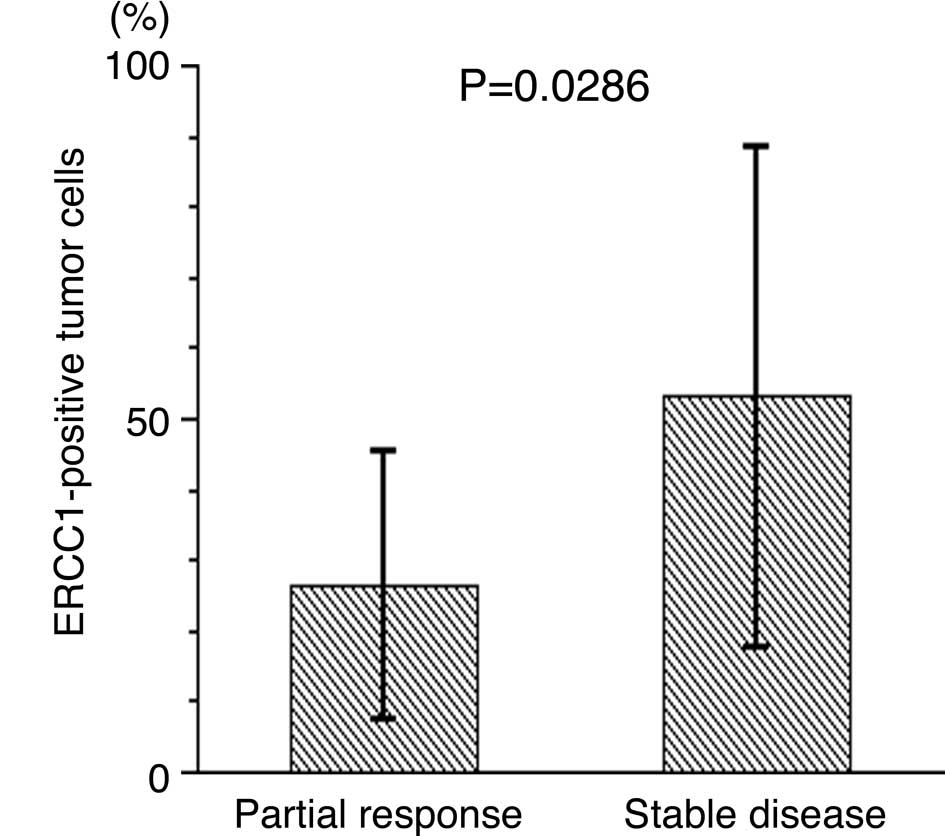
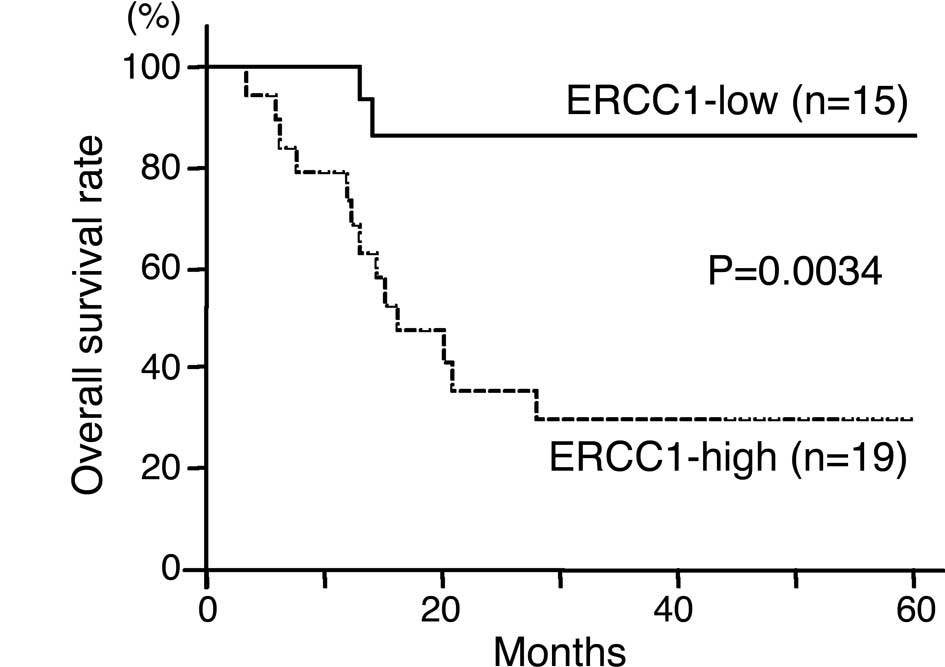
|
1.
