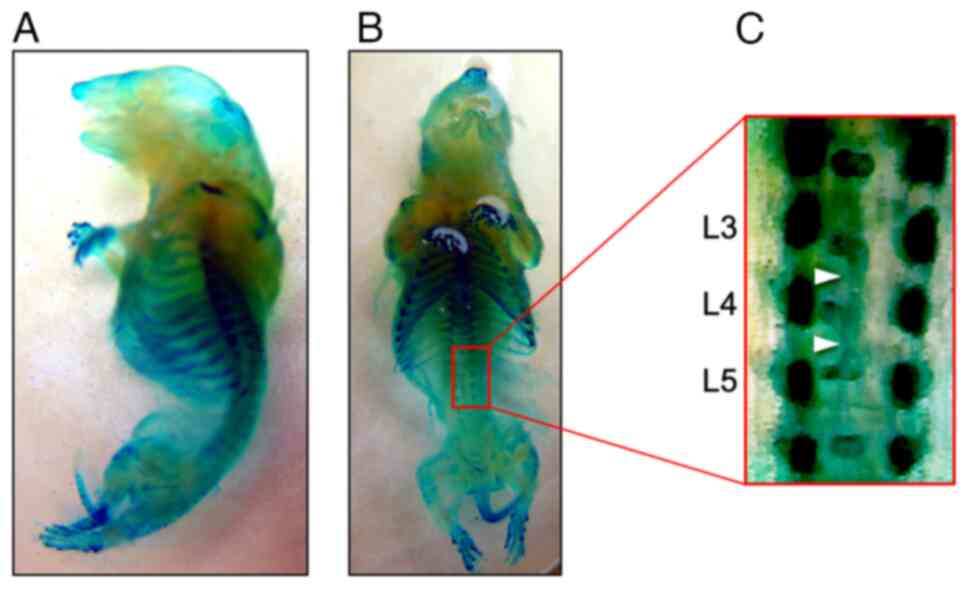
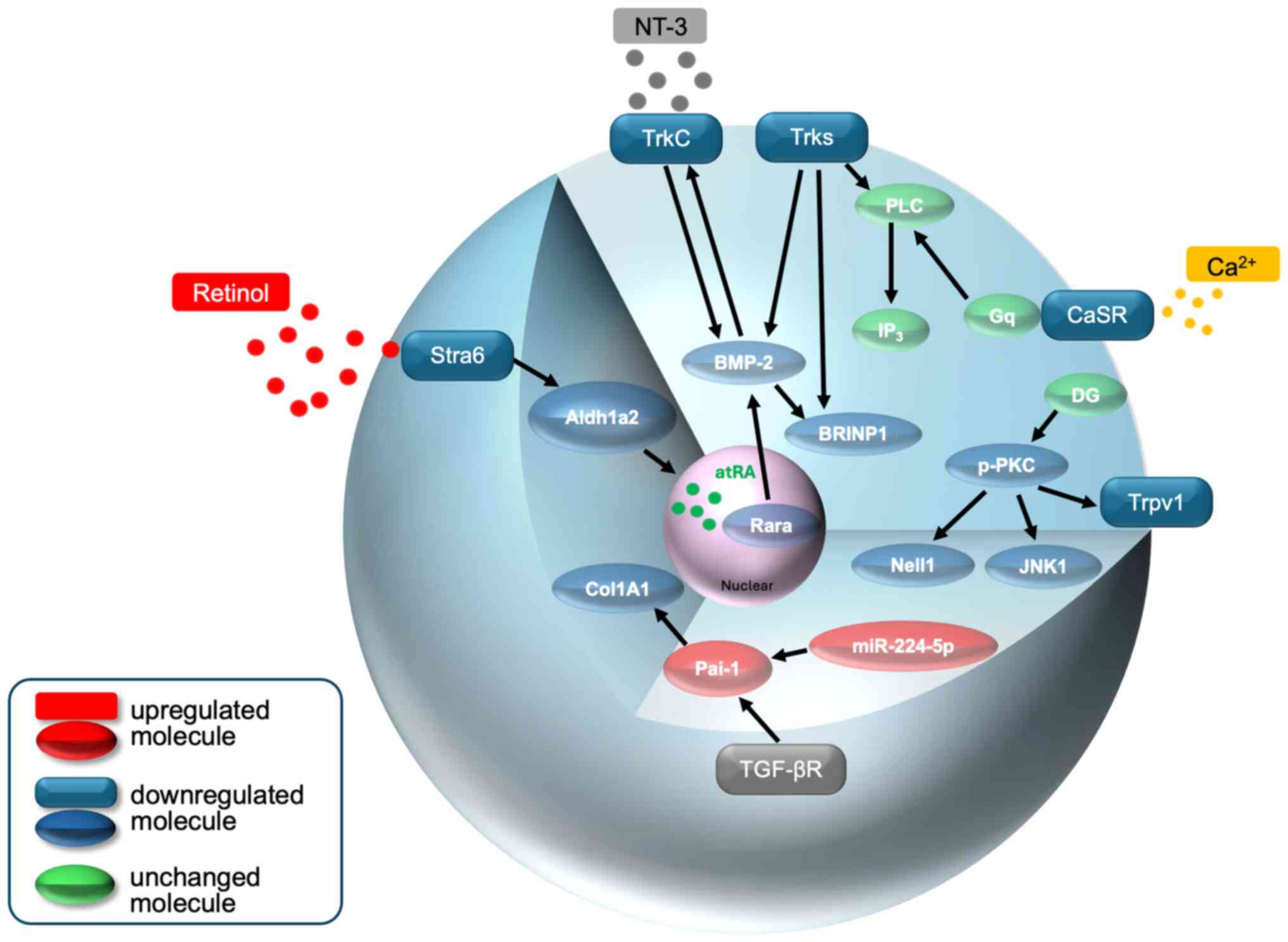
|
1
|
Frost BA, Camarero-Espinosa S and Foster
EJ: Materials for the Spine: Anatomy, problems, and solutions.
Materials (Basel). 12(253)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Galbusera F: The spine: Its evolution,
function, and shape. In: Biomechanics of the Spine Basic Concepts,
Spinal Disorders and Treatments. Galbusera F and Wilke HJ (eds).
Academic Press, New York, NY, pp3-9, 2018.
|
|
3
|
Izzoa R, Guarnieria G, Guglielmib G and
Muto M: Biomechanics of the spine. Part I: Spinal stability. Eur J
Radiol. 82:118–126. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Goldberg CJ, Moore DP, Fogarty EE and
Dowling FE: Scoliosis: A review. Pediatr Surg Int. 24:129–144.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Goldstein LA and Waugh TR: Classification
and terminology of scoliosis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 93:10–22.
1973.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Agabegi ED and Agabegi SS: Step-Up to
Medicine (Step-Up Series). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.,
Philadelphia PH, pp90, 2008.
|
|
7
|
Giampietro PF: Genetic aspects of
congenital and idiopathic scoliosis. Scientifica (Cairo).
2012(152365)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Giampietro PF, Raggio CL, Blank RD,
McCarty C, Broeckel U and Pickart MA: Clinical, genetic and
environmental factors associated with congenital vertebral
malformations. Mol Syndromol. 4:94–105. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Janssen MM, de Wilde RF, Kouwenhoven JW
and Castelein RM: Experimental animal models in scoliosis research:
