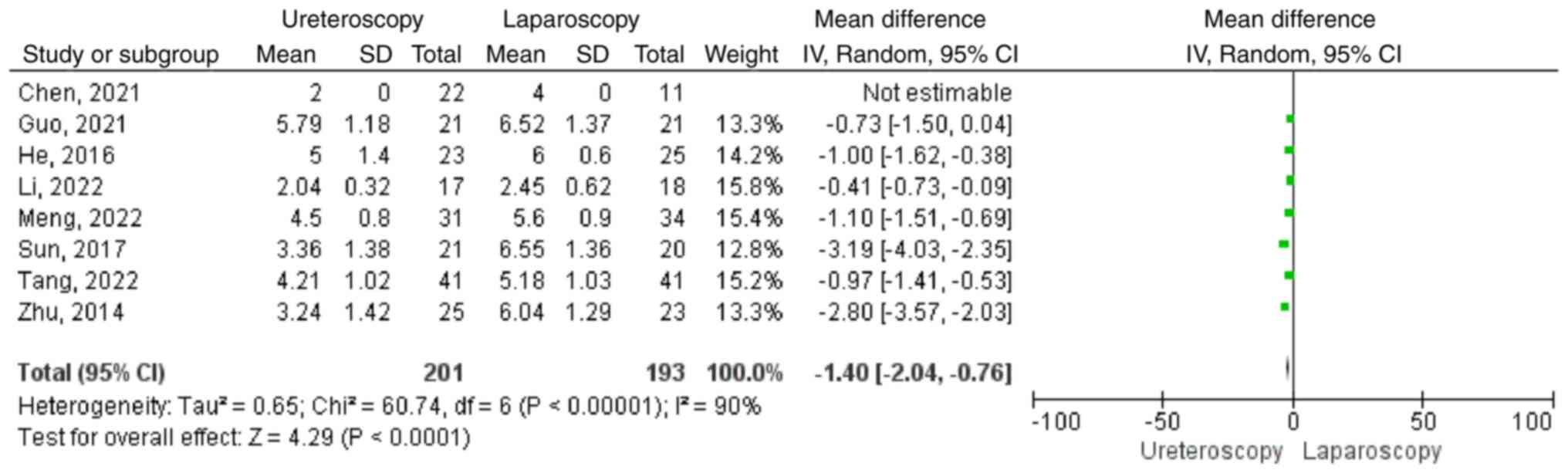
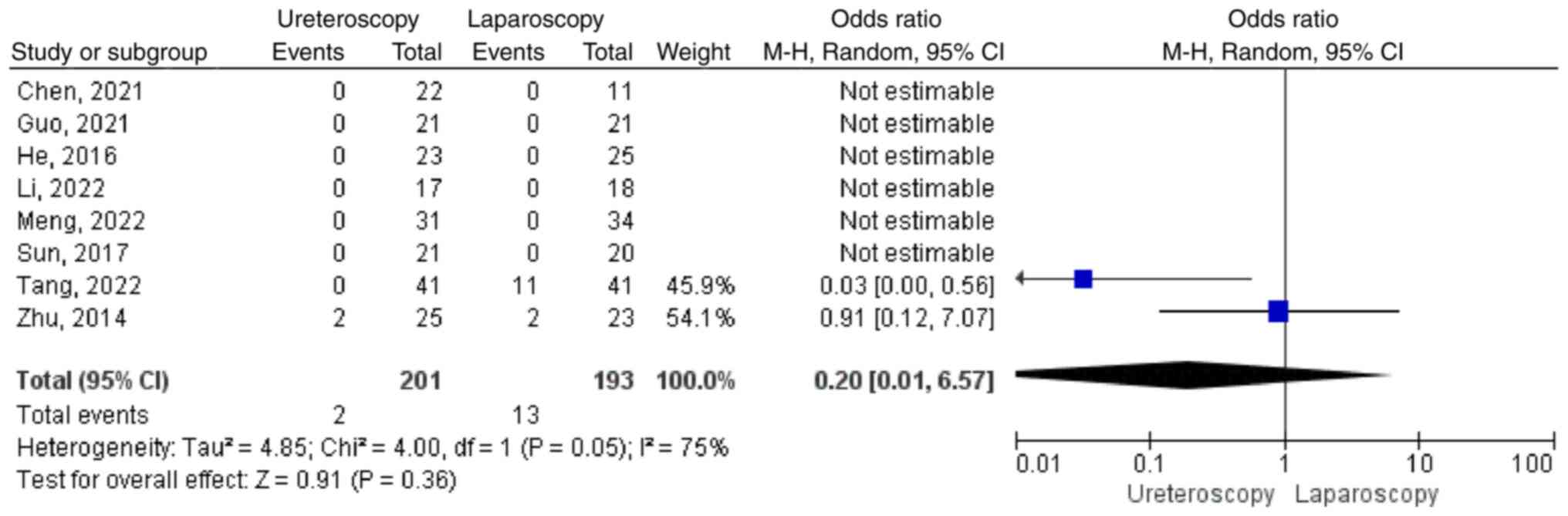
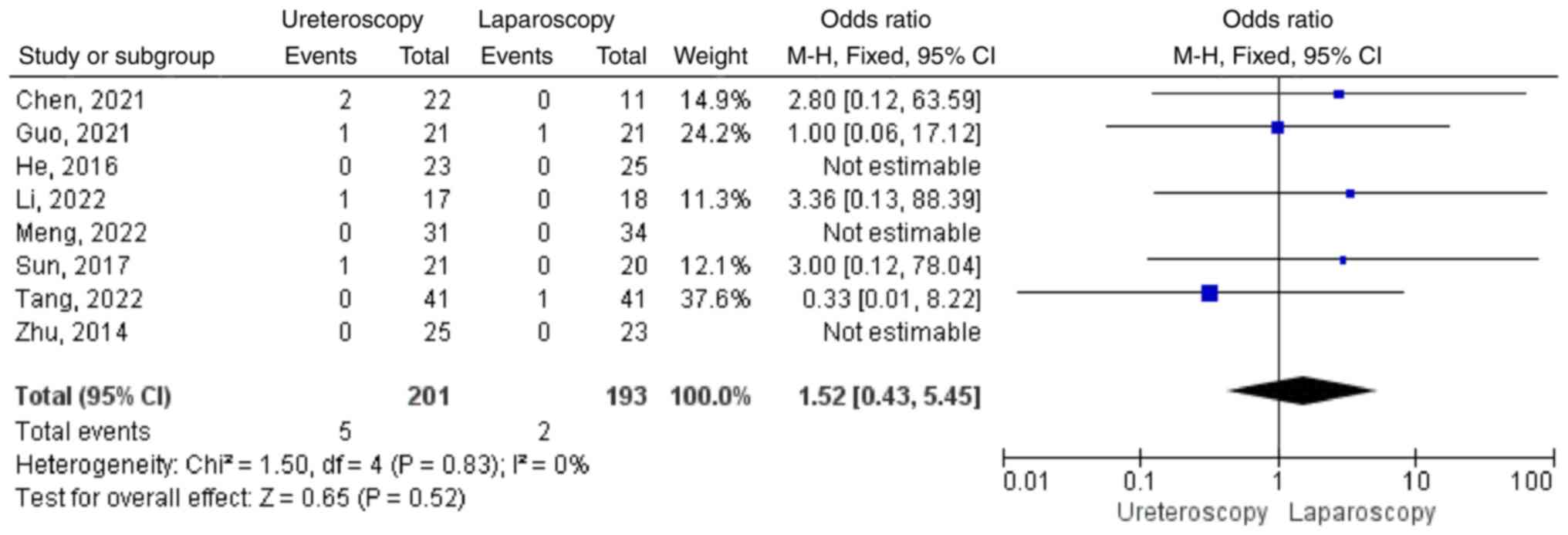
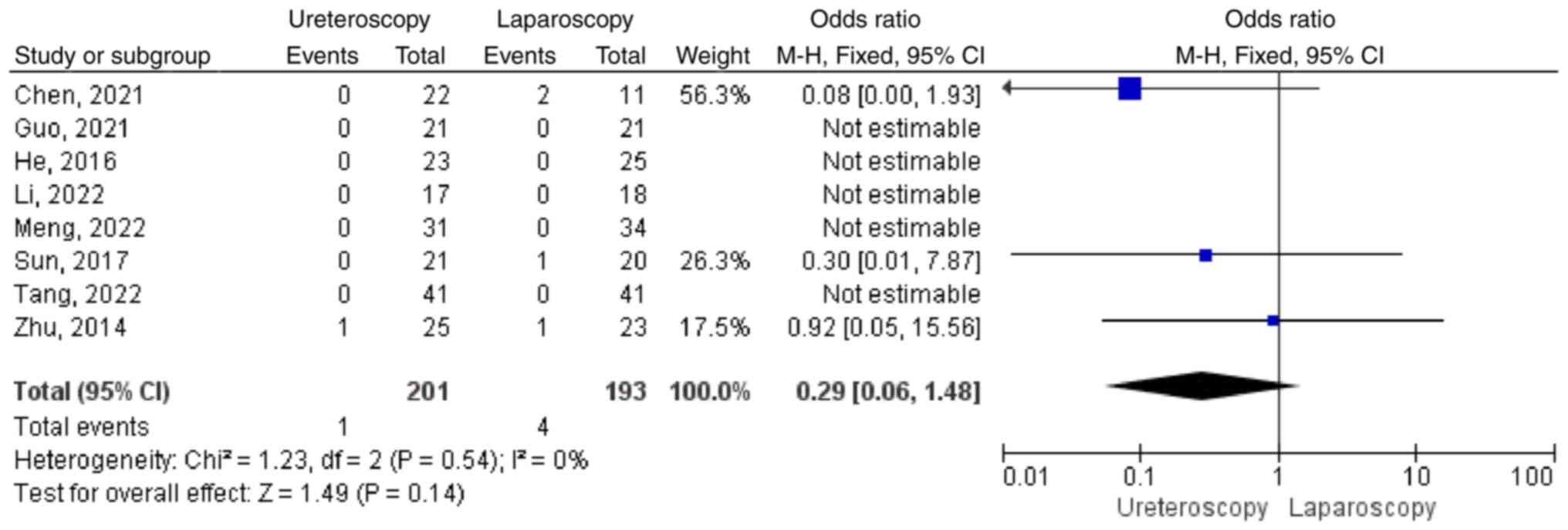
|
1
|
Basiri A, Hosseini SR, Tousi VN and
Sichani MM: Ureteroscopic management of symptomatic, simple
parapelvic renal cyst. J Endourol. 24:537–540. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Taguchi K, Harper JD, Stoller ML, Duty BD,
Sorensen MD, Sur RL, Usawachintachit M, Tzou DT, Wenzler DL,
Isaacson D, et al: Identifying factors associated with need for
flexible ureteroscope repair: A Western Endourology STone (WEST)
research consortium prospective cohort study. Urolithiasis.
46:559–566. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Wang R, Wang N, Tang J, Chen Y and Gao J:
The safety and efficacy of MPR-CTU combined with precise
intraoperative ultrasonography guided flexible ureteroscope in the
