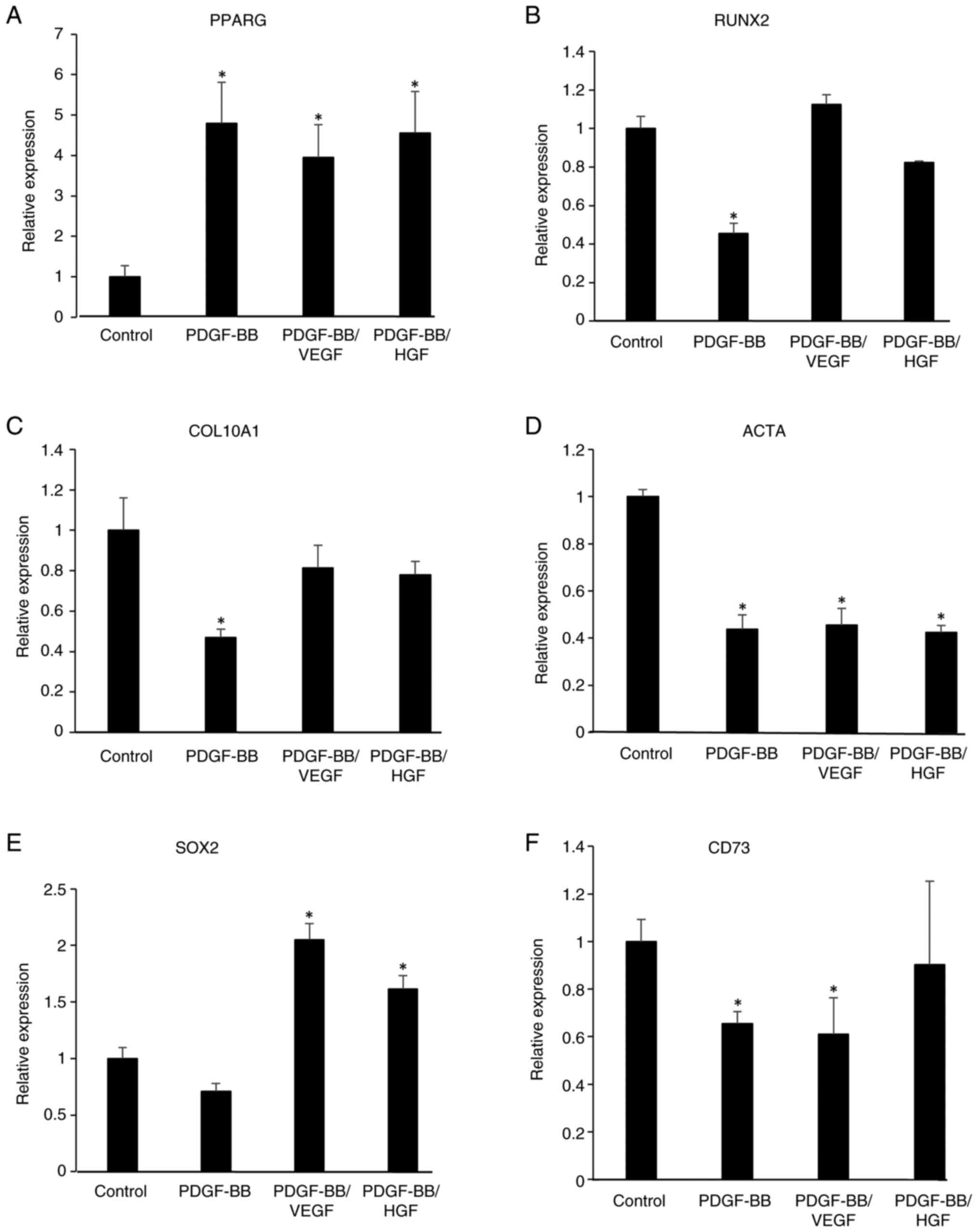
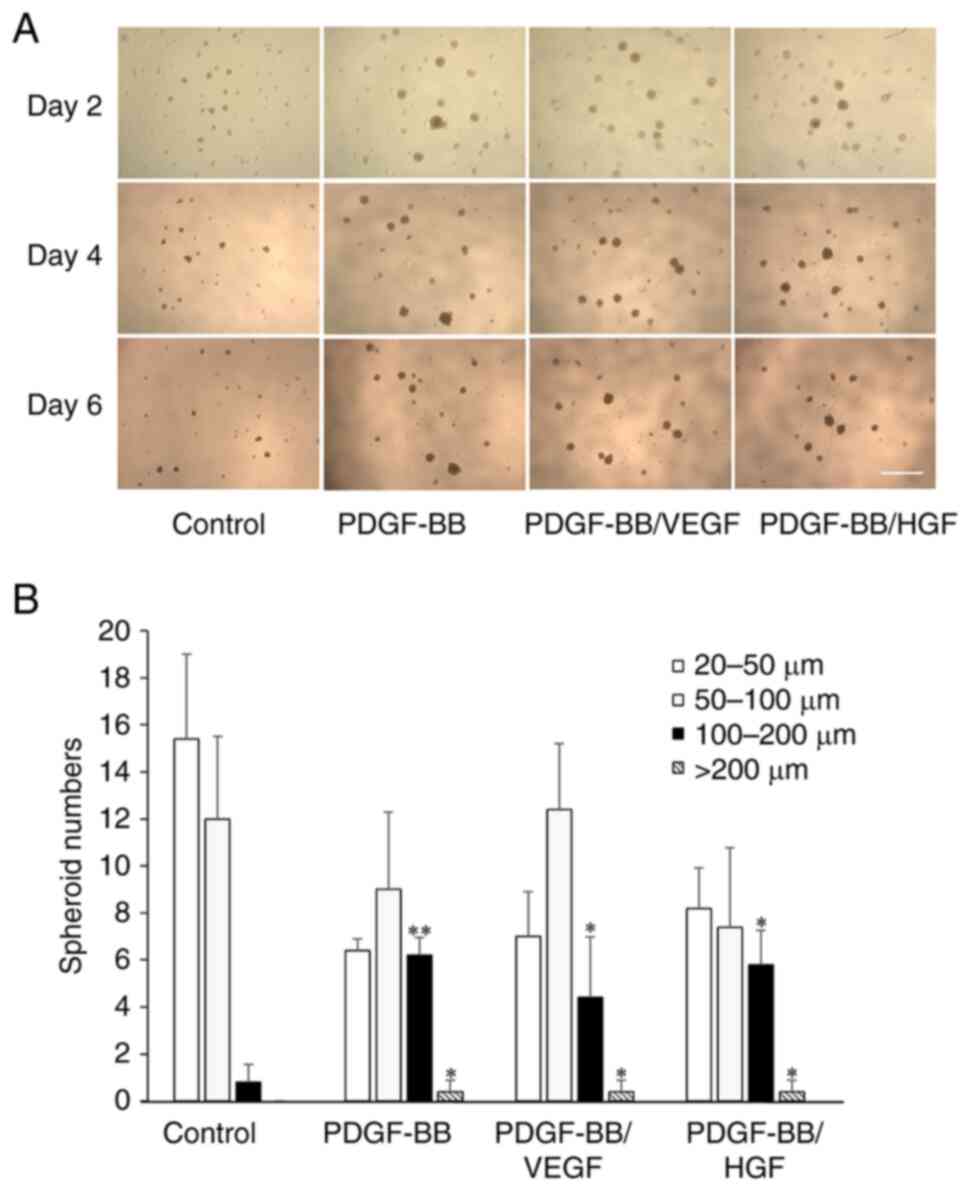
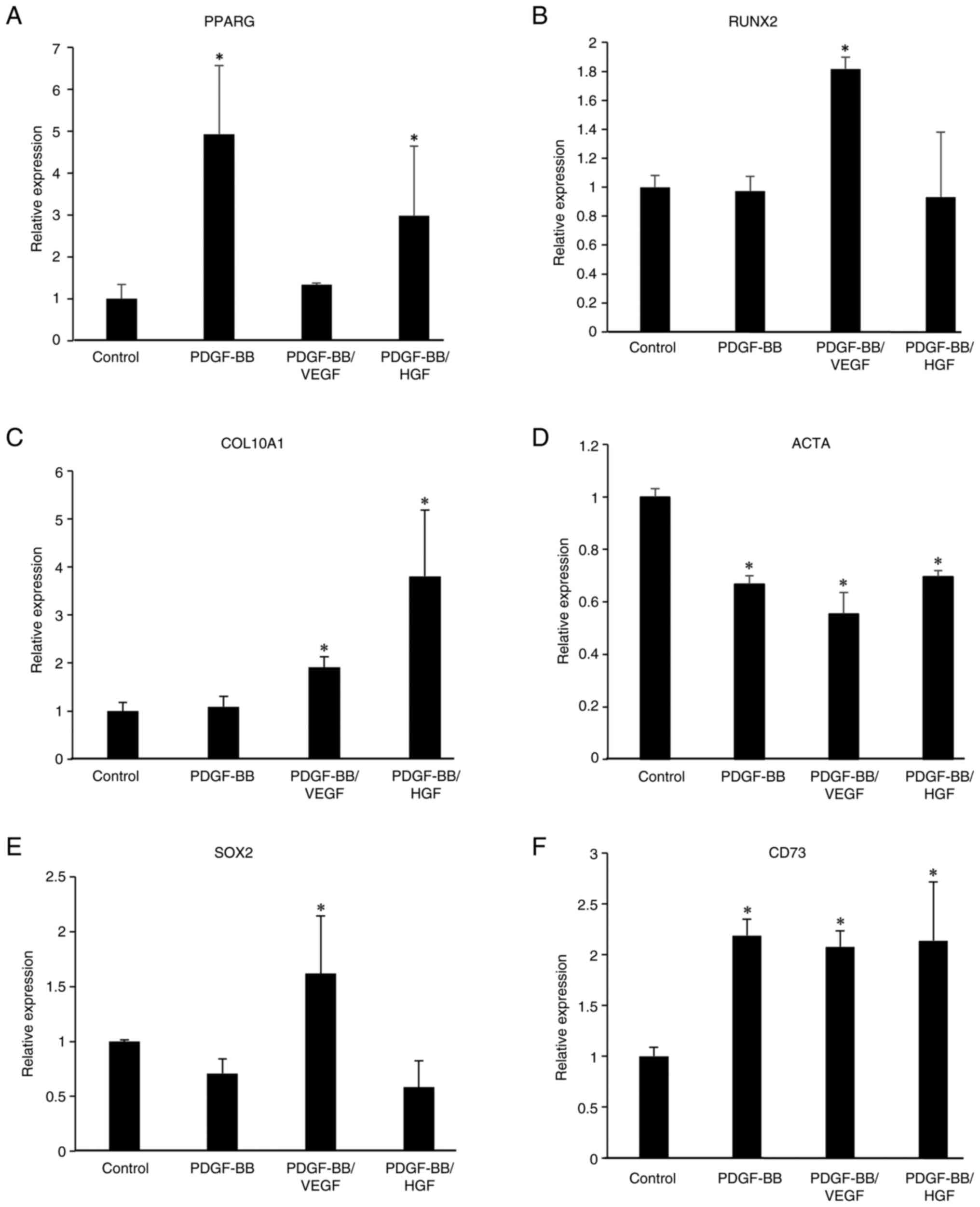
|
1
|
Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC, Jaiswal
RK, Douglas R, Mosca JD, Moorman MA, Simonetti DW, Craig S and
Marshak DR: Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem
cells. Science. 284:143–147. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Pittenger MF, Discher DE, Péault BM,
Phinney DG, Hare JM and Caplan AI: Mesenchymal stem cell
perspective: Cell biology to clinical progress. NPJ Regen Med.
4(22)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Koźlik M and Wójcicki P: The use of stem
cells in plastic and reconstructive surgery. Adv Clin Exp Med.
23:1011–1017. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Zhang M, Zhang P, Liu Y and Zhou Y: GSK3
inhibitor AR-A014418 promotes osteogenic differentiation of human
adipose-derived stem cells via ERK and mTORC2/Akt signaling
pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 490:182–188. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Galeano-Garces C, Camilleri ET, Riester
SM, Dudakovic A, Larson DR, Qu W, Smith J, Dietz AB, Im HJ, Krych
AJ, et al: Molecular validation of chondrogenic differentiation and
hypoxia responsiveness of platelet-lysate expanded adipose
tissue-derived human mesenchymal stromal cells. Cartilage.
8:283–299. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Paul NE, Denecke B, Kim BS, Dreser A,
Bernhagen J and Pallua N: The effect of mechanical stress on the
proliferation, adipogenic differentiation and gene expression of
human adipose-derived stem cells. J Tissue Eng Regen Med.