|
Arriagada R, Bergman B, Dunant A, et al:
Cisplatin-based chemotherapy in patients with completely resected
non-small cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 350:351–360. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Winton T, Livingston R, Johnson D, et al:
Vinorelbine plus cisplatin vs. observation in resected non-small
cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 352:2589–2597. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3.
|
Hotta K, Matsuo K, Ueoka H, Kiura K,
Tabata M and Tanimoto M: Role of adjuvant chemotherapy in patients
with resected non-small cell lung cancer: reappraisal with a
meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Clin Oncol.
22:3860–3867. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Huang C, Liu D, Masuya D, Nakashima T,
Kameyama K, Ishikawa S, Ueno M, Haba R and Yokomise H: Clinical
application of biological markers for treatments of resectable
non-small cell lung cancers. Br J Cancer. 92:1231–1239. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Bepler G: Using translational research to
tailor the use of chemotherapy in the treatment of NSCLC. Lung
Cancer. 50:S13–S14. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Huang C, Yokomise H, Fukushima M and
Kinoshita M: Tailor-made chemotherapy for non-small cell lung
cancer patients. Future Oncol. 2:289–299. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Mitsudomi T, Kosaka T, Endoh H, Horio Y,
Hida T, Mori S, Hatooka S, Shinoda M, Takahashi T and Yatabe Y:
Mutations of the epidermal growth factor receptor gene predict
prolonged survival after gefitinib treatment in patients with
non-small cell lung cancer with postoperative recurrence. J Clin
Oncol. 23:2513–2520. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8.
|
Nakano J, Huang C, Liu D, Masuya D,
Nakashima T, Yokomise H, Ueno M, Wada H and Fukushima M:
Evaluations of biomarkers associated with 5-FU sensitivity for
non-small cell lung cancer patients postoperatively treated with
UFT. Br J Cancer. 95:607–615. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Lord RV, Brabender J, Gandara D, et al:
Low ERCC1 expression correlates with prolonged survival after
cisplatin plus gemcitabine chemotherapy in non-small cell lung
cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 8:2286–2291. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Olaussen KA, Dunant A, Fouret P, et al:
DNA repair by ERCC1 in non-small cell lung cancer and
cisplatin-based adjuvant chemotherapy. N Engl J Med. 355:983–991.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Metzger R, Leichman CG, Danenberg KD, et
al: ERCC1 mRNA levels complement thymidylate synthase mRNA levels
in predicting response and survival for gastric cancer patients
receiving combination cisplatin and fluorouracil chemotherapy. J
Clin Oncol. 16:309–316. 1998.
|
|
12.
|
Shirota Y, Stoehlmacher J, Brabender J,
Xiong YP, Uetake H, Danenberg KD, Groshen S, Tsao-Wei DD, Danenberg
PV and Lenz HJ: ERCC1 and thymidylate synthase mRNA levels predict
survival for colorectal cancer patients receiving combination
oxaliplatin and fluorouracil chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol.
19:4298–4304. 2001.
|
|
13.
|
Seve P, Mackey J, Isaac S, Tredan O,
Souquet PJ, Perol M, Lai R, Voloch A and Dumontet C: Class III
β-tubulin expression in tumor cells predicts response and outcome
in patients with non-small cell lung cancer receiving paclitaxel.
