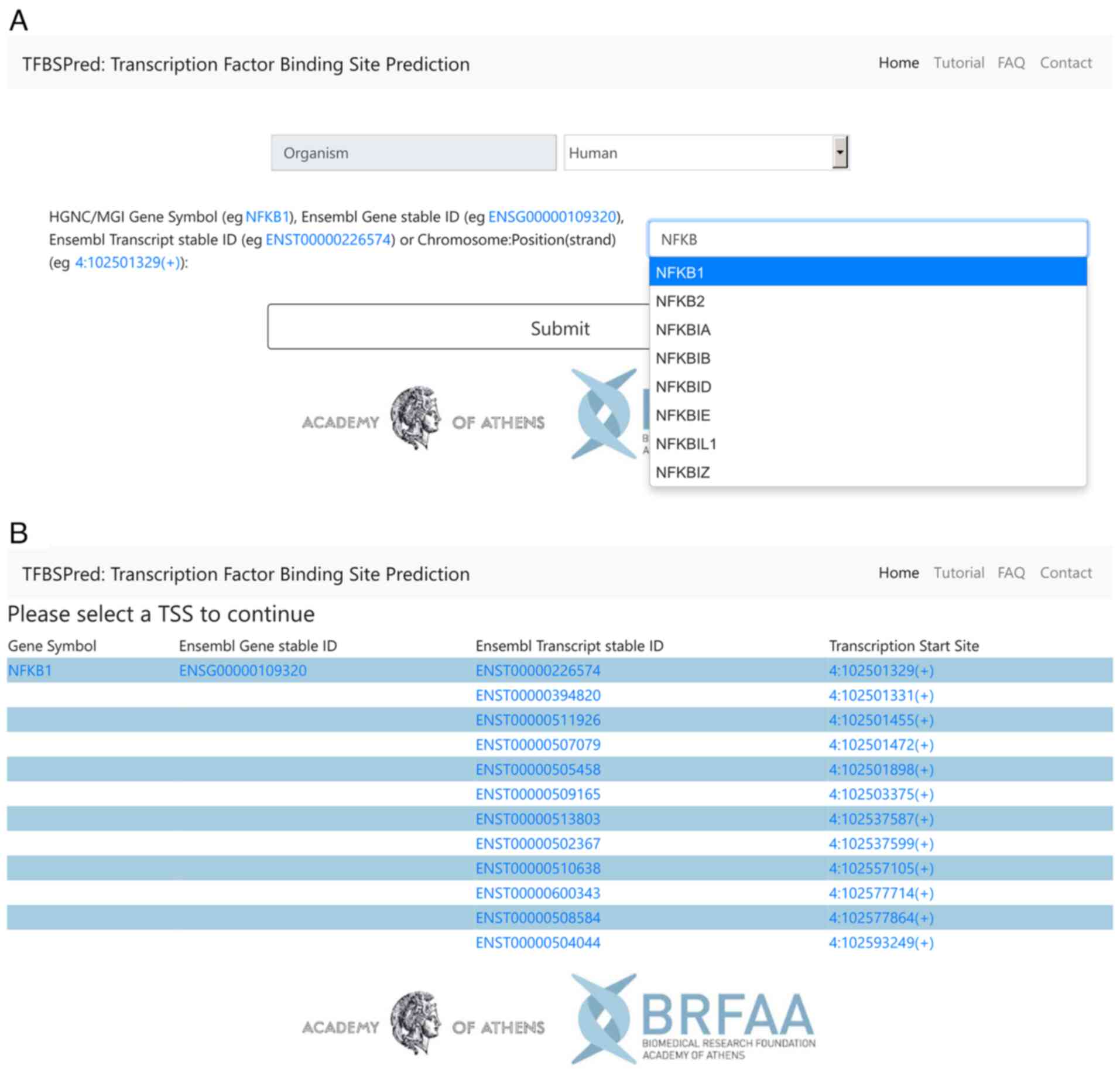
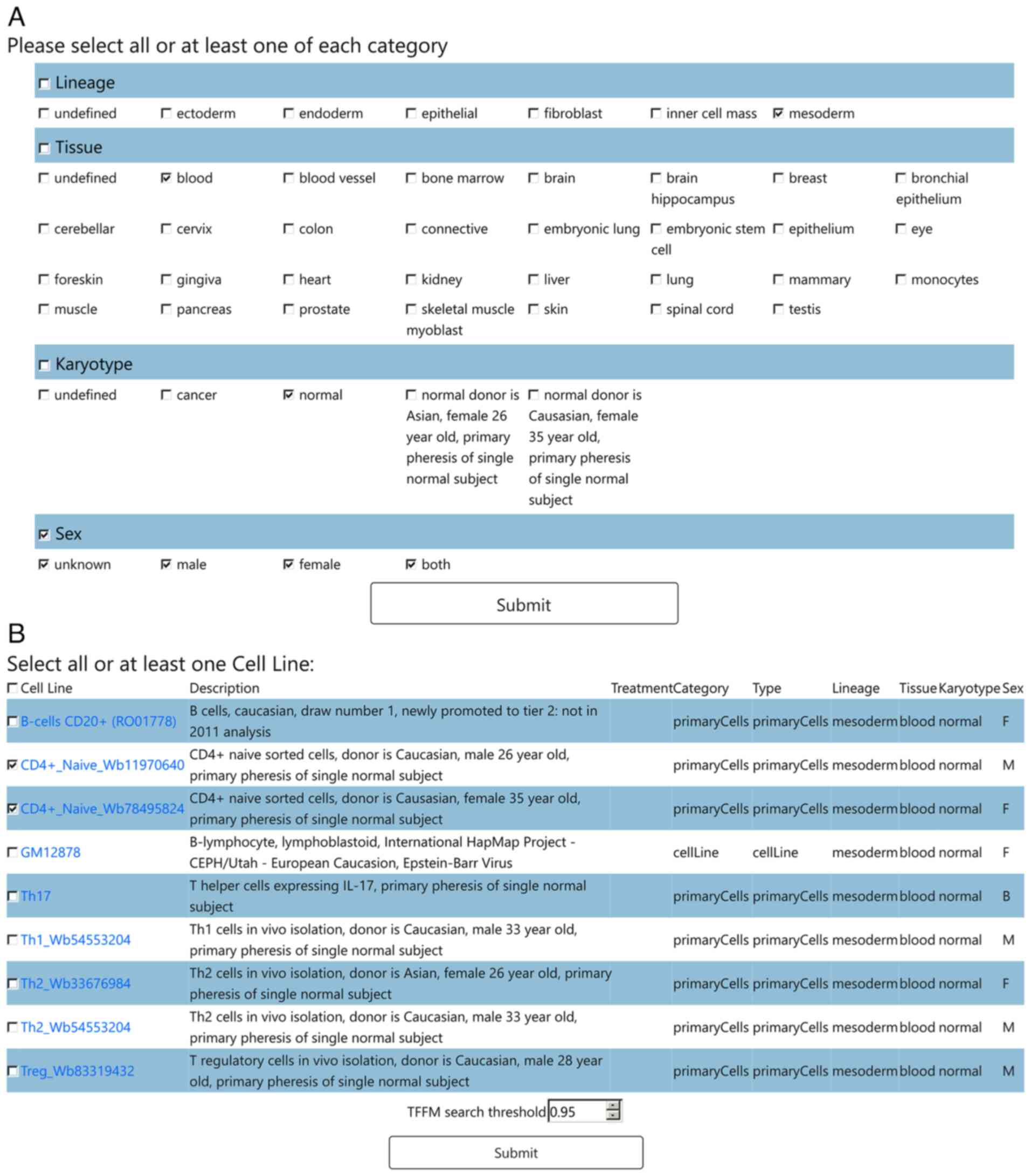
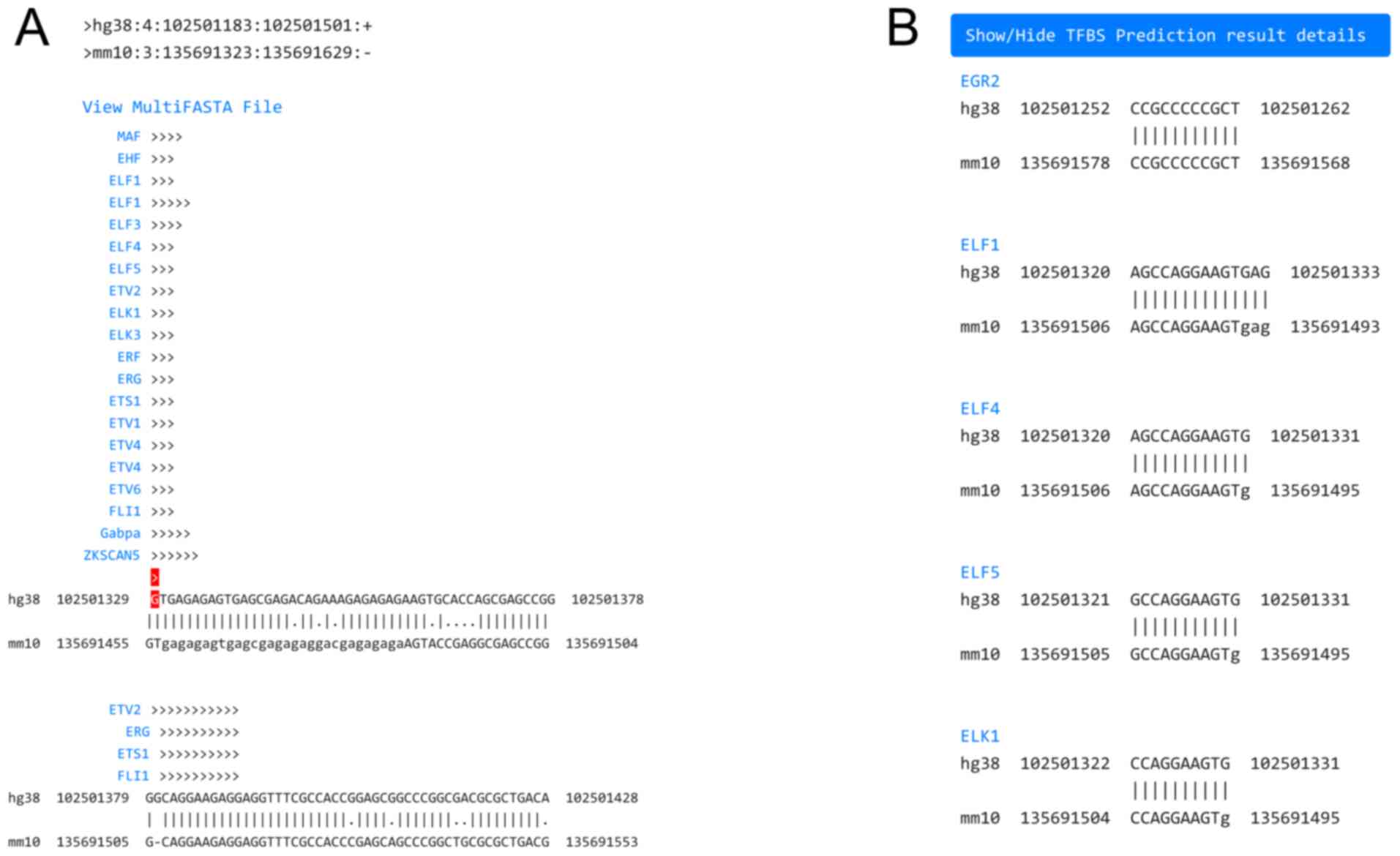
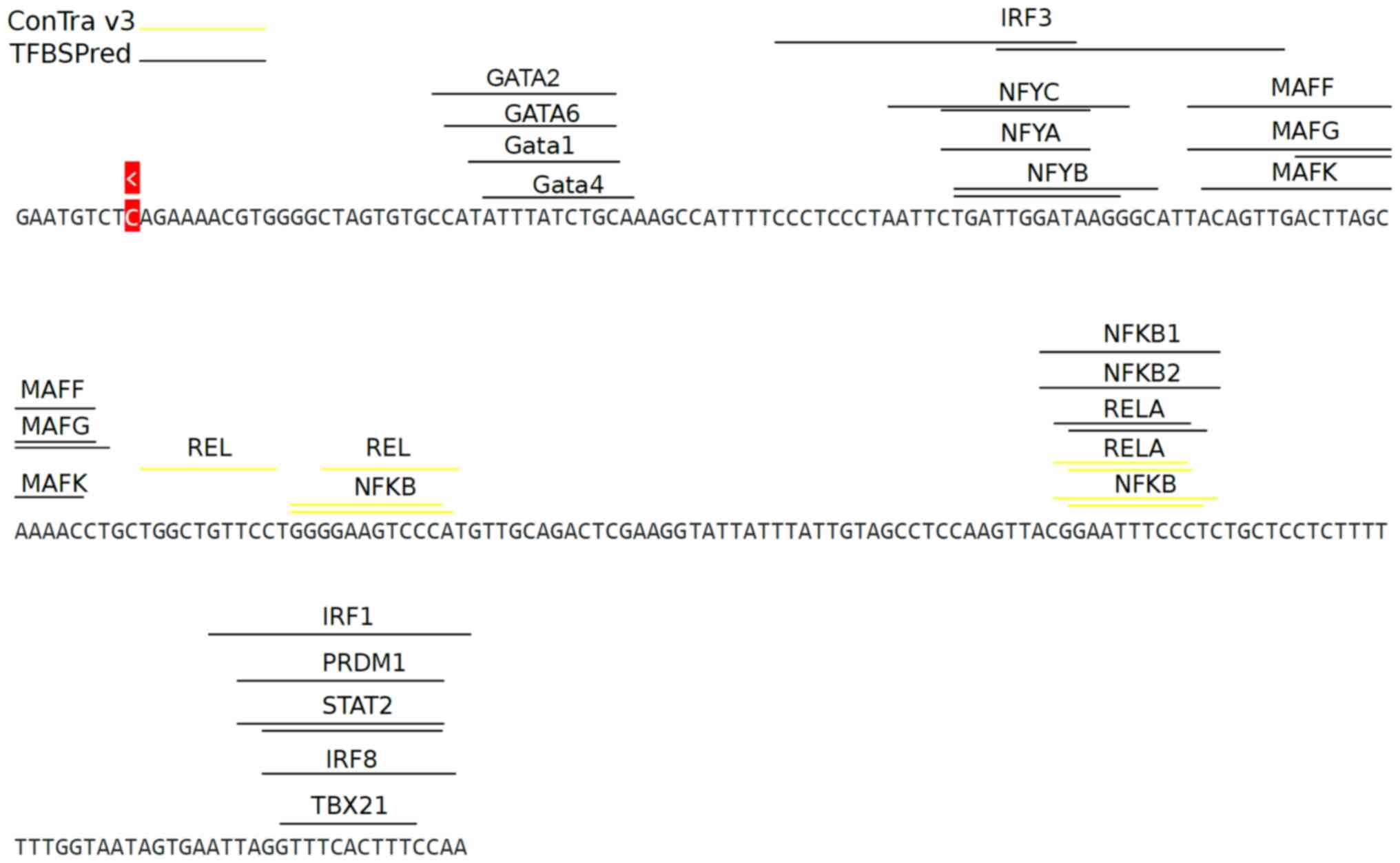
|
1
|
Wittkopp PJ and Kalay G: Cis-regulatory
elements: Molecular mechanisms and evolutionary processes
underlying divergence. Nat Rev Genet. 13:59–69. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Zawel L and Reinberg D: Initiation of
transcription by RNA polymerase II: A multi-step process. Prog
Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 44:67–108. 1993.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Liu X, Bushnell DA and Kornberg RD: RNA
polymerase II transcription: Structure and mechanism. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1829:2–8. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Haberle V and Stark A: Eukaryotic core
promoters and the functional basis of transcription initiation. Nat
Rev Mol Cell Biol. 19:621–637. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Lambert SA, Jolma A, Campitelli LF, Das
PK, Yin Y, Albu M, Chen X, Taipale J, Hughes TR and Weirauch MT:
The human transcription factors. Cell. 175:598–599. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Lee TI and Young RA: Transcriptional
regulation and its misregulation in disease. Cell. 152:1237–1251.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Singh H, Khan AA and Dinner AR: Gene
regulatory networks in the immune system. Trends Immunol.