A review of the literature. Spine J. 11:347–358. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Shimokawa N, Takahashi I and Iizuka H:
Spinal malformation-A biochemical analysis using congenital
kyphosis rats. J Cell Biochem. 123:501–505. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Terhune EA, Heyn PC, Piper CR and
Hadley-Miller N: Genetic variants associated with the occurrence
and progression of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: A systematic
review protocol. Syst Rev. 11(118)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Qiu Y, Mao SH, Qian BP, Jiang J, Qui XS,
Zhao Q and Liu Z: A promoter polymorphism of neurotrophin 3 gene is
associated with curve severity and bracing effectiveness in
adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 37:127–133.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Ryzhkov II, Borzilov EE, Churnosov MI,
Ataman AV, Dedkov AA and Polonikov AV: Transforming growth factor
beta 1 is a novel susceptibility gene for adolescent idiopathic
scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 38:E699–E704. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Ogura Y, Kou I, Miura S, Takahashi A, Xu
L, Takeda K, Takahashi Y, Kono K, Kawakami N, Uno K, et al: A
functional SNP in BNC2 is associated with adolescent idiopathic
scoliosis. Am J Hum Genet. 97:337–342. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Takahashi Y, Kou I, Takahashi A, Johnson
TA, Kono K, Kawakami N, Uno K, Ito M, Minami S, Yanagida H, et al:
A genome-wide association study identifies common variants near
LBX1 associated with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Nat Genet.
