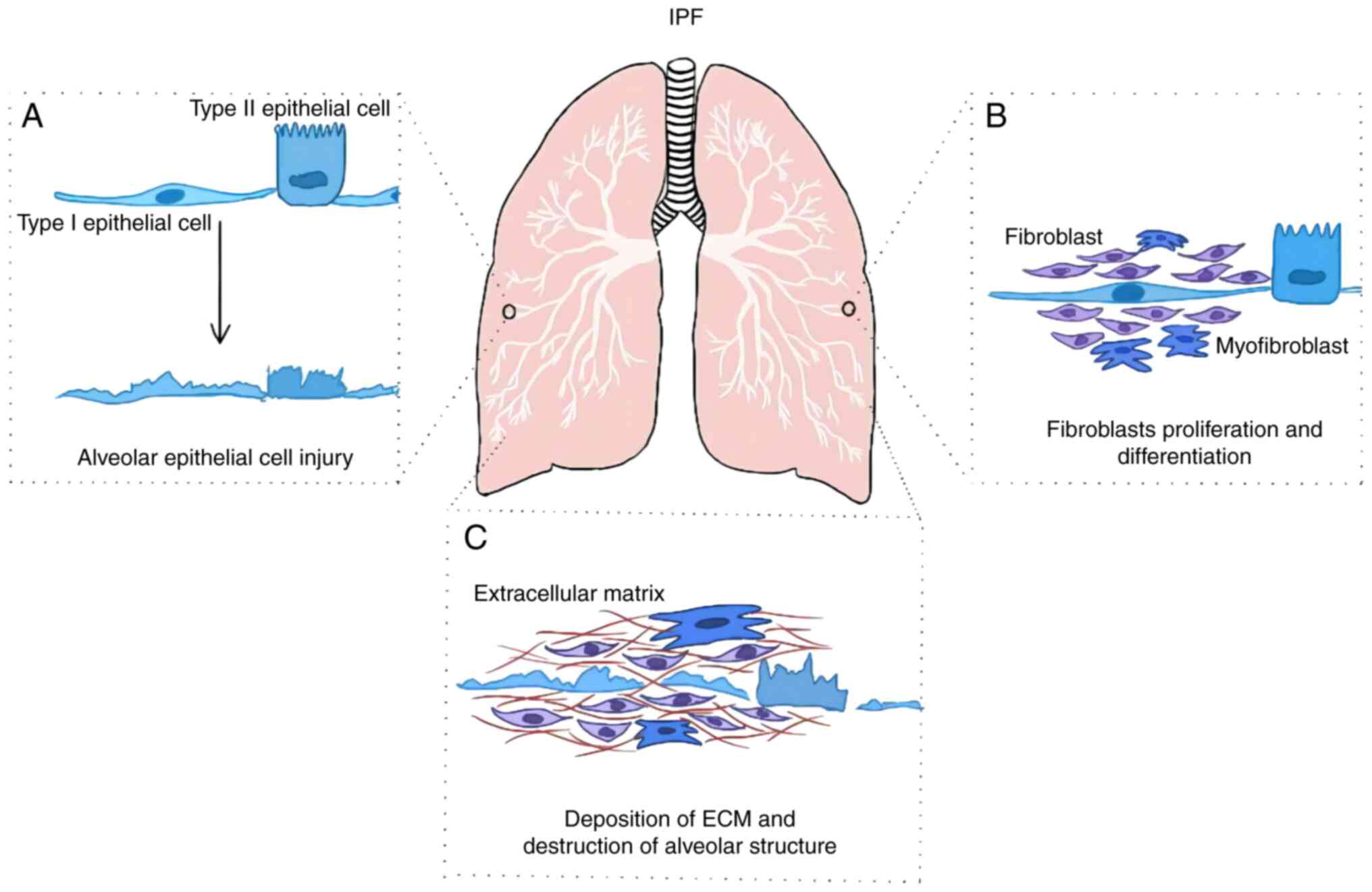
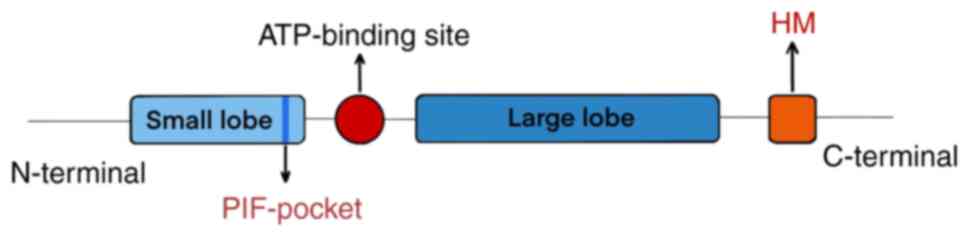
|
1
|
Noble PW, Barkauskas CE and Jiang D:
Pulmonary fibrosis: Patterns and perpetrators. J Clin Invest.