12:276–284. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Jahromi M, Razavi S, Amirpour N and
Khosravizadeh Z: Paroxetine can enhance neurogenesis during
neurogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells.
Avicenna J Med Biotechnol. 8:152–158. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gaur M, Dobke M and Lunyak VV: Mesenchymal
stem cells from adipose tissue in clinical applications for
dermatological indications and skin aging. Int J Mol Sci.
18(208)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Takahashi H, Ishikawa H and Tanaka A:
Regenerative medicine for Parkinson's disease using differentiated
nerve cells derived from human buccal fat pad stem cells. Hum Cell.
30:60–71. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Iudicone P, Fioravanti D, Bonanno G,
Miceli M, Lavorino C, Totta P, Frati L, Nuti M and Pierelli L:
Pathogen-free, plasma-poor platelet lysate and expansion of human
mesenchymal stem cells. J Transl Med. 12(28)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Huang CJ, Sun YC, Christopher K, Pai AS,
Lu CJ, Hu FR, Lin SY and Chen WL: Comparison of corneal
epitheliotrophic capacities among human platelet lysates and other
blood derivatives. PLoS One. 12(e0171008)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Doucet C, Ernou I, Zhang Y, Llense JR,
Begot L, Holy X and Lataillade JJ: Platelet lysates promote
mesenchymal stem cell expansion: A safety substitute for animal
serum in cell-based therapy applications. J Cell Physiol.
205:228–236. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Crespo-Diaz R, Behfar A, Butler GW, Padley
DJ, Sarr MG, Bartunek J, Dietz AB and Terzic A: Platelet lysate
consisting of a natural repair proteome supports human mesenchymal
stem cell proliferation and chromosomal stability. Cell Transplant.
20:797–811. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Díez JM, Bauman E, Gajardo R and Jorquera
JI: Culture of human mesenchymal stem cells using a candidate
pharmaceutical grade xeno-free cell culture supplement derived from
industrial human plasma pools. Stem Cell Res Ther.
6(28)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Stute N, Holtz K, Bubenheim M, Lange C,
Blake F and Zander AR: Autologous serum for isolation and expansion
of human mesenchymal stem cells for clinical use. Exp Hematol.
32:1212–1225. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Alonso-Camino V and Mirsch B: Rapid
expansion of mesenchymal stem/stromal cells using optimized media
supplemented with human platelet lysate PLTMax® or
PLTGold®, suitable for cGMP expansion at large scale.
Cytotherapy. 21 (Suppl)(S85)2019.
|
|
17
|
Kakudo N, Morimoto N, Ma Y and Kusumoto K:
Differences between the proliferative effects of human platelet
lysate and fetal bovine serum on human adipose-derived stem cells.
Cells. 8(1218)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Zhang JM, Feng FE, Wang QM, Zhu XL, Fu HX,
Xu LP, Liu KY, Huang XJ and Zhang XH: Platelet-derived growth
factor-bb protects mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) derived from
immune thrombocytopenia patients against apoptosis and senescence
and maintains MSC-mediated immunosuppression. Stem Cells Transl
Med. 5:1631–1643. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Papadopoulos N and Lennartsson J: The
PDGF/PDGFR pathway as a drug target. Mol Aspects Med. 62:75–88.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Lai F, Kakudo N, Morimoto N, Taketani S,
Hara T, Ogawa T and Kusumoto K: Platelet-rich plasma enhances the
proliferation of human adipose stem cells through multiple
signaling pathways. Stem Cell Res Ther. 9(107)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Imam SS, Al-Abbasi FA, Hosawi S, Afzal M,
Nadeem MS, Ghoneim MM, Alshehri S, Alzarea SI, Alquraini A, Gupta G
and Kazmi I: Role of platelet rich plasma mediated repair and
regeneration of cell in early stage of cardiac injury. Regen Ther.