43:1237–1240. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Guo L, Yamashita H, Kou I, Takimoto A,
Mrguro-Horie M, Horike S, Sakuma T, Miura S, Adachi T, Tamamoto T,
et al: Functional investigation of a non-coding variant associated
with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis in zebrafish: Elevated
expression of the ladybird homeobox gene causes body axis
deformation. PLoS Genet. 12(e1005802)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Kou I, Takahashi Y, Johnson TA, Tkahashi
A, Guo L, Dai J, Qiu X, Sharma S, Takimoto A, Ogura Y, et al:
Genetic variants in GPR126 are associated with adolescent
idiopathic scoliosis. Nat Genet. 45:676–679. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
De Salvatore S, Ruzzini L, Longo UG,
Marino M, Greco A, Piergentili I, Costici PF and Denaro V:
Exploring the association between specific genes and the onset of
idiopathic scoliosis: A systematic review. BMC Med Genomics.
15(115)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Fei Q, Wu Z, Wang H, Zhou X, Wang N, Ding
Y, Wang Y and Qiu G: The association analysis of TBX6 polymorphism
with susceptibility to congenital scoliosis in a Chinese Han
population. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 35:983–988. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Wu N, Ming X, Xiao J, Wu Z, Chen X,
Shinawi M, Shen Y, Yu G, Liu J, Xie H, et al: TBX6 null variants
and a common hypomorphic allele in congenital scoliosis. N Engl J
Med. 372:341–350. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Takeda K, Kou I, Kawakami N, Iida A,
Nakajima M, Ogura Y, Imagawa E, Miyake N, Matsumoto N, Yasuhiko Y,
et al: Compound heterozygosity for null mutations and a common
hypomorphic risk haplotype in TBX6 causes congenital scoliosis. Hum
Mutat. 38:317–323. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Otomo N, Takeda K, Kawai S, Kou I, Guo L,
Osawa M, Alev C, Kawakami N, Miyake N, Matsumoto N, et al:
Bi-allelic loss of function variants of TBX6 causes a spectrum of
malformation of spine and rib including congenital scoliosis and
spondylocostal dysostosis. J Med Genet. 56:622–628. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Chapman DL, Agulnik I, Hancock S, Silver
LM and Papaioannou VE: Tbx6, a mouse T-Box gene implicated in
paraxial mesoderm formation at gastrulation. Dev Biol. 180:534–542.
1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Sadahiro T, Isomi M, Muraoka N, Kojima H,
Haginiwa S, Kurotsu S, Tamura F, Tani H, Tohyama S, Fujita J, et
al: Tbx6 induces nascent mesoderm from pluripotent stem cells and
temporally controls cardiac versus somite lineage diversification.
Cell Stem Cell. 23:382–395.e5. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Chapman DL and Papaioannou VE: Three
neural tubes in mouse embryos with mutations in the T-box gene
Tbx6. Nature. 391:695–697. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Takemoto T, Uchikawa M, Yoshida M, Bell
DM, Lovell-Badge R, Papaioannou VE and Kondoh H: Tbx6-dependent
Sox2 regulation determines neural or mesodermal fate in axial stem
cells. Nature. 470:394–398. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Takeda K, Kou I, Mizumoto S, Yamada S,
Kawakami N, Nakajima M, Otomo N, Ogura Y, Miyake N, Matsumoto N, et
al: Screening of known disease genes in congenital scoliosis. Mol
Genet Genomic Med. 6:966–974. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Turnpenny PD, Sloman M, Dunwoodie S, Adam
MP, Feldman J, Mirzaa GM, Pagon RA, Wallace SE, Bean LJH, Gripp KW,
et al: Spondylocostal Dysostosis, Autosomal Recessive. 2009 Aug 25
(Updated 2023 Aug 17). Adam MP, Feldman J, Mirzaa GM, Pagon RA,
Wallace SE, Bean LJ, Gripp KW and Amemiya A (eds). GeneReviews,
Seattle, WA, 1993.