122:2756–2762. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Kreuter M, Ladner UM, Costabel U, Jonigk D
and Heussel CP: The diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary fibrosis.
Dtsch Arztebl Int. 118:152–162. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Richeldi L, Collard HR and Jones MG:
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Lancet. 389:1941–1952.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Günther A, Korfei M, Mahavadi P, von der
Beck D, Ruppert C and Markart P: Unravelling the progressive
pathophysiology of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Eur Respir Rev.
21:152–160. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Raghu G, Collard HR, Egan JJ, Martinez FJ,
Behr J, Brown KK, Colby TV, Cordier JF, Flaherty KR, Lasky JA, et
al: An official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT statement: Idiopathic pulmonary
fibrosis: Evidence-based guidelines for diagnosis and management.
Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 183:788–824. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Lederer DJ and Martinez FJ: Idiopathic
pulmonary fibrosis. N Engl J Med. 378:1811–1823. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Abuserewa ST, Duff R and Becker G:
Treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Cureus.
13(e15360)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Khor YH: Antifibrotic therapy for
idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Combining real world and clinical
trials for totality of evidence. Chest. 160:1589–1591.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Desai O, Winkler J, Minasyan M and Herzog
EL: The role of immune and inflammatory cells in idiopathic
pulmonary fibrosis. Front Med (Lausanne). 5(43)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Fujimoto H, Kobayashi T and Azuma A:
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Treatment and prognosis. Clin Med
Insights Circ Respir Pulm Med. 9 (Suppl 1):S179–S185.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Selman M and Pardo A: The leading role of
epithelial cells in the pathogenesis of idiopathic pulmonary
fibrosis. Cell Signal. 66(109482)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Tu M, Wei T, Jia Y, Wang Y and Wu J:
Molecular mechanisms of alveolar epithelial cell senescence and
idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A narrative review. J Thorac Dis.
15:186–203. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Katzen J and Beers MF: Contributions of
alveolar epithelial cell quality control to pulmonary fibrosis. J
Clin Invest. 130:5088–5099. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Parimon T, Yao C, Stripp BR, Noble PW and
Chen P: Alveolar epithelial type II cells as drivers of lung
fibrosis in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Int J Mol Sci.
21(2269)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Zhu W, Tan C and Zhang J: Alveolar
epithelial type 2 cell dysfunction in idiopathic pulmonary
fibrosis. Lung. 200:539–547. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Habermann AC, Gutierrez AJ, Bui LT, Yahn
SL, Winters NI, Calvi CL, Peter L, Chung MI, Taylor CJ, Jetter C,
et al: Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals profibrotic roles of
distinct epithelial and mesenchymal lineages in pulmonary fibrosis.
Sci Adv. 6(eaba1972)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Manning G, Whyte DB, Martinez R, Hunter T
and Sudarsanam S: The protein kinase complement of the human
genome. Science. 298:1912–1934. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Roskoski R Jr: A historical overview of
protein kinases and their targeted small molecule inhibitors.