35:211–218. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Narlikar L and Hartemink AJ: Sequence
features of DNA binding sites reveal structural class of associated
transcription factor. Bioinformatics. 22:157–163. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Stormo GD: Modeling the specificity of
protein-DNA interactions. Quant Biol. 1:115–130. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Staden R: Computer methods to locate
signals in nucleic acid sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 12:505–519.
1984.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Matys V, Kel-Margoulis OV, Fricke E,
Liebich I, Land S, Barre-Dirrie A, Reuter I, Chekmenev D, Krull M,
Hornischer K, et al: TRANSFAC and its module TRANSCompel:
Transcriptional gene regulation in eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res.
34 (Database Issue):D108–D110. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Fornes O, Castro-Mondragon JA, Khan A, van
der Lee R, Zhang X, Richmond PA, Modi BP, Correard S, Gheorghe M,
Baranašić D, et al: JASPAR 2020: Update of the open-access database
of transcription factor binding profiles. Nucleic Acids Res.
48:D87–D92. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Kel AE, Gossling E, Reuter I, Cheremushkin
E, Kel-Margoulis OV and Wingender E: MATCH: A tool for searching
transcription factor binding sites in DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids
Res. 31:3576–3579. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Grant CE, Bailey TL and Noble WS: FIMO:
Scanning for occurrences of a given motif. Bioinformatics.
27:1017–1018. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Zhao Y, Ruan S, Pandey M and Stormo GD:
Improved models for transcription factor binding site
identification using nonindependent interactions. Genetics.
191:781–790. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Khamis AM, Motwalli O, Oliva R, Jankovic
BR, Medvedeva YA, Ashoor H, Essack M, Gao X and Bajic VB: A novel
method for improved accuracy of transcription factor binding site
prediction. Nucleic Acids Res. 46(e72)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Toivonen J, Kivioja T, Jolma A, Yin Y,
Taipale J and Ukkonen E: Modular discovery of monomeric and dimeric
transcription factor binding motifs for large data sets. Nucleic
Acids Res. 46(e44)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Kulakovskiy I, Levitsky V, Oshchepkov D,
Bryzgalov L, Vorontsov I and Makeev V: From binding motifs in
ChIP-Seq data to improved models of transcription factor binding
sites. J Bioinform Comput Biol. 11(1340004)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Rabiner LR: A tutorial on hidden Markov
models and selected applications in speech recognition. Proceedings
IEEE. 77:257–286. 1989.
|
|
20
|
Xu D, Liu HJ and Wang YF: BSS-HMM3s: An
improved HMM method for identifying transcription factor binding
sites. DNA Seq. 16:403–411. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Wu J and Xie J: Hidden Markov model and
its applications in motif findings. Methods Mol Biol. 620:405–416.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Mathelier A and Wasserman WW: The next
generation of transcription factor binding site prediction. PLoS
Comput Biol. 9(e1003214)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Schneider TD and Stephens RM: Sequence
logos: A new way to display consensus sequences. Nucleic Acids Res.
18:6097–6100. 1990.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Frazer KA, Elnitski L, Church DM, Dubchak
I and Hardison RC: Cross-species sequence comparisons: A review of
methods and available resources. Genome Res. 13:1–12.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Emes RD, Goodstadt L, Winter EE and
Ponting CP: Comparison of the genomes of human and mouse lays the
foundation of genome zoology. Hum Mol Genet. 12:701–709.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Dolan ME, Baldarelli RM, Bello SM, Ni L,
McAndrews MS, Bult CJ, Kadin JA, Richardson JE, Ringwald M, Eppig
JT and Blake JA: Orthology for comparative genomics in the mouse
genome database. Mamm Genome. 26:305–313. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Elgin SC: DNAase I-hypersensitive sites of
chromatin. Cell. 27:413–415. 1981.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Pipkin ME and Lichtenheld MG: A reliable
method to display authentic DNase I hypersensitive sites at
long-ranges in single-copy genes from large genomes. Nucleic Acids
Res. 34(e34)2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Boyle AP, Davis S, Shulha HP, Meltzer P,
Margulies EH, Weng Z, Furey TS and Crawford GE: High-resolution
mapping and characterization of open chromatin across the genome.
