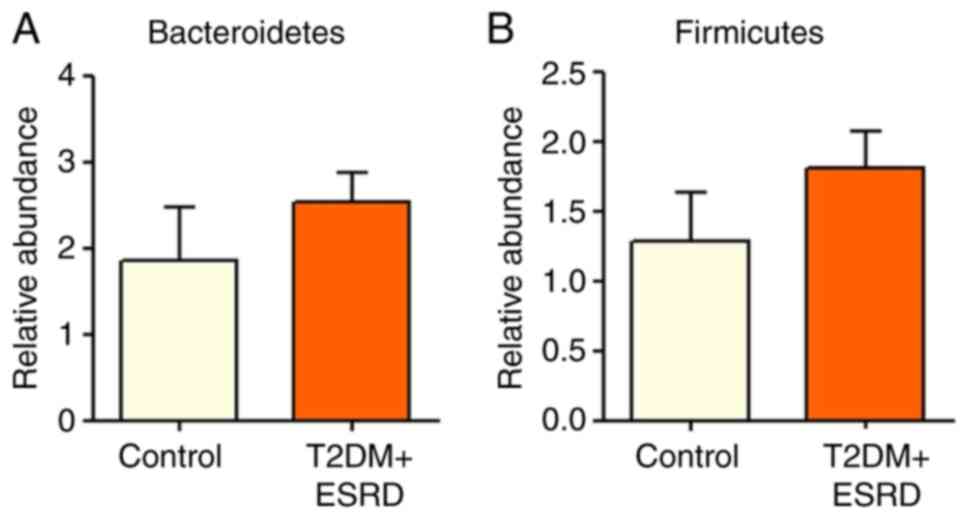
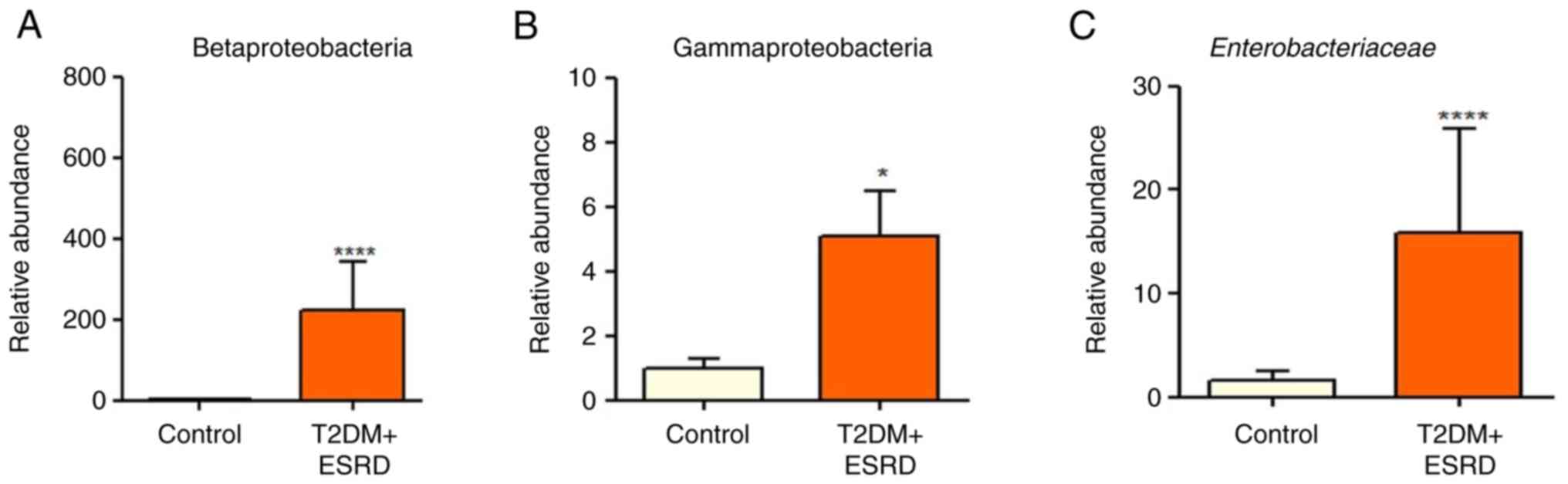
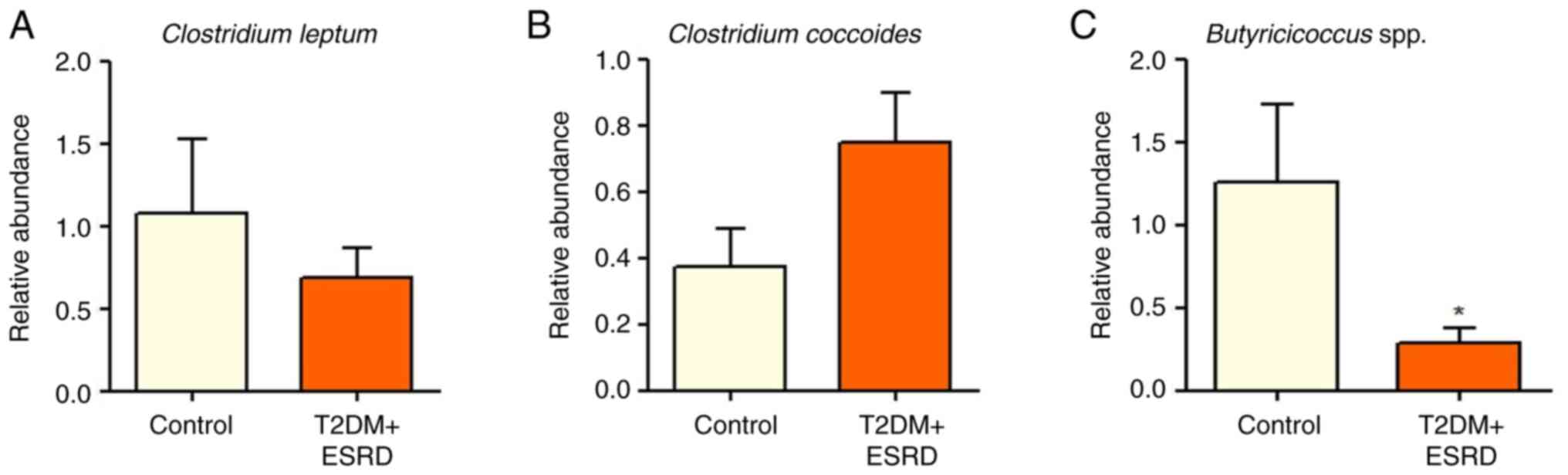
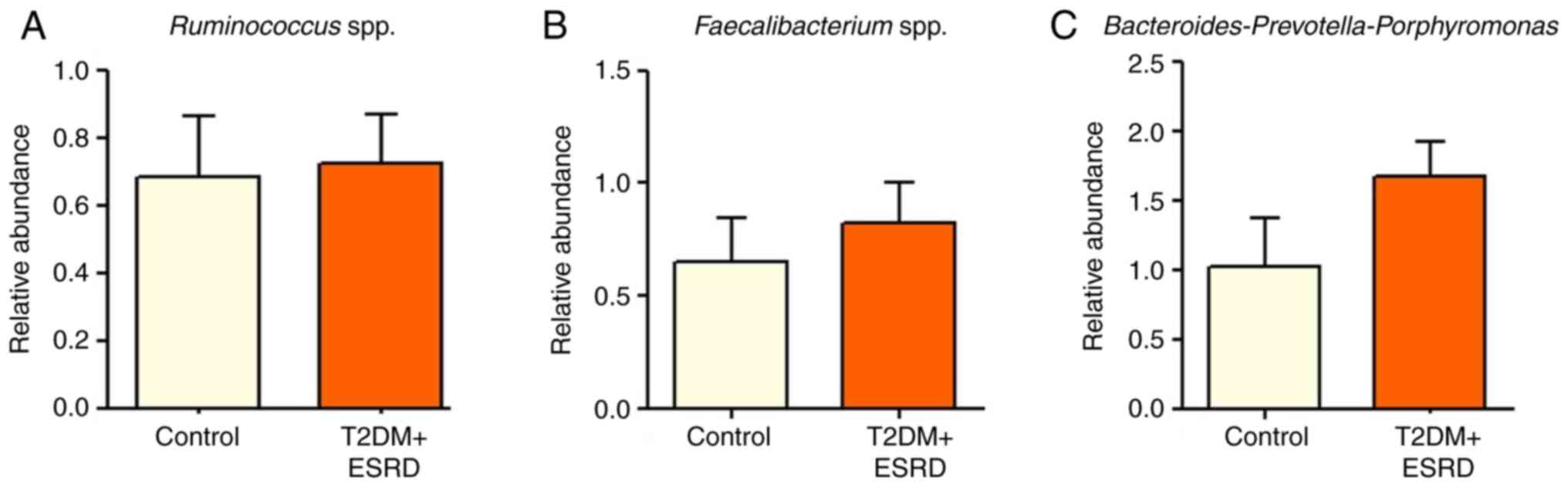
|
1
|
Luca M, Mauro MD, Mauro MD and Luca A: Gut
microbiota in Alzheimer's disease, depression, and type 2 diabetes
mellitus: The role of oxidative stress. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2019(4730539)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Neish AS: Microbes in gastrointestinal
health and disease. Gastroenterology. 136:65–80. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Bäckhed F, Ding H, Wang T, Hooper LV, Koh
GY, Nagy A, Semenkovich CF and Gordon JI: The gut microbiota as an
environmental factor that regulates fat storage. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 101:15718–15723. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Gill SR, Pop M, DeBoy RT, Eckburg PB,
Turnbaugh PJ, Samuel BS, Gordon JI, Relman DA, Fraser-Liggett CM
and Nelson KE: Metagenomic analysis of the human distal gut
microbiome. Science. 312:1355–1359. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Ursell LK, Metcalf JL, Parfrey LW and
Knight R: Defining the human microbiome. Nutr Rev. 70 (Suppl
1):S38–S44. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Thursby E and Juge N: Introduction to the
human gut microbiota. Biochem J. 474:1823–1836. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Yang T, Richards EM, Pepine CJ and Raizada
