Introduction
General anesthesia may lead to the development of
cognitive dysfunction (1,2); furthermore, due to the declined body
functions with age, it is difficult for geriatric patients (aged
≥60 years) to metabolize anesthetics (3,4).
Subsequently, in geriatric patients, these anesthetics remain in
the body and sustainably affect the central nervous system,
contributing to a high risk of developing post-operative cognitive
dysfunction, which is a major cause of the reduced quality of life
of these patients (2,5-7).
Therefore, exploring potential anesthesia regimens that may reduce
the risk of post-operative cognitive dysfunction is fundamental for
geriatric patients.
Propofol total intravenous anesthesia (TIVA) and
sevoflurane inhalation anesthesia (IA) are two anesthetic regimes
used for laparoscopic surgery (8-10).
Previous studies have compared the effects of propofol TIVA and
sevoflurane IA on post-operative cognitive dysfunction in geriatric
patients undergoing laparoscopic surgery (5,6). For
instance, a previous study reported that the incidence of
post-operative cognitive dysfunction was 16.8% in geriatric
patients undergoing laparoscopic abdominal surgery receiving
propofol TIVA, while it was 20.8% in those receiving sevoflurane IA
(5). Another study reported that
propofol TIVA led to a reduced incidence of post-operative
cognitive dysfunction compared with sevoflurane IA in geriatric
patients undergoing cholecystectomy (6). It should be clarified that the
existing relevant studies are randomized controlled trials, and
there is a lack of real-world clinical studies on the matter
(5,6). On the other hand, although there are
numerous studies comparing the effects of propofol TIVA and
sevoflurane IA on reducing cognitive dysfunction in geriatric
patients (5,6,11,12),
the optimal anesthetic is still disputable. Therefore, this aspect
should be further explored.
Inflammation plays a fundamental role in the
pathology and progression of cognitive dysfunction (13). In detail, the increased secretion
of proinflammatory cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor
(TNF)-alpha, interleukin (IL)-6 and IL-1β, leads to the disruption
of the blood-brain barrier permeability allowing the cytokines to
enter the central nervous system, which further facilitates the
activation of microglia. Subsequently, the activated microglia
amplify neuroinflammation and release reactive oxygen species,
which ultimately aggravates cognitive dysfunction (13). Considering the role of inflammation
in cognitive dysfunction (13,14),
the association between inflammation and cognitive dysfunction
should be explored in geriatric patients at different time points
after laparoscopic surgery.
Accordingly, the present prospective study aimed to
compare the effects of propofol TIVA and sevoflurane IA on
post-operative cognitive dysfunction and the expression of
inflammatory cytokines, as well as the intercorrelation between
inflammatory cytokines and cognitive dysfunction before and after
surgery in geriatric patients undergoing laparoscopic surgery.
Patients and methods
Patients
The present study was a prospective cohort study.
Geriatric patients undergoing laparoscopic surgery who received
propofol TIVA (97 cases) and or sevoflurane IA (100 cases) were
enrolled from Daqing Oil Field General Hospital (Daqing, China),
between April 2019 and March 2023. In the IA group 15 (15.0%), 81
(81.0%) and 4 (4.0%) patients had a surgical location of the upper,
middle and lower abdomen. In the TIVA group, 11 (11.3%), 80 (82.5%)
and 6 (6.2%) patients had a surgery location of upper, middle, and
lower abdomen. The inclusion criteria were as follows: i) Patients
who would need to undergo laparoscopic surgery; ii) the duration of
the surgery was expected to be >2 h; iii) patients were ≥60
years old; iv) the American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA)
classification of the patients was I-II (15); v) patients were to receive propofol
TIVA or sevoflurane IA as anesthesia methods; and vi) patients were
willing to participate in the present study. The exclusion criteria
were the following: i) Patients who had severe heart, liver or
kidney failure; ii) those who had active infections; iii) those
with allergies to the drugs used in the study; iv) those with
mental illness, cognitive impairment, Parkinson's disease or
Alzheimer's disease before surgery; and v) those with a history of
sedative addiction. The Ethics Committee of Daqing Oil Field
General Hospital approved the present study (approval no.
20190125). All patients provided written informed consent.
Anesthesia methods
The present study was a real-world clinical study
and no randomization was performed. According to the aforementioned
inclusion criterium v, the present study only enrolled patients who
were to receive propofol TIVA or sevoflurane IA as anesthesia
methods. However, the present study did not intervene in the choice
of anesthesia methods of the patients. The anesthesia methods were
decided by recommendations of the doctors and the willingness of
the patients. Therefore, patients were assigned to corresponding
groups according to actual anesthesia methods. All patients
received anesthesia induction using fentanyl (intravenously, 3-4
µg/kg), lidocaine (intravenously, 1.5 mg/kg), propofol
(intravenously, 1-1.5 mg/kg) and cisatracurium (intravenously,
0.1-0.15 mg/kg). For anesthesia maintenance, patients who received
propofol TIVA (50-150 µg/kg/min) and intravenous injection of
remifentanil (0.1-0.5 µg/kg/min) were assigned to the TIVA group;
patients who received sevoflurane IA (1.0-1.5 minimum alveolar
concentration) and intravenous injection of remifentanil (0.1-0.5
µg/kg/min) were assigned to the IA group. The intravenous injection
of remifentanil was performed using a micro-pump.
