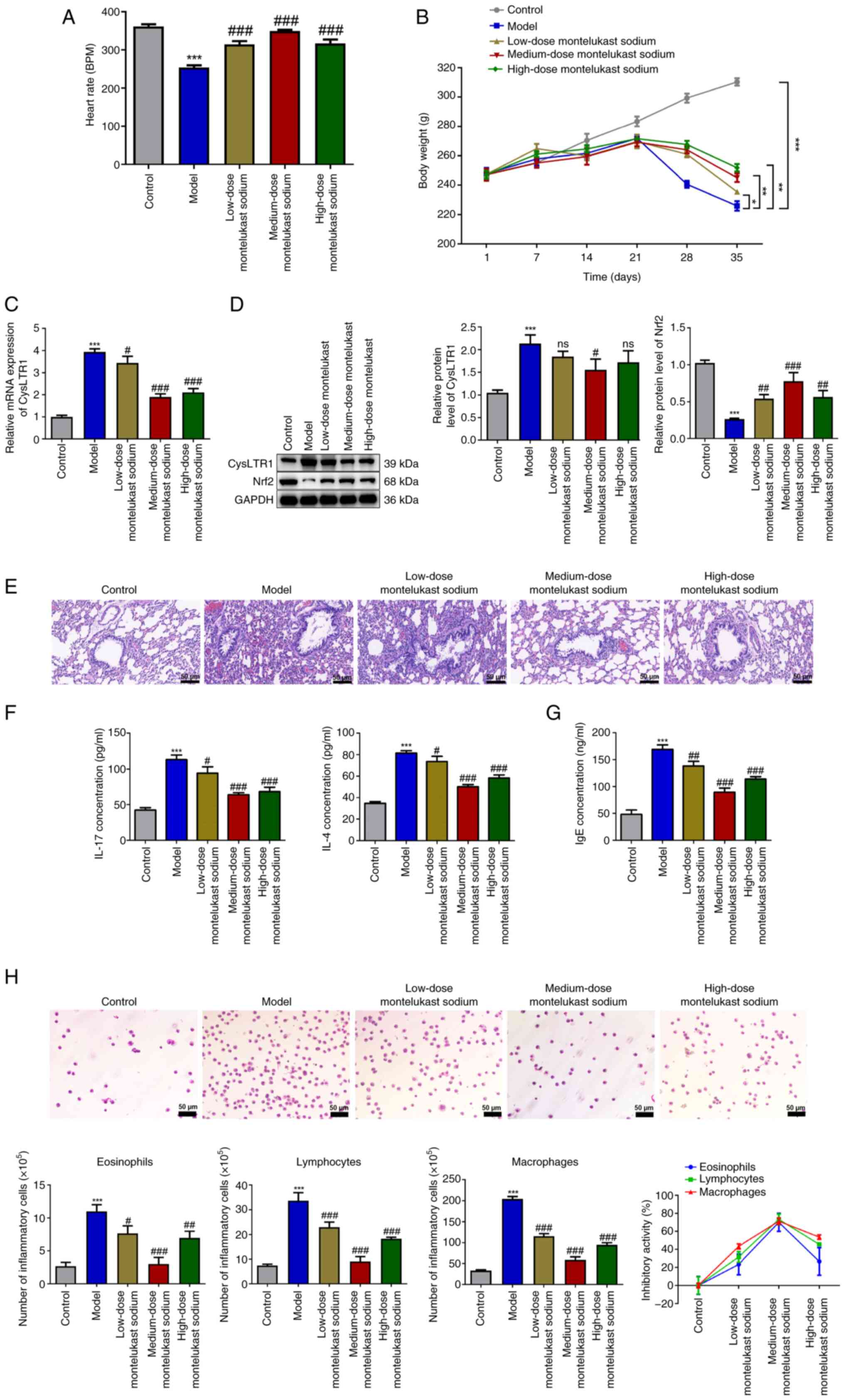
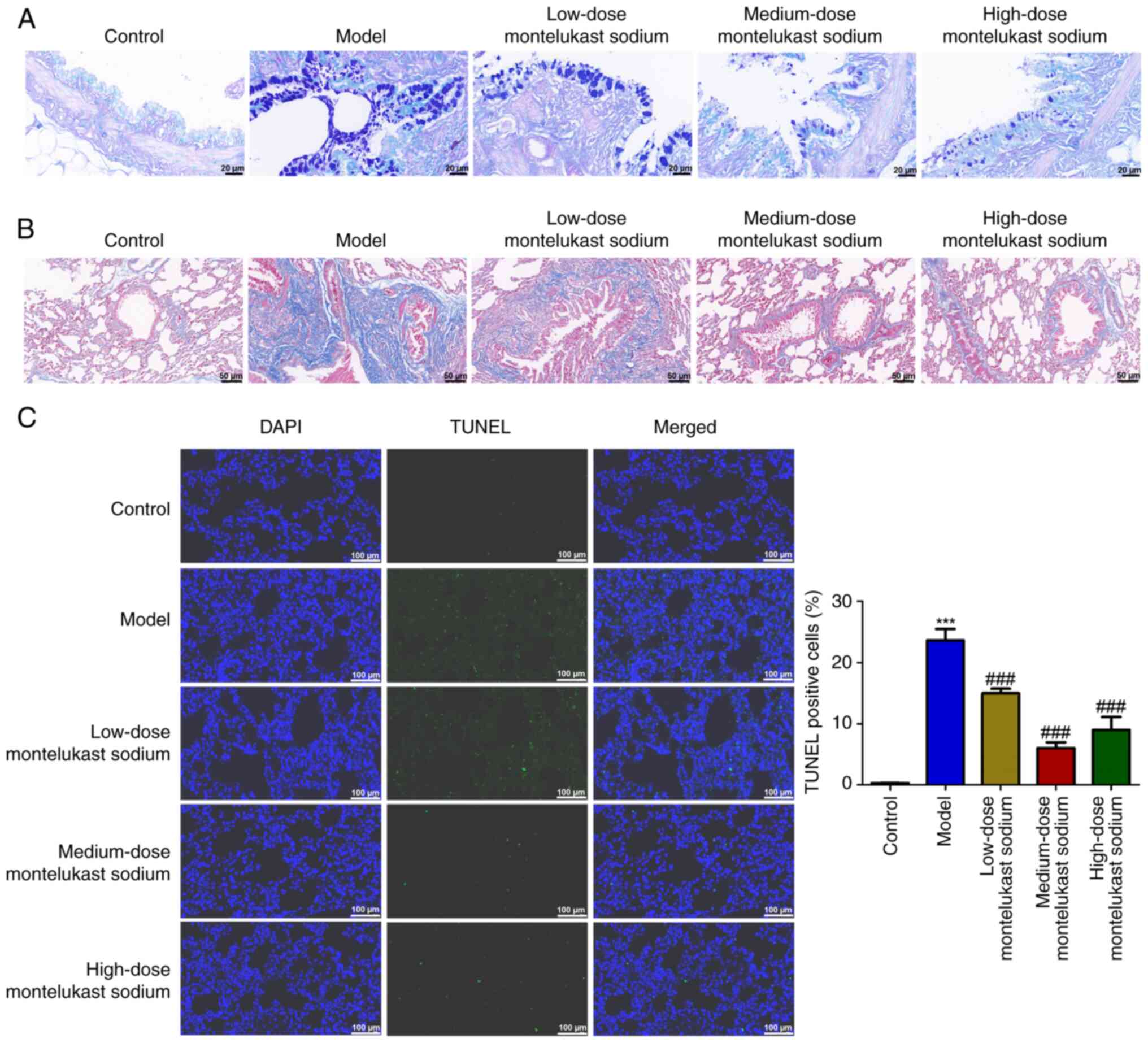
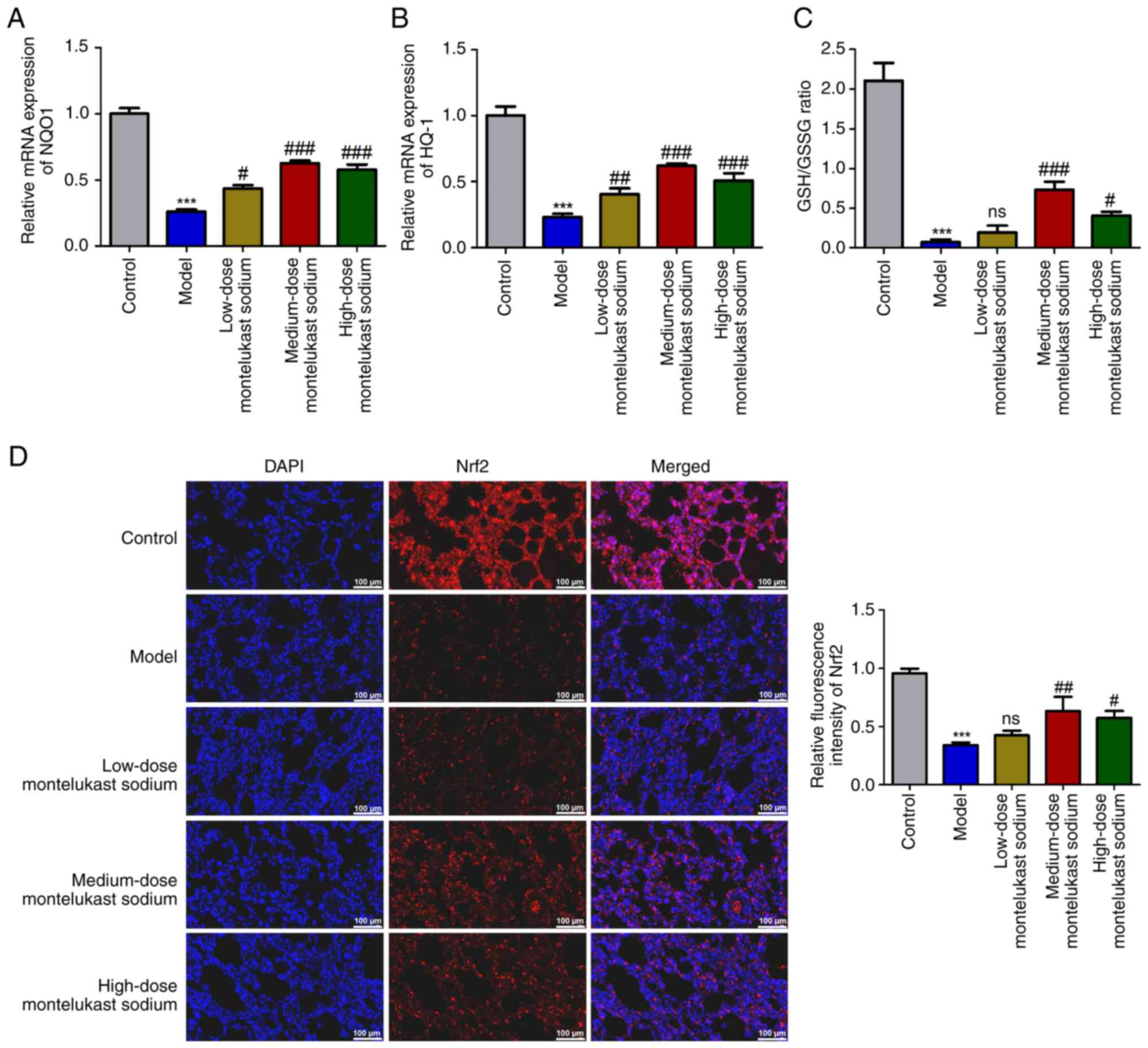
|
1
|
Cevhertas L, Ogulur I, Maurer DJ, Burla D,
Ding M, Jansen K, Koch J, Liu C, Ma S, Mitamura Y, et al: Advances
and recent developments in asthma in 2020. Allergy. 75:3124–3146.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Poon AH and Hamid Q: Severe Asthma: Have
we made progress? Ann Am Thorac Soc. 13 (Suppl 1):S68–S77.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Stern J, Pier J and Litonjua AA: Asthma
epidemiology and risk factors. Semin Immunopathol. 42:5–15.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
GBD 2019 Chronic Respiratory Diseases
Collaborators. Global burden of chronic respiratory diseases and
risk factors, 1990-2019: An update from the Global Burden of
Disease Study 2019. EClinicalMedicine. 59(101936)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Weinstock J, Chen XX, Nino G, Koumbourlis
A and Rastogi D: The interplay between airway epithelium and the
immune system-A primer for the respiratory clinician. Paediatr