MK: The gut microbiota and the brain-gut-kidney axis in
hypertension and chronic kidney disease. Nat Rev Nephrol.
14:442–456. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Vaziri ND, Wong J, Pahl M, Piceno YM, Yuan
J, DeSantis TZ, Ni Z, Nguyen TH and Andersen GL: Chronic kidney
disease alters intestinal microbial flora. Kidney Int. 83:308–315.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Ranganathan N, Friedman EA, Tam P, Rao V,
Ranganathan P and Dheer R: Probiotic dietary supplementation in
patients with stage 3 and 4 chronic kidney disease: A 6-month pilot
scale trial in Canada. Curr Med Res Opin. 25:1919–1930.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Chen YY, Chen DQ, Chen L, Liu JR, Vaziri
ND, Guo Y and Zhao YY: Microbiome-metabolome reveals the
contribution of gut-kidney axis on kidney disease. J Transl Med.
17(5)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Hida M, Aiba Y, Sawamura S, Suzuki N,
Satoh T and Koga Y: Inhibition of the accumulation of uremic toxins
in the blood and their precursors in the feces after oral
administration of Lebenin, a lactic acid bacteria preparation, to
uremic patients undergoing hemodialysis. Nephron. 74:349–355.
1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Mahmoodpoor F, Rahbar Saadat Y, Barzegari