treatment of renal cystic disease. Exp Ther Med. 15:283–287.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Liu Z, Zhao Y, Wang X, Song M and Shi B:
Critical reviews of 1470-nm laser vaporization on benign prostatic
hyperplasia. Laser Med Sci. 33:323–327. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Higgins JPT and Green S: Cochrane handbook
for systematic review of interventions. Version 5.1.0, The Cochrane
Collaboration, 2011.
|
|
6
|
Zhu W, Zhu Q, Zeng F, Gao X and He Y:
Comparison of holmium laser ureteroscopic intrapelvic drainage vs.
retroperitoneal laparoscopy for the treatment of peripelvic cyst.
Chin J Exp Surg. 31(2)2014.(In Chinese).
|
|
7
|
Li X and Lin C: A comparative study of
three different methods in the treatment of parapelvic cysts. J
Chin Phys. 1726–1728. 2022.(In Chinese).
|
|
8
|
He H, Li L, Tao Z and Wang W: Flexible
ureteroscopy versus laparoscopy in treatment of parapelvic cyst. J
Mod Clin Med. 42:417–419. 2016.
|
|
9
|
Sun Y, Du D and Wu Y: To compare the
effect of flexible ureteroscopy holmium laser incision and internal
drainage and retroperitoneal laparoscopic cyst unroofing in the
treatment of parapelvic cyst. Henan Med Res. 26:1570–1571. 2017.(In
Chinese).
|
|
10
|
Chen H, Chen G, Pan Y and Jin X: Minimally
invasive surgeries in the management of renal parapelvic cysts: A
retrospective comparative study. Urol J. 18:389–394.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Tang R, Yang J, Wan L and Yang Z: Clinical
effect of flexible ureteroscope and laparoscope in the treatment of
parapelvic cyst. Biomed Res Int. 2022(5718923)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Guo H, Liu C, Sun J and Zhang X:
Comparison of holmium laser incision and internal drainage under
flexible ureteroscope and retroperitoneal laparoscopic
decompression to stress response in patients with parapelvic cyst.
