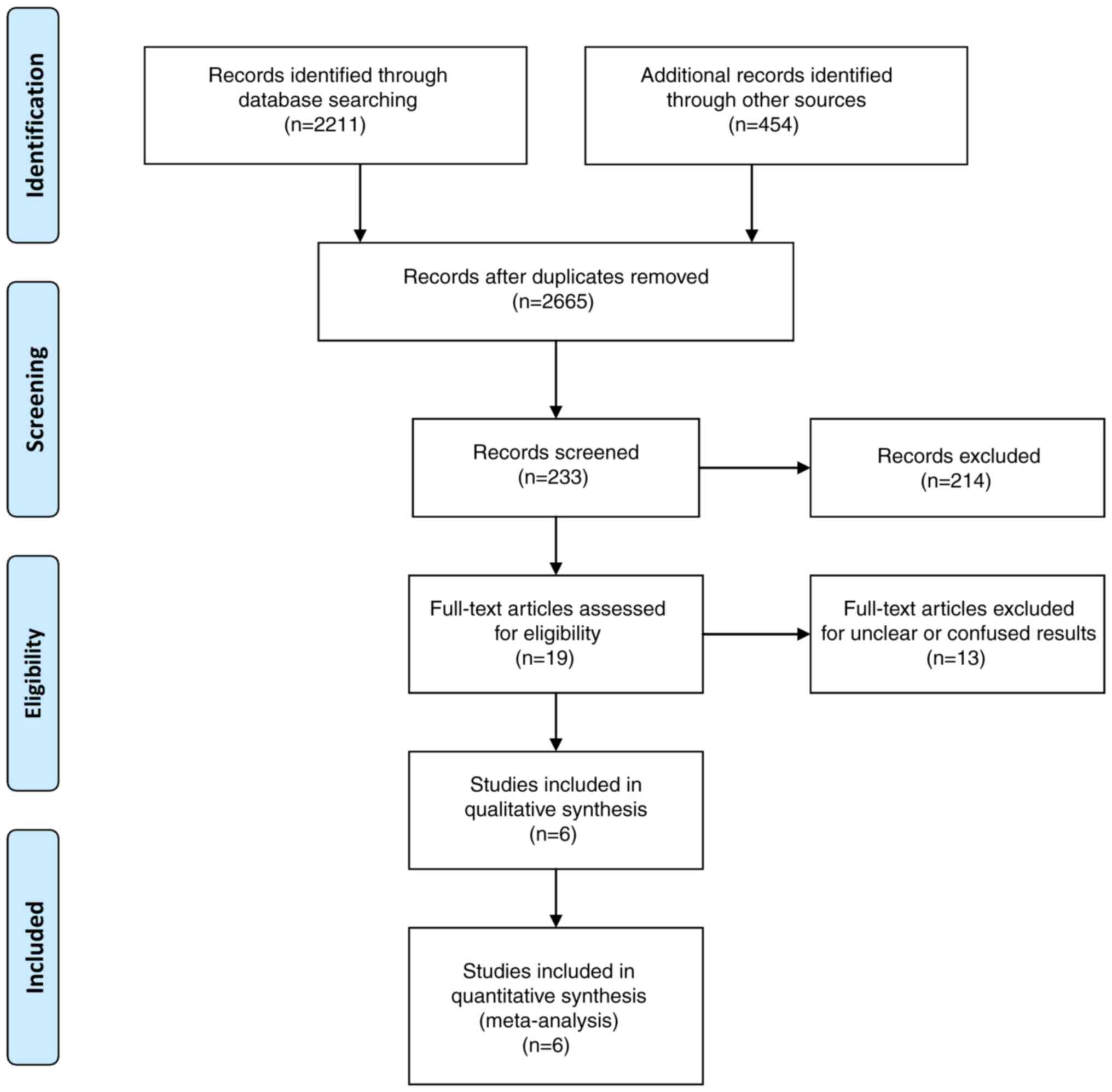
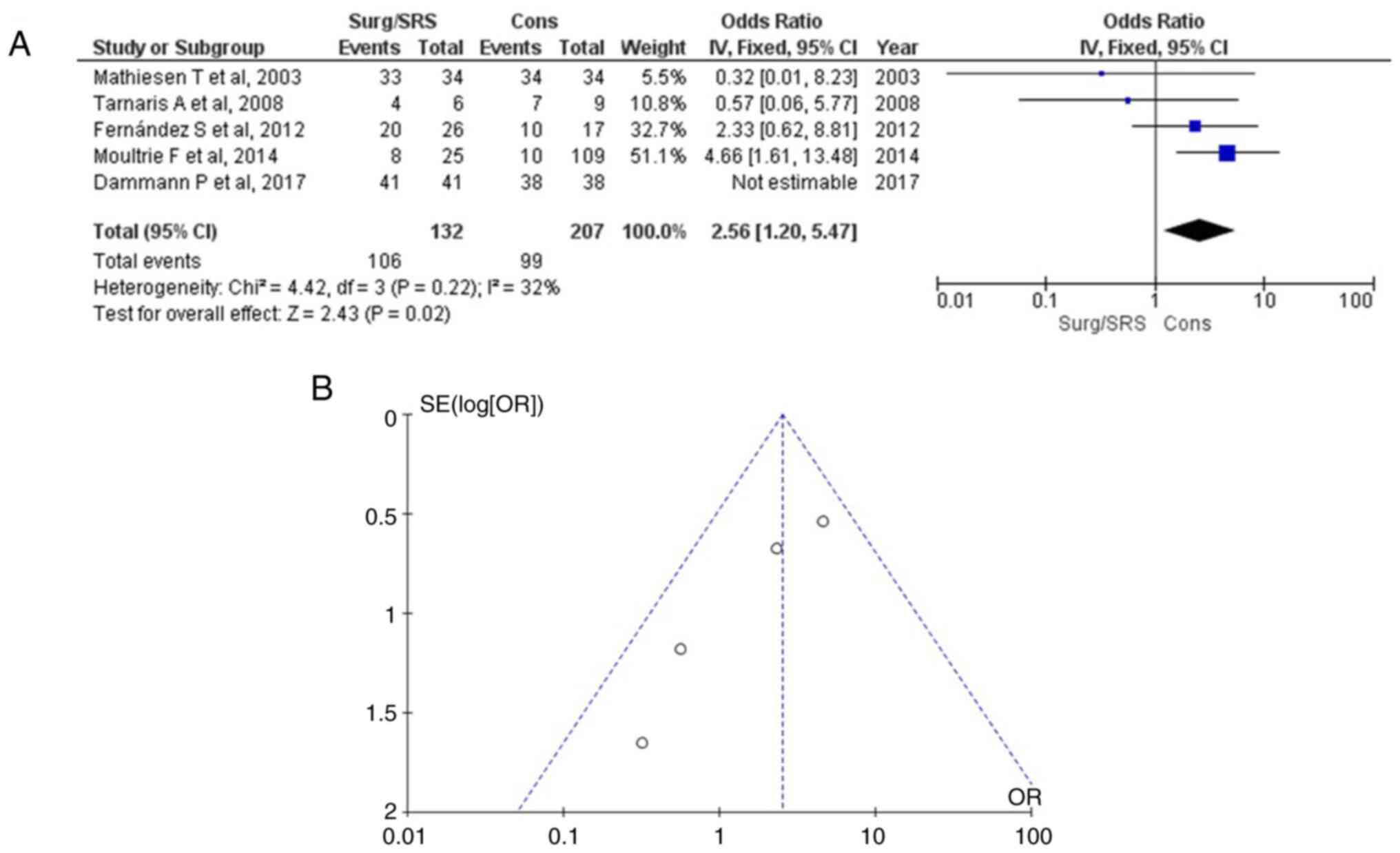
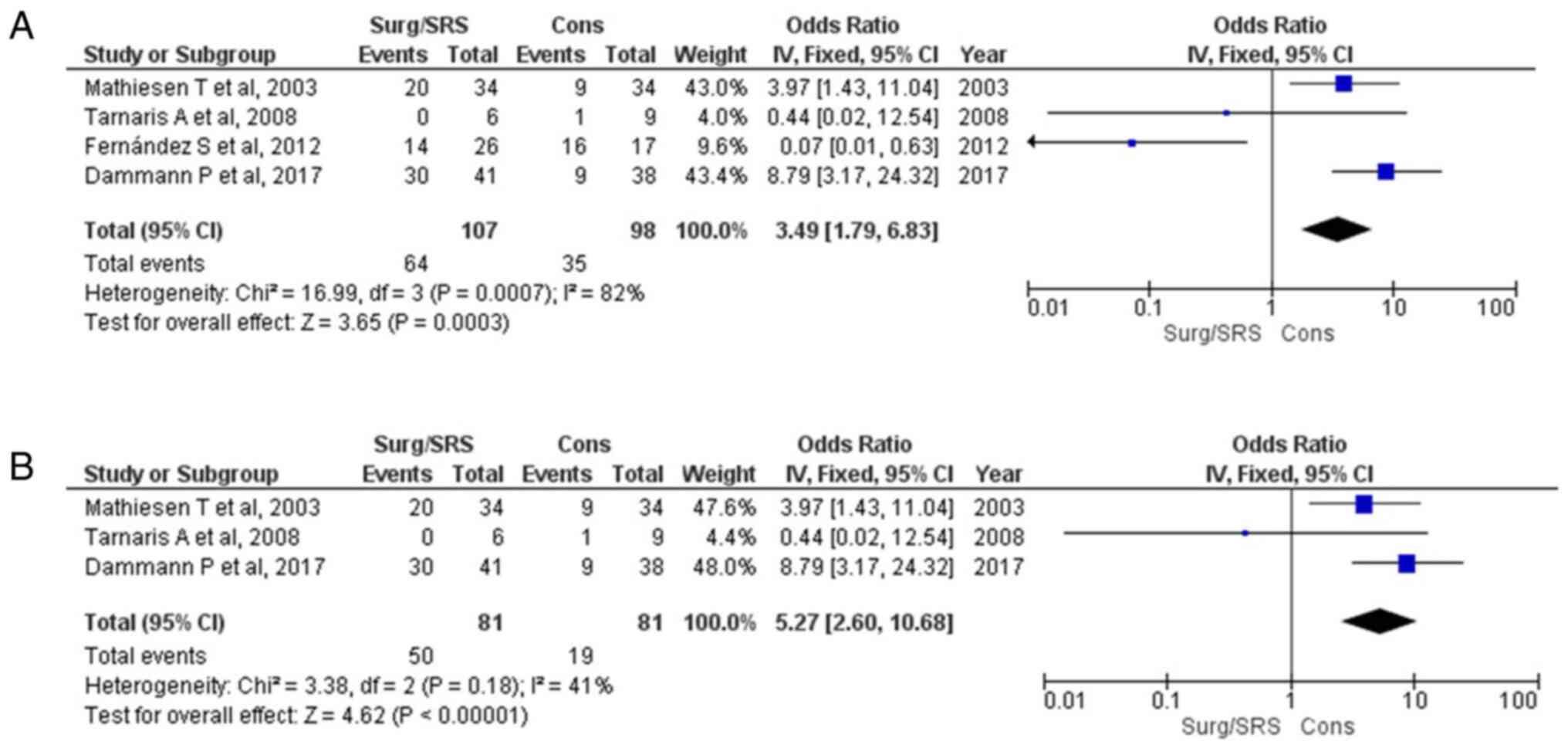
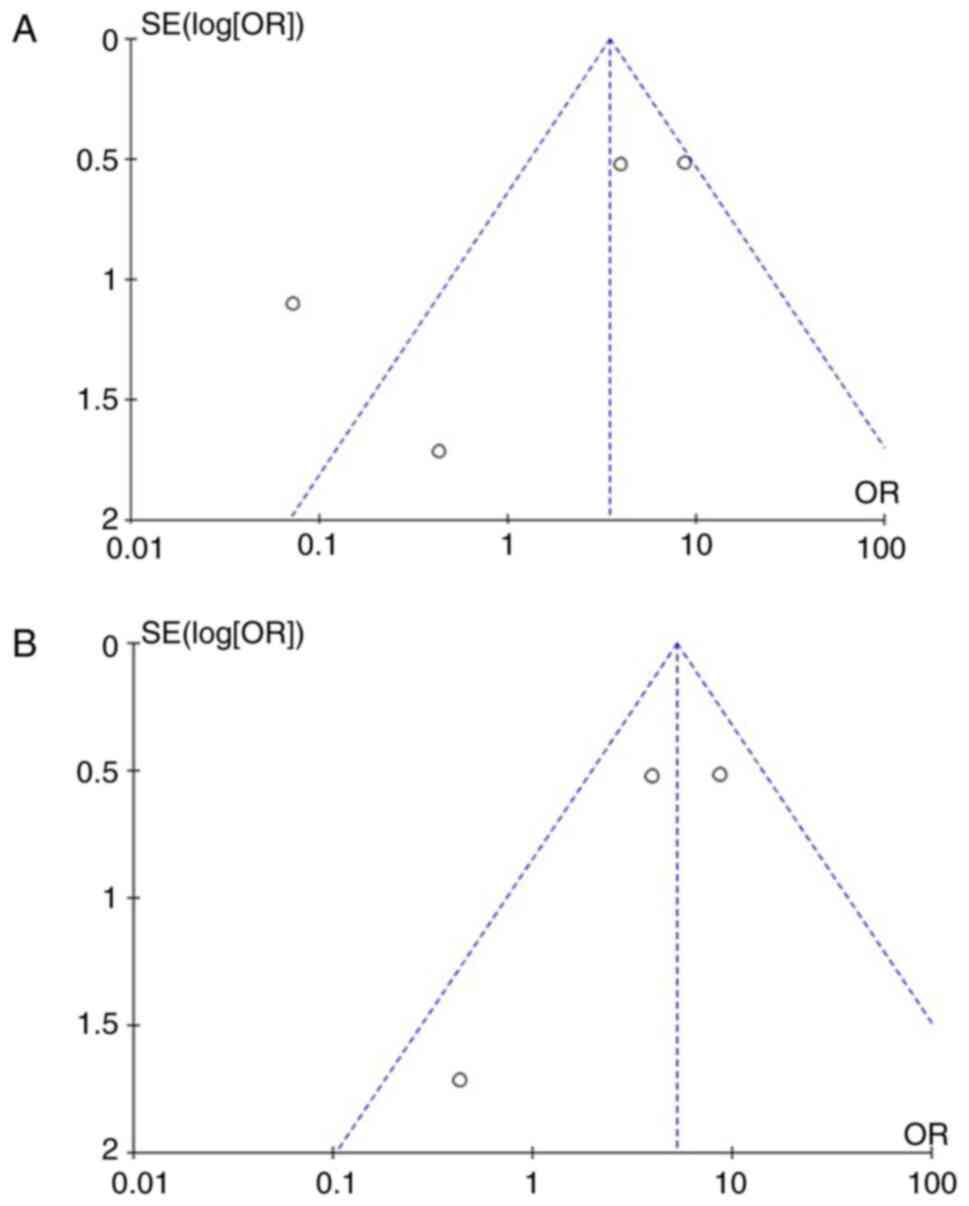
|
1
|
Fernández S, Miró J, Falip M, Coello A,
Plans G, Castañer S and Acebes JJ: Surgical versus conservative
treatment in patients with cerebral cavernomas and non refractory
epilepsy. Seizure. 21:785–788. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Steiner L, Karlsson B, Yen CP, Torner JC,
Lindquist C and Schlesinger D: Radiosurgery in cavernous
malformations: Anatomy of a controversy. J Neurosurg. 113:16–22.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Fotakopoulos G, Andrade-Barazarte H,
Kivelev J, Tjahjadi M, Goehre F and Hernesniemi J: Brainstem
cavernous malformations management: Microsurgery vs radiosurgery, a
meta-analysis. Front Surg. 8(630134)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Fotakopoulos G, Kivelev J,
Andrade-Barazarte H, Tjahjadi M, Goehre F and Hernesniemi J:
Outcome in patients with spinal cavernomas presenting with symptoms
due to mass effect and/or hemorrhage: Conservative versus surgical
management: Meta-analysis of direct comparison of approach-related
complications. World Neurosurg. 152:6–18. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Fotakopoulos G, Brotis AG and Fountas KN:
Dilemmas in managing coexisting arteriovenous and cavernous
malformations: Case report. Brain Circ. 8:45–49. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Robinson JR, Awad IA and Little JR:
Natural history of the cavernous angioma. J Neurosurg. 75:709–714.