|
|
29
|
Oda I, Cunningham BW, Buckley RA, Goebel
MJ, Haggerty CJ, Orbegoso CM and McAfee PC: Does spinal kyphotic
deformity influence the biomechanical characteristics of the
adjacent motion segments? An in vivo animal model. Spine (Phila Pa
1976). 24:2139–2146. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Chae U, Park NR, Kim ES, Choi JY, Yim M,
Lee HS, Lee SR, Lee S, Paerk JW and Lee DS: IDH2-deficient mice
develop spinal deformities with aging. Physiol Res. 67:487–494.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Zaghini A, Sarli G, Barboni C, Sanapo M,
Pellegrino V, Diana A, Linta N, Rambaldi J, D'Apice MR, Murdocca M,
et al: Long term breeding of the Lmna G609G progeric mouse:
Characterization of homozygous and heterozygous models. Exp
Gerontol. 130(110784)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Torres HM, Rodezno-Antunes T, VanCleave A,
Cao Y, Callahan DL, Westendorf JJ and Tao J: Precise detection of a
murine germline mutation of the Notch3 gene associated with
kyphosis and developmental disorders. J Adv Vet Anim Res. 8:7–13.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Ishibashi M: Congenital vertebral
malformation (Ishibashi rats). In: Handbook on Animal Models of
Human Diseases. Kawamata J and Matushita H (eds). Ishiyaku Shuppan,
Tokyo, pp430-434, 1979.
|
|
34
|
Seki T, Shimokawa N, Iizuka H, Takagishi K
and Koibuchi N: Abnormalities of vertebral formation and Hox
expression in congenital kyphoscoliotic rat. Mol Cell Biochem.
312:193–199. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Esapa CT, Piret SE, Nesbit MA, Thomas GP,
Coulton LA, Gallagher OM, Simon MM, Kumar S, Mallon AM, Bellantuono
I, et al: An N-Ethyl-N-Nitrosourea (ENU) mutagenized mouse model
for autosomal dominant nonsyndromic kyphoscoliosis due to vertebral
fusion. JBMR Plus. 2:154–163. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Moritake S, Yamamuro T, Yamada J and
Watanabe H: Progression of congenital kyphosis in Ishibashi rats.
Acta Orthop Scand. 53:841–846. 1983.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Moritake S, Yamamuro T and Yamada J:
Effects of sex hormones on congenital kyphosis in Ishibashi rats.
Acta Orthop Scand. 57:62–66. 1986.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Maekawa R, Yamada J and Nikaido H:
Genetical studies of low plasma alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity
in the IS strain of rats. Jikken Dobutsu. 31:13–19. 1982.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Yamada J, Nikaido H, Moritake S and
Maekawa R: Genetic analyses of the vertebral anomalies of the IS
strain of rat and the development of a BN congenic line with the
anomalies. Lab Anim. 16:40–47. 1982.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Takano M, Katsumata Y, Ogawa J, Ebata T,
Urasoko Y, Asano Y, Serikawa T and Kuramoto T: Morphological
features of mutant rat, IS-Tlk/Kyo, fetuses with caudal vertebral
anomalies. Congenit Anom (Kyoto). 52:42–47. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Takano M, Ogawa E, Saitou T, Yamaguchi Y,
Asano Y, Serikawa T and Kuramoto T: Morphological features of adult
rats of IS/Kyo and IS-Tlk/Kyo strains with lumbar and caudal
vertebral anomalies. Exp Anim. 63:269–275. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Satokata I, Benson G and Maas R: Sexually
dimorphic sterility phenotypes in Hoxa10-deficient mice. Nature.