Respir Rev. 38:2–8. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Miller RL, Grayson MH and Strothman K:
Advances in asthma: New understandings of asthma's natural history,
risk factors, underlying mechanisms, and clinical management. J
Allergy Clin Immunol. 148:1430–1441. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Yang Y, Jia M, Ou Y, Adcock IM and Yao X:
Mechanisms and biomarkers of airway epithelial cell damage in
asthma: A review. Clin Respir J. 15:1027–1045. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Yuan X, Wang E, Xiao X, Wang J, Yang X,
Yang P, Li G and Liu Z: The role of IL-25 in the reduction of
oxidative stress and the apoptosis of airway epithelial cells with
specific immunotherapy in an asthma mouse model. Am J Transl Res.
9:4137–4148. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Potaczek DP, Miethe S, Schindler V,
Alhamdan F and Garn H: Role of airway epithelial cells in the
development of different asthma phenotypes. Cell Signal.
69(109523)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Ngo V and Duennwald ML: Nrf2 and oxidative
stress: A general overview of mechanisms and implications in human
disease. Antioxidants (Basel). 11(2345)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Ahmed SA and Mohammed WI: Carvedilol
induces the antiapoptotic proteins Nrf(2) and Bcl(2) and inhibits
cellular apoptosis in aluminum-induced testicular toxicity in male
Wistar rats. Biomed Pharmacother. 139(111594)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Liu Q, Gao Y and Ci X: Role of Nrf2 and
its activators in respiratory diseases. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2019(7090534)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Helou DG, Noel B, Gaudin F, Groux H, El
Ali Z, Pallardy M, Chollet-Martin S and Kerdine-Römer S: Cutting
Edge: Nrf2 Regulates neutrophil recruitment and accumulation in
skin during contact hypersensitivity. J Immunol. 202:2189–2194.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Shintani Y, Maruoka S, Gon Y, Koyama D,
Yoshida A, Kozu Y, Kuroda K, Takeshita I, Tsuboi E, Soda K and
Hashimoto S: Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2)
regulates airway epithelial barrier integrity. Allergol Int. 64
(Suppl):S54–S63. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Hu J, Wang J, Li C and Shang Y:
Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase aggravates oxidative stress-induced
apoptosis in asthma by suppressing the Nrf2 pathway. J Cell Mol
Med. 25:5001–5014. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Sussan TE, Gajghate S, Chatterjee S,
Mandke P, McCormick S, Sudini K, Kumar S, Breysse PN, Diette GB,
Sidhaye VK and Biswal S: Nrf2 reduces allergic asthma in mice
through enhanced airway epithelial cytoprotective function. Am J
Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 309:L27–L36. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Zhang JH, Yang X, Chen YP, Zhang JF and Li
CQ: Nrf2 Activator RTA-408 Protects Against Ozone-Induced Acute
Asthma Exacerbation by Suppressing ROS and үδT17 Cells.
Inflammation. 42:1843–1856. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Yamamoto T, Miyata J, Arita M, Fukunaga K
and Kawana A: Current state and future prospect of the therapeutic
strategy targeting cysteinyl leukotriene metabolism in asthma.
