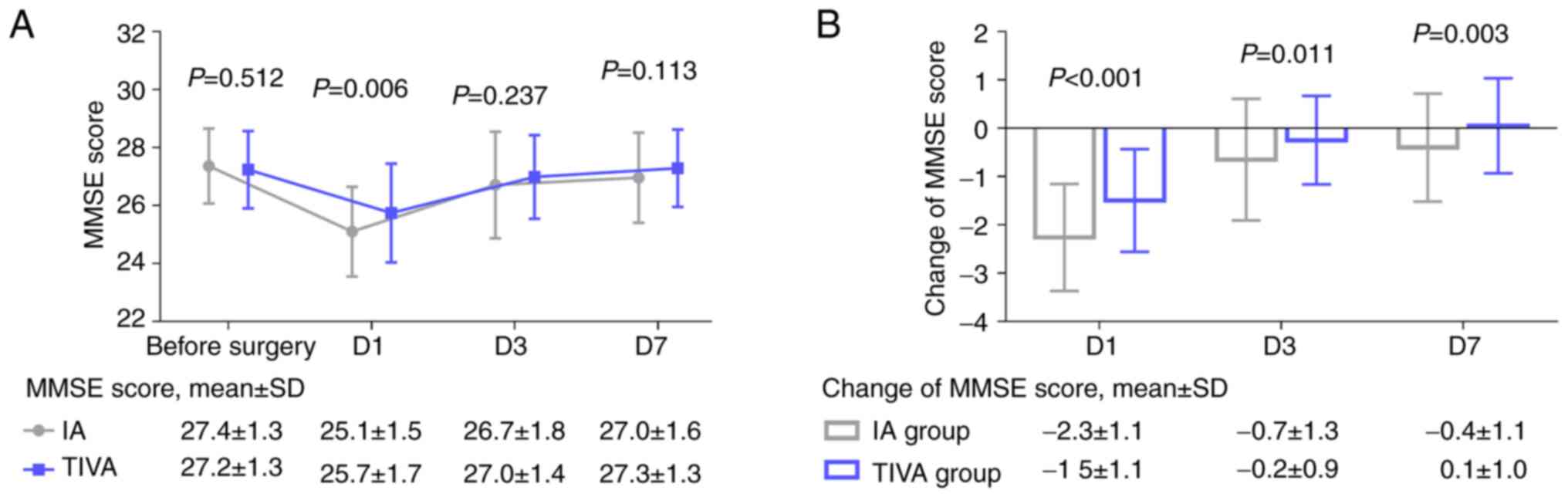
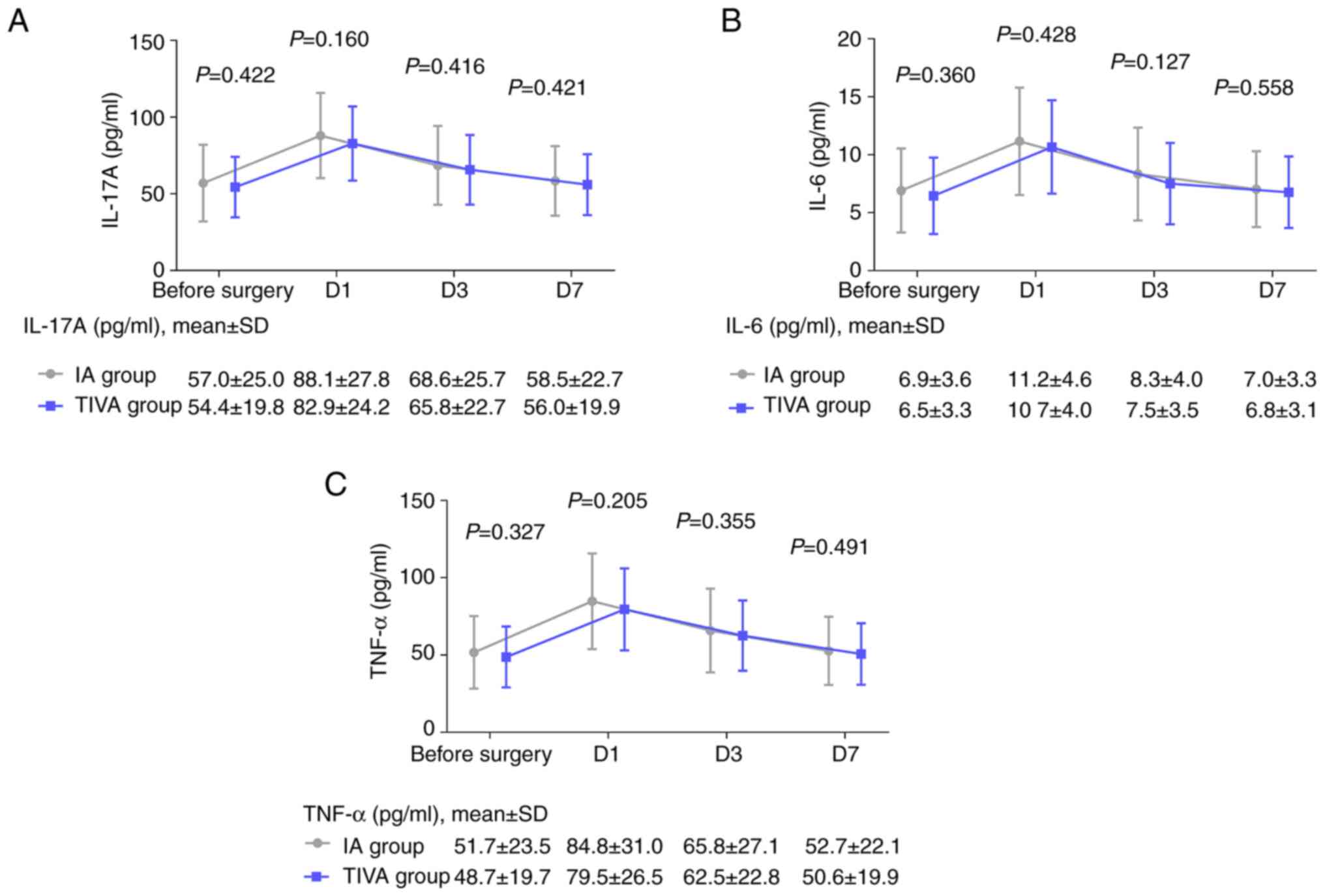
|
1
|
Avidan MS, Whitlock EL and Mashour GA:
General anesthesia and postoperative neurocognitive outcomes. JAMA.
327:36–38. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Li Z, Zhu Y, Kang Y, Qin S and Chai J:
Neuroinflammation as the underlying mechanism of postoperative
cognitive dysfunction and therapeutic strategies. Front Cell
Neurosci. 16(843069)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Olotu C: Anesthesia for the elderly: A
narrative review. Minerva Anestesiol. 87:1128–1138. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Gomez-Rios MA and Abad-Gurumeta A:
Anesthesia in the elderly patient. Resilience in frailty time. Med
Clin (Barc). 159:486–488. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Li Y, Chen D, Wang H, Wang Z, Song F, Li
H, Ling L, Shen Z, Hu C, Peng J, et al: Intravenous versus volatile
anesthetic effects on postoperative cognition in elderly patients
undergoing laparoscopic abdominal surgery. Anesthesiology.
134:381–394. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Geng YJ, Wu QH and Zhang RQ: Effect of
propofol, sevoflurane, and isoflurane on postoperative cognitive
dysfunction following laparoscopic cholecystectomy in elderly
patients: A randomized controlled trial. J Clin Anesth. 38:165–171.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Fan Y, Liu X, Wu S and Liu Y: The risk
factors for cognitive dysfunction in elderly patients after
laparoscopic surgery: A retrospective analysis. Medicine
(Baltimore). 100(e23977)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Riedel B, Dubowitz J, Yeung J, Jhanji S,
Kheterpal S and Avidan MS: On the horns of a dilemma: Choosing
total intravenous anaesthesia or volatile anaesthesia. Br J
Anaesth. 129:284–289. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Spruce L: Back to basics: Inhaled
anesthesia. AORN J. 102:389–393. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Jones C and Harris J: Total intravenous
anaesthesia. Br J Hosp Med (Lond). 82:1–2. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Zhang Y, Shan GJ, Zhang YX, Cao SJ, Zhu
SN, Li HJ, Ma D and Wang DX: First Study of Perioperative Organ
Protection (SPOP1) investigators. Propofol compared with
sevoflurane general anaesthesia is associated with decreased
delayed neurocognitive recovery in older adults. Br J Anaesth.