Data collection
The clinical characteristics of the patients were
documented; these included age, sex, body mass index (BMI), smoking
status, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, ASA classification,
location of surgery, duration of surgery and duration of
anesthesia. Moreover, serum samples were obtained from the patients
24 h prior to surgery, as well as on day (D)1, D3 and D7 following
surgery. Subsequently, the levels of IL-17A, IL-6 and TNF-α were
detected using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay with Human
Quantikine ELISA kits (cat. nos. D1700, D6050B and DTA00D; R&D
Systems, Inc.). The assays were performed according to the
instructions provided by the manufacturer.
Assessment
The mini-mental state examination (MMSE) was used to
assess the cognitive function of patients prior to surgery and on
D1, D3 and D7, as previously described (16). The MMSE was scored as 0-30, with a
lower score indicating improved cognitive function.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analyses were performed using SPSS v22.0
software (IBM Corp.). Normal distributed continuous variables are
presented as the mean value ± standard deviation, and categorized
variables are presented as n (%). The experiment was replicated
three times. Comparisons were made using unpaired Student's t-test,
χ2 test and Fisher's exact test. Correlations were
performed using Spearman's rank correlation analysis. Factors
related to the MMSE score were analyzed using multivariate linear
regression analysis with the enter mode. P<0.05 was considered
to indicate a statistically significant difference.
Results
Clinical information of the TIVA and
IA groups
There were 97 patients in the TIVA group and 100
patients in the IA group. The mean age of the patients in the TIVA
and IA groups was 68.5±5.3 and 67.2±4.7 years, respectively
(P=0.072). There were 29 (29.9%) female and 68 (70.1%) male
patients in the TIVA group and 37 (37.0%) female and 63 (63.0%)
male patients in the IA group (P=0.291). All clinical features,
including BMI (P=0.531), smoking status (P=0.289), hypertension
(P=0.364), diabetes mellitus (P=0.166), ASA classification
(P=0.587), surgery location (P=0.625), operation time (P=0.163) and
anesthesia time (P=0.149), were not different between the two
groups. The specific clinical data of the two groups are presented
in Table I.
 | Table IClinical characteristics of the
patients. |
Table I
Clinical characteristics of the
patients.
| Characteristic | IA group (n=100) | TIVA group
(n=97) | P-value |
|---|
| Age, years (mean ±
SD) | 67.2±4.7 | 68.5±5.3 | 0.072 |
| Sex, n (%) | | | 0.291 |
|
Female | 37 (37.0) | 29 (29.9) | |
|
Male | 63 (63.0) | 68 (70.1) | |
| BMI, kg/m2
(mean ± SD) | 22.1±2.6 | 22.3±2.5 | 0.531 |
| Smoker, n (%) | | | 0.289 |
|
No | 71 (71.0) | 62 (63.9) | |
|
Yes | 29 (29.0) | 35 (36.1) | |
| Hypertension, n
(%) | | | 0.364 |
|