374:460–463. 1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Favier B, Rijli FM, Fromental-Ramain C,
Fraulob V, Chambon P and Dollé P: Functional cooperation between
the non-paralogous genes Hoxa-10 and Hoxd-11 in the developing
forelimb and axial skeleton. Development. 122:449–460.
1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Davis AP, Witte DP, Hsieh-Li HM, Potter SS
and Capecchi MR: Absence of radius and ulna in mice lacking hoxa-11
and hoxd-11. Nature. 375:791–795. 1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Boulet AM and Capecchi MR: Duplication of
the Hoxd11 gene causes alterations in the axial and appendicular
skeleton of the mouse. Dev Biol. 249:96–107. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Tsunoda D, Iizuka H, Ichinose T, Iizuka Y,
Mieda T, Shimokawa N, Takagishi K and Koibuchi N: The Trk family of
neurotrophin receptors is downregulated in the lumbar spines of
rats with congenital kyphoscoliosis. Mol Cell Biochem. 412:11–18.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Sonoda H, Iizuka H, Ishiwata S, Tsunoda D,
Abe M, Takagishi K, Chikuda H, Koibuchi N and Shimokawa N: The
retinol-retinoic acid metabolic pathway is impaired in the lumbar
spine of a rat model of congenital kyphoscoliosis. J Cell Biochem.
120:15007–15017. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Ishiwata S, Iizuka H, Sonoda H, Tsunoda D,
Tajika Y, Chikuda H, Koibuchi N and Shimokawa N: Upregulated
miR-224-5p suppresses osteoblast differentiation by increasing the
expression of Pai-1 in the lumbar spine of a rat model of
congenital kyphoscoliosis. Mol Cell Biochem. 475:53–62.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Maskos U and Southern EM: A novel method
for the analysis of multiple sequence variants by hybridisation to
oligonucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 21:2267–2268. 1993.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Schena M, Shalon D, Davis RW and Brown PO:
Quantitative monitoring of gene expression patterns with a
complementary DNA microarray. Science. 270:467–470. 1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Emili AQ and Cagney G: Large-scale
functional analysis using peptide or protein arrays. Nat
Biotechnol. 18:393–397. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Uren RT and Turnley AM: Regulation of
neurotrophin receptor (Trk) signaling: Suppressor of cytokines
signaling 2 (SOCS2) is a new player. Front Mol Neurosci.
7(39)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Tomlinson RE, Li Z, Zhang Q, Goh BC, Li Z,
Thorek DLJ, Rajbhandari L, Brushart TM, Minichiello L, Zhou F, et
al: NGF-TrkA signaling by sensory nerves coordinates the
vascularization and ossification of developing endochondral bone.
Cell Rep. 16:2723–2735. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Li Z, Meyers CA, Chang L, Lee S, Li Z,
Tomlinson R, Hoke A, Clemens TL and James AW: Fracture repair
requires TrkA signaling by skeletal sensory nerves. J Clin Invest.
129:5137–5150. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Rivera KO, Russo F, Boileau RM, Tomlinson
RE, Miclau T, Marcucio RS, Desai TA and Bahney CS: Local injections
of beta-NGF accelerates endochondral fracture repair by promoting
cartilage to bone conversion. Sci Rep. 10(22241)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Wheeler EF, Gong H, Grimes R, Benoit D and
Vazquez L: p75NTR and Trk receptors are expressed in reciprocal
patterns in a wide variety of non-neural tissues during rat
embryonic development, indicating independent receptor functions. J
Comp Neurol. 391:407–428. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Yamashiro T, Fukunaga T, Yamashita K,
Kobashi N and Takano-Yamamoto T: Gene and protein expression of
brain-derived neurotrophic factor and TrkB in bone and cartilage.
Bone. 28:404–409. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Hutchison MR: BDNF alters ERK/p38 MAPK
activity ratios to promote differentiation in growth plate
chondrocytes. Mol Endocrinol. 26:1406–1416. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Hutchison MR: Mice with a conditional
deletion of the neurotrophin receptor TrkB are dwarfed, and are
similar to mice with a MAPK14 deletion. PLoS One.