Pharmacol Res. 100:1–23. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Deribe YL, Pawson T and Dikic I:
Post-translational modifications in signal integration. Nat Struct
Mol Biol. 17:666–672. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Attwood MM, Fabbro D, Sokolov AV, Knapp S
and Schiöth HB: Trends in kinase drug discovery: Targets,
indications and inhibitor design. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 20:839–861.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Arencibia JM, Pastor-Flores D, Bauer AF,
Schulze JO and Biondi RM: AGC protein kinases: From structural
mechanism of regulation to allosteric drug development for the
treatment of human diseases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1834:1302–1321.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Leroux AE, Schulze JO and Biondi RM: AGC
kinases, mechanisms of regulation and innovative drug development.
Semin Cancer Biol. 48:1–17. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Rath N and Olson MF: Rho-associated
kinases in tumorigenesis: Re-considering ROCK inhibition for cancer
therapy. EMBO Rep. 13:900–908. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Turnham RE and Scott JD: Protein kinase A
catalytic subunit isoform PRKACA; history, function and physiology.
Gene. 577:101–108. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Pearce LR, Komander D and Alessi DR: The
nuts and bolts of AGC protein kinases. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
11:9–22. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Zheng J, Knighton DR, ten Eyck LF,
Karlsson R, Xuong N, Taylor SS and Sowadski JM: Crystal structure
of the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase complexed
with MgATP and peptide inhibitor. Biochemistry. 32:2154–2161.
1993.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Biondi RM, Cheung PC, Casamayor A, Deak M,
Currie RA and Alessi DR: Identification of a pocket in the PDK1
kinase domain that interacts with PIF and the C-terminal residues
of PKA. EMBO J. 19:979–988. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Biondi RM, Komander D, Thomas CC, Lizcano
JM, Deak M, Alessi DR and van Aalten DM: High resolution crystal
structure of the human PDK1 catalytic domain defines the regulatory
phosphopeptide docking site. EMBO J. 21:4219–4228. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Zhang Y and McCormick S: AGCVIII kinases:
At the crossroads of cellular signaling. Trends Plant Sci.
14:689–695. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Sobko A: Systems biology of AGC kinases in
fungi. Sci STKE. 2006(re9)2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Lanassa Bassukas AE, Xiao Y and
Schwechheimer C: Phosphorylation control of PIN auxin transporters.
Curr Opin Plant Biol. 65(102146)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Jiang Y, Liu X, Zhou M, Yang J, Ke S and
Li Y: Genome-wide identification of the AGC protein kinase gene
family related to photosynthesis in rice (Oryza sativa). Int J Mol
Sci. 23(12557)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Glanc M, Van Gelderen K, Hoermayer L, Tan
S, Naramoto S, Zhang X, Domjan D, Včelařová L, Hauschild R, Johnson
A, et al: AGC kinases and MAB4/MEL proteins maintain PIN polarity
by limiting lateral diffusion in plant cells. Curr Biol.
31:1918–1930.e5. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Wick KL and Liu F: A new molecular target
of insulin action: Regulating the pivotal PDK1. Curr Drug Targets
Immune Endocr Metabol Disord. 1:209–221. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Alessi DR, James SR, Downes CP, Holmes AB,
Gaffney PR, Reese CB and Cohen P: Characterization of a
3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase which phosphorylates
and activates protein kinase Balpha. Curr Biol. 7:261–269.
1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Stokoe D, Stephens LR, Copeland T, Gaffney
PR, Reese CB, Painter GF, Holmes AB, McCormick F and Hawkins PT:
Dual role of phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate in the
activation of protein kinase B. Science. 277:567–570.