121:595–604. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Konishi Y, Evered LA, Scott DA and Silbert
BS: Postoperative cognitive dysfunction after sevoflurane or
propofol general anaesthesia in combination with spinal anaesthesia
for hip arthroplasty. Anaesth Intensive Care. 46:596–600.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Rump K and Adamzik M: Epigenetic
mechanisms of postoperative cognitive impairment induced by
anesthesia and neuroinflammation. Cells. 11(2954)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Liu Y, Yang W, Xue J, Chen J, Liu S, Zhang
S, Zhang X, Gu X, Dong Y and Qiu P: Neuroinflammation: The central
enabler of postoperative cognitive dysfunction. Biomed
Pharmacother. 167(115582)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Saklad M: Grading of patients for surgical
procedures. Anesthesiology. 2:281–284. 1941.
|
|
16
|
Folstein MF, Folstein SE and McHugh PR:
‘Mini-mental state’. A practical method for grading the cognitive
state of patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res. 12:189–198.
1975.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Yu W: Anesthesia with propofol and
sevoflurane on postoperative cognitive function of elderly patients
undergoing general thoracic surgery. Pak J Pharm Sci. 30:1107–1110.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Vutskits L and Xie Z: Lasting impact of
general anaesthesia on the brain: Mechanisms and relevance. Nat Rev
Neurosci. 17:705–717. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Eckenhoff RG, Johansson JS, Wei H, Carnini
A, Kang B, Wei W, Pidikiti R, Keller JM and Eckenhoff MF: Inhaled
anesthetic enhancement of amyloid-beta oligomerization and
cytotoxicity. Anesthesiology. 101:703–709. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Wang Y, Sands LP, Vaurio L, Mullen EA and
Leung JM: The effects of postoperative pain and its management on
postoperative cognitive dysfunction. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry.
15:50–59. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Deng H, Wu Y, Gao P, Kong D, Pan C, Xu S,
Tang D, Jiao Y, Wen D and Yu W: Preoperative pain facilitates
postoperative cognitive dysfunction via periaqueductal gray
matter-dorsal raphe circuit. Neuroscience. 524:209–219.
2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Peng K, Liu HY, Wu SR, Liu H, Zhang ZC and
Ji FH: Does propofol anesthesia lead to less postoperative pain
compared with inhalational anesthesia?: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Anesth Analg. 123:846–858. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Tian Y, Guo S, Guo Y and Jian L:
Anesthetic propofol attenuates apoptosis, Aβ accumulation, and
inflammation induced by sevoflurane through NF-κB pathway in human
neuroglioma cells. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 35:891–898. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Ye X, Lian Q, Eckenhoff MF, Eckenhoff RG
and Pan JZ: Differential general anesthetic effects on microglial
cytokine expression. PLoS One. 8(e52887)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Kothari V, Luo Y, Tornabene T, O'Neill AM,
Greene MW, Geetha T and Babu JR: High fat diet induces brain
insulin resistance and cognitive impairment in mice. Biochim
Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 1863:499–508. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Pignalosa FC, Desiderio A, Mirra P, Nigro
C, Perruolo G, Ulianich L, Formisano P, Beguinot F, Miele C, Napoli
R and Fiory F: Diabetes and cognitive impairment: A role for
glucotoxicity and dopaminergic dysfunction. Int J Mol Sci.
22(12366)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Yang ZY and Yuan CX: IL-17A promotes the
neuroinflammation and cognitive function in sevoflurane
anesthetized aged rats via activation of NF-κB signaling pathway.
BMC Anesthesiol. 18(147)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Tian A, Ma H, Zhang R, Tan W, Wang X, Wu
B, Wang J and Wan C: Interleukin17A promotes postoperative
cognitive dysfunction by triggering β-amyloid accumulation via the
transforming growth factor-β (TGFβ)/smad signaling pathway. PLoS
One. 10(e0141596)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Duan GY, Duan ZX, Chen H, Chen F, Chen F,
Du ZY, Chen LY, Lu KZ, Zuo ZY and Li H: Cognitive function and
delirium following sevoflurane or propofol anesthesia for valve
replacement surgery: A multicenter randomized controlled trial.
Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 39:166–174. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Evered LA, Chan MTV, Han R, Chu MHM, Cheng
BP, Scott DA, Pryor KO, Sessler DI, Veselis R, Frampton C, et al:
Anaesthetic depth and delirium after major surgery: A randomised
clinical trial. Br J Anaesth. 127:704–712. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|