8(e66206)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Asaumi K, Nakanishi T, Asahara H, Inoue H
and Takigawa M: Expression of neurotrophins and their receptors
(TRK) during fracture healing. Bone. 26:625–633. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Su YW, Chung R, Ruan CS, Chim SM, Kuek V,
Dwivedi PP, Hassanshahi M, Chen KM, Xie Y, Chen L, et al:
Neurotrophin-3 induces BMP-2 and VEGF activities and promotes the
bony repair of injured growth plate cartilage and bone in rats. J
Bone Miner Res. 31:1258–1274. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Blomhoff R and Blomhoff HK: Overview of
retinoid metabolism and function. J Neurobiol. 66:606–630.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
See AW, Kaiser ME, White JC and
Clagett-Dame M: A nutritional model of late embryonic vitamin A
deficiency produces defects in organogenesis at a high penetrance
and reveals new roles for the vitamin in skeletal development. Dev
Biol. 316:171–190. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Li Z, Shen J, Wu WK, Wang X, Liang J, Qiu
G and Liu J: Vitamin A deficiency induces congenital spinal
deformities in rats. PLoS One. 7(e46565)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Amengual J, Zhang N, Kemerer M, Maeda T,
Palczewski K and Von Lintig J: STRA6 is critical for cellular
vitamin A uptake and homeostasis. Hum Mol Genet. 23:5402–5417.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Boncinelli E, Simeone A, Acampora D and
Mavilio F: HOX gene activation by retinoic acid. Trends Genet.
7:329–334. 1991.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Marshall H, Morrison A, Studer M, Pöpperl
H and Krumlauf R: Retinoids and Hox genes. FASEB J. 10:969–978.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Wellik DM and Capecchi MR: Hox10 and Hox11
genes are required to globally pattern the mammalian skeleton.
Science. 301:363–367. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Rogers MB: Receptor-selective retinoids
implicate retinoic acid receptor alpha and gamma in the regulation
of bmp-2 and bmp-4 in F9 embryonal carcinoma cells. Cell Growth
Differ. 7:115–122. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Kobayashi M, Fujii M, Kurihara K and
Matsuoka I: Bone morphogenetic protein-2 and retinoic acid induce
neurotrophin-3 responsiveness in developing rat sympathetic
neurons. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 53:206–217. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Nordin BE: Calcium and osteoporosis.
Nutrition. 13:664–686. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Matikainen N, Pekkarinen T, Ryhänen EM and
Schalin-Jäntti C: Physiology of calcium homeostasis: An overview.
Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 50:575–590. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Brown EM, Gamba G, Riccardi D, Lombardi M,
Butters R, Kifor O, Sun A, Hediger MA, Lytton J and Hebert SC:
Cloning and characterization of an extracellular
Ca2+-sensing receptor from bovine parathyroid. Nature.
366:575–580. 1993.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Cianferotti L, Gomes AR, Fabbri S, Tanini
A and Brandi ML: The calcium-sensing receptor in bone metabolism:
From bench to bedside and back. Osteoporos Int. 26:2055–2071.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Takahashi I, Watanabe Y, Sonoda H, Tsunoda
D, Amano I, Koibuchi N, Iizuka H and Shimokawa N: Calcium sensing
and signaling are impaired in the lumbar spine of a rat model of
congenital kyphosis. Eur Spine J. 32:3403–3412. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Caterina MJ, Schumacher MA, Tominaga M,
Rosen TA, Levine JD and Julius D: The capsaicin receptor: A
heat-activated ion channel in the pain pathway. Nature.
389:816–824. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Lieben L and Carmeliet G: The involvement
of TRP channels in bone homeostasis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne).