1991.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Sandalcioglu IE, Wiedemayer H, Secer S,
Asgari S and Stolke D: Surgical removal of brain stem cavernous
malformations: Surgical indications, technical considerations, and
results. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 72:351–355. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Gross BA, Batjer HH, Awad IA and Bendok
BR: Brainstem cavernous malformations. Neurosurgery. 64:E805–E818.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Lippitz B: Treatment of cavernoma: An
evidence-based dilemma? Acta Neurochir Suppl. 116:99–101.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Rinkel LA, Al-Shahi Salman R, Rinkel GJ
and Greving JP: Radiosurgical, neurosurgical, or no intervention
for cerebral cavernous malformations: A decision analysis. Int J
Stroke. 14:939–945. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Wells GA, Shea B, O'Connell D, Peterson J,
Welch V, Losos mM and Tugwell P: The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS)
for assessing the quality of nonrandomised studies in
meta-analyses. Ottawa Hospital Research Institute, 2014. http://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp.
|
|
12
|
Bamford JM, Sandercock PA, Warlow CP and
Slattery J: Interobserver agreement for the assessment of handicap
in stroke patients. Stroke. 20(828)1989.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Higgins JPT, Altman DG, Gøtzsche PC, Jüni
P, Moher D, Oxman AD, Savovic J, Schulz KF, Weeks L, Sterne JA, et
al: The cochrane collaboration's tool for assessing risk of bias in
randomised trials. BMJ. 343(d5928)2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Higgins JPT and Green S (eds): Cochrane
handbook for systematic reviews of interventions version 5.1.0. The
Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. www.cochrane-handbook.org. Updated March 2011.
|
|
15
|
Mathiesen T, Edner G and Kihlström L: Deep
and brainstem cavernomas: A consecutive 8-year series. J Neurosurg.
99:31–37. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Tarnaris A, Fernandes RP and Kitchen ND:
Does conservative management for brain stem cavernomas have better
long-term outcome? Br J Neurosurg. 22:748–757. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Moultrie F, Horne MA, Josephson CB, Hall
JM, Counsell CE, Bhattacharya JJ, Papanastassiou V, Sellar RJ,
Warlow CP, Murray GD and Al-Shahi Salman R: Scottish Audit of
Intracranial Vascular Malformations (SAIVMs) steering committee and
collaborators. Outcome after surgical or conservative management of
cerebral cavernous malformations. Neurology. 83:582–589.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Dammann P, Wrede K, Jabbarli R, Neuschulte
S, Menzler K, Zhu Y, Özkan N, Müller O, Forsting M, Rosenow F and
Sure U: Outcome after conservative management or surgical treatment
for new-onset epilepsy in cerebral cavernous malformation. J
Neurosurg. 126:1303–1311. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Kang K, Ju Y, Wang D, Li H, Sun L, Ma K,
Zhao X and Lu J: Cerebral venous malformations in a chinese
population: Clinical manifestations, radiological characteristics,
and long-term prognosis. World Neurosurg. 120:e472–e479.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Liscák R, Vladyka V, Simonová G, Vymazal J
and Novotny J Jr: Gamma knife surgery of brain cavernous
hemangiomas. J Neurosurg. 102 (Suppl):S207–S213. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Kondziolka D, Lunsford LD, Flickinger JC
and Kestle JR: Reduction of hemorrhage risk after stereotactic
radiosurgery for cavernous malformations. J Neurosurg. 83:825–831.
1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Karlsson B, Kihlström L, Lindquist C,
Ericson K and Steiner L: Radiosurgery for cavernous malformations.
J Neurosurg. 88:293–297. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Steinberg GK, Chang SD, Gewirtz RJ and
Lopez JR: Microsurgical resection of brainstem, thalamic, and basal
ganglia angiographically occult vascular malformations.
Neurosurgery. 46:260–271. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Al-Shahi Salman R, Berg MJ, Morrison L and
Awad IA: Angioma Alliance Scientific Advisory Board. Hemorrhage
from cavernous malformations of the brain: Definition and reporting
standards. Angioma alliance scientific advisory board. Stroke.
39:3222–3230. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|