J Third Mil Med Univ. 43:1258–1262. 2021.
|
|
13
|
Meng X and Mi Q: Transurethral flexible
ureteroscopic incision and drainage with holmium laser in the
treatment of parapelvic renal cysts: A retrospective study. INT
BRAZ Journal of Urology. 48:842–849. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Meola M, Samoni S and Petrucci I: Clinical
scenarios in chronic kidney disease: cystic renal diseases. Contrib
Nephrol. 188:120–130. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Ishida K, Yuhara K and Kanimoto Y: A case
of acute renal failure due to parapelvic cyst in a solitary kidney.
Hinyokika Kiyo. 51:261–263. 2005.PubMed/NCBI(In Japanese).
|
|
16
|
Camargo AHLA, Cooperberg MR, Ershoff BD,
Rubenstein JN, Meng MV and Stoller ML: Laparoscopic management of
peripelvic renal cysts: University of California, San Francisco,
experience and review of literature. Urology. 65:882–887.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Hoenig DM, McDougall EM, Shalhav AL,
Elbahnasy AM and Clayman RV: Laparoscopic ablation of peripelvic
renal cysts. J Urol. 158:1345–1348. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yoder BM and Wolf JS Jr: Long-term outcome
of laparoscopic decortication of peripheral and peripelvic renal
and adrenal cysts. J Urol. 171:583–587. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Morgan C Jr and Rader D: Laparoscopic
unroofing of a renal cyst. J Urol. 148:1835–1836. 1992.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Yu W, Zhang D, He X, Zhang Y, Liao G, Deng
G and Jin B: Flexible ureteroscopic management of symptomatic renal
cystic diseases. J Surg Res. 196:118–123. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Mancini V, Cormio L, d'Altilia N,
Benedetto G, Ferrarese P, Balzarro M, Defidio L and Carrieri G:
Retrograde intrarenal surgery for symptomatic renal sinus cysts:
Long-term results and literature review. Urol Int. 101:150–155.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Zhao Q, Huang S, Li Q, Xu L, Wei X, Huang
S, Li S and Liu Z: Treatment of parapelvic cyst by internal
drainage technology using ureteroscope and holmium laser. West
Indian Med J. 64:230–235. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Li EC, Hou JQ, Yang LB, Yuan HX, Hang LH,
Alagirisamy KK, Li DP and Wang XP: Pure natural orifice
translumenal endoscopic surgery management of simple renal cysts:
2-Year follow-up results. J Endourol. 25:75–80. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Liaconis H, Pautler SE and Razvi HA:
Ureteroscopic decompression of an unusual uroepithelial cyst using
the holmium: YAG laser. J Endourol. 15:295–297. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Luo Q, Zhang X, Chen H, Liu Z, Chen X, Dai
Y and Zhao Z: Treatment of renal parapelvic cysts with a flexible
ureteroscope. Int Urol Nephrol. 46:1903–1908. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Mao X, Xu G, Wu H and Xiao J:
Ureteroscopic management of asymptomatic and symptomatic simple
parapelvic renal cysts. BMC Urol. 15(48)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Wang Z, Zeng X, Chen C, Wang T, Chen R and
Liu J: Methylene blue injection via percutaneous renal cyst
puncture used in flexible ureteroscope for treatment of parapelvic
cysts: A modified method for easily locating cystic wall. Urology.
125:243–247. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Shen J, Chen Y and Wang R: Efficacy and
complication of flexible ureteroscopic holmium laser incision for
simple renal cysts: A retrospective study. J Endourol. 33:881–886.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Chen Y, Wang R, Shen X, Tang J, Shen J,
Fang Z, Shi Z and Jin X: Ultrasonography-assisted flexible
ureteroscope for the treatment of parapelvic renal cysts: A
comparison between the 1470-nm diode laser and the holmium laser.
Exp Ther Med. 21(172)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Zhao Y, Liu C, Zhou G, Yu C, Zhang Y and
Ouyang Y: A retrospective evaluation of benign prostatic
hyperplasia treatment by transurethral vaporization using a 1470 nm
laser. Photomed Laser Surg. 31:626–629. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|