1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Dittrich ACN and Devarenne TP:
Perspectives in PDK1 evolution: Insights from photosynthetic and
non-photosynthetic organisms. Plant Signal Behav. 7:642–649.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Scheid MP, Parsons M and Woodgett JR:
Phosphoinositide-dependent phosphorylation of PDK1 regulates
nuclear translocation. Mol Cell Biol. 25:2347–2363. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Gagliardi PA, di Blasio L and Primo L:
PDK1: A signaling hub for cell migration and tumor invasion.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1856:178–188. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Cohen P, Alessi DR and Cross DA: PDK1, one
of the missing links in insulin signal transduction? FEBS Lett.
410:3–10. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Zhou Y, Guo Y, Ran M, Shan W, Granchi C,
Giovannetti E, Minutolo F, Peters GJ and Tam KY: Combined
inhibition of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 1 and lactate
dehydrogenase a induces metabolic and signaling reprogramming and
enhances lung adenocarcinoma cell killing. Cancer Lett.
577(216425)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Feng Q, Di R, Tao F, Chang Z, Lu S, Fan W,
Shan C, Li X and Yang Z: PDK1 regulates vascular remodeling and
promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cardiac development.
Mol Cell Biol. 30:3711–3721. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Lawlor MA, Mora A, Ashby PR, Williams MR,
Murray-Tait V, Malone L, Prescott AR, Lucocq JM and Alessi DR:
Essential role of PDK1 in regulating cell size and development in
mice. EMBO J. 21:3728–3738. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Pietri M, Dakowski C, Hannaoui S,
Alleaume-Butaux A, Hernandez-Rapp J, Ragagnin A, Mouillet-Richard
S, Haik S, Bailly Y, Peyrin JM, et al: PDK1 decreases TACE-mediated
α-secretase activity and promotes disease progression in prion and
Alzheimer's diseases. Nat Med. 19:1124–1131. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Hashimoto N, Kido Y, Uchida T, Asahara S,
Shigeyama Y, Matsuda T, Takeda A, Tsuchihashi D, Nishizawa A, Ogawa
W, et al: Ablation of PDK1 in pancreatic beta cells induces
diabetes as a result of loss of beta cell mass. Nat Genet.
38:589–593. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Choucair KA, Guérard KP, Ejdelman J,
Chevalier S, Yoshimoto M, Scarlata E, Fazli L, Sircar K, Squire JA,
Brimo F, et al: The 16p13.3 (PDPK1) genomic gain in prostate
cancer: A potential role in disease progression. Transl Oncol.
5:453–460. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Maurer M, Su T, Saal LH, Koujak S, Hopkins
BD, Barkley CR, Wu J, Nandula S, Dutta B, Xie Y, et al:
3-Phosphoinositide-dependent kinase 1 potentiates upstream lesions
on the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway in breast carcinoma.
Cancer Res. 69:6299–6306. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Kim JW, Tchernyshyov I, Semenza GL and
Dang CV: HIF-1-mediated expression of pyruvate dehydrogenase
kinase: A metabolic switch required for cellular adaptation to
hypoxia. Cell Metab. 3:177–185. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Papandreou I, Cairns RA, Fontana L, Lim AL
and Denko NC: HIF-1 mediates adaptation to hypoxia by actively
downregulating mitochondrial oxygen consumption. Cell Metab.
3:187–197. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Li J, Zhai X, Sun X, Cao S, Yuan Q and
Wang J: Metabolic reprogramming of pulmonary fibrosis. Front
Pharmacol. 13(1031890)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Hamanaka RB and Mutlu GM: Metabolic
requirements of pulmonary fibrosis: Role of fibroblast metabolism.
FEBS J. 288:6331–6352. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Henderson J and O'Reilly S: The emerging
role of metabolism in fibrosis. Trends Endocrinol Metab.