Respir Investig. 57:534–543. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Papi A, Brightling C, Pedersen SE and
Reddel HK: Asthma. Lancet. 391:783–800. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
van der Burg N, Stenberg H, Bjermer L,
Diamant Z and Tufvesson E: Cysteinyl-leukotriene and prostaglandin
pathways in bronchial versus alveolar lavage in allergic
asthmatics. Allergy. 77:2549–2551. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Ban GY, Kim SH and Park HS: Persistent
eosinophilic inflammation in adult asthmatics with high serum and
urine levels of leukotriene E(4). J Asthma Allergy. 14:1219–1230.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Polomska J, Bar K and Sozanska B: Exhaled
Breath Condensate-A non-invasive approach for diagnostic methods in
asthma. J Clin Med. 10(2697)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
da Cunha AA, Silveira JS, Antunes GL,
Abreu da Silveira K, Benedetti Gassen R, Vaz Breda R and Márcio
Pitrez P: Cysteinyl leukotriene induces eosinophil extracellular
trap formation via cysteinyl leukotriene 1 receptor in a murine
model of asthma. Exp Lung Res. 47:355–367. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Israel E, Chervinsky PS, Friedman B, Van
Bavel J, Skalky CS, Ghannam AF, Bird SR and Edelman JM: Effects of
montelukast and beclomethasone on airway function and asthma
control. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 110:847–854. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Quaranta VN, Dragonieri S, Crimi N, Crimi
C, Santus P, Menzella F, Pelaia C, Scioscia G, Caruso C, Bargagli
E, et al: Can leukotriene receptor antagonist therapy improve the
control of patients with severe asthma on biological therapy and
coexisting bronchiectasis? A Pilot Study. J Clin Med.
11(4702)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Miyata J, Fukunaga K, Kawashima Y, Ohara O
and Arita M: Cysteinyl leukotriene metabolism of human eosinophils
in allergic disease. Allergol Int. 69:28–34. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Meshram D, Bhardwaj K, Rathod C, Mahady GB
and Soni KK: The role of leukotrienes inhibitors in the management
of chronic inflammatory diseases. Recent Pat Inflamm Allergy Drug
Discov. 14:15–31. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Dholia N, Sethi GS, Naura AS and Yadav
UCS: Cysteinyl leukotriene D(4) (LTD(4)) promotes airway epithelial
cell inflammation and remodelling. Inflamm Res. 70:109–126.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Chen X, Peng W, Zhou R, Zhang Z and Xu J:
Montelukast improves bronchopulmonary dysplasia by inhibiting
epithelial-mesenchymal transition via inactivating the TGF-β1/Smads
signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep. 22:2564–2572. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Du C, Zhang Q, Wang L, Wang M, Li J and
Zhao Q: Effect of montelukast sodium and graphene oxide
nanomaterials on mouse asthma model. J Nanosci Nanotechnol.
21:1161–1168. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Fei X, Zhang X, Zhang GQ, Bao WP, Zhang
YY, Zhang M and Zhou X: Cordycepin inhibits airway remodeling in a
rat model of chronic asthma. Biomed Pharmacother. 88:335–341.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Bai F, Fang L, Hu H, Yang Y, Feng X and
Sun D: Vanillic acid mitigates the ovalbumin (OVA)-induced asthma
in rat model through prevention of airway inflammation. Biosci
Biotechnol Biochem. 83:531–537. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Bianchi M and Panerai AE:
Anti-hyperalgesic effects of tramadol in the rat. Brain Res.