No | 70 (70.0) | 62 (63.9) | |
|
Yes | 30 (30.0) | 35 (36.1) | |
| Diabetes mellitus,
n (%) | | | 0.166 |
|
No | 91 (91.0) | 82 (84.5) | |
|
Yes | 9 (9.0) | 15 (15.5) | |
| ASA classification,
n (%) | | | 0.587 |
|
I | 26 (26.0) | 22 (22.7) | |
|
II | 74 (74.0) | 75 (77.3) | |
| Surgery location, n
(%) | | | 0.625 |
|
Upper
abdomen/stomach | 15 (15.0) | 11 (11.3) | |
|
Middle
abdomen/colon | 81 (81.0) | 80 (82.5) | |
|
Lower
abdomen/uterus | 4 (4.0) | 6 (6.2) | |
| Operation time, min
(mean ± SD) | 177.4±26.4 | 183.2±31.5 | 0.163 |
| Anesthesia time,
min (mean ± SD) | 199.9±26.9 | 206.0±31.9 | 0.149 |
Comparison of MMSE score and its
change between the TIVA and IA groups
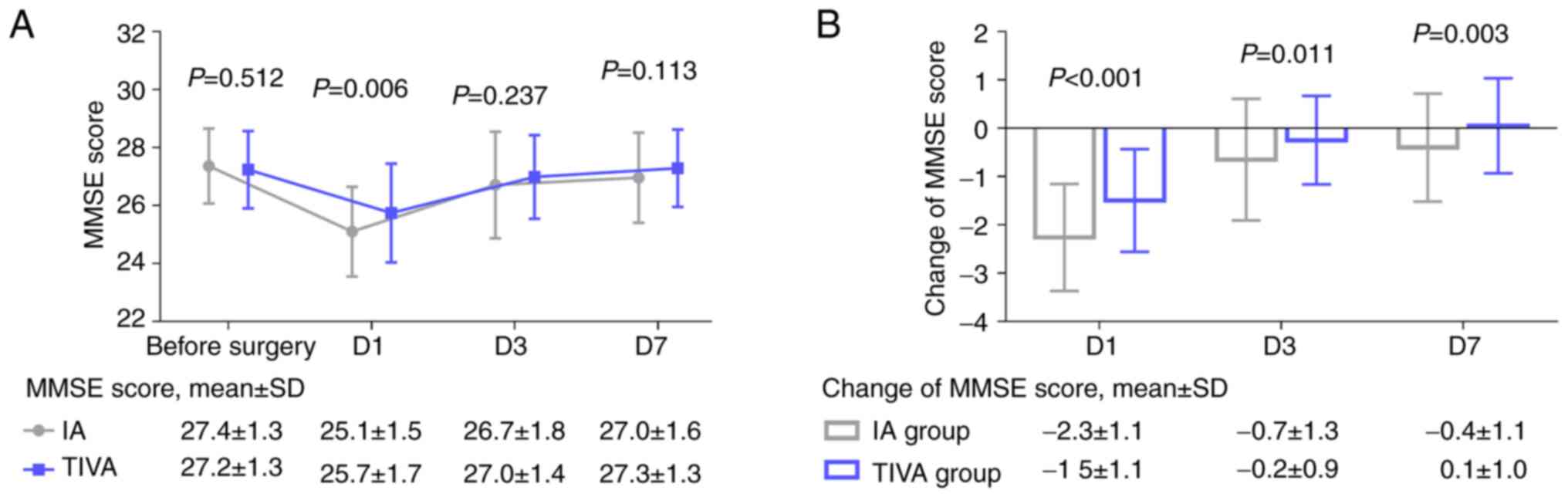
The MMSE score before surgery did not differ
significantly between the two groups (P=0.512). Of note, the MMSE
score on D1 was higher in the TIVA group compared with the IA group
(P=0.006). However, the MMSE score on D3 (P=0.237) and D7 (P=0.113)
did not differ significantly between the two groups (Fig. 1A). The change in the MMSE score
from before surgery to D1 (P<0.001), D3 (P=0.011) and D7
(P=0.003) was less prominent in the TIVA group compared with the IA
group (Fig. 1B).
Independent factors are associated
with the MMSE score on D1, D3 and D7
The anesthesia method of TIVA (vs. IA) was
independently related to a higher MMSE score on D1 (b=0.803;
P=0.001). By contrast, diabetes mellitus (vs. non-diabetes
mellitus) (b=-0.965; P=0.009) was independently associated with a
lower MMSE score on D1 in geriatric patients undergoing
laparoscopic surgery (Table
II).
 | Table IIMultivariate linear regression
analyses. |
Table II
Multivariate linear regression
analyses.
| A, Model for MMSE
score on D1 |
|---|
| Item | Unadjusted b | SE | Adjusted b | t-value | P-value | VIF |
|---|
| Anesthesia method
of TIVA (vs. IA) | 0.803 | 0.233 | 0.243 | 3.443 | 0.001 | 1.048 |
| Age, year | -0.030 | 0.027 | -0.093 | -1.141 | 0.255 | 1.396 |
| Male (vs.
female) | -0.444 | 0.270 | -0.127 | -1.646 | 0.101 | 1.248 |
| BMI,
kg/m2 | -0.055 | 0.057 | -0.086 | -0.969 | 0.334 | 1.640 |
| Smoker (vs.
non-smoker) | 0.069 | 0.258 | 0.019 | 0.266 | 0.791 | 1.122 |
| Hypertension (vs.
non-hypertension) | 0.038 | 0.275 | 0.011 | 0.139 | 0.890 | 1.287 |
| Diabetes mellitus
(vs. non-diabetes mellitus) | -0.965 | 0.365 | -0.191 | -2.641 | 0.009 | 1.100 |
| ASA classification
II (vs. I) | -0.350 | 0.338 | -0.091 | -1.036 | 0.302 | 1.622 |
| Surgery location of
middle or lower abdomen (vs. upper abdomen) | -0.209 | 0.342 | -0.043 | -0.609 | 0.543 | 1.034 |
| Operation time,
min | -0.001 | 0.004 | -0.009 | -0.125 | 0.901 | 1.072 |
| B, Model for MMSE
score on D3 |
| Item | Unadjusted b | SE | Adjusted b | t-value | P-value | VIF |
| Anesthesia method
of TIVA (vs. IA) | 0.434 | 0.239 | 0.131 | 1.814 | 0.071 | 1.048 |
| Age, years | -0.031 | 0.027 | -0.095 | -1.132 | 0.259 | 1.396 |
| Male (vs.