32:639–653. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Goodwin J, Choi H, Hsieh MH, Neugent ML,
Ahn JM, Hayenga HN, Singh PK, Shackelford DB, Lee IK, Shulaev V, et
al: Targeting hypoxia-inducible factor-1α/pyruvate dehydrogenase
kinase 1 axis by dichloroacetate suppresses bleomycin-induced
pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 58:216–231.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Stacpoole PW: Review of the pharmacologic
and therapeutic effects of diisopropylammonium dichloroacetate
(DIPA). J Clin Pharmacol J New Drugs. 9:282–291. 1969.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Stacpoole PW, Kurtz TL, Han Z and Langaee
T: Role of dichloroacetate in the treatment of genetic
mitochondrial diseases. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 60:1478–1487.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Yang K, Li B and Chen J: Knockdown of
phosphoinositide-dependent kinase 1 (PDK1) inhibits fibrosis and
inflammation in lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury rat
model by attenuating NF-κB/p65 pathway activation. Ann Transl Med.
9(1671)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Liu Y, Xie X, Wang P, Luo J, Chen Y, Xu Q,
Zhou J, Lu X, Zhao J, Chen Z and Zuo D: Mannan-binding lectin
reduces epithelial-mesenchymal transition in pulmonary fibrosis via
inactivating the store-operated calcium entry machinery. J Innate
Immun. 15:37–49. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Loirand G, Guérin P and Pacaud P: Rho
kinases in cardiovascular physiology and pathophysiology. Circ Res.
98:322–334. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Shimizu Y, Dobashi K, Iizuka K, Horie T,
Suzuki K, Tukagoshi H, Nakazawa T, Nakazato Y and Mori M:
Contribution of small GTPase Rho and its target protein rock in a
murine model of lung fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
163:210–217. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Barcelo J, Samain R and Sanz-Moreno V:
Preclinical to clinical utility of ROCK inhibitors in cancer.
Trends Cancer. 9:250–263. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Shimokawa H and Takeshita A: Rho-kinase is
an important therapeutic target in cardiovascular medicine.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 25:1767–1775. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Knipe RS, Tager AM and Liao JK: The Rho
kinases: Critical mediators of multiple profibrotic processes and
rational targets for new therapies for pulmonary fibrosis.
Pharmacol Rev. 67:103–117. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Jiang C, Huang H, Liu J, Wang Y, Lu Z and
Xu Z: Fasudil, a Rho-kinase inhibitor, attenuates bleomycin-induced
pulmonary fibrosis in mice. Int J Mol Sci. 13:8293–8307.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Shimizu Y, Dobashi K, Sano T and Yamada M:
ROCK activation in lung of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis with
oxidative stress. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 27:37–44.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Ghatak S, Hascall VC, Markwald RR,
Feghali-Bostwick C, Artlett CM, Gooz M, Bogatkevich GS,
Atanelishvili I, Silver RM, Wood J, et al: Transforming growth
factor β1 (TGFβ1)-induced CD44V6-NOX4 signaling in pathogenesis of
idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. J Biol Chem. 292:10490–10519.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Fu S, Wen Y, Peng B, Tang M, Shi M, Liu J,
Yang Y, Si W, Guo Y, Li X, et al: Discovery of indoline-based
derivatives as effective ROCK2 inhibitors for the potential new
treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Bioorg Chem.
137(106539)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Wu X, Verschut V, Woest ME, Ng-Blichfeldt
JP, Matias A, Villetti G, Accetta A, Facchinetti F, Gosens R and
Kistemaker LEM: Rho-kinase 1/2 inhibition prevents transforming
growth factor-β-induced effects on pulmonary remodeling and repair.
Front Pharmacol. 11(609509)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Hong AW, Meng Z and Guan KL: The Hippo
pathway in intestinal regeneration and disease. Nat Rev
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 13:324–337. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Wu Z and Guan KL: Hippo signaling in
embryogenesis and development. Trends Biochem Sci. 46:51–63.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Landry NM, Rattan SG, Filomeno KL, Meier
TW, Meier SC, Foran SJ, Meier CF, Koleini N, Fandrich RR, Kardami
E, et al: SKI activates the Hippo pathway via LIMD1 to inhibit
cardiac fibroblast activation. Basic Res Cardiol.