Cell. 132:311–322. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Sabo PJ, Hawrylycz M, Wallace JC, Humbert
R, Yu M, Shafer A, Kawamoto J, Hall R, Mack J, Dorschner MO, et al:
Discovery of functional noncoding elements by digital analysis of
chromatin structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:16837–16842.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Thurman RE, Rynes E, Humbert R, Vierstra
J, Maurano MT, Haugen E, Sheffield NC, Stergachis AB, Wang H,
Vernot B, et al: The accessible chromatin landscape of the human
genome. Nature. 489:75–82. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Tweedie S, Braschi B, Gray K, Jones TEM,
Seal RL, Yates B and Bruford EA: Genenames.org. The
HGNC and VGNC resources in 2021. Nucleic Acids Res. 49:D939–D946.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Smith CL, Blake JA, Kadin JA, Richardson
JE and Bult CJ: Mouse Genome Database Group = Mouse Genome Database
(MGD)-2018: Knowledgebase for the laboratory mouse. Nucleic Acids
Res. 46:D836–D842. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Cunningham F, Achuthan P, Akanni W, Allen
J, Amode MR, Armean IM, Bennett R, Bhai J, Billis K, Boddu S, et
al: Ensembl 2019. Nucleic Acids Res. 47:D745–D751. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Kinsella RJ, Kahari A, Haider S, Zamora J,
Proctor G, Spudich G, Almeida-King J, Staines D, Derwent P,
Kerhornou A, et al: Ensembl BioMarts: A hub for data retrieval
across taxonomic space. Database (Oxford).
2011(bar030)2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
John S, Sabo PJ, Thurman RE, Sung MH,
Biddie SC, Johnson TA, Hager GL and Stamatoyannopoulos JA:
Chromatin accessibility pre-determines glucocorticoid receptor
binding patterns. Nat Genet. 43:264–268. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Casper J, Zweig AS, Villarreal C, Tyner C,
Speir ML, Rosenbloom KR, Raney BJ, Lee CM, Lee BT, Karolchik D, et
al: The UCSC Genome Browser database: 2018 update. Nucleic Acids
Res. 46:D762–D769. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Hinrichs AS, Karolchik D, Baertsch R,
Barber GP, Bejerano G, Clawson H, Diekhans M, Furey TS, Harte RA,
Hsu F, et al: The UCSC Genome Browser database: Update 2006.
Nucleic Acids Res. 34 (Database Issue):D590–D598. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Rosenbloom KR, Sloan CA, Malladi VS,
Dreszer TR, Learned K, Kirkup VM, Wong MC, Maddren M, Fang R,
Heitner SG, et al: ENCODE data in the UCSC Genome Browser: Year 5
update. Nucleic Acids Res. 41 (Database Issue):D56–D63.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Herrero J, Muffato M, Beal K, Fitzgerald
S, Gordon L, Pignatelli M, Vilella AJ, Searle SM, Amode R, Brent S,
et al: Ensembl comparative genomics resources. Database (Oxford).
2016(bav096)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Harris RS: Improved pairwise alignment of
genomic DNA (unpublished PhD thesis). The Pennsylvania State
University, 2007.
|
|
42
|
Schliepm A, Georgi B, Rungsarityotin W,
Costa IG and Schönhuth A: The general hidden markov model library:
Analyzing systems with unobservable states. In: Forschung und
wissenschaftliches Rechnen: Beiträge zum Heinz-Billing-Preis. 2004,
Gesellschaft f ür wissenschaftliche Datenverarbeitung. Kremer K and
Macho V (eds) Gesellschaft für wissenschaftliche Datenverarbeitung
mbH Göttingen, Göttingen, pp121-136, 2005.
|
|
43
|
Cock PJ, Antao T, Chang JT, Chapman BA,
Cox CJ, Dalke A, Friedberg I, Hamelryck T, Kauff F, Wilczynski B
and de Hoon MJ: Biopython: Freely available Python tools for
computational molecular biology and bioinformatics. Bioinformatics.
25:1422–1423. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Quinlan AR: BEDTools: The swiss-army tool
for genome feature analysis. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics.