female) | -0.316 | 0.276 | -0.090 | -1.142 | 0.255 | 1.248 |
| BMI,
kg/m2 | -0.068 | 0.058 | -0.105 | -1.159 | 0.248 | 1.640 |
| Smoker (vs.
non-smoker) | 0.056 | 0.264 | 0.016 | 0.211 | 0.833 | 1.122 |
| Hypertension (vs.
non-hypertension) | -0.059 | 0.282 | -0.017 | -0.209 | 0.835 | 1.287 |
| Diabetes mellitus
(vs. non-diabetes mellitus) | -0.770 | 0.374 | -0.153 | -2.057 | 0.041 | 1.100 |
| ASA classification
II (vs. I) | -0.314 | 0.346 | -0.082 | -0.907 | 0.366 | 1.622 |
| Surgery location of
middle or lower abdomen (vs. upper abdomen) | -0.309 | 0.351 | -0.063 | -0.881 | 0.379 | 1.034 |
| Operation time,
min | -0.001 | 0.004 | -0.014 | -0.194 | 0.847 | 1.072 |
| C, Model for MMSE
score on D7 |
| Item | Unadjusted b | SE | Adjusted b | t-value | P-value | VIF |
| Anesthesia method
of TIVA (vs. IA) | 0.472 | 0.209 | 0.163 | 2.262 | 0.025 | 1.048 |
| Age, years | -0.017 | 0.024 | -0.060 | -0.729 | 0.467 | 1.396 |
| Male (vs.
female) | -0.323 | 0.241 | -0.105 | -1.340 | 0.182 | 1.248 |
| BMI,
kg/m2 | -0.028 | 0.051 | -0.050 | -0.551 | 0.582 | 1.640 |
| Smoker (vs.
non-smoker) | 0.031 | 0.230 | 0.010 | 0.133 | 0.894 | 1.122 |
| Hypertension (vs.
non-hypertension) | -0.098 | 0.246 | -0.032 | -0.400 | 0.690 | 1.287 |
| Diabetes mellitus
(vs. non-diabetes mellitus) | -0.842 | 0.327 | -0.190 | -2.578 | 0.011 | 1.100 |
| ASA classification
II (vs. I) | -0.262 | 0.302 | -0.078 | -0.868 | 0.387 | 1.622 |
| Surgery location of
middle or lower abdomen (vs. upper abdomen) | -0.348 | 0.306 | -0.081 | -1.135 | 0.258 | 1.034 |
| Operation time,
min | -0.002 | 0.004 | -0.040 | -0.553 | 0.581 | 1.072 |
The anesthesia method of TIVA (vs. IA) exhibited a
trend for an association with a higher MMSE score on D3, which did
not achieve statistical significance (b=0.434; P=0.071). By
contrast, diabetes mellitus (vs. non-diabetes mellitus) (b=-0.770;
P=0.041) was independently associated with a lower MMSE score on D3
in geriatric patients undergoing laparoscopic surgery (Table II).
The anesthesia method of TIVA (vs. IA) (b=0.472;
P=0.025) was independently associated with a higher MMSE score on
D7. By contrast, diabetes mellitus (vs. non-diabetes mellitus)
(b=-0.842; P=0.011) was independently associated with a lower MMSE
score on D7 in geriatric patients undergoing laparoscopic surgery
(Table II).
However, age (years), male (vs. female), BMI
(kg/m2), smoker (vs. non-smoker), hypertension (vs.
non-hypertension), ASA classification of II (vs. I), surgical
location of the middle or lower abdomen (vs. upper abdomen) and
operation time (min) was not associated with MMSE score on D1, D3
and D7 in geriatric patients undergoing laparoscopic surgery (all
P>0.05) (Table II).
Comparison of IL-17A, IL-6 and TNF-α
levels between the TIVA and IA groups
The IL-17A levels on D1 (P=0.160), D3 (P=0.416) and
D7 (P=0.421) exhibited a slightly decreasing trend in the TIVA
group compared with the IA group, but did not achieve statistical
significance (Fig. 2A). Similarly,
the IL-6 levels on D1 (P=0.428), D3 (P=0.127) and D7 (P=0.558)
(Fig. 2B), as well as the TNF-α
levels on D1 (P=0.205), D3 (P=0.355) and D7 (P=0.491) (Fig. 2C), exhibited a reducing trend to a
certain extent in the TIVA group compared with the IA group, but
did not achieve statistical significance.