Mol Cancer Ther. 4:2001–2007. 2005.
|
|
14.
|
Mozzetti S, Ferlini C, Concolino P, et al:
Class III β-tubulin overexpression is a prominent mechanism of
paclitaxel resistance in ovarian cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res.
11:298–305. 2005.
|
|
15.
|
Paradiso A, Mangia A, Chiriatti A, Tommasi
S, Zito A, Latorre A, Schittulli F and Lorusso V: Biomarkers
predictive for clinical efficacy of taxol-based chemotherapy in
advanced breast cancer. Ann Oncol. 16(Suppl 4): 14–19. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Yokomise H, Gotoh M, Okamoto T, Yamamoto
Y, Ishikawa S, Nakashima T, Masuya D, Liu D and Huang CL: Induction
chemoradiotherapy (carboplatin-taxane and concurrent 50-Gy
radiation) for bulky cN2,N3 non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac
Cardiovasc Surg. 133:1179–1185. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Therasse P, Arbuck SG, Eisenhauer EA, et
al: New guidelines to evaluate the response to treatment in solid
tumors. European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer
National Cancer Institute of the United States, National Cancer
Institute of Canada. J Natl Cancer Inst. 92:205–216. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18.
|
The Japanese Lung Cancer Society. Rule for
Clinical and Pathological Record of Lung Cancer. 6th edition.
Kanehara; Tokyo: pp. 168–169. 2003
|
|
19.
|
Rosell R, Taron M, Barnadas A, Scagliotti
G, Sarries C and Roig B: Nucleotide excision repair pathways
involved in cisplatin resistance in non-small cell lung cancer.
Cancer Control. 10:297–305. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Rigas JR: Taxane-platinum combinations in
advanced non-small cell lung cancer: a review. Oncologist. 9:16–23.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Kelly K, Crowley J, Bunn PA Jr, et al:
Randomized phase III trial of paclitaxel plus carboplatin versus
vinorelbine plus cisplatin in the treatment of patients with
advanced non-small cell lung cancer: a Southwest Oncology Group
trial. J Clin Oncol. 19:3210–3218. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Burkhart CA, Kavallaris M and Horwitz SB:
The role of β-tubulin isotypes in resistance to antimitotic drugs.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1471:1–9. 2001.
|
|
23.
|
Jordan MA and Wilson L: Microtubules as a
target for anticancer drugs. Nat Rev Cancer. 4:253–265. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Katsetos CD, Legido A, Perentes E and Mork
SJ: Class III β-tubulin isotype: a key cytoskeletal protein at the
crossroads of developmental neurobiology and tumor neuropathology.
J Child Neurol. 18:851–866. 2003.
|
|
25.
|
Lu Q and Luduena RF: Removal of β-III
isotype enhances taxol induced microtubule assembly. Cell Struct
Funct. 18:173–182. 1993.
|
|
26.
|
Kamath K, Wilson L, Cabral F and Jordan
MA: β III-tubulin induces paclitaxel resistance in association with
reduced effects on microtubule dynamic instability. J Biol Chem.
280:12902–12907. 2005.
|
|
27.
|
Derry WB, Wilson L, Khan IA, Luduena RF
and Jordan MA: Taxol differentially modulates the dynamics of
microtubules assembled from unfractionated and purified β-tubulin
isotypes. Biochemistry. 36:3554–3562. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Hari M, Yang H, Zeng C, Canizales M and
Cabral F: Expression of class III β-tubulin reduces microtubule
assembly and confers resistance to paclitaxel. Cell Motil
Cytoskeleton. 56:45–56. 2003.
|
|
29.
|
Kavallaris M, Kuo DY, Burkhart CA, Regl
DL, Norris MD, Haber M and Horwitz SB: Taxol-resistant epithelial
ovarian tumors are associated with altered expression of specific
β-tubulin isotypes. J Clin Invest. 100:1282–1293. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Ranganathan S, Benetatos CA, Colarusso PJ,
Dexter DW and Hudes GR: Altered β-tubulin isotype expression in
paclitaxel-resistant human prostate carcinoma cells. Br J Cancer.
77:562–566. 1998.
|