peptide modified
dual-functional liposomes for treatment of hepatocellular cancer.
Curr Top Med Chem. 20:2493–2505. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Li ZJ, Dai HQ, Huang XW, Feng J, Deng JH,
Wang ZX, Yang XM, Liu YJ, Wu Y, Chen PH, et al: Artesunate
synergizes with sorafenib to induce ferroptosis in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 42:301–310. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Yin S, Yang H, Zhao X, Wei S, Tao Y, Liu
M, Bo R and Li J: Antimalarial agent artesunate induces G0/G1 cell
cycle arrest and apoptosis via increasing intracellular ROS levels
in normal liver cells. Hum Exp Toxicol. 39:1681–1689.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Pan X, Liu S, Ju L, Xi J, He R, Zhao Y,
Zhuang R and Huang J: Preparation, evaluation, and in vitro
cytotoxicity studies of artesunate-loaded glycyrrhetinic acid
decorated PEG-PLGA nanoparticles. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 46:1889–1897.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Ye RR, Peng W, Chen BC, Jiang N, Chen XQ,
Mao ZW and Li RT: Mitochondria-targeted artesunate conjugated
cyclometalated iridium(iii) complexes as potent anti-HepG2
hepatocellular carcinoma agents. Metallomics. 12:1131–1141.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
McComb S, Chan PK, Guinot A,
Hartmannsdottir H, Jenni S, Dobay MP, Bourquin JP and Bornhauser
BC: Efficient apoptosis requires feedback amplification of upstream
apoptotic signals by effector caspase-3 or -7. Sci Adv.
5(eaau9433)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Martínez-Limón A, Joaquin M, Caballero M,
Posas F and de Nadal E: The p38 pathway: From biology to cancer
therapy. Int J Mol Sci. 21(1913)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Slade D: PARP and PARG inhibitors in
cancer treatment. Genes Dev. 34:360–394. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Zhu H, Wei M, Xu J, Hua J, Liang C, Meng
Q, Zhang Y, Liu J, Zhang B, Yu X and Shi S: PARP inhibitors in
pancreatic cancer: Molecular mechanisms and clinical applications.
Mol Cancer. 19(49)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Wilhelm S, Tavares AJ, Qin D, Ohta S,
Audet J, Dvorak HF and Chan WCW: Analysis of nanoparticle delivery
to tumours. Nat Rev Mater. 1(16014)2016.
|
|
49
|
von Maltzahn G, Park JH, Lin KY, Singh N,
Schwöppe C, Mesters R, Berdel WE, Ruoslahti E, Sailor MJ and Bhatia
SN: Nanoparticles that communicate in vivo to amplify tumour
targeting. Nat Mater. 10:545–552. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Chen F, Zhang J, He Y, Fang X, Wang Y and
Chen M: Glycyrrhetinic acid-decorated and reduction-sensitive
micelles to enhance the bioavailability and anti-hepatocellular
carcinoma efficacy of tanshinone IIA. Biomater Sci. 4:167–182.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Rahman M, Almalki WH, Alrobaian M, Iqbal
J, Alghamdi S, Alharbi KS, Alruwaili NK, Hafeez A, Shaharyar A,
Singh T, et al: Nanocarriers-loaded with natural actives as newer
therapeutic interventions for treatment of hepatocellular
carcinoma. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 18:489–513. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Yang X, Zheng Y, Liu L, Huang J, Wang F
and Zhang J: Progress on the study of the anticancer effects of
artesunate. Oncol Lett. 22(750)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Zhao F, Vakhrusheva O, Markowitsch SD,
Slade KS, Tsaur I, Cinatl J Jr, Michaelis M, Efferth T, Haferkamp A
and Juengel E: Artesunate impairs growth in cisplatin-resistant
bladder cancer cells by cell cycle arrest, apoptosis and autophagy
induction. Cells. 9(2643)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Zhao L, Liang L, Guo M, Li M, Yu X and
Wang Y and Wang Y: Hepatocellular carcinoma targeting and
pharmacodynamics of paclitaxel nanoliposomes modified by
glycyrrhetinic acid and ferric tetroxide. Curr Top Med Chem.
21:1268–1284. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Cao M, Gao Y, Zhan M, Qiu N, Piao Y, Zhou
Z and Shen Y: Glycyrrhizin acid and glycyrrhetinic acid modified
polyethyleneimine for targeted DNA delivery to hepatocellular
carcinoma. Int J Mol Sci. 20(5074)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Sang L, Li J, Zhang F, Jia J, Zhang J,
Ding P, Sun T and Wang D: Glycyrrhetinic acid modified chlorambucil
prodrug for hepatocellular carcinoma treatment based on DNA
replication and tumor microenvironment. Colloids Surf B
Biointerfaces. 220(112864)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|