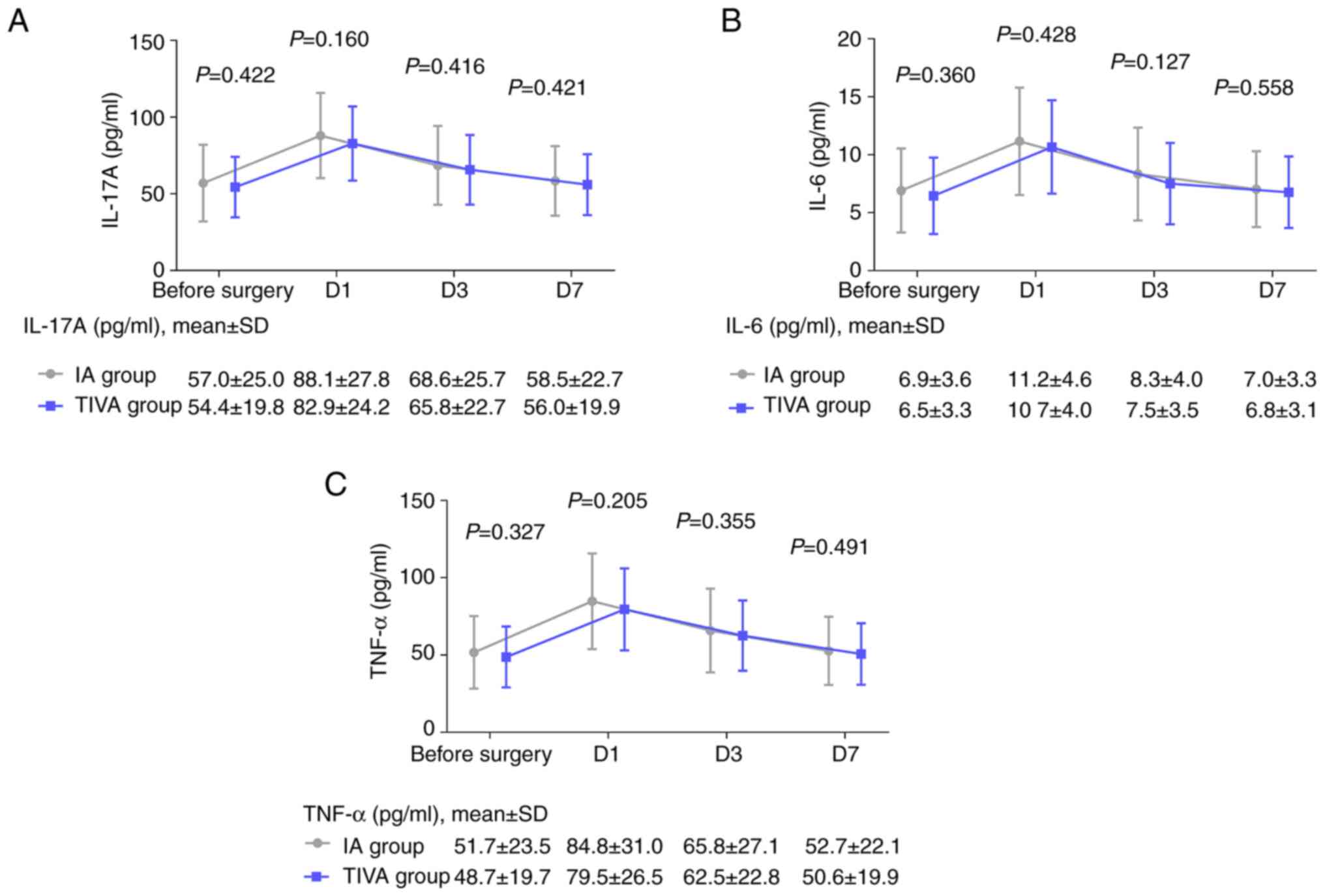 | Figure 2IL-17A, IL-6 and TNF-α levels prior to
surgery and on D1, D3 and D7 in the TIVA and IA groups. Comparison
of (A) IL-17A, (B) IL-6 and (C) TNF-α levels prior to surgery and
on D1, D3 and D7 in the TIVA and IA groups. IL, interleukin; TNF,
tumor necrosis factor; D1, D3 and D7, day 1, 3 and 7 following
surgery; TIVA, total intravenous anesthesia; IA, inhalation
anesthesia. |
Correlation between IL-17A, IL-6 or
TNF-α and the MMSE score before surgery, on D1, D3 and D7 in all
geriatric patients
The IL-17A levels prior to surgery (P=0.015), on D3
(P=0.016) and on D7 (P=0.002) were negatively correlated with the
MMSE score at the corresponding time points (Fig. S1A). IL-6 levels on D1 (P=0.027)
were inversely correlated with the MMSE score on D1 (Fig. S1B). However, TNF-α levels prior to
surgery and on D1, D3 or D7 were not correlated with the MMSE score
in geriatric patients undergoing laparoscopic surgery (all
P>0.05) (Fig. S1C).
Discussion
Anesthesia affects the central nervous system
inducing post-operative cognitive dysfunction, and previous studies
have compared the effects of propofol TIVA and sevoflurane IA on
cognitive dysfunction in geriatric patients undergoing laparoscopic
surgery (5,6). According to previous studies,
propofol TIVA exhibits a smaller rate of cognitive dysfunction
induction compared with sevoflurane IA in geriatric patients
(6,11,17).
Of these three studies, two have focused on geriatric patients
undergoing different types of surgeries, such as major cancer
surgery and general thoracic surgery (11,17).