797:163–166. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Costa PPC, Waller SB, Dos Santos GR,
Gondim FL, Serra DS, Cavalcante FSÁ, Gouveia Júnior FS, de Paula
Júnior VF, Sousa EHS, Lopes LGF, et al: Anti-asthmatic effect of
nitric oxide metallo-donor FOR811A
[cis-[Ru(bpy)2(2-MIM)(NO)](PF6)3] in the respiratory mechanics of
Swiss mice. PLoS One. 16(e0248394)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Jurisic V: Multiomic analysis of cytokines
in immuno-oncology. Expert Rev Proteomics. 17:663–674.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Vuletic A, Konjevic G, Milanovic D,
Ruzdijic S and Jurisic V: Antiproliferative effect of
13-cis-retinoic acid is associated with granulocyte differentiation
and decrease in cyclin B1 and Bcl-2 protein levels in G0/G1
arrested HL-60 cells. Pathol Oncol Res. 16:393–401. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Jurisic V, Srdic-Rajic T, Konjevic G,
Bogdanovic G and Colic M: TNF-alpha induced apoptosis is
accompanied with rapid CD30 and slower CD45 shedding from K-562
cells. J Membr Biol. 239:115–122. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Thornton CA, Holloway JA, Popplewell EJ,
Shute JK, Boughton J and Warner JO: Fetal exposure to intact
immunoglobulin E occurs via the gastrointestinal tract. Clin Exp
Allergy. 33:306–311. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Alobaidi AH, Alsamarai AM and Alsamarai
MA: Inflammation in asthma pathogenesis: Role of T cells,
macrophages, epithelial cells and type 2 inflammation. Antiinflamm
Antiallergy Agents Med Chem. 20:317–332. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Zeki AA, Bratt JM, Rabowsky M, Last JA and
Kenyon NJ: Simvastatin inhibits goblet cell hyperplasia and lung
arginase in a mouse model of allergic asthma: A novel treatment for
airway remodeling? Transl Res. 156:335–349. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Yamauchi K and Inoue H: Airway remodeling
in asthma and irreversible airflow limitation-ECM deposition in
airway and possible therapy for remodeling. Allergol Int.
56:321–329. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Poprac P, Jomova K, Simunkova M, Kollar V,
Rhodes CJ and Valko M: Targeting free radicals in oxidative
stress-related human diseases. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 38:592–607.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Pandey V, Yadav V, Singh R, Srivastava A
and Subhashini : β-Endorphin (an endogenous opioid) inhibits
inflammation, oxidative stress and apoptosis via Nrf-2 in asthmatic
murine model. Sci Rep. 13(12414)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Ozdermir C, Kucuksezer UC, Ogulur I, Pat
Y, Yazici D, Ardicli S, Akdis M, Nadeau K and Akdis CA: Lifestyle
changes and industrialization in the development of allergic
diseases. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 24:331–345. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Agache I, Eguiluz-Gracia I, Cojanu C,
Laculiceanu A, Del Giacco S, Zemelka-Wiacek M, Kosowska A, Akdis CA
and Jutel M: Advances and highlights in asthma in 2021. Allergy.
76:3390–3407. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Patel SJ and Teach SJ: Asthma. Pediatr
Rev. 40:549–567. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Kumar RK, Herbert C and Foster PS: The
‘classical’ ovalbumin challenge model of asthma in mice. Curr Drug
Targets. 9:485–494. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Nakagome K and Nagata M: Involvement and
possible role of eosinophils in asthma exacerbation. Front Immunol.
9(2220)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Garcia G, Taille C, Laveneziana P, Bourdin
A, Chanez P and Humbert M: Anti-interleukin-5 therapy in severe
asthma. Eur Respir Rev. 22:251–257. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Price DB, Rigazio A, Campbell JD, Bleecker
ER, Corrigan CJ, Thomas M, Wenzel SE, Wilson AM, Small MB, Gopalan
G, et al: Blood eosinophil count and prospective annual asthma
disease burden: A UK cohort study. Lancet Respir Med. 3:849–858.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Ying S, Meng Q, Zeibecoglou K, Robinson
DS, Macfarlane A, Humbert M and Kay AB: Eosinophil chemotactic
chemokines (eotaxin, eotaxin-2, RANTES, monocyte chemoattractant
protein-3 (MCP-3), and MCP-4), and C-C chemokine receptor 3
expression in bronchial biopsies from atopic and nonatopic
(Intrinsic) asthmatics. J Immunol. 163:6321–6329. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Poowuttikul P, Saini S and Seth D:
Inner-City Asthma in Children. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol.