19:144–153. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Chun SY, Lim JO, Lee EH, Han MH, Ha YS,
Lee JN, Kim BS, Park MJ, Yeo M, Jung B and Kwon TG: Preparation and
characterization of human adipose tissue-derived extracellular
matrix, growth factors, and stem cells: A concise review. Tissue
Eng Regen Med. 16:385–393. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Ma Y, Kakudo N, Morimoto N, Lai F,
Taketani S and Kusumoto K: Fibroblast growth factor-2 stimulates
proliferation of human adipose-derived stem cells via Src
activation. Stem Cell Res Ther. 10(350)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Kakudo N, Minakata T, Mitsui T, Kushida S,
Notodihardjo FZ and Kusumoto K: Proliferation-promoting effect of
platelet-rich plasma on human adipose-derived stem cells and human
dermal fibroblasts. Plast Reconstr Surg. 122:1352–1360.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Fukui M, Matsuoka Y, Taketani S, Higasa K,
Hihara M, Kuro A and Kakudo N: Accelerated angiogenesis of human
umbilical vein endothelial cells under negative pressure was
associated with the regulation of gene expression involved in the
proliferation and migration. Ann Plast Surg. 89:e51–e59.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Kang YJ, Jeon ES, Song HY, Woo JS, Jung
JS, Kim YK and Kim JH: Role of c-Jun N-terminal kinase in the
PDGF-induced proliferation and migration of human adipose
tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells. J Cell Biochem.
95:1135–1145. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Haber M, Cao Z, Panjwani N, Bedenice D, Li
WW and Provost PJ: Effects of growth factors (EGF, PDGF-BB and
TGF-beta 1) on cultured equine epithelial cells and keratocytes:
Implications for wound healing. Vet Ophthalmol. 6:211–217.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Knorr M, Völker M, Denk PO, Wunderlich K
and Thiel HJ: Proliferative response of cultured human tenon's
capsule fibroblasts to platelet-derived growth factor isoforms.
Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 235:667–671. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Seppä H, Grotendorst G, Seppä S,
Schiffmann E and Martin GR: Platelet-derived growth factor in
chemotactic for fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 92:584–588.
1982.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Donovan J, Abraham D and Norman J:
Platelet-derived growth factor signaling in mesenchymal cells.
Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 18:106–119. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Bellas RE, Bendori R and Farmer SR:
Epidermal growth factor activation of vinculin and beta 1-integrin
gene transcription in quiescent Swiss 3T3 cells. Regulation through
a protein kinase C-independent pathway. J Biol Chem.
266:12008–12014. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Celotti F, Colciago A, Negri-Cesi P,
Pravettoni A, Zaninetti R and Sacchi MC: Effect of platelet-rich
plasma on migration and proliferation of SaOS-2 osteoblasts: Role
of platelet-derived growth factor and transforming growth
factor-beta. Wound Repair Regen. 14:195–202. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Li JF, Yin HL, Shuboy A, Duan HF, Lou JY,
Li J, Wang HW and Wang YL: Differentiation of hUC-MSC into
dopaminergic-like cells after transduction with hepatocyte growth
factor. Mol Cell Biochem. 381:183–190. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Lopatina T, Favaro E, Grange C, Cedrino M,
Ranghino A, Occhipinti S, Fallo S, Buffolo F, Gaykalova DA, Zanone
MM, et al: PDGF enhances the protective effect of adipose stem
cell-derived extracellular vesicles in a model of acute hindlimb
ischemia. Sci Rep. 8(17458)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Lopatina T, Bruno S, Tetta C, Kalinina N,
Porta M and Camussi G: Platelet-derived growth factor regulates the
secretion of extracellular vesicles by adipose mesenchymal stem
cells and enhances their angiogenic potential. Cell Commun Signal.
12(26)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : Veevers-Lowe J,
Ball SG, Shuttleworth A and Kielty CM: Mesenchymal stem cell
migration is regulated by fibronectin through
α5β1-integrin-mediated activation of PDGFR-β and potentiation of
growth factor signals. J Cell Sci 124: 1288-1300, 2011.
|
|
37
|
Ball SG, Shuttleworth CA and Kielty CM:
Mesenchymal stem cells and neovascularization: Role of
platelet-derived growth factor receptors. J Cell Mol Med.
11:1012–1030. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Veevers-Lowe J, Ball SG, Shuttleworth A
and Kielty CM: Mesenchymal stem cell migration is regulated by
fibronectin through α5β1-integrin-mediated activation of PDGFR-β
and potentiation of growth factor signals. J Cell Sci.