Therefore, more evidence regarding geriatric patients undergoing
laparoscopic surgery is required. Additionally, although the
surgery type was laparoscopic cholecystectomy in one study, this
was a randomized controlled trial (6). Thus, there is a lack of real-world
clinical evidence on the effect of propofol TIVA and sevoflurane IA
on post-operative cognitive dysfunction.
Therefore, the present study collected real-world
evidence data to explore the effect of propofol TIVA and
sevoflurane IA on post-operative cognitive dysfunction in geriatric
patients undergoing laparoscopic surgery. In line with the
aforementioned previous studies (6,11,17),
the present study revealed that the MMSE score was higher, and the
change in the MMSE score from before surgery to D1, D3 and D7 was
less prominent in the geriatric patients undergoing laparoscopic
surgery who received propofol TIVA compared with those who received
sevoflurane IA; these findings suggested that the effects of
propofol TIVA on post-operative cognitive function were less
prominent compared with those of sevoflurane IA in geriatric
patients undergoing laparoscopic surgery.
The potential reasons for this may be the following:
i) Sevoflurane acts on the cerebral cortex via pulmonary
inhalation, which induces neurotoxicity, enhances β-amyloid
accumulation and damages neuronal cells, thereby leading to
cognitive dysfunction, while propofol may exert a less prominent
effect (18,19); ii) pain plays a fundamental role in
post-operative cognitive dysfunction (20,21),
and the use of propofol may lead to less post-operative pain
compared with sevoflurane (11,22);
and iii) laparoscopic surgery can induce neuroinflammation, and
sevoflurane can further facilitate the production of
pro-inflammatory cytokines, leading to a high risk of
post-operative cognitive dysfunction, while propofol may only have
a limited effect (18,23,24).
Taken together, the risk of post-operative cognitive dysfunction
was reduced in geriatric patients undergoing laparoscopic surgery
who received propofol TIVA compared with those who received
sevoflurane IA.
The present study further conducted multivariate
linear regression analyses to explore the independent factors that
can affect post-operative cognitive dysfunction in geriatric
patients undergoing laparoscopic surgery. Of note, it was revealed
that propofol TIVA (vs. sevoflurane IA) was independently
associated with a higher MMSE score in geriatric patients
undergoing laparoscopic surgery; this finding is in accordance with
that of a previous study (6). It
was also demonstrated that diabetes mellitus (vs. non-diabetes
mellitus) was independently associated with a lower MMSE score in
geriatric patients undergoing laparoscopic surgery. A potential
explanations for this may involve the following: i) Insulin
resistance can facilitate inflammation and β-amyloid deposition,
but decreases synaptic plasticity, leading to post-operative
cognitive dysfunction (25); and
ii) diabetes mellitus induces an increase in the levels of
glycation end products and their precursor, methylglyoxal, which
further impairs the dopaminergic system, thereby contributing to
post-operative cognitive dysfunction (26).
Inflammation is involved in the occurrence and
progression of post-operative cognitive dysfunction (2). According to a previous study,
propofol exhibits a limited effect in lowering the levels of IL-1β,
IL-6 and TNF-α compared with sevoflurane, but without statistical
significance (6). In accordance
with this previous study, the present study revealed that the
levels of IL-17A, IL-6 and TNF-α on D1, D3 and D7 were lower in the
geriatric patients undergoing laparoscopic surgery who received
propofol TIVA compared with those who received sevoflurane IA;
however, the difference between the two groups of patients was not
statistically significant. A potential reason for this may be that,
as aforementioned, sevoflurane may facilitate the production of
pro-inflammatory cytokines following laparoscopic surgery, while
propofol may have a less prominent effect (18).
In addition, the present study also observed that
IL-6 was negatively associated with the MMSE score on D1 in
geriatric patients undergoing laparoscopic surgery. This finding is
partly in line with that of a previous study (5). In addition, the present study
revealed that the level of IL-17A was negatively associated with
the MMSE score before surgery, on D3 and on D7 in geriatric
patients undergoing laparoscopic surgery. It was hypothesized that
the reasons for this may be the following: i) IL-17A may exacerbate
neuroinflammation and oxidative stress by activating the nuclear
factor-κB pathway, leading to cognitive dysfunction (27); and ii) IL-17A may induce β-amyloid
accumulation by activating the transforming growth factor-β/Smad
pathway, which further promotes cognitive dysfunction (28).
Of note, a number of previous studies have compared
the effects of propofol TIVA and sevoflurane IA on cognitive
dysfunction in geriatric patients (5,6,11,12,29).
However, the optimal anesthetic is still disputable. For instance,
certain studies have indicated that post-operative cognitive
dysfunction is reduced by propofol TIVA compared with sevoflurane
IA (6,11), while another study revealed the
opposite outcome (29). Moreover,
certain studies hypothesized that post-operative cognitive
dysfunction is not influenced by either propofol TIVA or
sevoflurane IA (5,12). In line with previous studies
(6,11), the present study revealed that
propofol TIVA reduced post-operative cognitive dysfunction compared
with sevoflurane IA in geriatric patients undergoing laparoscopic
surgery. The present findings provided additional evidence to
support the benefit of propofol TIVA in reducing post-operative
cognitive dysfunction compared with sevoflurane IA in geriatric
patients undergoing laparoscopic surgery.