47:11.12.1–34. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Grabe N: AliBaba2: Context specific
identification of transcription factor binding sites. In Silico
Biol. 2 (Suppl):S1–15. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Tsunoda T and Takagi T: Estimating
transcription factor bindability on DNA. Bioinformatics.
15:622–630. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Oshchepkov DY, Vityaev EE, Grigorovich DA,
Ignatieva EV and Khlebodarova TM: SITECON: A tool for detecting
conservative conformational and physicochemical properties in
transcription factor binding site alignments and for site
recognition. Nucleic Acids Res. 32:W208–W212. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Messeguer X, Escudero R, Farre D, Nunez O,
Martinez J and Alba MM: PROMO: Detection of known transcription
regulatory elements using species-tailored searches.
Bioinformatics. 18:333–334. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Mahony S and Benos PV: STAMP: A web tool
for exploring DNA-binding motif similarities. Nucleic Acids Res.
35:W253–W258. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Sandelin A, Wasserman WW and Lenhard B:
ConSite: Web-based prediction of regulatory elements using
cross-species comparison. Nucleic Acids Res. 32:W249–W252.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Benos PV, Corcoran DL and Feingold E:
Web-based identification of evolutionary conserved DNA
cis-regulatory elements. Methods Mol Biol. 395:425–436.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Loots GG and Ovcharenko I: rVISTA 2.0:
Evolutionary analysis of transcription factor binding sites.
Nucleic Acids Res. 32:W217–W221. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Ovcharenko I, Loots GG, Hardison RC,
Miller W and Stubbs L: zPicture: Dynamic alignment and
visualization tool for analyzing conservation profiles. Genome Res.
14:472–477. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Lee C and Huang CH: LASAGNA-Search 2.0:
Integrated transcription factor binding site search and
visualization in a browser. Bioinformatics. 30:1923–1925.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Kreft L, Soete A, Hulpiau P, Botzki A,
Saeys Y and De Bleser P: ConTra v3: A tool to identify
transcription factor binding sites across species, update 2017.
Nucleic Acids Res. 45:W490–W494. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Zerbino DR, Wilder SP, Johnson N,
Juettemann T and Flicek PR: The ensembl regulatory build. Genome
Biol. 16(56)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Panne D: The enhanceosome. Curr Opin
Struct Biol. 18:236–242. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Merika M and Thanos D: Enhanceosomes. Curr
Opin Genet Dev. 11:205–208. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Panne D, Maniatis T and Harrison SC: An
atomic model of the interferon-beta enhanceosome. Cell.
129:1111–1123. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Keller AD and Maniatis T: Identification
and characterization of a novel repressor of beta-interferon gene
expression. Genes Dev. 5:868–879. 1991.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Elias S, Robertson EJ, Bikoff EK and Mould
AW: Blimp-1/PRDM1 is a critical regulator of type III Interferon
responses in mammary epithelial cells. Sci Rep.
8(237)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Fish RJ and Neerman-Arbez M: Fibrinogen
gene regulation. Thromb Haemost. 108:419–426. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Vazirinejad R, Ahmadi Z, Kazemi Arababadi
M, Hassanshahi G and Kennedy D: The biological functions, structure
and sources of CXCL10 and its outstanding part in the
pathophysiology of multiple sclerosis. Neuroimmunomodulation.
21:322–330. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Brownell J, Bruckner J, Wagoner J, Thomas
E, Loo YM, Gale M Jr, Liang TJ and Polyak SJ: Direct,
interferon-independent activation of the CXCL10 promoter by NF-κB
and interferon regulatory factor 3 during hepatitis C virus
infection. J Virol. 88:1582–1590. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Korhonen JH, Palin K, Taipale J and
Ukkonen E: Fast motif matching revisited: High-order PWMs, SNPs and
indels. Bioinformatics. 33:514–521. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Kumar S, Stecher G, Suleski M and Hedges
SB: TimeTree: A resource for timelines, timetrees, and divergence
times. Mol Biol Evol. 34:1812–1819. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Kahara J and Lahdesmaki H: BinDNase: A
discriminatory approach for transcription factor binding prediction
using DNase I hypersensitivity data. Bioinformatics. 31:2852–2859.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|