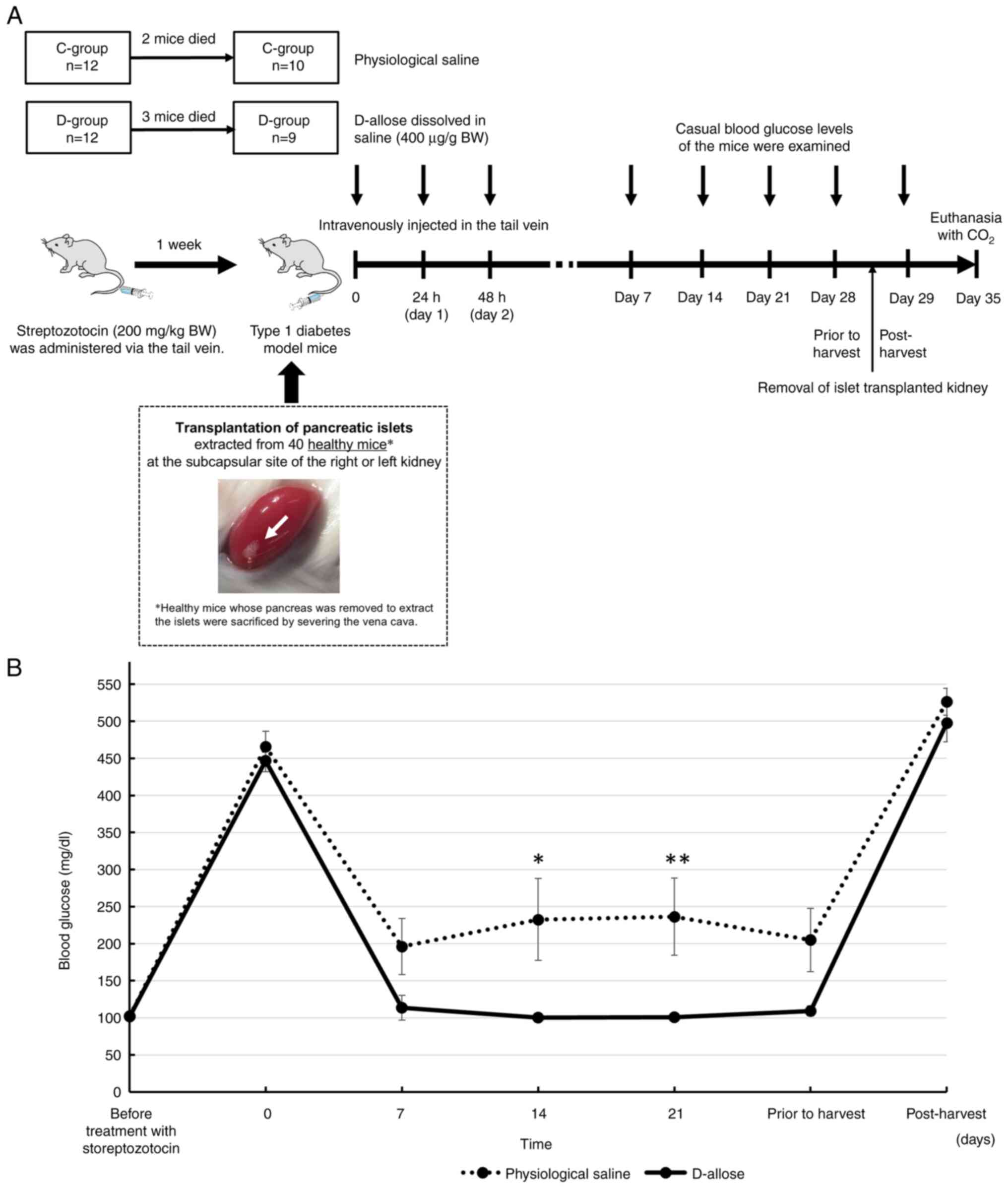
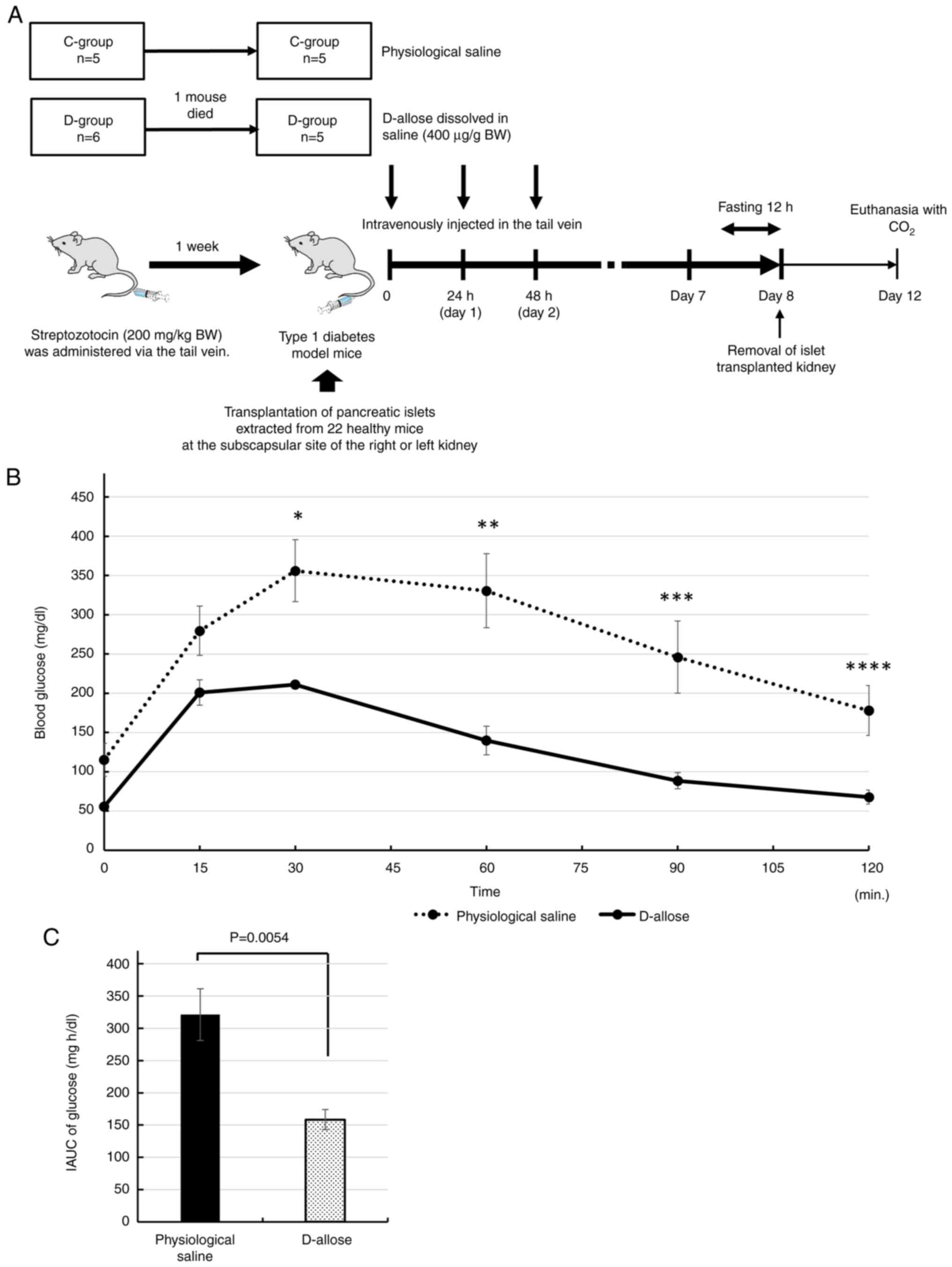
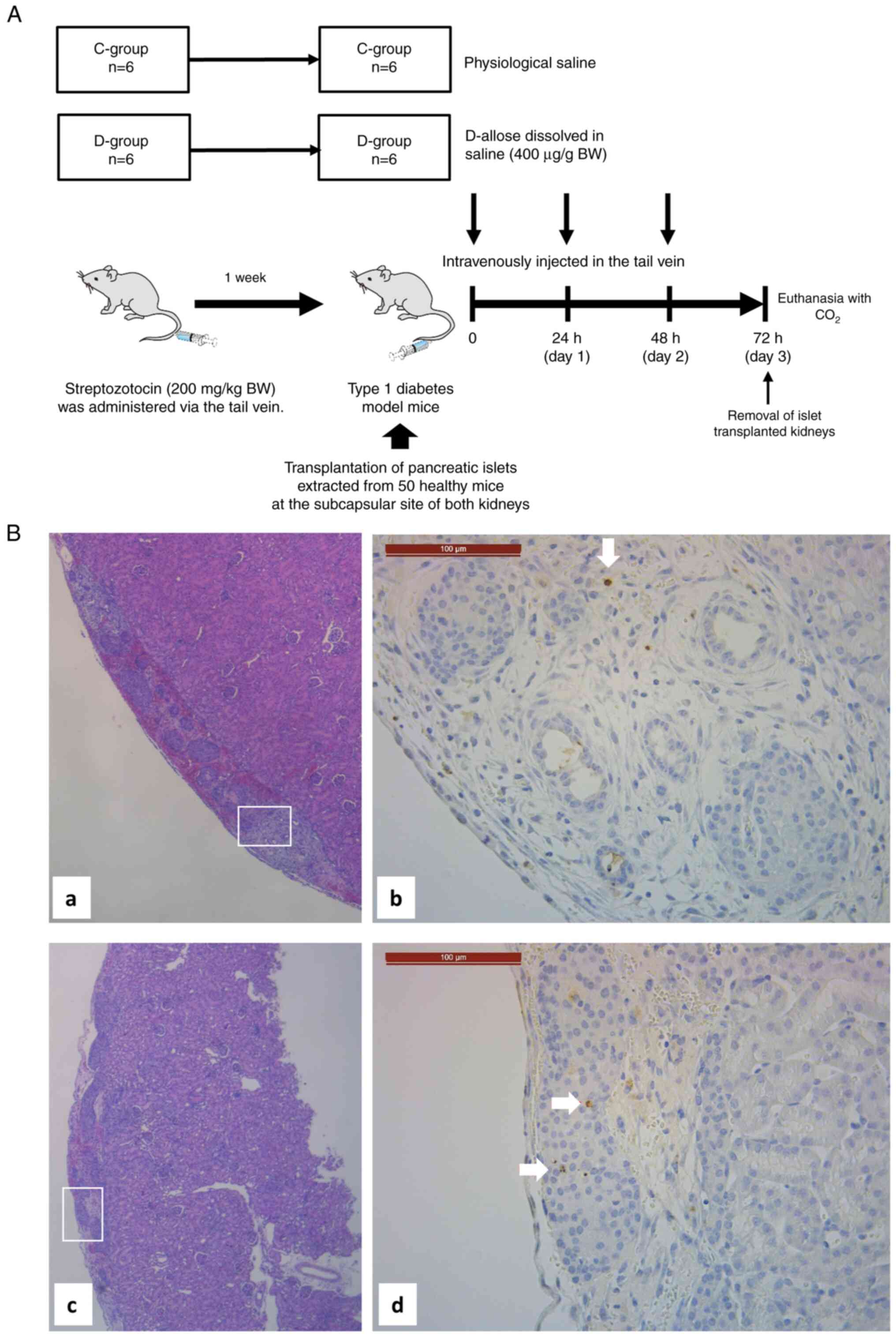
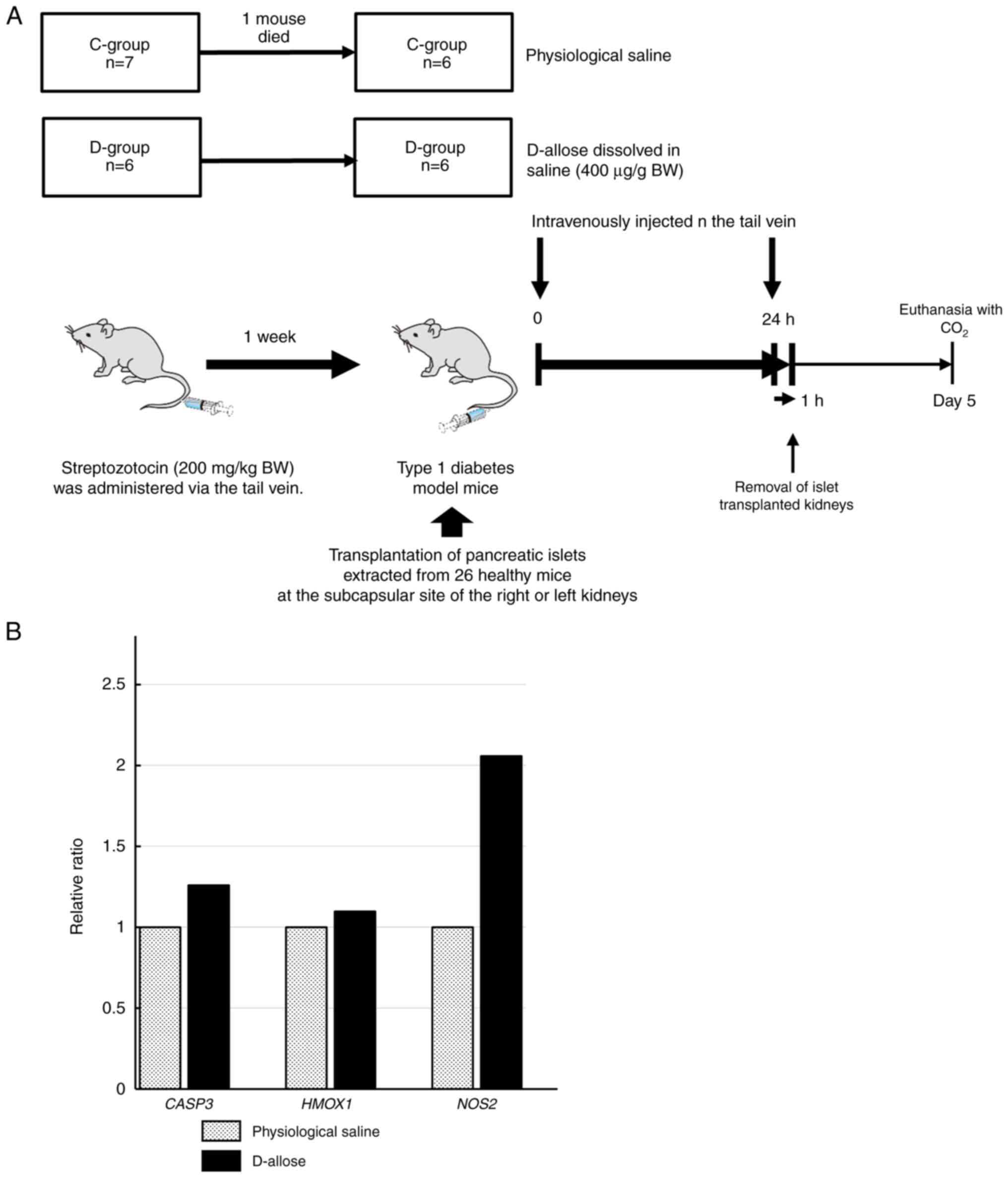
|
1
|
Barton FB, Rickels MR, Alejandro R, Hering
BJ, Wease S, Naziruddin B, Oberholzer J, Odorico JS, Garfinkel MR,
Lev M, et al: Improvement in outcomes of clinical islet
transplantation: 1999-2010. Diabetes Care. 35:1436–1445.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Shapiro AM, Lakey JR, Ryan EA, Korbutt GS,
Toth E, Warnock GL, Kneteman NM and Rajotte RV: Islet
transplantation in seven patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus
using a glucocorticoid-free immunosuppressive regimen. N Engl J
Med. 343:230–238. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Shapiro AM, Ricordi C, Hering BJ,
Auchincloss H, Lindblad R, Robertson RP, Secchi A, Brendel MD,
Berney T, Brennan DC, et al: International trial of the Edmonton
protocol for islet transplantation. N Engl J Med. 355:1318–1830.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Ryan EA, Paty BW, Senior PA, Bigam D,
Alfadhli E, Kneteman NM, Lakey JR and Shapiro AM: Five-year
follow-up after clinical islet transplantation. Diabetes.