A, Ardalan M and Zununi Vahed SV: The impact of gut microbiota on
kidney function and pathogenesis. Biomed Pharmacother. 93:412–419.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Lau WL, Savoj J, Nakata MB and Vaziri ND:
Altered microbiome in chronic kidney disease: Systemic effects of
gut-derived uremic toxins. Clin Sci (Lon). 132:509–522.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Jiang S, Xie S, Lv D, Wang P, He H, Zhang
T, Zhou Y, Lin Q, Zhou H, Jiang J, et al: Alteration of the gut
microbiota in Chinese population with chronic kidney disease. Sci
Rep. 7(2870)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Wong J, Piceno YM, DeSantis TZ, Pahl M,
Andersen GL and Vaziri ND: Expansion of urease- and
uricase-containing, indole- and p-cresol-forming and contraction of
short-chain fatty acid-producing intestinal microbiota in ESRD. Am
J Nephrol. 39:230–237. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Ramezani A and Raj DS: The gut microbiome,
kidney disease, and targeted interventions. J Am Soc Nephrol.
25:657–670. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Dunne JL, Triplett EW, Gevers D, Xavier R,
Insel R, Danska J and Atkinson MA: The intestinal microbiome in
type 1 diabetes. Clin Exp Immunol. 177:30–37. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Al Khodor S and Shatat IF: Gut microbiome
and kidney disease: A bidirectional relationship. Pediatr Nephrol.