There were some limitations to the present study,
which should be mentioned. Firstly, the present study was limited
by the sample size and study region; thus, the generalizability of
the results needs to be confirmed in subsequent studies. Secondly,
a single evaluation scale may not accurately reflect the situation
of post-operative cognitive dysfunction in geriatric patients
undergoing laparoscopic surgery, and further studies could consider
applying both MMSE and the Montreal Cognitive Assessment to assess
post-operative cognitive dysfunction. Thirdly, the surgical
locations were not unified, which may have influenced the results
of the present study. Fourthly, to reduce the effect of potential
confounding factors, further randomized-controlled trials are
required to validate the findings of the present study. Lastly, the
current study did not record the depth of anesthesia. However, the
depth of anesthesia could influence post-operative cognitive
dysfunction (30). Therefore,
further studies should explore the correlation between the depth of
anesthesia and cognitive dysfunction in geriatric patients
undergoing laparoscopic surgery.
In conclusion, the present study demonstrated that
propofol TIVA has potential value in attenuating post-operative
cognitive dysfunction on D1 compared with sevoflurane IA in
geriatric patients undergoing laparoscopic surgery. In addition,
propofol TIVA also exerted a potential suppressive effect on
inflammation in geriatric patients undergoing laparoscopic surgery.
Moreover, it was also observed that IL-6 was correlated with MMSE
score on D1, and IL-17A was correlated with MMSE score before
surgery, on D3 and on D7 in geriatric patients undergoing
laparoscopic surgery. The present study indicated the benefit of
propofol TIVA in reducing post-operative cognitive dysfunction in
geriatric patients undergoing laparoscopic surgery, and may provide
theoretical evidence for the clinical application of propofol TIVA
in this patient population. However, more large-scale studies or
meta-analyses are required to validate the findings of the present
study.
Supplementary Material
Correlation of MMSE score with the
levels of IL-17A, IL-6 and TNF-α prior to surgery and on D1, D3 and
D7 following surgery in all geriatric patients. Correlation of (A)
IL-17A, (B) IL-6, and (C) TNF-α with the MMSE score before surgery,
and on D1, D3 and D7 in all geriatric patients. IL, interleukin;
TNF, tumor necrosis factor; D1, D3 and D7, day 1, 3 and 7 following
surgery; MMSE, mini-mental state examination.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
Funding: No funding was received.
Availability of data and materials
The data generated in the present study may be
requested from the corresponding author.
Authors' contributions
JL substantially contributed to the conception and
the design of the study. JY acquired the data. ZG was responsible
for the analysis and interpretation of the data. WQ contributed to
methodology and statistical analysis. All authors were involved in
manuscript drafting or critical revisions of the intellectual
content. JL and JY confirm the authenticity of all the raw data.
All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
The Ethics Committee of Daqing Oil Field General
Hospital (Daqing, China) approved the present study (approval no.
20190125). All patients provided written informed consent.
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
References
|
1
|
Avidan MS, Whitlock EL and Mashour GA:
General anesthesia and postoperative neurocognitive outcomes. JAMA.
327:36–38. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Li Z, Zhu Y, Kang Y, Qin S and Chai J:
Neuroinflammation as the underlying mechanism of postoperative
cognitive dysfunction and therapeutic strategies. Front Cell
Neurosci. 16(843069)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Olotu C: Anesthesia for the elderly: A
narrative review. Minerva Anestesiol. 87:1128–1138. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Gomez-Rios MA and Abad-Gurumeta A:
Anesthesia in the elderly patient. Resilience in frailty time. Med
Clin (Barc). 159:486–488. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Li Y, Chen D, Wang H, Wang Z, Song F, Li
H, Ling L, Shen Z, Hu C, Peng J, et al: Intravenous versus volatile
anesthetic effects on postoperative cognition in elderly patients
undergoing laparoscopic abdominal surgery. Anesthesiology.
134:381–394. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Geng YJ, Wu QH and Zhang RQ: Effect of
propofol, sevoflurane, and isoflurane on postoperative cognitive
dysfunction following laparoscopic cholecystectomy in elderly
patients: A randomized controlled trial. J Clin Anesth. 38:165–171.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Fan Y, Liu X, Wu S and Liu Y: The risk
factors for cognitive dysfunction in elderly patients after
laparoscopic surgery: A retrospective analysis. Medicine
(Baltimore). 100(e23977)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Riedel B, Dubowitz J, Yeung J, Jhanji S,
Kheterpal S and Avidan MS: On the horns of a dilemma: Choosing
total intravenous anaesthesia or volatile anaesthesia. Br J
Anaesth. 129:284–289. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Spruce L: Back to basics: Inhaled
anesthesia. AORN J. 102:389–393. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Jones C and Harris J: Total intravenous
anaesthesia. Br J Hosp Med (Lond). 82:1–2. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Zhang Y, Shan GJ, Zhang YX, Cao SJ, Zhu
SN, Li HJ, Ma D and Wang DX: First Study of Perioperative Organ
Protection (SPOP1) investigators. Propofol compared with
sevoflurane general anaesthesia is associated with decreased
delayed neurocognitive recovery in older adults. Br J Anaesth.