116(25)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Dong L and Li L: Lats2-underexpressing
bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate LPS-induced
acute lung injury in mice. Mediators Inflamm.
2019(4851431)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Antebi B, Walker KP III, Mohammadipoor A,
Rodriguez LA, Montgomery RK, Batchinsky AI and Cancio LC: The
effect of acute respiratory distress syndrome on bone
marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther.
9(251)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Kuwano K, Miyazaki H, Hagimoto N, Kawasaki
M, Fujita M, Kunitake R, Kaneko Y and Hara N: The involvement of
Fas-Fas ligand pathway in fibrosing lung diseases. Am J Respir Cell
Mol Biol. 20:53–60. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Cai SX, Liu AR, Chen S, He HL, Chen QH, Xu
JY, Pan C, Yang Y, Guo FM, Huang YZ, et al: The orphan receptor
tyrosine kinase ROR2 facilitates MSCs to repair lung injury in ARDS
animal model. Cell Transplant. 25:1561–1574. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Han J, Lu X, Zou L, Xu X and Qiu H:
E-prostanoid 2 receptor overexpression promotes mesenchymal stem
cell attenuated lung injury. Hum Gene Ther. 27:621–630.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Fernández-Hernando C, Ackah E, Yu J,
Suárez Y, Murata T, Iwakiri Y, Prendergast J, Miao RQ, Birnbaum MJ
and Sessa WC: Loss of Akt1 leads to severe atherosclerosis and
occlusive coronary artery disease. Cell Metab. 6:446–457.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Iliopoulos D, Polytarchou C,
Hatziapostolou M, Kottakis F, Maroulakou IG, Struhl K and Tsichlis
PN: MicroRNAs differentially regulated by Akt isoforms control EMT
and stem cell renewal in cancer cells. Sci Signal.
2(ra62)2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Revathidevi S and Munirajan AK: Akt in
cancer: Mediator and more. Semin Cancer Biol. 59:80–91.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Risso G, Blaustein M, Pozzi B, Mammi P and
Srebrow A: Akt/PKB: One kinase, many modifications. Biochem J.
468:203–214. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Toker A and Yoeli-Lerner M: Akt signaling
and cancer: Surviving but not moving on. Cancer Res. 66:3963–3966.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Wang J, Hu K, Cai X, Yang B, He Q, Wang J
and Weng Q: Targeting PI3K/AKT signaling for treatment of
idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Acta Pharm Sin B. 12:18–32.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Virtakoivu R, Pellinen T, Rantala JK,
Perälä M and Ivaska J: Distinct roles of AKT isoforms in regulating
β1-integrin activity, migration, and invasion in prostate cancer.
Mol Biol Cell. 23:3357–3369. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Arboleda MJ, Lyons JF, Kabbinavar FF, Bray
MR, Snow BE, Ayala R, Danino M, Karlan BY and Slamon DJ:
Overexpression of AKT2/protein kinase Bbeta leads to up-regulation
of beta1 integrins, increased invasion, and metastasis of human
breast and ovarian cancer cells. Cancer Res. 63:196–206.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Baek ST, Copeland B, Yun EJ, Kwon SK,
Guemez-Gamboa A, Schaffer AE, Kim S, Kang HC, Song S, Mathern GW
and Gleeson JG: An AKT3-FOXG1-reelin network underlies defective
migration in human focal malformations of cortical development. Nat
Med. 21:1445–1454. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Kang HR, Lee CG, Homer RJ and Elias JA:
Semaphorin 7A plays a critical role in TGF-beta1-induced pulmonary
fibrosis. J Exp Med. 204:1083–1093. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Horowitz JC, Rogers DS, Sharma V, Vittal
R, White ES, Cui Z and Thannickal VJ: Combinatorial activation of
FAK and AKT by transforming growth factor-beta1 confers an
anoikis-resistant phenotype to myofibroblasts. Cell Signal.