32:921–931. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Patterson E, Ryan PM, Cryan JF, Dinan TG,
Ross RP, Fitzgerald GF and Stanton C: Gut microbiota, obesity and
diabetes. Postgrad Med J. 92:286–300. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Salgaço MK, Oliveira LGS, Costa GN,
Bianchi F and Sivieri K: Relationship between gut microbiota,
probiotics, and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Appl Microbiol
Biotechnol. 103:9229–9238. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Xu Q, Ni JJ, Han BX, Yan SS, Wei XT, Feng
GJ, Zhang H, Zhang L, Li B and Pei YF: Causal relationship between
gut microbiota and autoimmune diseases: A two-sample mendelian
randomization study. Front Immunol. 12(746998)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Estrada V and Gonzalez N: Gut microbiota
in diabetes and HIV: Inflammation is the link. EBioMedicine.
38:17–18. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Schéle E, Grahnemo L, Anesten F, Halleń A,
Backhed F and Jansson JO: The gut microbiota reduces leptin
sensitivity and the expression of the obesity-suppressing
neuropeptides proglucagon (Gcg) and brain-derived neurotrophic
factor (Bdnf) in the central nervous system. Endocrinology.
154:3643–3651. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Kreznar JH, Keller MP, Traeger LL,
Rabaglia ME, Schueler KL, Stapleton DS, Zhao W, Vivas EI, Yandell
BS, Broman AT, et al: Host genotype and gut microbiome modulate
insulin secretion and diet-induced metabolic phenotypes. Cell Rep.
18:1739–1750. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Wahlström A, Sayin SI, Marschall HU and
Bäckhed F: Intestinal crosstalk between bile acids and microbiota
and its impact on host metabolism. Cell Metab. 24:41–50.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Sharma S and Tripathi P: Gut microbiome
and type 2 diabetes: Where we are and where to go? J Nutr Biochem.
63:101–108. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Rosario D, Benfeitas R, Bidkhori G, Zhang
C, Uhlen M, Shoaie S and Mardinoglu A: Understanding the
representative gut microbiota dysbiosis in metformin-treated Type 2
diabetes patients using genome-scale metabolic modeling. Front
Physiol. 9(775)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
American Diabetes Association. Standards
of care in diabetes-2023 abridged for primary care providers. Clin
Diabetes. 41:4–31. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Acosta-Ochoa I, Bustamante-Munguira J,
Mendiluce-Herrero A, Bustamante-Bustamante J and Coca-Rojo A:
Impact on outcomes across KDIGO-2012 AKI criteria according to
baseline renal function. J Clin Med. 8(1323)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Takada T, Watanabe K, Makino H and Kushiro
A: Reclassification of Eubacterium desmolans as Butyricicoccus
desmolans comb. nov., and description of Butyricicoccus
faecihominis sp. nov., a butyrate-producing bacterium from human
faeces. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 66:4125–4131. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Koshida T, Gohda T, Sugimoto T, Asahara T,
Asao R, Ohsawa I, Gotoh H, Murakoshi M, Suzuki Y and Yamashiro Y:
Gut microbiome and microbiome-derived metabolites in patients with
end-stage kidney disease. Int J Mol Sci. 24(11456)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Sabatino A, Regolisti G, Cosola C,
Gesualdo L and Fiaccadori E: Intestinal microbiota in type 2
diabetes and chronic kidney disease. Curr Diab Rep.
17(16)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Kim SM and Song IH: The clinical impact of
gut microbiota in chronic kidney disease. Korean J Intern Med.
35:1305–1316. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Kambay M, Onal EM, Afsar B, Dagel T,
Yerlikaya A, Covic A and Vaziri ND: The crosstalk of gut microbiota
and chronic kidney disease: Role of inflammation, proteinuria,
hypertension, and diabetes mellitus. Int Urol Nephrol.
50:1453–1466. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Rizzatti G, Lopetuso LR, Gibiino G, Binda
C and Gasbarrini A: Proteobacteria: A common factor in human
diseases. Biomed Res Int. 2017(9351507)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Dang H, Chen R, Wang L, Shao S, Dai L, Ye
Y, Guo L, Huang G and Klotz MG: Molecular characterization of
putative biocorroding microbiota with a novel niche detection of
Epsilon- and Zetaproteobacteria in Pacific Ocean coastal seawaters.