124:1288–1300. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Jung KH, Chu K, Lee ST, Bahn JJ, Jeon D,
Kim JH, Kim S, Won CH, Kim M, Lee SK and Roh JK: Multipotent
PDGFRβ-expressing cells in the circulation of stroke patients.
Neurobiol Dis. 41:489–497. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Gao Z, Daquinag AC, Su F, Snyder B and
Kolonin MG: PDGFRα/PDGFRβ signaling balance modulates progenitor
cell differentiation into white and beige adipocytes. Development.
145(dev155861)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Yan L, Zhou L, Yan B, Zhang L, Du W, Liu
F, Yuan Q, Tong P, Shan L and Efferth T: Growth factors-based
beneficial effects of platelet lysate on umbilical cord-derived
stem cells and their synergistic use in osteoarthritis treatment.
Cell Death Dis. 11(857)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Brizzi MF, Tarone G and Defilippi P:
Extracellular matrix, integrins, and growth factors as tailors of
the stem cell niche. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 24:645–651.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Magnusson PU, Looman C, Ahgren A, Wu Y,
Claesson-Welsh L and Heuchel RL: Platelet-derived growth factor
receptor-beta constitutive activity promotes angiogenesis in vivo
and in vitro. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 27:2142–2149.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Kilpatrick LE and Hill SJ: Transactivation
of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) and receptor tyrosine
kinases (RTKs): Recent insights using luminescence and fluorescence
technologies. Curr Opin Endocr Metab Res. 16:102–112.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Hu F, Wang X, Liang G, Lv L, Zhu Y, Sun B
and Xiao Z: Effects of epidermal growth factor and basic fibroblast
growth factor on the proliferation and osteogenic and neural
differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells. Cell Reprogram.
15:224–232. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Khan S, Villalobos MA, Choron RL, Chang S,
Brown SA, Carpenter JP, Tulenko TN and Zhang P: Fibroblast growth
factor and vascular endothelial growth factor play a critical role
in endotheliogenesis from human adipose-derived stem cells. J Vasc
Surg. 65:1483–1492. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Mamer SB, Chen S, Weddell JC, Palasz A,
Wittenkeller A, Kumar M and Imoukhuede PI: Discovery of
high-affinity pdgf-vegfr interactions: Redefining RTK dynamics. Sci
Rep. 7(16439)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Bergeron JJ, Di Guglielmo GM, Dahan S,
Dominguez M and Posner BI: Spatial and temporal regulation of
receptor tyrosine kinase activation and intracellular signal
transduction. Annu Rev Biochem. 85:573–597. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Kim WS, Park HS and Sung JH: The pivotal
role of PDGF and its receptor isoforms in adipose-derived stem
cells. Histol Histopathol. 30:793–799. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Younesi Soltani F, Javanshir S, Dowlati G,
Parham A and Naderi-Meshkin H: Differentiation of human
adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells toward tenocyte by
platelet-derived growth factor-BB and growth differentiation
factor-6. Cell Tissue Bank. 23:237–246. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Artemenko Y, Gagnon A, Aubin D and Sorisky
A: Anti-adipogenic effect of PDGF is reversed by PKC inhibition. J
Cell Physiol. 204:646–653. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Hye Kim J, Gyu Park S, Kim WK, Song SU and
Sung JH: Functional regulation of adipose-derived stem cells by
PDGF-D. Stem Cells. 33:542–556. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Lee CS, Nicolini AM, Watkins EA, Burnsed
OA, Boyan BD and Schwartz Z: Adipose stem cell microbeads as
production sources for chondrogenic growth factors. J Stem Cells
Regen Med. 10:38–48. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Carrancio S, López-Holgado N,
Sánchez-Guijo FM, Villarón E, Barbado V, Tabera S, Díez-Campelo M,
Blanco J, San Miguel JF and Del Cañizo MC: Optimization of
mesenchymal stem cell expansion procedures by cell separation and
culture conditions modification. Exp Hematol. 36:1014–1021.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Huang CT, Chu HS, Hung KC, Chen LW, Chen
MY, Hu FR and Chen WL: The effect of human platelet lysate on
corneal nerve regeneration. Br J Ophthalmol. 105:884–890.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Verma R, Kumar S, Garg P and Verma YK:
Platelet-rich plasma: A comparative and economical therapy for
wound healing and tissue regeneration. Cell Tissue Bank.
24:285–306. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|