3(99)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Liu N, Lu W, Dai X, Qu X and Zhu C: The
role of TRPV channels in osteoporosis. Mol Biol Rep. 49:577–585.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Idris AI, Landao-Bassonga E and Ralston
SH: The TRPV1 ion channel antagonist capsazepine inhibits
osteoclast and osteoblast differentiation in vitro and ovariectomy
induced bone loss in vivo. Bone. 46:1089–1099. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
He LH, Liu M, He Y, Xiao E, Zhao L, Zhang
T, Yang HQ and Zhang Y: TRPV1 deletion impaired fracture healing
and inhibited osteoclast and osteoblast differentiation. Sci Rep.
7(42385)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Lu SS, Zhang X, Soo C, Hsu T, Napoli A,
Aghaloo T, Wu BM, Tsou P, Ting K and Wang JC: The osteoinductive
properties of Nell-1 in a rat spinal fusion model. Spine J.
7:50–60. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Li C, Zhang X, Zheng Z, Nguyen A, Ting K
and Soo C: Nell-1 is a key functional modulator in
osteochondrogenesis and beyond. J Dent Res. 98:1458–1468.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Xu R, Zhang C, Shin DY, Kim JM, Lalani S,
Li N, Yang YS, Liu Y, Eiseman M, Davis RJ, et al: c-Jun N-terminal
kinases (JNKs) are critical mediators of osteoblast activity in
vivo. J Bone Miner Res. 32:1811–1815. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Ke D, Ji L, Wang Y, Fu X, Chen J, Wang F,
Zhao D, Xue Y, Lan X and Hou J: JNK1 regulates RANKL-induced
osteoclastogenesis via activation of a novel
Bcl-2-Beclin1-autophagy pathway. FASEB J. 33:11082–11095.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Fukada T, Civic N, Furuichi T, Shimoda S,
Mishima K, Higashiyama H, Idaira Y, Asada Y, Kitamura H, Yamasaki
S, et al: The zinc transporter SLC39A13/ZIP13 is required for
connective tissue development; its involvement in BMP/TGF-beta
signaling pathways. PLoS One. 3(e3642)2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Lee RC, Feinbaum RL and Ambros V: The C.
elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense
complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 75:843–854. 1993.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Moore BT and Xiao P: MiRNAs in bone
diseases. Microrna. 2:20–31. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Yang N, Wang G, Hu C, Shi Y, Liao L, Shi
S, Cai Y, Cheng S, Wang X, Liu Y, et al: Tumor necrosis factor
alpha suppresses the mesenchymal stem cell osteogenesis promoter
miR-21 in estrogen deficiency-induced osteoporosis. J Bone Miner
Res. 28:559–573. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Li H, Xie H, Liu W, Hu R, Huang H, Tan YF,
Xu K, Sheng ZF, Zhou HD, Wu XP and Luo XH: A novel microRNA
targeting HDAC5 regulates osteoblast differentiation in mice and
contributes to primary osteoporosis in humans. J Clin Invest.
119:3666–3677. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Zhang Y, Xie RL, Croce CM, Stein JL, Lian
JB, Wijnen AJ and Stein GS: A program of microRNAs controls
osteogenic lineage progression by targeting transcription factor
Runx2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:9863–9868. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
91
|
Luo Y, Cao X, Chen J, Gu J, Zhao J and Sun
J: MicroRNA-224 suppresses osteoblast differentiation by inhibiting
SMAD4. J Cell Physiol. 233:6929–6937. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Ghosh AK, Bradham WS, Gleaves LA, De Taeye
B, Murphy SB, Covington JW and Vaughan DE: Genetic deficiency of
plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 promotes cardiac fibrosis in aged
mice: Involvement of constitutive transforming growth factor-beta
signaling and endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Circulation.
122:1200–1209. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
93
|
Mao L, Kawao N, Tamura Y, Okumoto K, Okada
K, Yano M, Matsuo O and Kaji H: Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1
is involved in impaired bone repair associated with diabetes in
female mice. PLoS One. 9(e92686)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
94
|
Ghali N, Sobey G and Burrows N:
Ehlers-Danlos syndromes. BMJ. 366(l4966)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
95
|
Nuytinck L, Freund M, Lagae L, Pierard GE,
Hermanns-Le T and De Paepe A: Classical Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
caused by a mutation in type I collagen. Am J Hum Genet.
66:1398–1402. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|