Environ Microbiol. 13:3059–3074. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Gomes-Neto JC, Mantz S, Held K, Sinha R,
Segura Munoz RR, Schmaltz R, Benson AK, Walter J and Ramer-Tait AE:
A real-time PCR assay for accurate quantification of the individual
members of the altered schaedler flora microbiota in gnotobiotic
mice. J Microbiol Methods. 135:52–62. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Lambeth SM, Carson T, Lowe J, Ramaraj T,
Leff JW, Luo L, Bell CJ and Shah VO: Composition, diversity and
abundance of gut microbiome in prediabetes and type 2 diabetes. J
Diabetes Obes. 2:1–7. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Ohtani N and Kawada N: Role of the
gut-liver axis in liver inflammation, fibrosis, and cancer: A
special focus on the gut microbiota relationship. Hepatol Commun.
3:456–470. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Furusawa Y, Obata Y, Fukuda S, Endo TA,
Nakato G, Takahashi D, Nakanishi Y, Uetake C, Kato K, Kato T, et
al: Commensal microbe-derived butyrate induces the differentiation
of colonic regulatory T cells. Nature. 504:446–450. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Bäckhed F, Ley RE, Sonnenburg JL, Peterson
DA and Gordon JI: Host-bacterial mutualism in the human intestine.
Science. 307:1915–1920. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Gérard C and Vidal H: Impact of gut
microbiota on host glycemic control. Front Endocrinol (Lousanne).
10(29)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Matsuki T, Watanabe K, Fujimoto J, Takada
T and Tanaka R: Use of 16S rRNA gene-targeted group-specific
primers for real-time PCR analysis of predominant bacteria in human
feces. Appl Environ Microbiol. 70:7220–7228. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Qin J, Li Y, Cai Z, Li S, Zhu J, Zhang F,
Liang S, Zhang W, Guan Y, Shen D, et al: A metagenome-wide
association study of gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes. Nature.
490:55–60. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Duggan S, Essig F, Hünniger K, Mokhtari Z,
Bauer L, Lehnert T, Brandes S, Häder A, Jacobsen ID, Martin R, et
al: Neutrophil activation by Candida glabrata but not Candida
albicans promotes fungal uptake by monocytes. Cell Microbiol.
17:1259–1276. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Motta-Silva AC, Aleva NA, Chavasco JK,
Armond MC, França JP and Pereira LJ: Erythematous oral candidiasis
in patients with controlled type II diabetes mellitus and complete
dentures. Mycopathologia. 169:215–223. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Rodrigues CF, Rodrigues ME and Henriques
M: Candida sp. Infections in patients with diabetes mellitus. J
Clin Med. 8(76)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Balan P, B Gogineni S, Kumari NS, Shetty
V, Lakshman Rangare A, L Castelino R and Areekat KF: Candida
carriage rate and growth characteristics of saliva in diabetes
mellitus patients: A case-control study. J Dent Res Dent Clin Dent
Prospects. 9:274–279. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Kadir T, Pisiriciler R, Akyüz S, Yarat A,
Emekli N and Ipbüker A: Mycological and cytological examination of
oral candidal carriage in diabetic patients and non-diabetic
control subjects: Thorough analysis of local aetiologic and
systemic factors. J Oral Rehab. 29:452–457. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Gosiewski T, Salamon D, Szopa M, Sroka A,
Malecki MT and Bulanda M: Quantitative evaluation of fungi of the
genus Candida in the feces of adult patients with type 1 and 2
diabetes-a pilot study. Gut Pathogens. 6(43)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Albuquerque RCMF, Brandão ABP, de Abreu
ICME, Ferreira FG, Santos LB, Moreira LN, Taddei CR, Aimbire F and
Cunha TS: Saccharomyces boulardii Tht 500101 changes gut microbiota
and ameliorates hyperglycaemia, dyslipidaemia, and liver
inflammation in streptozotocin-diabetic mice. Beneficial Microbes.