54:2060–2069. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Bellin MD, Barton FB, Heitman A, Harmon
JV, Kandaswamy R, Balamurugan AN, Sutherland DE, Alejandro R and
Hering BJ: Potent induction immunotherapy promotes long-term
insulin independence after islet transplantation in type 1
diabetes. Am J Transplant. 12:1576–1583. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Izumori K: Izumoring: A strategy for
bioproduction of all hexoses. J Biotechnol. 124:717–722.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Murata A, Sekiya K, Watanabe Y, Yamaguchi
F, Hatano N, Izumori K and Tokuda M: A novel inhibitory effect of
D-allose on production of reactive oxygen species from neutrophils.
J Biosci Bioeng. 96:89–91. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Hossain MA, Wakabayashi H, Goda F,
Kobayashi S, Maeba T and Maeta H: Effect of the immunosuppressants
FK506 and D-allose on allogenic orthotopic liver transplantation in
rats. Transplant Proc. 32:2021–2023. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Hossain MA, Izuishi K and Maeta H:
Protective effects of D-allose against ischemia reperfusion injury
of the rat liver. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 10:218–225.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Gao D, Kawai N, Nakamura T, Lu F, Fei Z
and Tamiya T: Anti-inflammatory effect of D-allose in cerebral
ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo).
53:365–374. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Huang T, Gao D, Hei Y, Zhang X, Chen X and
Fei Z: D-allose protects the blood brain barrier through
PPARγ-mediated anti-inflammatory pathway in the mice model of
ischemia reperfusion injury. Brain Res. 1642:478–486.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Muneuchi G, Hossain A, Yamaguchi F, Ueno
M, Tanaka Y, Suzuki S and Tokuda M: The rare sugar D-allose has a
reducing effect against ischemia-reperfusion injury on the rat
abdominal skin island flap model. J Surg Res. 183:976–981.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Ju J, Hou R and Zhang P: D-allose
alleviates ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury in skin flap via
MKP-1. Mol Med. 26(21)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Kashiwagi H, Asano E, Noguchi C, Sui L,
Hossain A, Akamoto S, Okano K, Tokuda M and Suzuki Y: Beneficial
effect of D-allose for isolated islet culture prior to islet
transplantation. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 23:37–42.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
American Veterinary Medical Association
(AVMA): AVMA guidelines for the euthanasia of animals: 2013
edition. AVMA, Schaumburg, Il, 2013. https://www.in.gov/boah/files/AVMA_Euthanasia_Guidelines.pdf.
|
|
16
|
Ueki M, Taie S, Chujo K, Asaga T, Iwanaga
Y and Maekawa N: Inhibitory effect of d-allose on neutrophil
activation after rat renal ischemia/reperfusion. J Biosci Bioeng.
104:304–308. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Nakamura T, Tanaka S, Hirooka K, Toyoshima
T, Kawai N, Tamiya T, Shiraga F, Tokuda M, Keep RF, Itano T and
Miyamoto O: Anti-oxidative effects of d-allose, a rare sugar, on
ischemia-reperfusion damage following focal cerebral ischemia in
rat. Neurosci Lett. 487:103–106. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Wolever TM and Jenkins DJ: The use of the
glycemic index in predicting the blood glucose response to mixed
meals. Am J Clin Nutr. 43:167–172. 1986.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: . Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Hashimoto F, Nishiumi S, Miyake O,
Takeichi H, Chitose M, Ohtsubo H, Ishimori S, Ninchoji T, Hashimura
Y, Kaito H, et al: Metabolomics analysis of umbilical cord blood
clarifies changes in saccharides associated with delivery method.
Early Hum Dev. 89:315–320. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Hossain A, Yamaguchi F, Matsuo T,
Tsukamoto I, Toyoda Y, Ogawa M, Nagata Y and Tokuda M: Rare sugar
D-allulose: Potential role and therapeutic monitoring in
maintaining obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Pharmacol Ther.
155:49–59. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Iwasaki Y, Sendo M, Dezaki K, Hira T, Sato
T, Nakata M, Goswami C, Aoki R, Arai T, Kumari P, et al: GLP-1
release and vagal afferent activation mediate the beneficial
metabolic and chronotherapeutic effects of D-allulose. Nat Commun.
