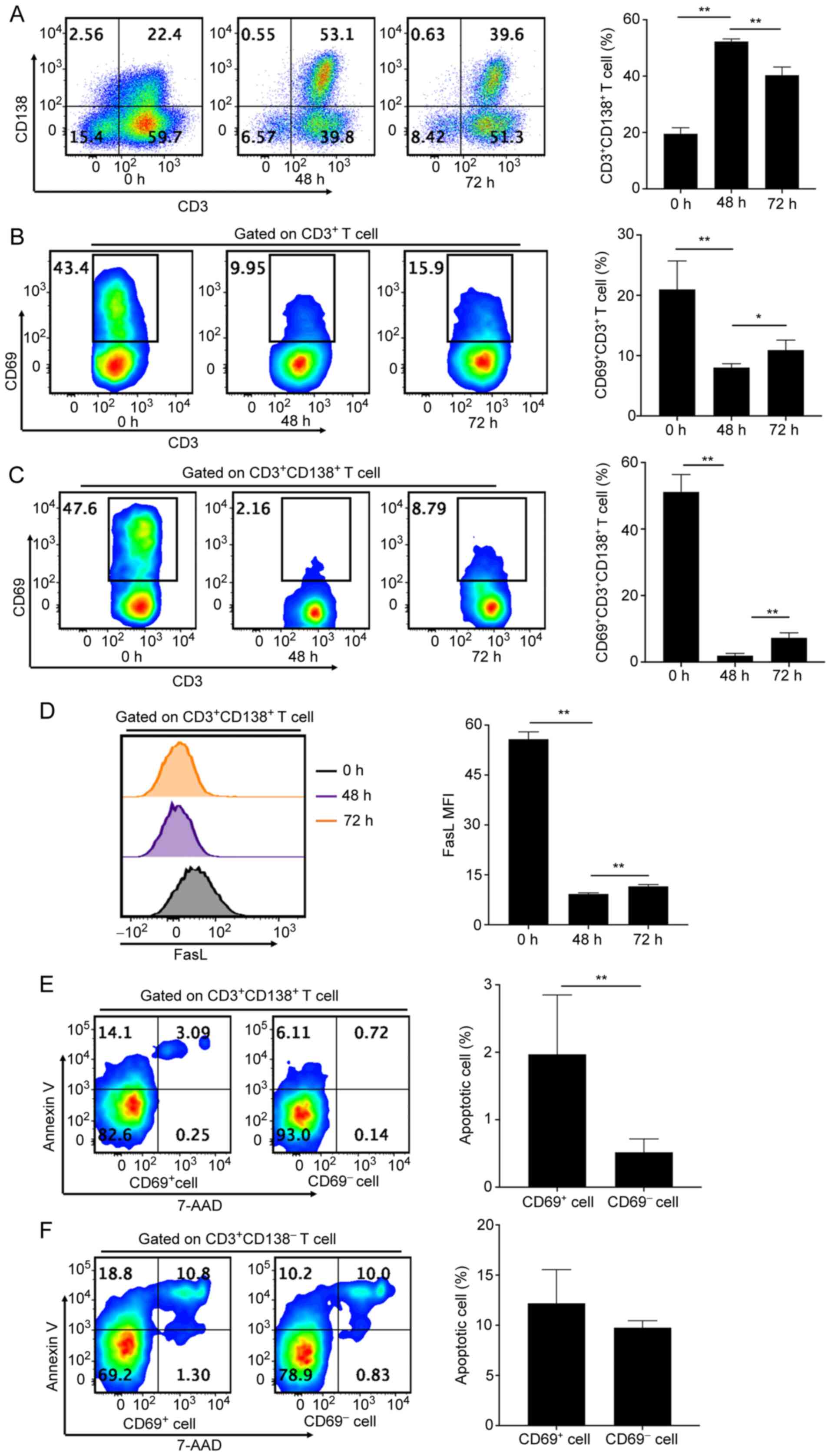
|
1
|
Lisnevskaia L, Murphy G and Isenberg D:
Systemic lupus erythematosus. Lancet. 384:1878–1888.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Zharkova O, Celhar T, Cravens PD,
Satterthwaite AB, Fairhurst AM and Davis LS: Pathways leading to an
immunological disease: Systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatology
(Oxford). 56 (Suppl 1):i55–i66. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
You M, Dong G, Li F, Ma F, Ren J, Xu Y,
Yue H, Tang R, Ren D and Hou Y: Ligation of CD180 inhibits IFN-α
signaling in a Lyn-PI3K-BTK-dependent manner in B cells. Cell Mol
Immunol. 14:192–202. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Dörner T, Giesecke C and Lipsky PE:
Mechanisms of B cell autoimmunity in SLE. Arthritis Res Ther.