10:901–912. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Silva Vde O, Lobato RV, Andrade EF, de
Macedo CG, Napimoga JT, Napimoga MH, Messora MR, Murata RM and
Pereira LJ: B-glucans (Saccharomyces cereviseae) reduce glucose
levels and attenuate alveolar bone loss in diabetic rats with
periodontal disease. PLoS One. 10(e0134742)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
De Sales Guilarducci J, Marcelino BAR,
Konig IFM, Orlando TM, Varaschin MS and Pereira LJ: Therapeutic
effects of different doses of prebiotic (isolated from
Saccharomyces cerevisiae) in comparison to n-3 supplement on
glycemic control, lipid profiles and immunological response in
diabetic rats. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 12(69)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Barssotti L, Abreu ICME, Brandão ABP,
Albuquerque RCMF, Ferreira FG, Salgado MAC, Dias DDS, De Angelis K,
Yokota R, Casarini DE, et al: Saccharomyces boulardii modulates
oxidative stress and renin angiotensin system attenuating
diabetes-induced liver injury in mice. Sci Rep.
11(9189)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Yang YW, Chen MK, Yang BY, Huang XJ, Zhang
XR, He LQ, Zhang J and Hua ZC: Use of 16S rRNA gene-targeted
group-specific primers for real-time PCR analysis of predominant
bacteria in mouse feces. Appl Environ Microbiol. 81:6749–6756.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
DeBruyn JM, Nixon LT, Fawaz MN, Johnson AM
and Radosevich M: Global biogeography and quantitative seasonal
dynamics of Gemmatimonadetes in soil. Appl Environ Microbiol.
77:6295–6300. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Ferreira RB, Gill N, Willing BP, Antunes
LC, Russell SL, Croxen MA and Finlay BB: The intestinal microbiota
plays a role in Salmonella-induced colitis independent of pathogen
colonization. PLoS One. 6(e20338)2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Dong Y, Fan H, Zhang Z, Jiang F, Li M,
Zhou H, Guo W, Zhang Z, Kang Z, Gui Y, et al: Berberine ameliorates
DSS-induced intestinal mucosal barrier dysfunction through
microbiota-dependence and Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Int JBiol Sci.
18:1381–1397. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Rinttilä T, Kassinen A, Malinen E, Krogius
L and Palva A: Development of an extensive set of 16S rDNA-targeted
primers for quantification of pathogenic and indigenous bacteria in
faecal samples by real-time PCR. J Appl Microbiol. 97:1166–1177.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Furet JP, Firmesse O, Gourmelon M,
Bridonneau C, Tap J, Mondot S, Doré J and Corthier G: Comparative
assessment of human and farm animal faecal microbiota using
real-time quantitative PCR. FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 68:351–362.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Noratto GD, Garcia-Mazcorro JF, Markel M,
Martino HS, Minamoto Y, Steiner JM, Byrne D, Suchodolski JS and
Mertens-Talcott SU: Carbohydrate-free peach (Prunus persica) and
plum (Prunus salicina) [corrected] juice affects fecal microbial
ecology in an obese animal model. PLoS One.
9(e101723)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Guo X, Xia X, Tang R, Zhou J, Zhao H and
Wang K: Development of a real-time PCR method for Firmicutes and
Bacteroidetes in faeces and its application to quantify intestinal
population of obese and lean pigs. Lett Appl Microbiol. 47:367–373.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Ou J, Carbonero F, Zoetendal EG, DeLany
JP, Wang M, Newton K, Gaskins HR and O'Keefe SJ: Diet, microbiota,
and microbial metabolites in colon cancer risk in rural Africans
and African Americans. Am J Clin Nutr. 98:111–120. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Gradisteanu Pircalabioru G, Chifiriuc MC,
Picu A, Petcu LM, Trandafir M and Savu O: Snapshot into the
type-2-diabetes-associated microbiome of a Romanian cohort. Int J
Mol Sci. 23(15023)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Loeffler J, Hebart H, Magga S, Schmidt D,
Klingspor L, Tollemar J, Schumacher U and Einsele H: Identification
of rare Candida species and other yeasts by polymerase chain
reaction and slot blot hybridization. Diagn Microb Infect Dis.
38:207–212. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Sokol H, Leducq V, Aschard H, Pham HP,
Jegou S, Landman C, Cohen D, Liguori G, Bourrier A and
Nion-Larmurier I: Fungal microbiota dysbiosis in IBD. Gut.
66:1039–1048. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Frykman PK, Nordenskjöld A, Kawaguchi A,
Hui TT, Granström AL, Cheng Z, Tang J, Underhill DM, Iliev I,
Funari VA, et al: Characterization of bacterial and fungal
microbiome in children with hirschsprung disease with and without a
history of enterocolitis: A multicenter study. PLoS One.
10(e0124172)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|