56:248–268. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Matucci A, Vultaggio A, Maggi E and
Kasujee I: Is IgE or eosinophils the key player in allergic asthma
pathogenesis? Are we asking the right question? Respir Res.
19(113)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Kanaoka Y and Boyce JA: Cysteinyl
leukotrienes and their receptors: Cellular distribution and
function in immune and inflammatory responses. J Immunol.
173:1503–1510. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Zhou X, Cai J, Liu W, Wu X and Gao C:
Cysteinyl leukotriene receptor type 1 (CysLT1R) antagonist
zafirlukast protects against TNF-α-induced endothelial
inflammation. Biomed Pharmacother. 111:452–459. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Patel B, Gupta N and Ahsan F: Aerosolized
montelukast polymeric particles-an alternative to oral
montelukast-alleviate symptoms of asthma in a rodent model. Pharm
Res. 31:3095–3105. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Basyigit I, Sahin M, Sahin D, Yildiz F,
Boyaci H, Sirvanci S and Ercan F: Anti-inflammatory effects of
montelukast on smoke-induced lung injury in rats. Multidiscip
Respir Med. 5:92–98. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Wu AY, Chik SC, Chan AW, Li Z, Tsang KW
and Li W: Anti-inflammatory effects of high-dose montelukast in an
animal model of acute asthma. Clin Exp Allergy. 33:359–366.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Wu Y, Zhou C, Tao J and Li S: Montelukast
prevents the decrease of interleukin-10 and inhibits NF-kappaB
activation in inflammatory airway of asthmatic guinea pigs. Can J
Physiol Pharmacol. 84:531–537. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Abdel Aziz RR, Helaly NY, Zalata KR and
Gameil NM: Influence of inhaled beclomethasone and montelukast on
airway remodeling in mice. Inflammopharmacology. 21:55–66.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Holgate ST, Peters-Golden M, Panettieri RA
and Henderson WR Jr: Roles of cysteinyl leukotrienes in airway
inflammation, smooth muscle function, and remodeling. J Allergy
Clin Immunol. 111 (1 Suppl):S18–S34; discussion S34-16.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Berair R, Hartley R, Mistry V, Sheshadri
A, Gupta S, Singapuri A, Gonem S, Marshall RP, Sousa AR, Shikotra
A, et al: Associations in asthma between quantitative computed
tomography and bronchial biopsy-derived airway remodelling. Eur
Respir J. 49(1601507)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Jurisic V, Bogdanovic G, Kojic V, Jakimov
D and Srdic T: Effect of TNF-alpha on Raji cells at different
cellular levels estimated by various methods. Ann Hematol.
85:86–94. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Jurisic V, Terzic T, Colic S and Jurisic
M: The concentration of TNF-alpha correlate with number of
inflammatory cells and degree of vascularization in radicular
cysts. Oral Dis. 14:600–605. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Jurisic V, Bumbasirevic V, Konjevic G,
Djuricic B and Spuzic I: TNF-alpha induces changes in LDH isotype
profile following triggering of apoptosis in PBL of non-Hodgkin's
lymphomas. Ann Hematol. 83:84–91. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Michaeloudes C, Abubakar-Waziri H, Lakhdar
R, Raby K, Dixey P, Adcock IM, Mumby S, Bhavsar PK and Chung KF:
Molecular mechanisms of oxidative stress in asthma. Mol Aspects
Med. 85(101026)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Audousset C, McGovern T and Martin JG:
Role of Nrf2 in Disease: Novel molecular mechanisms and therapeutic
approaches-pulmonary disease/asthma. Front Physiol.
12(727806)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Yachie A: Heme oxygenase-1 deficiency and
oxidative stress: A review of 9 independent human cases and animal
models. Int J Mol Sci. 22(1514)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Ross D and Siegel D: The diverse
functionality of NQO1 and its roles in redox control. Redox Biol.
41(101950)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|