19:761–771. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Nie Y, Sun L, Wu Y, Yang Y, Wang J, He H,
Hu Y, Chang Y, Liang Q, Zhu J, et al: AKT2 regulates pulmonary
inflammation and fibrosis via modulating macrophage activation. J
Immunol. 198:4470–4480. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Larson-Casey JL, Deshane JS, Ryan AJ,
Thannickal VJ and Carter AB: Macrophage Akt1 kinase-mediated
mitophagy modulates apoptosis resistance and pulmonary fibrosis.
Immunity. 44:582–596. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Nie Y, Hu Y, Yu K, Zhang D, Shi Y, Li Y,
Sun L and Qian F: Akt1 regulates pulmonary fibrosis via modulating
IL-13 expression in macrophages. Innate Immun. 25:451–461.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Kazanietz MG and Cooke M: Protein kinase C
signaling ‘in’ and ‘to’ the nucleus: Master kinases in
transcriptional regulation. J Biol Chem: 105692, 2024 (Epub ahead
of print).
|
|
91
|
Silnitsky S, Rubin SJS, Zerihun M and Qvit
N: An update on protein kinases as therapeutic targets-part I:
Protein kinase C activation and its role in cancer and
cardiovascular diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 24(17600)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Kang JH, Toita R, Kim CW and Katayama Y:
Protein kinase C (PKC) isozyme-specific substrates and their
design. Biotechnol Adv. 30:1662–1672. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
93
|
Abe MK, Kartha S, Karpova AY, Li J, Liu
PT, Kuo WL and Hershenson MB: Hydrogen peroxide activates
extracellular signal-regulated kinase via protein kinase C, Raf-1,
and MEK1. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 18:562–569. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
94
|
Barman SA: Potassium channels modulate
canine pulmonary vasoreactivity to protein kinase C activation. Am
J Physiol. 277:L558–L565. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
95
|
Das M, Stenmark KR, Ruff LJ and Dempsey
EC: Selected isozymes of PKC contribute to augmented growth of
fetal and neonatal bovine PA adventitial fibroblasts. Am J Physiol.
273:L1276–L1284. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
96
|
Harrington EO, Löffler J, Nelson PR, Kent
KC, Simons M and Ware JA: Enhancement of migration by protein
kinase Calpha and inhibition of proliferation and cell cycle
progression by protein kinase Cdelta in capillary endothelial
cells. J Biol Chem. 272:7390–7397. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
97
|
Wang J, Sun L, Nie Y, Duan S, Zhang T,
Wang W, Ye RD, Hou S and Qian F: Protein kinase C δ (PKCδ)
attenuates bleomycin induced pulmonary fibrosis via inhibiting
NF-κB signaling pathway. Front Physiol. 11(367)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
98
|
Jimenez SA, Gaidarova S, Saitta B,
Sandorfi N, Herrich DJ, Rosenbloom JC, Kucich U, Abrams WR and
Rosenbloom J: Role of protein kinase C-delta in the regulation of
collagen gene expression in scleroderma fibroblasts. J Clin Invest.
108:1395–1403. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
99
|
Song JS, Kang CM, Park CK and Yoon HK:
Thrombin induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition via PAR-1, PKC,
and ERK1/2 pathways in A549 cells. Exp Lung Res. 39:336–348.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
100
|
Barosova H, Meldrum K, Karakocak BB, Balog
S, Doak SH, Petri-Fink A, Clift MJD and Rothen-Rutishauser B:
Inter-laboratory variability of A549 epithelial cells grown under
submerged and air-liquid interface conditions. Toxicol In Vitro.
75(105178)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
101
|
McMullen JR, Shioi T, Zhang L, Tarnavski
O, Sherwood MC, Dorfman AL, Longnus S, Pende M, Martin KA, Blenis
J, et al: Deletion of ribosomal S6 kinases does not attenuate
pathological, physiological, or insulin-like growth factor 1
receptor-phosphoinositide 3-kinase-induced cardiac hypertrophy. Mol
Cell Biol. 24:6231–6240. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
102
|
Ludwik KA and Lannigan DA: Ribosomal S6
kinase (RSK) modulators: A patent review. Expert Opin Ther Pat.