13(243)2011.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Kotzin BL: Systemic lupus erythematosus.
Cell. 85:303–306. 1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Alexander JJ, Jacob A, Chang A, Quigg RJ
and Jarvis JN: Double negative T cells, a potential biomarker for
systemic lupus erythematosus. Precis Clin Med. 3:34–43.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Chesnutt MS, Finck BK, Killeen N, Connolly
MK, Goodman H and Wofsy D: Enhanced lymphoproliferation and
diminished autoimmunity in CD4-deficient MRL/lpr mice. Clin Immunol
Immunopathol. 87:23–32. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Nagasu A, Mukai T, Iseki M, Kawahara K,
Tsuji S, Nagasu H, Ueki Y, Ishihara K, Kashihara N and Morita Y:
Sh3bp2 gain-of-function mutation ameliorates lupus phenotypes in
B6.MRL-Faslpr mice. Cells. 8(402)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Lu LD, Stump KL, Wallace NH, Dobrzanski P,
Serdikoff C, Gingrich DE, Dugan BJ, Angeles TS, Albom MS, Mason JL,
et al: Depletion of autoreactive plasma cells and treatment of
lupus nephritis in mice using CEP-33779, a novel, orally active,
selective inhibitor of JAK2. J Immunol. 187:3840–3853.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Calame KL: Plasma cells: Finding new light
at the end of B cell development. Nat Immunol. 2:1103–1108.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Pan Z, Chen M, Zhang Q, Wang E, Yin L, Xu
Y, Huang Q, Yuan Y, Zhang X, Zheng G and Yuan J: CD3-positive
plasmablastic B-cell neoplasms: A diagnostic pitfall. Mod Pathol.
31:718–731. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Liu L, Takeda K and Akkoyunlu M: Disease
stage-specific pathogenicity of CD138 (Syndecan 1)-expressing T
cells in systemic lupus erythematosus. Front Immunol.
11(1569)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Seagal J, Leider N, Wildbaum G, Karin N
and Melamed D: Increased plasma cell frequency and accumulation of
abnormal syndecan-1plus T-cells in Igmu-deficient/lpr mice. Int
Immunol. 15:1045–1052. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Mohamood AS, Bargatze D, Xiao Z, Jie C,
Yagita H, Ruben D, Watson J, Chakravarti S, Schneck JP and Hamad
AR: Fas-mediated apoptosis regulates the composition of peripheral
alphabeta T cell repertoire by constitutively purging out double
negative T cells. PLoS One. 3(e3465)2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Getachew Y, Cusimano FA, James LP and
Thiele DL: The role of intrahepatic CD3+/CD4-/CD8-double negative T
(DN T) cells in enhanced acetaminophen toxicity. Toxicol Appl
Pharmacol. 280:264–271. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Benihoud K, Bonardelle D, Bobé P and Kiger
N: MRL/lpr CD4- CD8- and CD8+ T cells, respectively, mediate
Fas-dependent and perforin cytotoxic pathways. Eur J Immunol.
27:415–420. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Hidalgo Y, Núñez S, Fuenzalida MJ,
Flores-Santibáñez F, Sáez PJ, Dorner J, Lennon-Dumenil AM, Martínez
V, Zorn E, Rosemblatt M, et al: Thymic B cells promote germinal
center-like structures and the expansion of follicular helper T
cells in lupus-prone mice. Front Immunol. 11(696)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Menon M, Blair PA, Isenberg DA and Mauri
C: A regulatory feedback between plasmacytoid dendritic cells and
regulatory B cells Is aberrant in systemic lupus erythematosus.
Immunity. 44:683–697. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Xie T, Liu X, Liu H, Han X, Zhao J, Zhou
D, Wang Y, Zhang H, Wang P and Li P: LangChuangHeJi decoction
ameliorates lupus via preventing accumulation of CD138+ T cells in
MRL/lpr mice. Am J Transl Res. 13:12440–12460. 2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chatila T, Silverman L, Miller R and Geha
R: Mechanisms of T cell activation by the calcium ionophore
ionomycin. J Immunol. 143:1283–1289. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Straube F and Herrmann T: Differential
modulation of CD8beta by rat gammadelta and alphabeta T cells after
activation. Immunology. 104:252–258. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Carvalho MUWB, Vendramini P, Kubo CA,
Soreiro-Pereira PV, de Albuquerque RS, Antunes E and Condino-Neto
A: BAY 41-2272 inhibits human T lymphocyte functions. Int
Immunopharmacol. 77(105976)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Xie H, Xie S, Wang M, Wei H, Huang H, Xie
A, Li J, Fang C, Shi F, Yang Q, et al: Properties and roles of γδT
Cells in plasmodium yoelii nigeriensis NSM infected C57BL/6 mice.
Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 11(788546)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Gao M, Jin W, Qian Y, Ji L, Feng G and Sun
J: Effect of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonist on T helper
cell differentiation induced by phorbol-myristate-acetate and
ionomycin. Cytokine. 56:458–465. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Han S, Tie X, Meng L, Wang Y and Wu A: PMA
and ionomycin induce glioblastoma cell death: Activation-induced
cell-death-like phenomena occur in glioma cells. PLoS One.
8(e76717)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Shan ZG, Zhao YL, Zhang JY, Yan ZB, Wang
TT, Mao FY, Teng YS, Peng LS, Chen WY, Wang P, et al:
FasL+ PD-L2+ identifies a novel
immunosuppressive neutrophil population in human gastric cancer
that promotes disease progression. Adv Sci (Weinh).
9(e2103543)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Wu Y, He S, Bai B, Zhang L, Xue L, Lin Z,
Yang X, Zhu F, He P, Tang W and Zuo J: Therapeutic effects of the
artemisinin analog SM934 on lupus-prone MRL/lpr mice via inhibition
of TLR-triggered B-cell activation and plasma cell formation. Cell
Mol Immunol. 13:379–390. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Park EK, Jung HS, Yang HI, Yoo MC, Kim C
and Kim KS: Optimized THP-1 differentiation is required for the
detection of responses to weak stimuli. Inflamm Res. 56:45–50.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Zeng CW, Wang WT, Yu XB, Yang LJ, Chen SH
and Li YQ: Pathways related to PMA-differentiated THP1 human
monocytic leukemia cells revealed by RNA-Seq. Sci China Life Sci.
58:1282–1287. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Martina MN, Noel S, Saxena A, Rabb H and
Hamad ARA: Double negative (DN) αβ T cells: Misperception and
overdue recognition. Immunol Cell Biol. 93:305–310. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Corneth OBJ, Schaper F, Luk F, Asmawidjaja
PS, Mus AMC, Horst G, Heeringa P, Hendriks RW, Westra J and
Lubberts E: Lack of IL-17 receptor a signaling aggravates
lymphoproliferation in C57BL/6 lpr mice. Sci Rep.
9(4032)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Tsokos GC, Lo MS, Reis PC and Sullivan KE:
New insights into the immunopathogenesis of systemic lupus
erythematosus. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 12:716–730. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Dik WA, Pike-Overzet K, Weerkamp F, de
Ridder D, de Haas EF, Baert MR, van der Spek P, Koster EE, Reinders
MJ, van Dongen JJ, et al: New insights on human T cell development
by quantitative T cell receptor gene rearrangement studies and gene
expression profiling. J Exp Med. 201:1715–1723. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Anderson G and Jenkinson EJ: Lymphostromal
interactions in thymic development and function. Nat Rev Immunol.
1:31–40. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Trimble LA, Prince KA, Pestano GA, Daley J
and Cantor H: Fas-dependent elimination of nonselected CD8 cells
and lpr disease. J Immunol. 168:4960–4967. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Watanabe-Fukunaga R, Brannan CI, Copeland
NG, Jenkins NA and Nagata S: Lymphoproliferation disorder in mice
explained by defects in Fas antigen that mediates apoptosis.
Nature. 356:314–317. 1992.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Suda T, Takahashi T, Golstein P and Nagata
S: Molecular cloning and expression of the Fas ligand, a novel
member of the tumor necrosis factor family. Cell. 75:1169–1178.
1993.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Zhou T, Bluethmann H, Eldridge J, Berry K
and Mountz JD: Origin of CD4-CD8-B220+ T cells in MRL-lpr/lpr mice.
Clues from a T cell receptor beta transgenic mouse. J Immunol.
150:3651–3667. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Chun DH, Jung KC, Park WS, Lee IS, Choi
WJ, Kim CJ, Park SH and Bae Y: Costimulatory effect of Fas in mouse
T lymphocytes. Mol Cells. 10:642–646. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|