121:595–604. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Konishi Y, Evered LA, Scott DA and Silbert
BS: Postoperative cognitive dysfunction after sevoflurane or
propofol general anaesthesia in combination with spinal anaesthesia
for hip arthroplasty. Anaesth Intensive Care. 46:596–600.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Rump K and Adamzik M: Epigenetic
mechanisms of postoperative cognitive impairment induced by
anesthesia and neuroinflammation. Cells. 11(2954)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Liu Y, Yang W, Xue J, Chen J, Liu S, Zhang
S, Zhang X, Gu X, Dong Y and Qiu P: Neuroinflammation: The central
enabler of postoperative cognitive dysfunction. Biomed
Pharmacother. 167(115582)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Saklad M: Grading of patients for surgical
procedures. Anesthesiology. 2:281–284. 1941.
|
|
16
|
Folstein MF, Folstein SE and McHugh PR:
‘Mini-mental state’. A practical method for grading the cognitive
state of patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res. 12:189–198.
1975.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Yu W: Anesthesia with propofol and
sevoflurane on postoperative cognitive function of elderly patients
undergoing general thoracic surgery. Pak J Pharm Sci. 30:1107–1110.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Vutskits L and Xie Z: Lasting impact of
general anaesthesia on the brain: Mechanisms and relevance. Nat Rev
Neurosci. 17:705–717. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Eckenhoff RG, Johansson JS, Wei H, Carnini
A, Kang B, Wei W, Pidikiti R, Keller JM and Eckenhoff MF: Inhaled
anesthetic enhancement of amyloid-beta oligomerization and
cytotoxicity. Anesthesiology. 101:703–709. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Wang Y, Sands LP, Vaurio L, Mullen EA and
Leung JM: The effects of postoperative pain and its management on
postoperative cognitive dysfunction. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry.
15:50–59. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Deng H, Wu Y, Gao P, Kong D, Pan C, Xu S,
Tang D, Jiao Y, Wen D and Yu W: Preoperative pain facilitates
postoperative cognitive dysfunction via periaqueductal gray
matter-dorsal raphe circuit. Neuroscience. 524:209–219.
2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Peng K, Liu HY, Wu SR, Liu H, Zhang ZC and
Ji FH: Does propofol anesthesia lead to less postoperative pain
compared with inhalational anesthesia?: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Anesth Analg. 123:846–858. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Tian Y, Guo S, Guo Y and Jian L:
Anesthetic propofol attenuates apoptosis, Aβ accumulation, and
inflammation induced by sevoflurane through NF-κB pathway in human
neuroglioma cells. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 35:891–898. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Ye X, Lian Q, Eckenhoff MF, Eckenhoff RG
and Pan JZ: Differential general anesthetic effects on microglial
cytokine expression. PLoS One. 8(e52887)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Kothari V, Luo Y, Tornabene T, O'Neill AM,
Greene MW, Geetha T and Babu JR: High fat diet induces brain
insulin resistance and cognitive impairment in mice. Biochim
Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 1863:499–508. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Pignalosa FC, Desiderio A, Mirra P, Nigro
C, Perruolo G, Ulianich L, Formisano P, Beguinot F, Miele C, Napoli
R and Fiory F: Diabetes and cognitive impairment: A role for
glucotoxicity and dopaminergic dysfunction. Int J Mol Sci.
22(12366)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Yang ZY and Yuan CX: IL-17A promotes the
neuroinflammation and cognitive function in sevoflurane
anesthetized aged rats via activation of NF-κB signaling pathway.
BMC Anesthesiol. 18(147)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Tian A, Ma H, Zhang R, Tan W, Wang X, Wu
B, Wang J and Wan C: Interleukin17A promotes postoperative
cognitive dysfunction by triggering β-amyloid accumulation via the
transforming growth factor-β (TGFβ)/smad signaling pathway. PLoS
One. 10(e0141596)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Duan GY, Duan ZX, Chen H, Chen F, Chen F,
Du ZY, Chen LY, Lu KZ, Zuo ZY and Li H: Cognitive function and
delirium following sevoflurane or propofol anesthesia for valve
replacement surgery: A multicenter randomized controlled trial.
Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 39:166–174. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Evered LA, Chan MTV, Han R, Chu MHM, Cheng
BP, Scott DA, Pryor KO, Sessler DI, Veselis R, Frampton C, et al:
Anaesthetic depth and delirium after major surgery: A randomised
clinical trial. Br J Anaesth. 127:704–712. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|