26:1061–1078. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
103
|
Shima H, Pende M, Chen Y, Fumagalli S,
Thomas G and Kozma SC: Disruption of the p70(s6k)/p85(s6k) gene
reveals a small mouse phenotype and a new functional S6 kinase.
EMBO J. 17:6649–6659. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
104
|
Magnuson B, Ekim B and Fingar DC:
Regulation and function of ribosomal protein S6 kinase (S6K) within
mTOR signalling networks. Biochem J. 441:1–21. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
105
|
Pullen N, Dennis PB, Andjelkovic M, Dufner
A, Kozma SC, Hemmings BA and Thomas G: Phosphorylation and
activation of p70s6k by PDK1. Science. 279:707–710. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
106
|
Roux PP, Shahbazian D, Vu H, Holz MK,
Cohen MS, Taunton J, Sonenberg N and Blenis J: RAS/ERK signaling
promotes site-specific ribosomal protein S6 phosphorylation via RSK
and stimulates cap-dependent translation. J Biol Chem.
282:14056–14064. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
107
|
Soares HP, Ni Y, Kisfalvi K, Sinnett-Smith
J and Rozengurt E: Different patterns of Akt and ERK feedback
activation in response to rapamycin, active-site mTOR inhibitors
and metformin in pancreatic cancer cells. PLoS One.
8(e57289)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
108
|
Frödin M and Gammeltoft S: Role and
regulation of 90 kDa ribosomal S6 kinase (RSK) in signal
transduction. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 151:65–77. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
109
|
Madala SK, Thomas G, Edukulla R, Davidson
C, Schmidt S, Schehr A and Hardie WD: p70 ribosomal S6 kinase
regulates subpleural fibrosis following transforming growth
factor-α expression in the lung. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol
Physiol. 310:L175–L186. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
110
|
Han Q, Lin L, Zhao B, Wang N and Liu X:
Inhibition of mTOR ameliorates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis
by regulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 500:839–845. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
111
|
Zou W, Zhang X, Zhao M, Zhou Q and Hu X:
Cellular proliferation and differentiation induced by single-layer
molybdenum disulfide and mediation mechanisms of proteins via the
Akt-mTOR-p70S6K signaling pathway. Nanotoxicology. 11:781–793.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
112
|
Kim S, Han JH, Kim S, Lee H, Kim JR, Lim
JH and Woo CH: p90RSK inhibition ameliorates TGF-β1 signaling and
pulmonary fibrosis by inhibiting smad3 transcriptional activity.
Cell Physiol Biochem. 54:195–210. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
113
|
Jia S, Agarwal M, Yang J, Horowitz JC,
White ES and Kim KK: Discoidin domain receptor 2 signaling
regulates fibroblast apoptosis through PDK1/Akt. Am J Respir Cell
Mol Biol. 59:295–305. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
114
|
Wang L, Li Z, Wan R, Pan X, Li B, Zhao H,
Yang J, Zhao W, Wang S, Wang Q, et al: Single-cell RNA sequencing
provides new insights into therapeutic roles of thyroid hormone in
idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol.
69:456–469. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
115
|
Adams TS, Schupp JC, Poli S, Ayaub EA,
Neumark N, Ahangari F, Chu SG, Raby BA, DeIuliis G, Januszyk M, et
al: Single-cell RNA-seq reveals ectopic and aberrant lung-resident
cell populations in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Sci Adv.
6(eaba1983)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
116
|
Yang L, Gilbertsen A, Smith K, Xia H,
Higgins L, Guerrero C and Henke CA: Proteomic analysis of the IPF
mesenchymal progenitor cell nuclear proteome identifies
abnormalities in key nodal proteins that underlie their fibrogenic
phenotype. Proteomics. 22(e2200018)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|