9(113)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Kunjathoor VV, Wilson DL and LeBoeuf RC:
Increased atherosclerosis in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice.
J Clin Invest. 97:1767–1773. 1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Eich T, Eriksson O and Lundgren T: Nordic
Network for Clinical Islet Transplantation. Visualization of early
engraftment in clinical islet transplantation by positron-emission
tomography. N Engl J Med. 356:2754–2755. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Nir T, Melton DA and Dor Y: Recovery from
diabetes in mice by beta cell regeneration. J Clin Invest.
117:2553–2561. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Sassa S: Biological implication of heme
metabolism. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 38:138–155. 2006.
|
|
27
|
Chang M, Xue J, Sharma V and Habtezion A:
Protective role of hemeoxygenase-1 in gastrointestinal diseases.
Cell Mol Life Sci. 72:1161–1173. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Broniowska KA, Oleson BJ and Corbett JA:
β-Cell responses to nitric oxide. Vitam Horm. 95:299–322.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Panagiotidis G, Akesson B, Rydell EL and
Lundquist I: Influence of nitric oxide synthase inhibition, nitric
oxide and hydroperoxide on insulin release induced by various
secretagogues. Br J Pharmacol. 114:289–296. 1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Atiya A, Cohen G, Ignarro L and Brunicardi
FC: Nitric oxide regulates insulin secretion in the isolated
perfused human pancreas via a cholinergic mechanism. Surgery.
120:322–327. 1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Coiro V, Volpi R, Capretti L, Speroni G,
Caffarri G and Chiodera P: Involvement of nitric oxide in arginine,
but not glucose, induced insulin secretion in normal men. Clin
Endocrinol (Oxf). 46:115–119. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Kaneko Y, Ishikawa T, Amano S and Nakayama
K: Dual effect of nitric oxide on cytosolic Ca2+ concentration and
insulin secretion in rat pancreatic beta-cells. Am J Physiol Cell
Physiol. 284:C1215–C1222. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Luo Y, Cheng J, Fu Y, Zhang M, Gou M, Li
J, Li X, Bai J, Zhou Y, Zhang L and Gao D: D-allose inhibits
TLR4/PI3K/AKT signaling to attenuate neuroinflammation and neuronal
apoptosis by inhibiting Gal-3 following ischemic stroke. Biol
Proced Online. 25(30)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Auer VJ, Janas E, Ninichuk V, Eppler E,
Weiss TS, Kirchner S, Otto AM and Stangl MJ: Extracellular factors
and immunosuppressive drugs influencing insulin secretion of murine
islets. Clin Exp Immunol. 170:238–247. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Rossini AA, Williams RM, Appel MC and Like
AA: Sex differences in the multiple-dose streptozotocin model of
diabetes. Endocrinology. 103:1518–1520. 1978.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Paik SG, Michelis MA, Kim YT and Shin S:
Induction of insulin-dependent diabetes by streptozotocin.
Inhibition by estrogens and potentiation by androgens. Diabetes.
31:724–729. 1982.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Deeds MC, Anderson JM, Armstrong AS,
Gastineau DA, Hiddinga HJ, Jahangir A, Eberhardt NL and Kudva YC:
Single dose streptozotocin-induced diabetes: Considerations for
study design in islet transplantation models. Lab Anim. 45:131–140.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Jindal RM, Sidner RA, McDaniel HB, Johnson
MS and Fineberg SE: Intraportal vs kidney subcapsular site for
human pancreatic islet transplantation. Transplant Proc.
30:398–399. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Fujikura J, Anazawa T, Toyoda T, Ito R,
Kimura Y and Yabe D: Toward a cure for diabetes: iPSC and
ESC-derived islet cell transplantation trials. J Diabetes Investig.
22(14366)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Iga Y, Nakamichi K, Shirai Y and Matsuo T:
Acute and sub-chronic toxicity of D-allose in rats. Biosci
Biotechnol Biochem. 74:1476–1478. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Shintani T, Yanai S, Kanasaki A, Tanaka M,
Iida T, Ozawa G, Kunihiro T and Endo S: Long-term D-allose
administration favorably alters the intestinal environment in aged
male mice. J Appl Glycosci. 69:97–102. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|